Welding cast iron is very difficult, and not every specialist undertakes this work. However, it can be done even at home. Features of the process, preparation requirements, choice of consumables - this and much more is discussed in the article.
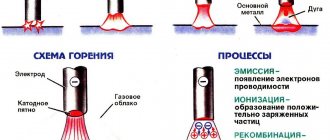
- Manual arc welding
Cast iron as a material is an alloy of carbon and iron. In addition to the main ones, the composition also contains additional components - alloying additives. This mixture is difficult to perform welding work. But despite the specifics, they can be performed even at home. There are methods to correct casting defects, wear or destruction of parts of a cast iron structure. Moreover, cast iron can be combined with steel parts.
Cast iron as a material
Cast iron is divided into two types. The lighter one is usually called white: at the break it has a light gray almost white color. Carbon in its composition is presented in the form of cementite. This material is characterized by high fragility and cannot be machined. It is rarely used for the production of various types of products and cannot be welded.
After additional processing of white cast iron, namely long-term melting at a temperature of 1000 degrees Celsius, another type of cast iron is obtained - gray. Unlike the first, the product is more technologically advanced and can be machined and welded. It is used to produce a wide range of parts that are resistant to vibration and mechanical stress. Malleable cast iron is in demand in the production of agricultural machinery, machinery, machine tools, ships and many other equipment.
| Type of cast iron | Carbon content | Form of carbon | Properties | Marking |
| grey | 3,2-3,5 | Flake graphite | Low shrinkage, pours well, high fluidity in the molten state | SCh-10 SCh-35 |
| white | 2,14-6,67 | Cementite (iron carbide) | Hardness, brittleness, high shrinkage, cannot be machined | |
| malleable | 2,4-3,0 | Flaked graphite | Plasticity, good mechanical properties, corrosion resistance | KCH33-8 |
| high strength | 3,2-3,8 | Nodular graphite | Fluidity, almost no hot cracks, low shrinkage | HF60-2 |
If a certain amount of alloying additives is added to the composition of a malleable material, high-strength cast iron will be obtained. The material is used in the production of high-pressure pipes, critical parts for the automotive industry and mechanical engineering. When fractured, the color of such cast iron will have a silver-gray tint. Carbon in its composition is represented by graphite. This type is widely used as a structural material, processed by cutting turning tools, has wear resistance, excellent casting performance, vibration resistance.
Characteristics of cast iron
The material is an iron alloy containing a large amount of carbon.
The substance gives cast iron hardness. Carbon, which is not a metal, is not capable of forming bonds with iron; it is contained in the alloy in the form of graphite inclusions.
The alloy has the following characteristics:
- Porosity of the structure. The voids quickly fill with gases or absorb oil.
- Relatively low melting point (1200-1250 °C). This explains the high fluidity of the alloy when heated.
- Fragility. Cast iron is not recommended for the manufacture of structures subject to high loads.
- Low ductility.
- Resistant to acids and alkalis. At the same time, the material is sensitive to prolonged exposure to moisture.
Features of cast iron welding
The material is endowed with specific properties that influence the charka process. The main ones:
- Rapid cooling results in a so-called bleaching effect. A thin film of white cast iron, unsuitable for machining due to its high fragility, forms on the surface.
- Incorrect temperature setting, which causes many microcracks to form near the seam.
- During welding, a large amount of gases are formed in the pool, which can lead to increased porosity of the welded joint.
- Cast iron has high fluidity, which complicates the formation of a weld, since a melt of such consistency quickly flows out of the bath.
- The metal has a high heat capacity, due to which it heats up and cools unevenly. In combination with fragility, “disparity” in temperatures leads to the formation of cracks.
- Oxidation of silicon initiates the formation of refractory oxides. As a result, lack of penetration is formed.
Despite a decent list of difficulties, welding cast iron is a popular and very common method of repair, as well as the manufacture of new welded-cast products. But welders need to carefully analyze the initial data and carefully select the welding method and consumables. The quality of the future welded joint and comfort during the work depend on this.
Argon welding
Welding cast iron with argon is used by many novice welders on the advice of experienced comrades, and they often resort to semi-automatic welding in an argon environment. This method is not justified for products made of cast iron alloys. The connection is obtained as in heated air, but the costs increase greatly.
The technology for welding cast iron and steel with argon usually requires the presence of a neutral environment. Of course, a seam can be obtained in an atmospheric environment, but its quality will greatly deteriorate. When welding in this environment, microcracks may form in the joint, and uneven hardening will also be observed.
If, in addition to welding, the inert gas argon is supplied, the chemical composition in the weld pool will not change in any way. If argon is used, the welding method does not matter at all. The quality of the welds is equally good for any connection of parts - butt, overlap, patch.
