Cleaning of welds after GOST welding
Today, welding is one of the most popular technologies for connecting metal structures, since uniformity of the material in the bonding areas can only be achieved by welding.
The resulting welds ensure reliable connection of individual elements of metal structures and do not allow moisture to pass through. The procedure for cleaning welds after welding plays an important role in this regard.
Cleaning of welded joints is a mandatory step after welding work, which is regulated by GOST 9.402-80. To carry out this type of work, different technologies can be used that have different effects on the metal surfaces being processed, for example, mechanical grinding, chemical etching, neutralization.
Weld seam cleaning technologies
There are three main methods for cleaning joints after welding:
- Thermal treatment . The method allows you to remove residual stresses from the material that are formed during the welding process. Heat treatment is of two types: local (heating/cooling is carried out exclusively on the weld itself) and general (heat treatment of the entire metal structure).
- Mechanical processing . Residual slag is removed from the surface of the material, and the cleaned seam is checked for strength. For example, the welding joint is cleaned of slag formation and tapped with a hammer.
- Chemical cleaning . A special anti-corrosion material is applied to the area where metal structural elements are connected. For example, welding seams are treated with a primer paint and varnish composition.
Important to remember! Residues of slag on the joint surface will contribute to the development of metal corrosion.
Tool selection
Cleaning of weld seams after welding must be approached individually, and the correct equipment and consumables must be selected.
For example, the following tools can be used:
- ordinary brush for metal;
- special grinding machine;
- angle grinder with abrasive wheels.
Example:
- In the shipbuilding industry, mobile-type grinding machines are effectively used, since it is much easier to approach a metal structure of a sufficiently large size than to constantly move the tool from one area to another.
Machining Technology
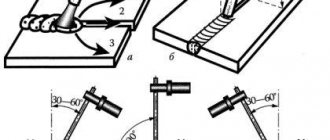
The manual method of mechanically cleaning a weld seam is the simplest. To do this, you just need to have a regular metal brush.
But it is easier and more efficient to clean surfaces using a special grinding machine equipped with an abrasive wheel (special grinding attachment).
Mechanical cleaning of the weld after welding allows you to eliminate the following defects from metal surfaces: burrs, oxides, scale, traces of tarnish. This technique is especially popular among welders due to its low cost.
But in order for the job to be done efficiently, it is important to choose the right grinding attachment.
Aluminum zirconate is the best material for cleaning welding joints of stainless steel products, since it surpasses aluminum oxide in its strength characteristics and does not expose the metal to corrosive effects.
The most effective and efficient way to clean welded joints is to use simultaneous mechanical and chemical treatment (passivation, etching).
Etching stripping
Cleaning of weld seams by etching is usually carried out before mechanical grinding of the surface. For this purpose, a special composition is used, with the help of which a homogeneous layer is formed on the treated metal surface.
The etching technology can be used both for straightening the joint of a welded joint and for processing the entire area of a metal workpiece.
This method helps to get rid of tarnish on the metal surface formed during welding.
Conclusion
For high-quality production of metal products using welding, surface treatment is an integral process regulated by technical conditions and GOSTs.
Sergey Odintsov
How to clean welds after welding
(Last Updated On: 10/03/2017)
Cleaning up the weld after welding
Welding is one of the most common technologies for fastening metal parts today, because it is by welding surfaces that it is possible to obtain a homogeneous connection that does not allow moisture to pass through and ensures strong bonding of elements.
However, the weld itself is a weak point of the structure, which must be protected from premature damage and destruction. Therefore, a mandatory stage of any welding work is cleaning the weld seams after welding - the need to carry out such work is a norm enshrined in GOST 9.
402-80 “Unified system of protection against corrosion and aging. Paint and varnish coatings. Preparation of metal surfaces before painting."
To perform such work, various tools can be used that have different effects on the surface being treated - this is ordinary mechanical grinding, chemical etching, and neutralization. Each of these technologies has its own characteristics and indications for use.
Mechanical cleaning of the weld
The simplest option for mechanical cleaning is manual cleaning with a wire brush. However, such processing is much simpler and more effective when performed with a portable grinding machine or an ordinary grinder equipped with a flap sanding attachment or an abrasive wheel. Using this method you can get rid of many weld defects:
- scale;
- oxides and burrs;
- traces of discoloration.
This technology is loved by many welding professionals also because it is perhaps the most profitable in terms of price-quality ratio.