TIG welding of cast iron using argon is considered the most optimal option, which allows you to make a strong seam. Using gas you can cook almost any combination. If there are some difficulties in purchasing argon, then it is better to leave it for joining cast iron and steel.
Preparation
The presence or absence of defects largely depends on how competently the preparatory work is carried out. Cracks in cast iron have a thin and deep structure. To get rid of them, you need to cut the edges to the full depth. For these purposes, you can resort to simple mechanical methods - grinding or cutting, or you can use heat treatment - arc or oxygen cutting.
The length of the groove should be approximately 5 millimeters longer than the visible part of the crack on each side. Closer to the edge, the cutting groove should become shallower so that it eventually comes out flush with the surface of the workpiece. The depth of cutting through defects is 1-2 mm less than the thickness of the walls of the product. Regarding non-through cracks, it’s the other way around: the cutting should exceed the depth of the crack by at least 1-2 mm.
Proper cutting of edges eliminates overheating of cast iron. If everything is done correctly, the metal will heat up evenly throughout the entire area. To do this, you need to ensure that the bevel of the edges is exactly 45 degrees. It is important that the edges are free of sharp corners. It is advisable to clean the surface with sandpaper, a sandblaster, a grinder or a regular metal brush. If some contaminants cannot be removed mechanically, then you can resort to heat treatment.
Cast iron parts with thin walls are welded using graphite molds. They serve as a lining. Thanks to this technique, the temperature is evenly distributed throughout the entire volume and the original shape of the workpiece is preserved.
Preparation for welding
Preparatory operations must be carried out carefully and carefully, as this is one of the fundamental principles of obtaining a high-quality connection:
- the structure is cleaned of dirt, debris and dust;
- then you should degrease the parts with a solvent, for example, acetone;
- when working with thin cast iron, you need to use pads to remove heat;
- edge cutting should be done before welding thick-walled products; for this, a file or grinder is used;
- cracks must be drilled along the edges and cut to their entire length; an alternative method is to cut out the cracks and round the ends;
Cast iron welding technology
There are two widely used technologies for welding cast iron parts. They are divided depending on the temperature regime of the process, as well as the presence or absence of preheating of the workpieces.
hot
The method was developed for industrial production. It is of little use for home workshops, since it will not be possible to heat the workpieces to a temperature of 600-650 degrees Celsius in the garage without special equipment. Preheating technology makes it possible to eliminate the formation of cracks in the weld.
It is important to ensure uniform heating of the workpieces. It is fundamentally important to avoid temperature differences between the main product and the weld seam. Otherwise, there is a high probability of a fault. Before heating, the parts are fixed in the desired position. This is necessary in order to avoid internal stress, which can lead to cracks.
There is no need to overheat the workpieces. If the preheating temperature is raised to 750 degrees Celsius, the cast iron will simply begin to melt.
Semi-hot
The process is completely identical to hot pre-preparation. The only difference is maintaining the temperature. In this case, the workpieces are heated to a temperature of 400-450 degrees. The technology is used both in production and in small workshops.
Cold
Pre-heating of the workpieces is not required. Technology is used everywhere, including in everyday life. It is justified in the case where there is no equipment for preliminary preparation, and cast iron connections are one-time or irregular in nature. The quality of the weld is low. The reliability of the welded joint can be improved by using special electrodes.
Welding methods
Three methods have been developed to create strong seams:
- Hot welding technology is complex, but practically eliminates the formation of cracks. It is performed with preheating to a temperature of 600 - 650⁰C with subsequent slow cooling. In production, this procedure is performed on induction installations. Some beginners doubt whether it is possible to cook cast iron using this method on their own. This is possible if you use a forge, gas burner, or blowtorch for heating, and hot sand for slow cooling.
- Semi-hot welding is similar to the previous method, but the heating temperature is 300 - 350⁰C.
- Cold welding is carried out with special electrodes without preheating the parts. However, in order to brew cast iron using this method, it is necessary to take into account the technological features of the material.
Methods of welding cast iron
Manual arc welding
A universal option that allows you to work with all cast iron joining technologies - hot, semi-hot and cold. Consumables are selected for each method. Manual arc welding with preliminary preparation of parts is performed in several stages:
- joint preparation;
- heating of workpieces;
- welding;
- cooling.
To connect ductile cast iron, electrodes of the following brands are used: OZCh-2, MNCh-2, TsCh-4, OZCh-6. Gray cast iron is welded with consumables OZCh-2, MNCh-2, OZCH-4, OZCH-6, OZZHN-1 and OZZHN-2. High-strength grades are connected by OZZHN, MNCh-2, OZCh-3 and OZCh-4 electrodes. The welding seam is formed at high current settings in a continuous manner. What specific current settings should be depends on the brand of electrode.
Disadvantages of technology:
- the welding process is labor-intensive;
- it is quite difficult to heat the work area evenly;
- it takes a lot of time to complete the work;
- The equipment required for welding is expensive.
In cases where strict requirements are not imposed on the quality of the seam, you can resort to the technology of semi-hot or even cold welding of cast iron. You can choose ordinary steel electrodes. If possible, it is better to use cast iron electrodes with a copper and nickel base.
Non-consumable electrodes
A wide range of consumables is used - tungsten, graphite, carbon. Special rods containing nickel, copper, aluminum and other metals are suitable for the additive. The seam formation zone is protected by inert gases. Most often, argon or borax-based flux is used. Regarding technology, the best option is AC TIG - welding with tungsten electrodes in a protective environment from an alternating current source.
Cold, semi-hot and automatic
You can resort to MIG technology (performed in a protective inert gas environment) or MAG technology (in an active gas cloud). The process goes as follows. The wire is fed into the welding zone, where under the influence of high temperature it melts and forms a connecting seam. This occurs in a protected environment, as an inert gas is continuously supplied, isolating the connection from atmospheric air.
Semi-automatic hot welding is used in cases where it is necessary to make a welded joint of very high quality, when the joint must have good resistance to fracture and tearing. To minimize the number of microcracks, the weld should be cooled gradually.
Semi-hot welding technology is used in situations where the seam will experience relatively light loads during operation. Cold technology is suitable if no load is planned on the welded joint.
Semi-automatic welding involves the continuous supply of consumables to the work area. This makes it possible to reduce the time spent on work. In the case of connecting cast iron parts using a semi-automatic machine, you can count on good and mediocre results.
Argon-arc
The TIG method is characterized by the complexity of the welding process. Argon is used as a shielding gas that insulates the working space and cuts off atmospheric air. The best option for filler material is aluminum-bronze or nickel rods. In cases where the welded joint will be exposed to high temperatures during operation, nickel additives and tungsten electrodes should be used.
TIG technology requires the performer to comply with a number of requirements:
- Before welding, the workpieces must be warmed up. This will reduce the number of cracks.
- A small alternating current is selected.
- To prevent overheating of the metal, it is necessary to connect in short sections.
- Each section should be forged (tapped with a hammer) to relieve the internal stress of the cast iron.
- At the end of the work, the weld should cool slowly.
Gas
It is important to heat the workpieces evenly before starting work. Therefore, preparation takes longer. Gradual, continuous heating reduces the likelihood of white spots developing. Edge processing is also required provided that their thickness exceeds 4 millimeters. A V-shaped bevel is made with an opening angle of 90 degrees.
The filler materials are cast iron rods. It is important to choose the right thickness. It is calculated using the following algorithm. The wall thickness of the workpieces must be divided in half. This will be the diameter of the rod. It may deviate from the obtained result by 1 millimeter in a larger direction. In addition, you need to use flux. Brands FSC-1, BM-1, FSC-2 are well suited. It is advisable to coat the additive with flux and add it to the weld pool. There should be plenty of material, since it performs a number of important functions:
- protects the weld pool from oxidation;
- increases the fusion of dissimilar inclusions;
- refractory oxides are converted into low-melting slags;
- melt fluidity increases.
The welding flame should be medium level. The connection is made in the down position. Large workpieces are processed with torches. To make the seam cool more slowly, it is covered with a layer of asbestos.
Electroslag (ESS)
The technology is used to connect parts made of gray cast iron and makes it possible to obtain a connection with satisfactory performance. Subject to the requirements of the technological process, the formation of pores, cracks, bleached areas and a number of other effects is eliminated. This method is optimal in cases where it is necessary to correct defects in cast iron castings, that is, in a situation where it is planned to deposit a large amount of metal. ESH is in demand for the production of massive structures made of high-strength cast iron. Cast iron plates and fluxes are used as consumables.
Laser
Safe method for high quality welding of cast iron. The technology makes it possible to obtain a crack-free welded joint. There are two varieties of it:
- With induction heating. Workpieces can be heated both beforehand and during operation. Using heat treatment, internal stress is relieved and the number of cracks is reduced; and the deposit turns out to be moderately soft, without excessive hardness. Naturally, the speed of work completion increases significantly.
- With additive. The method is effective for joining cast iron to each other and to structural, hardened, case-hardened steel. The method is used in the production of housings for various units, axles, gears, and other parts and assemblies in mechanical engineering and other industries.
Contact
The best option for working with pipes of different diameters. Pre-heating and melting of the joints of the workpieces to be joined is required. In this case, the formation of hardening structures is excluded. Welded joints are characterized by high density.