However, it is very important to choose the right grinding wheel, otherwise you cannot count on excellent results.
The best material for treating welds on stainless steels is aluminum zirconate because it is non-corrosive to the metal and is significantly stronger than aluminum oxide, also used to make flap abrasives.
It is also important that the petals have a fabric backing, because it is more reliable and durable than a paper backing, which is necessary for such an aggressive type of work as grinding welds.
It should be noted that nozzles with a fabric base, and even coated with aluminum zirconate, are much more expensive than conventional paper nozzles coated with aluminum oxide, but the price is worth it - the work will be easier and more efficient.
In addition, the use of such attachments minimizes the possibility of the formation of a corrosion center at the grinding site, which is very important for the high-quality performance of important work.
Depending on the scale and subtlety of the work being performed, you should use attachments with different abrasive grain sizes - the product line of the main manufacturers offers a variety of grain sizes, so you need to have several sizes in your arsenal. Moreover, to perform high-quality work, sequential processing with different attachments will be required to reduce the grain size.
In this case, the size must be changed sequentially; no more than one size can be skipped. And if you need to achieve mirror-like evenness and shine of the weld, then it is forbidden to skip even 1 size. Otherwise, untreated risks may appear, and all work will have to start from the very beginning.
Grinding welds in hard-to-reach places - cavities, holes, on thin edges - is difficult and at the same time responsible; special tools are used here - burrs, which are mounted in a straight grinder. Burrs come in many different shapes and sizes, so choosing the right tool for the job is easy.
Chemical treatment of welds
As practice shows, the best results when processing welds can be achieved by combining mechanical processing with chemical action on the seam. Such an effect can be different - this is etching and passivation.
Etching is a weld processing stage that precedes mechanical grinding.
Etching is carried out using special compounds that create a uniform anti-corrosion coating on the surface of the part. Also, with the help of etching, areas with tarnish are removed - oxidized chromium and nickel accumulate in such places, so these areas are more quickly affected by corrosion.
Pickling welds (video):
For small areas of welds, etching is best done by simply applying an etching compound to the seam; in some cases, the part is completely immersed in a container with an etching solution. The required time of its exposure to the metal is determined individually in each case.
After etching, passivation is performed to give the weld additional strength.
Passivation is the treatment of a metal surface with a special composition, which forms a protective film on the treated part that is passive to the formation of corrosion - hence the name of the technology.
The chemical essence of this process is as follows: mild oxidants, when interacting with stainless steel, remove free metal from its surface and activate the formation of a protective film on the surface.
Passivation of stainless steel (video):
After chemical cleaning of weld seams after welding has been carried out, it is necessary to wash off the reagents with water.
At the same time, you need to take care of the proper disposal of wastewater after such a flush - it contains a large amount of acids and heavy metals, so such wastewater has a high level of danger to the environment.
First of all, it is necessary to neutralize acids using alkaline compounds, then it is recommended to filter and dispose of it in accordance with the norms of natural legislation.
Weld processing - overview of methods
Welds are responsible for the integrity of the metal structure. In particular, the connection must be strong enough, resistant to rust and moisture. Weld seam processing is designed to ensure the fulfillment of these tasks.
Processing methods
There are three methods by which welded joints are protected:
- Heat treatment. Thanks to this method, it is possible to remove residual stresses in the material resulting from welding work. Heat treatment is carried out using one of two technologies: local, when only the connection itself is heated or cooled, or general - the entire part is subject to temperature treatment.
- Mechanical restoration. In this case, the task is to remove slag residues and check the reliability of the connection. A typical example of machining is tapping a seam with a hammer or sanding it. If the slag is not removed, corrosion may develop.
- Chemical treatment. Applying protective coatings to joints is one of the ways to combat corrosion processes. The most affordable option for chemical protection is treating the seam with a primer paint and varnish material.
Communities › Body Repair › Blog › The eternal question, processing of welded parts before or after?