Plasma soldering
The structure of cast iron contains graphite, which makes adhesion between the solder and the surface of the material difficult. It needs to be removed. The easiest way to do this is with a sandblaster. Next, the surface at a temperature of 600-700 degrees Celsius is treated with flux No. 209 or 284. After this, the edges must be degreased with acetone, solvent or alkaline solution. Soldering can be done either with a soldering iron or with a gas torch using zinc chloride fluxes.
Light alloy solders, including tin-lead, are suitable for soldering at low temperatures. Copper and silver solders are suitable for high-temperature joints.
Welding with non-consumable electrodes
Welding cast iron using this technology is carried out in a protective environment of argon or fluxes, the main component of which is borax. Cast iron or special rods containing nickel, aluminum and copper are used as filler materials. Welding cast iron is carried out using tungsten, carbon and graphite electrodes.
The most common method is argon arc welding (AC TIG). In order for the work to be successful, you should adhere to several rules:
- Thorough cleaning of the surface from debris and dirt;
- the workpiece must be fixed at several points;
- It is recommended to use slight preheating of the product; for this you can use improvised means. It should be remembered that the presence or absence of heating depends on the type of cast iron being welded;
- the additive is supplied at an angle of 20-30 degrees;
- it is necessary to use small amounts of current;
- the connection should be carried out in stages : the performer welds a small section of 2-3 cm and forges the deposited metal so that
- avoid residual stress. Forging is done with a small hammer, the weight of which does not exceed 1.2 kg, the hammer is of a rounded type.
- Cooling of the part after welding is carried out gradually .
This method is not the main one when connecting cast iron products. This is due to certain difficulties that arise during the work process, as well as an increased level of labor and financial costs.
Multilayer welding using annealing bead technology
The method is used to eliminate cracks on parts with thin walls - up to 8 millimeters. Rollers are formed sequentially in such a way that each new one thermally affects the previous layer. This reduces the hardness of the deposit.
The crack is pre-cut: V-shaped processing, opening angle is 45 degrees. Preparatory beads are first welded onto each edge, and annealing beads are welded onto them. The rollers are applied in small sections up to 50 mm long.
Each transition from one area to another should be leisurely, so that the metal has time to cool to a temperature of 50-60 degrees Celsius. At this point, the rollers need to be forged and the scale removed. Preparatory rollers are applied earlier, and therefore warm up better and cool down more slowly. In the hardened part, the metal is partially tempered and normalized. When the formation of the beads on both sides of the crack is completed, the weld itself is applied. It is also formed in the same small segments.
Features of the welding process
Now we’ll tell you how to weld cast iron using electric welding. When the master is convinced of the reliability of the equipment, he can begin the process. To do this, you need to choose how to cook cast iron with simple electrodes:
- on studs;
- multi-layered.
In the first case, the master first installs the pins themselves, and forms a seam around them. Experienced welders recommend performing the procedure in a staggered manner to prevent overheating of the material. The work is completed with a connecting seam - it goes from one pin and its “surroundings” to the other.
The multilayer method is as follows: chamfers are created, then the initial layer is fused, it is hammered, then a second layer is laid, tapped again, and so on. After the seam has cooled, it must be sanded to give the product an aesthetic appearance. If it is possible to access the inside of the product, then the initial layer in the multilayer method is placed on the outside and inside. This makes the connection even stronger.
In general, there is nothing complicated about how to properly cook cast iron with electrodes. The main thing is to follow safety rules.
Welding cast iron using steel studs
The weld metal can peel off, making the melting zone the most vulnerable area. To more evenly distribute the load during cooling and associated shrinkage, so-called “wraps” are used - steel studs. If the wall thickness of the workpiece exceeds 6 mm, then the edges are pre-cut at an angle of 45 degrees.
Then holes are drilled in a checkerboard pattern into which steel pins are screwed. They partially protrude on the surface. The wrappers are scalded in a circle, after which a fusion layer is formed by applying annealing rollers. The peculiarity of the seam is that most of the mechanical loads are borne by steel studs, while the seam is subject to a small force.
Security measures
Carrying out welding work at home requires careful and precise adherence to safety precautions. The most important points:
- the room in which welding work is carried out must be illuminated and ventilated ;
- It is mandatory to use means for grounding ;
- Cast iron does not respond well to rapid cooling, so its surface must be protected from moisture ;
- personal protective equipment when working .
Operating the inverter in pulse mode
The essence of the method is that the main welding current is supplemented by high-frequency pulses of greater strength superimposed on top of it. The ratio of current strength and pulse duration is adjusted in the device settings and is maintained automatically. Technology contributes to:
- improving the quality and strength of the welded joint;
- increasing the level of arc control and process control;
- welding efficiency increases;
- the likelihood of burning through the metal is reduced;
- the seam is neat.