Hello everyone, I’m going to restore the body, and I’ve been racking my brains for a week now, how to process body parts with cavities that will be welded? There are a couple of ideas, but I still don’t understand which one is better, please help and explain =)
1 - Stripping to bare, clean metal without rye, after welding, if you can’t get into the cavity, drill a hole, spray with Movil, trying to cover the entire internal part, especially the welded part and welding points, thereby blocking the access of oxygen, and therefore rye, that is you get clean bare metal immediately
2 - Stripping down to bare metal, treating both parts with anti-corrosion primer ABRO, for example, or with an acid primer brush, after drying, clean the welded areas to a minimum in the mating areas, and cook, and then seal the cavity
It seems natural that the second method is the smartest, but!, the thing is that we are racking my brain: After welding, the acidic primer burns out, in its place in the cavity there are husks, bubbles and all sorts of nasty things left, but the acidic primer is no longer at all, especially in the places welding, those places that are most susceptible to corrosion than pure metal...
And the first method is both easier and simpler, but! Movil doesn’t know how it will behave, for example, in a year, it can crack, curl, and we get the same husk, but in about a year, let’s say, clean bare metal, which will happily begin to rot, but compared to the second method, after welding, Movil will completely cover pure metal , but in the example with an acidic primer, it won’t cover everything at all, since the resulting husk from the burnt acid agent will not allow it to be perfectly absorbed into the seams, and it turns out that Movil on bare metal takes even longer than hemorrhoids with an acid agent, drying, cleaning, but I haven’t seen Why do they do this, who can explain to me, a fool?
source
Cleaning welds
In fastening metal structures and various parts, welding is the most common and economically acceptable method.
By connecting surfaces, you can ultimately achieve a homogeneous connection, which ensures strong bonding of individual elements.
The joint is the weak link in any welding method. Therefore, cleaning welds is a necessity.
Uncleaned weld after welding
It’s not for nothing that cleaning of welds after welding is regulated by GOST 9.402-80.
For cleaning, various tools are used and certain technologies are used. It could be:
- Cleaning the weld seam by mechanical grinding.
- Etching using chemical materials.
- Neutralization method.
It is clear that a particular technology has its own nuances and recommendations for use in a given situation.
Stripping equipment
The choice of technology must be approached carefully. You need to select the right consumables and work equipment.
This could be a wire brush, an angle grinder/machine with abrasive wheels, or a grinder.
"Important!
When choosing grinding equipment, you should focus primarily on the power output. And only then look at consumption indicators.”
For example, mobile sanding machines are successfully used in the shipbuilding industry. It’s easier to approach a large workpiece than to try to move it to a new location.
Mobile grinding machine
The need to clean welds
The final stage of welding includes cleaning the joint from slag and scale. Cleaning of welds after welding is carried out in three stages:
- the area around the welding joint is processed;
- polishing after treatment with antioxidant;
- tinning the connection point.
Cleaning of welds is regulated by GOST 9.402-80 and is carried out to eliminate, among other things, defects in the working surface. According to approved standards, these can be:
- Holes.
- Craters.
- Fistulas.
- Cracks in the seams.
It is important to carry out the work process in accordance with accepted standards. Violations of established standards must not be allowed. It is necessary to make full use of the capabilities of grinding equipment and other cleaning mechanisms.
Mechanical cleaning of the docking area
How to clean welding seams with a grinder? The simplest method of mechanical action is manual stripping with a grinder. In this case, you can get rid of defects that are inevitable when welding:
- From scale.
- Burrs and oxides.
- And also traces of tarnish.
Cleaning a weld seam with a grinder
Many note the cost-effectiveness of this method, and this is a proven fact.
"For your information!
Cleaning welds will be done professionally if you choose the right grinding wheel.”
Chemical cleaning of the connection
As practice shows, the interaction of two methods: mechanical and chemical influence is the most effective and efficient option. Cleaning of welds can be performed:
- etching method;
- passivation method.
Let's look at both options. Let's determine the differences and find out what each of the above methods consists of.
- Cleaning welds using pickling method.
This is one of the processing stages of a welded joint, which is performed before mechanical grinding.
The work is carried out using a special composition that allows you to create a homogeneous layer on the working (processed) surface.
Using the etching method, areas with tarnish can be removed. Etching is allowed both for individual sections and for complete workpieces.
Workpiece etching method
In the latter case, it is best to place the material completely in a container with an etching solution. There are no clear regulations and time for the etching process during complete immersion.
The time in this case is determined individually. Cleaning of weld seams after welding will be more effective if passivation is performed after pickling. This will give the joint a bonus of extra strength.
Processing of welds after welding can be carried out using the passivation method. The process looks like this. Surface treatment is carried out with a special composition.
An even layer applied on the working surface forms a film. This is necessary to prevent metal aging, or more precisely, corrosion.
Using the passivation method
From a chemical point of view, it looks like this: oxidants from the softened surface of a part or workpiece, interacting with stainless steel, eliminate the resulting free excess.
They also activate the formation of a film to protect the work object.
Cleaning of fillet welds is carried out in accordance with the established rules of state technical supervision. The shift foreman is responsible for the quality of cleaning. The results of the work are entered into the weld repair flow sheet.
Safety precautions
When performing welding work, regardless of the method, it is necessary to initially prepare the workplace and check the equipment.
The process involves the use of special protective equipment and work clothes for the welder. Including the need for training and compliance with fire safety standards.
Before welding begins, instructions are given, the results of which are recorded in the work log. Admission is granted to persons at least 18 years of age who have undergone special training.
Conclusion
For high-quality manufacturing of products using welding work, surface treatment is a prerequisite. Processing can be done in different ways.
But the goal is one: to bring the working element to a state of complete readiness. The importance of this process is regulated by the provisions of GOST and other documents at the state level.
We can conclude that surface treatment and removal of welding residues is an important and integral process that ultimately allows us to obtain the desired result.
Types of connections
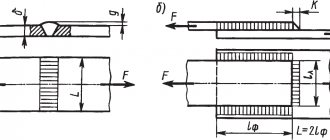
Butt joint is a welded connection of two elements adjacent to each other with end surfaces and located in the same plane or on the same surface (Fig. 2). The surfaces of the elements may be slightly displaced when connecting sheets of different thicknesses (see Fig. 2, b).
Rice. 2. Butt joints
Corner connection is a welded connection of two elements located at an angle and welded at the junction of their edges (Fig. 3).
Rice. 3. Corner joints
T-joint is a welded joint in which the end of one element adjoins at an angle and is welded to the side surface of another element (Fig. 4).
Rice. 4. T-joint
Lap joint is a welded joint in which the welded elements are located parallel and partially overlap each other (Fig. 5, a, b). The absence of the danger of burn-through during welding facilitates the use of high-performance welding modes. The use of overlap joints facilitates the assembly and welding of seams performed during the installation of structures (assembly seams).
End connection is a welded connection in which the side surfaces of the welded elements are adjacent to each other (Fig. 5, e).
Welds are divided according to different criteria: by type of seam, by length, by method of execution, by spatial position and by the shape of the edges.
Preparation of edges for welding: processing and cleaning of welds and stainless steel
Welding is one of the most common methods used to join metal parts. This is due to the fact that it allows high-quality and reliable fastening of parts of the product, forming a uniform seam that does not allow moisture to pass through.
Nevertheless, it is the seam that is the weak point of any structure, especially if the edges for welding were not prepared correctly. Therefore, it is very important to follow all technological processes in order to obtain a reliable connection of parts.
Features of cleaning products after welding
The final stage of welding work is to clean the joint from slag and scale.
This procedure is performed in several stages:
- seam treatment;
- antioxidant polishing;
- tinning the connection.
The first stage is performed to eliminate defects. These include holes, craters, fistulas, and cracks in sutures.
Main types of welded joints.
There are three main methods for processing a weld seam:
- thermal;
- mechanical;
- chemical.
The first method allows you to significantly reduce or completely eliminate residual stresses in the metal after welding. Heat treatment can be carried out in accordance with two technologies: local - only the joint area is heated, and general - the entire part is heated.
In addition to reducing stress, thermal annealing makes the structure of the seam and the area around it more resistant to external factors. In addition, the performance indicators of the product increase: corrosion resistance, heat resistance, etc. increase.
The essence of heat treatment is to heat a joint or part to a certain temperature. The product is then cooled at the required rate, depending on the type of part.
Heat treatment is carried out using specialized equipment.
There are four types of devices for performing this procedure:
- Induction units are used for pipelines. The operating principle of such devices is the use of air-cooled stranded copper wires that make up the inductor. The inductor is installed on the pipeline at a certain distance from it. The larger the gap, the worse the power of the device is used, so it should be installed flush to the weld.
- Flexible resistance heaters are one of the most common devices.
- Muffle furnaces. This type of device requires special attention to control the uniformity of heating of the product. Off-center installation of a part in a furnace can lead to disruption of heat treatment technology.
- Processing using gas-flame equipment. This method uses gas flame burners.