Alternating impulses and pauses replaces the need to perform complex actions with the tip of the rod. The method is not suitable for joining parts that will experience vibration, shaking and shock.
Gas welding
Gas welding of cast iron is mainly used in cases where it is required to obtain a high-strength weld, but subject to a small penetration of the surface of the base metal. At the same time, the technology of gas welding of cast iron is accompanied by the use of several welding modes, on which the quality of the final joint will depend.
The quality indicator of a welded joint is influenced by the following components:
- types of supply voltage modes;
- type of technique of the superimposed welded joint;
- current indicator;
- passing speed.
How to weld cast iron and steel using gas arc welding in order to ultimately obtain a connection with high strength without cracks, pores and other defects? To do this, you need to comply with some requirements during the workflow:
- the arc voltage indicator should be from 18 to 21 V;
- current strength - 100-120 A;
- travel speed no more than 12 m per hour;
- Welding work must be carried out using special welding wires 09G2SA or PANCH 11 with a diameter of 1 mm.
Surfacing of cast iron
The work is performed with electrodes of the following brands:
- OZZHN-1. Suitable for eliminating serious casting or processing defects.
- MNC-2. Used for surfacing critical connections. Pre-heating of the surface is not required.
- OZCH-2. Surfacing of gray and ductile cast iron.
The operation of gas surfacing is based on thermal energy, which is released as a result of the combustion of acetylene, as well as its substitutes, and oxygen. Consumable materials are fluxes and light rods.
Cast iron: types, application
Cast iron is a kind of mixture of iron and carbon. The material is hard and wear-resistant, but, paradoxically, quite fragile if not handled correctly. This is why welding cast iron with an electrode at home using an inverter should only be done after careful preparation (this will be discussed below).
Cast iron has been known in the world for a long time - it is believed that it appeared in the 6th century BC.
The average melting point is over 1000 degrees Celsius. You can work with the material when heated to 600 degrees.
By type, cast iron metal is divided into the following categories:
- white;
- half-hearted;
- grey;
- high strength;
- malleable.
Over time, cast iron does not lose its relevance; it is used in various spheres of human activity. The material is used for the following purposes and tasks:
- forging fences;
- production of machine tools;
- production of frying pans for household use;
- manufacturing of heating radiators, pipes, plumbing connections;
- creating baths;
- in the automotive industry - for the production of crankshafts, cylinders, engines and other things.
This is only a small part of the tasks that ordinary cast iron can successfully cope with. An important feature is that surfacing cast iron with electrodes can be done at home without the help of a professional welder.
Features of cast iron welding
Depending on the form in which carbon is present, cast iron is divided into several types:
- White cast iron. It contains carbon in the form of cementite. It is characterized by high hardness and cannot be processed with cutting tools. It is extremely difficult to cook.
- Gray cast iron. It contains carbon in the form of graphite. The alloy is quite easy to process. When welding cast iron with an electrode at home with an inverter, a reliable connection is ensured.
- Malleable type. It is produced by specially treating white cast iron to convert the carbon into flake graphite form. This alloy is actively used in mechanical engineering. It can be welded with special electrodes.
- Half cast iron. Contains carbon in both forms - cementite and graphite. Used for the manufacture of products with increased wear resistance.
- High strength cast iron. The carbon in it has a spherical shape, acquired during crystallization. Metal is used for especially critical products, including pipes.
The last 2 types of alloy can be welded with an electrode, but require a special approach. Welding technology for different types of cast iron differs significantly, which must be taken into account when working.
Welding cast iron is associated with the following difficulties:
- Some alloy components are easily oxidized upon melting to form refractory oxides. They lead to inhomogeneity of the weld and the appearance of unwelded areas.
- With rapid cooling of the heat-affected zone, cementite is formed, which subsequently cannot be machined.
- The cast iron melt has increased fluidity, which makes it difficult to form a seam and retain it in the weld pool.
- Any uneven heating and cooling of the welding zone leads to cracking of the metal.
- When cast iron melts, gases are released that can cause pores to appear in the weld.
Important! The special structure and properties of cast iron lead to poor weldability at home. However, if you follow the regimes, choose the right method and consumables, you can brew most cast iron products used at home with high quality.
How to cook cast iron using electric welding/electrode at home
Small defects in unloaded connections can be corrected yourself. If the quality of welding does not require strength requirements, but tightness is important, then it is quite possible to resort to the simplest technology - cold welding.
With this connection method, the temperature in the working area cannot be greatly increased. Therefore, the seam is formed in intermittent sections, the length of which does not exceed 50 millimeters. It is necessary to take breaks from time to time so that the metal cools down to a temperature of 50 degrees. This reduces the likelihood of cracks forming.