Tools that enable heat treatment are selected based on installation conditions, availability, and other factors. The main criteria that such units must satisfy are compliance with the set requirements, clear joining with seams, uniform heating of the joints, and low weight.
Quite often, to avoid heating losses, various heat insulators are used.
There are several metal processing technologies. Preheating is used both before and during welding when working with low-carbon steels.
High tempering involves heating the material to 650-750 °C. The exact temperature value is determined by the grade of steel. This treatment lasts up to five hours and reduces stress by 80%, and also increases the elasticity and resistance of the metal to mechanical stress.
Normalization is applied to carbon and low-alloy steel grades. The process is carried out at 950 °C. Upon completion of processing, the part is held and cooled under normal conditions. As a result, grain size and stress are reduced and joint strength is increased.
Mechanical cleaning
An important stage of welding is not only the implementation of preparatory work, but also the correct cleaning of the welds. This process is mandatory and is enshrined in the relevant GOST.
Symbols for welds.
So how do you clean a welded joint? The easiest way to clean a weld is to simply brush with a wire brush. However, using a portable sander or a simple grinder with a sanding wheel for stripping will be more effective.
This simple processing method will allow you to get rid of the most common defects, which include scale, oxides, traces of tarnish, and burrs. As a result, the joint of the workpiece will be of higher quality.
In terms of price-quality ratio, this technology is one of the most profitable methods for preparing edges before and after welding. In this regard, it is not surprising that most masters use this method.
When choosing a grinding wheel to clean a seam after welding, it is important to take into account some nuances, otherwise you should not expect a good processing result. Preference should be given to attachments with fabric-based petals.
It is characterized by higher wear resistance compared to paper versions, which is necessary in such an aggressive type of work as grinding welding joints.
It should be borne in mind that fabric-based attachments with this coating are expensive. However, in this case it is better not to save money, because with the right tool the job will be easier and the end result will be of better quality.
Chemical purification of the compound
As already described above, mechanical processing allows you to achieve acceptable results, however, the best quality of cleaning the weld after welding is achieved when this method is combined with chemical cleaning. This includes etching and passivation.
Chemical for cleaning seams.
Etching is carried out using specialized compounds. They allow you to obtain a uniform anti-corrosion coating on the surface of the product. In addition, areas with tarnish are removed - places where chromium and nickel oxides accumulate, which are characterized by low corrosion resistance.
Small areas of the seams to be treated are etched by simply applying the compound to the required area. In some cases, the product is completely dipped into a container with a special solution. The interaction time of the part with the mixture is different in each specific case and is selected individually.
Passivation is the process of treating a metal product with a special solution. As a result of this process, a protective film is formed on the treated surface of the part. A distinctive feature of the resulting coating is its resistance to corrosion.
The essence of this technology for cleaning edges for welding is the use of mild oxidants. As a result of interaction with stainless steel, free metal is removed from its surface and the formation of a protective coating on the surface of the product is activated.
Passivation can be carried out using sprays for treating stainless steel or a special paste.
The fact is that such water contains an increased amount of acids and heavy metals, so such wastewater is characterized by an increased danger to the environment. First, acids should be neutralized using alkaline solutions, and then the water should be filtered. The resulting waste must be disposed of.
Bottom line
To understand how to properly clean welding seams, you need to familiarize yourself with GOST, which describes in detail the technology for processing joints. There are two main methods for cleaning a weld seam: mechanical treatment and chemical treatment.
In the first case, the metal, for example stainless steel, is subjected to grinding and polishing. In the second case, etching and passivation technology is used. Special solutions are used to pickle stainless steel after welding. Most often, these methods are combined to achieve the best results.
Chemical treatment
The best results when processing welded joints are achieved with a combination of mechanical and chemical means. Two methods of working with seams are used: etching and passivation.
Etching is performed before mechanical grinding. To carry out this operation, chemical compounds are used to provide a uniform coating that prevents corrosion processes. In addition, etching allows you to eliminate areas affected by tarnish. The fact is that in such places there is an accumulation of nickel and chromium oxides, as a result of which the steel becomes rusty.
In small areas of welded joints, it is recommended to carry out etching by directly applying the composition to the surface to be treated. If the part is large enough or has a complex configuration, it should be placed in a container with an etching solution. The time the metal remains in the etching flow is calculated individually in each situation.
When etching is completed, passivation begins. The process involves applying a special composition to the metal, resulting in the formation of a film. This protective coating prevents corrosion. From a chemical point of view, passivation can be explained as follows: oxidants, interacting with steel, remove free metal from the surface, thereby activating the formation of a protective film.
The chemical treatment is completed by cleaning the welded joints from reagents. The flushed water contains many toxic substances, heavy metals and acids. Acids are neutralized with alkalis, and then the remaining liquid is filtered. Waste material must be disposed of only in specially designated areas in accordance with environmental protection legislation.
Cleaning of welds after welding GOST - Metalworker's Handbook
The car body is its most expensive part. As long as the skeleton of a vehicle is alive, so long is its service life. All damage to the car body can be divided into the following types:
- Destruction by corrosion;
- Surface damage due to mechanical damage (including road accidents).
Each type of repair work has its own methodology. To combat corrosion, all kinds of primers are used, which reliably protect the metal from further destruction.
ATTENTION! A completely simple way to reduce fuel consumption has been found! Don't believe me? An auto mechanic with 15 years of experience also didn’t believe it until he tried it. And now he saves 35,000 rubles a year on gasoline! Read more"
Mechanical damage and defects are most often welded. At this stage of repair work, cleaning the weld seam plays a key role in controlling the quality of the operations performed. Ideally, the junction of the parts should be inconspicuous and not attract attention.
Welding methods and equipment used
If the surface of the body is heavily corroded, welding is also used for repairs. The equipment that a master chooses to perform welding work can have different performance levels and ultimately determines the quality of the seam. Welding used in body repair can be of several types:
- Gas;
- Electric arc;
- Manual semi-automatic electric arc (environment with protective gas);
- Contact point.
Hobbyists repair their hardware using gas welding; this is the most affordable equipment for private use. Hand tools are not helpful in this matter, as the operation becomes very labor-intensive.
Professional welders are skeptical about the use of manual electric arc welding, what about amateurs? Resistance welding is an expensive tool used by skilled craftsmen.
Quality criteria for welds
You can check the quality of the connection of parts after welding using various devices and devices. An important detail is that all welding areas must be well cleaned. Only after this is quality control carried out.
Methods used:
- Carrying out a visual inspection. To do this, use a magnifying glass or a simple glance. All defects found during the inspection need to be eliminated;
- Performing translucency of the seam. For this, gamma radiation or X-rays are used. In this way, all undercooked areas in the thickness of the metal up to 6 cm are identified;
- Magnetographic method. The tool used for such a check is accurate and is designed to work with metal no thicker than 0.4-1.2 cm;
- Ultrasonic testing is more often used to check weld seams on steel or non-ferrous metals;
- Opening a weld seam is a radical measure, for which special equipment is also used;
- Chemical method;
- Performing color flaw detection;
- Kerosene test;
- Pneumatic tests;
- Creating a vacuum;
- Other techniques.
The abundance of technologies for checking the quality of welds is an excellent incentive to more carefully perform this type of work. By purchasing a machine for cleaning weld seams, the master gains a lot of advantages:
- Flawless completion of workpiece processing;
- Removing the seam after welding;
- Preparing the product for the final stage of processing.
Equipment that can be used to properly and aesthetically clean weld seams can be used in production or for personal consumption. This tool is designed for processing different materials:
- Copper;
- Aluminum;
- Stainless steel, etc.
On stainless steel or other metal surfaces, cleaning equipment successfully replaces abrasive paste, a grinding wheel, or a special milling cutter (the listed devices are often used by amateurs after welding metal surfaces). Professionals recommend using precise, modern tools that guarantee high results without surprises.
Selection of equipment for stripping seams
After welding, all seams need to be cleaned. On black steel, it is necessary to get rid of oxides and scales on the weld. For this, special wire brushes are used. In this case, the scale of the stripping zone is determined by the tool used - hand brushes or special machines.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xqIxVODfGtM
The world market leader in the production of wire brushes is German. This brush can be installed in an angle grinder or angle grinder. Many stainless steel surfaces are cleaned in this way.
Often, cleaning the weld is accompanied by removing the reinforcement. In this case, tools and consumables are selected more carefully. Experts recommend using a mobile version of a grinding machine or an angle grinder equipped with abrasive wheels.
Efficient and modern equipment for automotive repair - a mobile machine. The tool is well controlled and can be used by 1 person.
from Germany produces 2 modifications of this machine, which involve the use of belts of varying degrees of grinding.