It is much easier to prevent the metal from overheating if you cook at constant current and connect the electrode to the positive terminal, that is, work with reverse polarity. An additional way to combat overheating is to constantly move the tip of the electrode in a zigzag manner.
The speed of movement of the electrode must be constantly monitored. If you move the rod quickly, lack of penetration will form. If you do it too slowly, you can overheat and even burn through the metal.
Types of welding
To know how to weld cast iron with a conventional electrode, it is important to understand the types of welding in general. They are divided into:
- hot;
- semi-hot;
- cold.
Hot is indeed such, occurring at temperatures between 600 and 700 degrees Celsius. The metal is heated in industrial furnaces, which are considered heavy-duty equipment. Cast iron becomes flexible, like plasticine, and is easy to work with. During the process, no cracks or pores appear on the product that would interfere with normal operation in the future.
Experts call this welding method the most ideal for cast iron. Naturally, to the question: is it possible to cook cast iron using conventional electrodes at home using the hot welding method, the answer will be negative. Creating such a colossal temperature in an apartment or garage, for example, is dangerous to life and health.
Semi-hot welding is also impossible at home. It is carried out at a temperature of 300-400 degrees Celsius. For heating, special hair dryers or heating elements are used. This method is used in industry. Its main advantage is faster cooling compared to the hot method. For a novice master, the semi-hot technology of welding cast iron with electrodes is practically impossible.
Cold welding is suitable for home use. It occurs at a maximum temperature of 80 degrees Celsius.
How to cook cast iron
The physical and chemical characteristics of cast iron require careful attention to the choice of consumables. The structure of the electrode is very simple - a metal rod coated with a special compound. It is important that the rod is made of metal compatible with cast iron. When heated, the coating of the rod releases gas, which serves as a protective medium for the welding zone.
| Electrode diameter, mm | Thickness of welded parts, mm | Welding current strength, A |
| 2,5 | 2 | 65-80 |
| 3 | up to 5 | 90-100 |
| 4 | 5 or more | 130-160 |
| 5 | from 10 to 13 | 180-220 |
The table shows the main characteristics for welding workpieces in the lower position for cast iron electrodes. Copper-nickel consumables consist of 30% copper and 65% nickel. They are used when a strong weld is not required. The quality of the connection is satisfactory, and the seam itself can be machined.
Welding with inverter
Many inexperienced welders often wonder whether it is possible to weld cast iron and steel with an inverter welding machine? Of course you can, but you should prepare first. The cast iron preparation process should be carried out taking into account the following recommendations:
- First of all, the required area is cleaned with a grinder. For stripping, it is recommended to use a flap wheel or other most suitable attachment;
- After the top layer has been stripped down to non-oxidized metal, degreasing is required. This process can be performed using gasoline or any other solvent;
- If it is necessary to repair a crack, then it must be cleared until it is completely finished. After this, a hole with a diameter of 10 mm must be drilled in this place.
Welding cast iron with an inverter can be carried out layer by layer and using support elements - studs. They are entirely made of steel. The use of these support elements must be accompanied by taking into account the following important requirements:
- the dimensions of these elements must be accurate, their diameter should not be more than 40% of the thickness of the cast iron;
- the protrusion of the stud above the metal is no more than 4-6 mm;
- the distance between them should not exceed 6 mm;
- the number of studs used should depend on the connection parameters, but they should not exceed 25% of the fracture area.
Electrodes can also be used, but they must be special. It is not recommended to brew cast iron with conventional electrodes. For this type of alloy, electrodes with the addition of nickel, copper, chromium and other alloys are suitable, which contribute to durable deposition of cast iron.
How is it carried out?
How to weld cast iron using an inverter to get a good and high-quality weld? To do this, you will need to study important recommendations:
- the polarity of the connection must be reversed;
- the operation of the welding machine must be carried out at minimum power, it must correspond to the thickness of the cast iron element;
- the length of one continuous weld should not be more than 3-5 centimeters;
- there should be no overheating of the metal, which can occur as a result of frequent breaks;
- The first and last layers in multi-layer welding should be forged with a hammer with little force.
The welding process itself can be multi-layer or using studs. After the studs are installed correctly, each layer is welded. Metal must be placed around each stud to create a patch. At the end, a weld is made that connects the welded metal between the studs.
Multilayer welding is performed using electrodes. After fusing the first layer, forging is carried out with a hammer; it should be done hot. If there is access to the back side of the product, then a layer is also applied to it, and then it is forged. At the end, the following layers of metal are applied.
Before answering the question of whether cast iron can be welded, it is worth considering the main features of this alloy. The choice of a certain type of welding depends on its type and structure. Different types of welding can be used for it - electric, semi-automatic, gas, argon, inverter. But for the process to be successful, preliminary preparation of cast iron and steel is required.