Professionals recommend cleaning the seams after welding with tapes produced by the manufacturer of the equipment itself.
Grinders and grinding wheels are the choice of craftsmen who prefer cheap and affordable equipment. This method can be used to process any seams - steel, stainless steel and other metals.
The choice of tool for cleaning weld seams when carrying out body repairs determines the speed of work and the quality of the finished coating.
Tired of paying fines? There is an exit!
Forget about fines from cameras! An absolutely legal new product - NANOFILM, which hides your license plates from IR cameras (which are installed in all cities). Read more about this at the link.
- Absolutely legal (Article 12.2.4).
- Hides from photo and video recording.
- Installs independently in 2 minutes.
- Invisible to the human eye, does not deteriorate due to weather.
- 2 year warranty
Heat treatment
In addition to reducing residual stresses in the metal, heat treatment allows you to achieve the following goals:
- make the structure of the seam and heat-affected zones more adapted to external factors;
- optimize the physical and operational properties of the material, in particular, increase rust resistance, heat resistance, etc.
Heat treatment of welded joints involves heating the welded joint or the entire metal to a given temperature for a certain time. Next comes artificial cooling, which is also carried out according to a certain scenario.
Heat treatment equipment
Four types of technological equipment can be used for heat treatment of joints:
- Induction devices. Induction heating is often used during pipeline installation. The essence of this method is the use of copper inductors, including multi-core air-cooled copper cable. When installing the inductor on the pipeline, the distance between the pipe and the inductor must be taken into account. The general rule is: the larger the gap between objects, the worse the equipment's power is used.
- Flexible resistance heaters. This method is considered one of the most convenient and affordable methods for processing welds.
- Muffle furnaces. When working with this type of equipment, special attention must be paid to the uniform heating of the connection, which is achieved by non-centered installation of the part in the furnace.
- Heating using gas-flame equipment. When using gas flame heating, welding and special multi-flame gas burners are used. Gas heaters produce thermal energy resulting from the combustion of a mixture of combustible gas and oxygen.
Video text
Greetings! To begin with, I recommend good online stores - goods and services at an affordable price:
Useful products - online store "Gearbest": https://goo.gl/riFbzo Necessary and useful - online store - "Aliexpress": https://goo.gl/242qIr Lots of necessary products - online store - "Banggood": https ://goo.gl/U7l3Kp Knife store - “Knives”: https://goo.gl/pPjgRj
Earn money from your video with affiliate programs:
Make money on your video with - "AIR": https://goo.gl/R7C0pK Make money on advertising in videos with - "Admitad": https://goo.gl/1qvZqN
Greetings! To start with the recommendations, the channel is Autobreaker https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCsrH. And to our topic today. In this video I will tell you and show you how to properly clean (file) weld seams. It seems that this is a simple process, but it has its own nuances, namely, do not burn the metal, do not take more than necessary samples and, of course, go over with a brush to prepare the surface for puttying.. I will talk about all this in detail in the video. Well, as usual, like the video if you liked it, ask if something was not clear... Comment and don’t forget to subscribe to my channel! Enjoy watching!
Melody in the video, author: Routenote Tvoi Rai · Air Tvoi Rai ℗ Air
source
Defects and sewing defects
The most common defect in a beginner’s work is a crooked seam with uneven filling. This picture is the result of uneven guidance of the electrode; it literally dances in the hands of the young master. Here you will need perseverance and work: with experience, all this passes without a trace. The second most common mistake is the incorrect choice of current strength or arc length, which leaves “undercuts” or uneven filling. With some defects, aesthetics suffer more, with others - strength.
Lack of penetration - insufficient filling of the joint of parts with metal. It needs to be corrected, since we are talking about the strength of the connection.
In what cases does lack of penetration appear:
- Poor quality processing (or lack thereof) of surface edges;
- The current is too weak;
- Electrode movement too fast.
An undercut is an unnecessary groove along a seam. The diagnosis is simple: choosing an arc that is too long. The treatment is also clear: either a shorter arc, or a higher current intensity.
A burn-through is a banal hole in a seam for the following reasons:
- Wide gap between edges;
- The current is too high;
- Low electrode speed
And here we are looking for the optimal ratio of three components: current, gap width, electrode movement.
Pores and nodules are multiple small holes. This is a critical defect that affects the strength of the connection.
- Dirt and rust on metal;
- Oxygen reaching the molten metal (in a draft);
- Poor quality edge processing;
- Low quality electrodes;
- Use of filler wires;
Cracks are serious violations of the integrity of the seams. They appear after the metal has cooled and are essentially harbingers of the destruction of the seam itself. In this case, only new welding or complete removal of the old seam and re-applying a new one will save.
We cook pipelines, special requirements
Only experienced, certified and highly qualified craftsmen are allowed to work with industrial pipelines.
Pipe connections belong to the vertical method with all the “vertical” nuances. The peculiarity lies in the angle at which the electrode is held, this is an angle of 45 degrees. The width of the pipe seam can reach 4 cm, it depends on the thickness of the pipe itself. There are separate standards for this type of welding, for example, GOST 16037-80 describes the dimensions of seams for various connections of pipeline structures.
Type of connections os (bp) os (sp) ds (bz) ds (zk)
Welded joints are divided into the following types:
- welded connections made on one side (one-sided welding) - os (ss) and on both sides (double-sided welding) - ds (bs);
- welded joints made on a removable or remaining lining, backing ring - sp (mb) and without a lining (in weight) - bp (nb);
- welded joints made with stripping the weld root - zk (gg), without stripping the weld root - bz (ng);
- welded joints made with gas protection of the weld root (gas injection) - gz (gb);
Types of connections os [sp, bp], ds [bz, zk]
Compare, evaluate
Of the above options, butt welding is considered the most reliable and economical. In terms of current loads, they are almost equal to whole elements that were not welded, in other words, to the base material. Naturally, such strength is achieved only with adequate quality of work.
At the same time, it must be remembered that the reliability and efficiency of the method does not mean that it is easy to implement. Requirements for edge processing, adjustment of many factors to the conditions of a specific welding, certain restrictions in application due to the shape - all this requires strict professional discipline.
T-joints (including corner ones) are also quite popular. They are especially often used when welding massive structures.
The simplest ones to perform are overlapping joints. They do not require edge processing, and general preparation is also much simpler. Very popular in welding sheets of small thickness (thickness up to 60 mm is allowed). Simplicity does not mean efficiency: excessive consumption of deposited and base metals is a common situation for such options.
Seams according to position in space
The next classification criterion is the position of surfaces in space. There are four such provisions:
- Bottom seams
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Ceiling
If it were possible to choose, experienced craftsmen would choose welding in the lower position. This is the most convenient method, and the weld pool is better controlled. A suitable method for debut works of beginners - there are practically no difficulties here. But the other three spatial options are associated with technical nuances and special requirements for execution.
Choose, try, the main thing is that the bathtub does not tend to fall down. If the metal still drains, you need to reduce its heating - this can be done by increasing the speed of movement. The second option is to periodically tear off the arc so that the metal cools at least a little. The arc lift method is more suitable for beginners
In vertical connections, the same problem is the force of gravity, but here it is not the entire bath that tends down, but drops of metal. Usually in such cases they take a shorter arc. The seam can be welded in any direction. In the Welding Certification Regulations RD 03-495-02, these options are designated as “welding position B1” - vertical from bottom to top (this method is more convenient). “Welding position B2” is vertical from top to bottom, it is used less often, since strict control of the weld pool is required here.
The ceiling connection is the most difficult in the subgroup, which will require real skill. There are no other options in the position of the electrode - keep it only at a right angle to the ceiling. Make the arc shorter, the speed of the circular motion should be constant. In this case, the release of gases and slags is difficult, and it is difficult to keep the melt from flowing down. Even if the craftsmanship is at the proper level, and all technological requirements are met correctly, the ceiling method is inferior in strength and overall quality to welding seams in all other positions.
What is a weld seam
To begin with, let’s define the concepts of “welding seam” and “welding joint”, because some sources consider them to be one and the same thing, others separate the formulations.
The shortest definition: a weld is a permanent connection by welding.
The second option reveals the physics of the welding process as such: a weld is a section in which two or more parts are connected as a result of crystallization or deformation of a substance, or one and the other together. One way or another, it is more logical to take welding seams and joints as one and the same process.
One of the oldest and most famous standards among specialists is “GOST 5264 – 80 Manual arc welding. Welded connections." This GOST was put into effect back in 1981, it still copes with its tasks perfectly: the main types of welds, their sizes, structural elements and instructions on how to correctly lay a weld are clearly listed. An excellent example of a document that does not need adjustments over time.