Process
After everything for welding cast iron is ready, begin the welding itself. Work using both hot and cold technology is carried out by:
- gas welding;
- fusible electrodes, rod or wire (inverter or semi-automatic with carbon dioxide);
- welding with a non-fusible electrode, with filler rods, including in an inert gas environment (argon, helium).
The seam zone, or fusion of parts, is the most “capricious” part of the connection . A common defect in this case is peeling of the deposited material. The stud welding technique helps to avoid it.
They are screwed into holes with cut metric threads. The quantity depends on the size of the parts. The correct diameter is taken according to special tables.
Welding is carried out using inverter machines, including semi-automatic ones. The latter, due to the cooling effect of carbon dioxide, provide a high-quality compound
When welding, each pin is first scalded, then the space between them is filled.
In this way, it is possible to cope even with such a complex task as welding a cast-iron engine block using electric welding.
The cutting width when cutting a crack, and therefore the future seam, is kept within 3-5 mm. A smaller gap will give high-quality penetration. On the other hand, the thicker the seam, the higher the “whitening” of the welded edges, increasing their fragility.
Applications of argon arc welding
The use of refractory electrodes and copper-nickel filler wire gives good results.
How to weld steel to cast iron (several recommendations):
- The additive is selected according to the type of metal and type of cast iron. Nickel-based flux-cored wire is most often chosen; the coating is first removed from it.
- Argon is used as a protective atmosphere; it saves the seam from oxidation.
- Refractory tungsten electrodes are chosen for work.
- To work with thin-walled elements, experienced welders use small thin pieces of cast iron instead of wire.
- For connections that experience only static loads (compression), nickel alloys can be used. They adhere perfectly to any grade of steel.
How to weld cast iron using electric welding
Correctly welding cast iron by electric welding is possible only if you use the correct electrodes, as well as the necessary equipment. The peculiarity of the work is that in the area where the seam is applied, the fragility of the metal increases.
The fragility is due to the fact that during work, cast iron experiences excessive and intense hardening. For this reason, the technology for welding cast iron with electrodes in industrial conditions differs significantly from the conventional processing of other metals and requires heating the material to a temperature of about 600-650° degrees.
The following types of electrodes are used for work:
- OZCH-2 – have a copper rod coated with a special composition that includes graphite.
- MNCh-2 - an alloy of metals from nickel, copper, manganese and iron is used for the rod. MNCh-2 electrodes are the optimal solution, but they are significantly more expensive.
Electric welding of cast iron products using the cold method requires compliance with a certain rate of welding and control so that the surface does not heat up above the required levels. The welder performs work “randomly”, in small sections with mandatory forging and breaks.
Since the peculiarity of cast iron is its slow cooling, welding a cast iron part may require a large amount of time. When restoring small defects, it is mandatory to use a graphite substrate to avoid metal leakage.
Gas
Heating with a gas burner is performed slowly so that when the joint is brought to a liquid state, the graphite has time to dissolve in the liquid bath . Burning it out and blowing it out will lead to bleaching, which means increasing the fragility of the joint.
The torch is held at a greater distance than when welding steels in order to obtain uniform heating of as large a surface as possible.
To absorb the released carbon monoxide (carbon monoxide), special fluxes are used. The simplest is fused borax (sodium tetraborate hydrate).
For the additive, welding rods made of cast iron are used . As they melt, they are introduced into the welded zone, distributing them in oscillatory or spiral movements.
When working with alloyed cast irons, similar additives are added to the additive composition (of the simple ones - stainless steel).
Which electrodes to choose
To weld cast iron with an inverter, special electrodes are required, the wire composition of which will interact well with the base metal and prevent the release of carbon and the formation of pores. The following brands have proven themselves to be excellent in this regard:
- TsCh-4;
- MNC-2;
- OZCh-2;
- OZZHN-1.
Nickel and copper are added to their composition, which prevents the release of carbon. Additionally, the tensile properties of these admixtures contribute to a stronger weld that can withstand tensile and fracture loads.
If it is not possible to purchase electrodes for welding cast iron, and repair work cannot wait, then you can make them yourself. To do this, copper wire is wound onto conventional electrodes (E-46, ANO-21). The coils are laid tightly to each other in one layer. It is necessary to start winding from the end of the electrode that will burn. The diameter of the copper wire does not matter and can range from 0.5 to 1.0 mm. When an electric arc burns, the rod of the electrode itself and the wound copper melt, and the coating of the electrode will protect the weld pool from the external environment.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MTSXk7FjMhw
Features of the material
Cast iron is an alloy of carbon and iron, where the carbon content is 2.14%. Which negatively affects the quality of the connection.
The process is labor intensive due to:
- formation of cracks and pores;
- during processing, the appearance of hardened structures and rapid dulling of the tool;
- thin material crumbles from overheating.
According to its composition, cast iron is divided into gray and white:
- White ones cannot be welded due to their fragility and hardness. Suitable for grinding;
- Gray (high strength, malleable) are easy to machine and have limited weldability.
Technology of welding cast iron with electrodes
There are 2 methods of welding cast iron - hot and cold.
Hot also includes semi-hot.
When hot joining, the part is heated to a temperature of 600-700°C, welding is performed and the cast iron product is slowly cooled in the furnace. With a semi-hot connection, the temperature is maintained at 300-400°C.
Hot and semi-hot welding requires additional equipment. In domestic conditions, a cold connection is used.
Edge cutting
Welding cast iron with an electrode at home requires chamfering. There is no need to degrease or clean the parts.
Chamfering is performed:
- file;
- emery;
- Bulgarian
Note: sharp edges are not allowed. The sharpness is removed with a suitable tool.
How to cold weld cast iron parts
When connecting, do not overheat the heat-affected area (no more than 80°C). Take frequent breaks between passes. Use multi-pass welding.
- first perform surfacing along the edges of the chamfers;
- then gradually filling the seam;
- After each pass, hot forge the roller.
Make rollers 40 mm long, scattered to reduce heating of the part.
How to weld cast iron using electric welding at home. What you will need:
- current source (inverter);
- electrodes 3 mm;
- seam cleaning brush;
- hammer for forging and removing slag;
- cutter or cutter for cutting chamfers;
- shield and gloves.
- first, cutting edges and blunting sharp corners;
- then surfacing along the edges of the chamfers;
- then gradually fill the seam.
Forge each roller hot. Don’t rush, give the part time to cool (heating of the heat-affected zone is no more than 80°C).
After filling the weld, turn the part over and cut the edges on the reverse side. Perform welding as described above. Observing the temperature regime and forging each roller. At the end of the process, grind the deposited surface if desired.
Video:
Cold welding is used to repair batteries, vices, engine cylinder blocks and other structures made of gray cast iron.
Brands of electrodes for welding cast iron
In this article, you can get acquainted with factory electrodes and homemade electrodes for connecting different types of cast iron.
The table below will help you set the current on the device for different diameters of electrode brands:
The current values are indicated for the lower position of the electrode. For a vertical position, the current is reduced by 15-20 A, except for TsCh-2.
In order to save money, home craftsmen have adapted to welding cast iron with a conventional electrode with copper wire. Video below:
Also, copper wire will help in welding cast iron with steel.
Some craftsmen ask how to cook cast iron with a semi-automatic machine? On metalworking forums, experienced welders advise using PUNCH 11 wire. The connection is made with 2-5 cm stitches with forging, without gas protection on straight polarity. Current 90-110 Amperes depending on the thickness of the metal.
How to cut cast iron
Types of cutting are divided into thermal and mechanical. List of tools and methods:
- The grinder is a simple and affordable way. Minus: the cut occurs in a straight line.
- Pipe cutters have proven themselves well when working with pipes.
- Reciprocating saw.
- Electrode.
- Oxy-fuel cutting is a good option. Oxygen flux will improve the quality of cutting cast iron.
- Mobile installations Thermal cutter 2M (weight up to 5 kg).
- Oxygen-lance cutting and plasma.
As you can see, there is plenty to choose from! The grinder is widely used in everyday life.
Electrodes and wire
Metal cored wire is a layer of flux “wrapped” in metal . Its various types are used for both hot and cold processes. It is designated by the abbreviation PPCh-1 (cored wire for cast iron), PPCh-2, etc.
To weld parts using semi-automatic machines, wire type ESAB OK Nicore 55 is used. It can only be used in an argon environment.
It is used for malleable and high-strength cast irons, allowing to obtain a durable, easy-to-process seam. For electrode welding, electrodes of the TsCh-4 type with a rod made of low-carbon wire and a coating of a slag-forming flux mixture are used .
In addition to them, there are other types, in particular OZCh, OZZHN, etc. Which electrodes to use to cook cast iron is decided in each specific case, depending on the conditions, grade of metal, required strength, etc.
Cast iron welding options and their brief characteristics
Depending on the strength requirements and the nature of damage to cast iron parts, one of several welding methods is used.
Hot welding
Hot welding is used in cases where it is necessary to obtain high machinability of the seam and the proximity of its composition and structure to the rest of the cast iron. The parts to be welded are prepared as described above and heated to a temperature of 700°C. If necessary, before heating, a mold is made from materials used in foundry. This is required for through and edge (chip) damage. Sanded surfaces and threads should be protected with clay.