The famous MAW is manual arc welding, a people's favorite and the most popular welding technology for a long time. Such an achievement is worth a lot. The method is based on the use of special electrodes.
All actions in the RDS are performed manually by the welder. Despite the popularity and seemingly well-studied nature of this method, it would not be harmful for you and me to repeat the basic facts and check how our dear RDS is doing today.
general information
This method has additional international names; abbreviations are widely used in the manufacture of components. You can find - MMA (Manual Metal Arc - the literal translation of our term), the Russian abbreviation RDS, or in short - RD. The method was invented by Russian engineer Nikolai Bernardos, who subsequently improved his device and created varieties. The patent for the invention was purchased and introduced into the production of metal structures around the world. The classic material is a carbon electrode, but there are new inventions, methods that use melting rods.
Stages of the procedure
All professional and amateur welders operate according to the following algorithm:
- Preparation involves thoroughly cleaning all surfaces and securing the workpiece in the workplace.
- The appearance of an arc. For it to form, you need to apply voltage and touch the metal with the tip 2-3 times with quick movements.
- Carrying out a seam - speed and angle varies depending on the physical characteristics of the material.
- Final processing - unevenness should be removed, excess scale should be removed, and the joint should be cleaned.
Sometimes additional operations are required, such as preheating the workpiece or supplying shielding gas. However, the main elements of the algorithm are reflected correctly.
A few words about seams and their edges
A few words about edges. If you want to get a welded and even seam of high quality in all respects, you need to make edges on metal blanks.
A detailed description of the cutting of edges depending on the type of seam is perfectly described in GOST 5264-80, which is entirely dedicated to RDS. There are three types of edges, which differ only in shape: V, R, X.
After welding, the edge must be removed. This can be done simply with a chisel. But in this case, you will have to forget about the quality and aesthetics of the seam. Smooth and accurate removal can be achieved using a milling or lathe.
If the use of the machine is impossible due to difficult access, the edges are removed by oxygen cutting. Cleaning the edges with a wire brush to remove dirt, corrosion and scale is also a must.
Types of welding seams. Welding seams also vary in shape:
- butt type;
- overlapping seams;
- corner;
- tee seams.
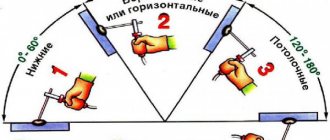
Also, welded joints are divided based on their position in space:
- bottom type - the most common, in which the workpieces to be welded are under the electrode;
- horizontal type: the workpiece is fixed at an angle, and the electrode and welding process are fixed in a horizontal position;
- vertical type of seam that is formed from bottom to top. This is a difficult look due to the flow of molten metal downwards;
- ceiling type, when the seam is located above the electrode;
In difficult positions in space, a reduced current is used, and the welding itself is performed with short movements.
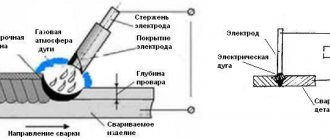
Operating principle of equipment and technology of manual arc welding
From the power source, alternating or direct current is supplied to the electric holder (both options are found). The voltage allows you to create an electric arc that heats two metal surfaces. When the handle moves behind the conductor, a weld pool is formed. In this area, diffusion joining of molten alloys occurs. After they cool, the substance crystallizes and again turns into a solid element - already monolithic. To prevent the seam from oxidizing under the influence of oxygen, the wire in the electrode is coated with a special compound, which, when melted, releases an inert gas that displaces O2.
How is RDS done?
The electric arc is maintained by the supplied current. In this case, different polarities are possible. The classic option is that a minus is applied, and a plus is supported on the workpiece, but a situation occurs with the opposite supply of voltage. Electric arc length is the distance between the weld pool and the electrode. It depends on the speed of the electrical holder. In addition to the gas from the conductor coating, slags are formed in the area of iron smelting, which contribute to:
- increasing the speed of metal processing;
- longer maintenance of high temperature;
- good, even welded joint;
- protection from oxygen and oxidation.
How to strike an arc
It is necessary to lightly touch the workpiece with the end of a vertically directed electrode 2-3 times. If you do not quickly remove your hand, sticking will occur and the surface will be damaged. The second method for manual electric arc welding is to move the end of the material along the future seam. Let's watch the training video:
How to move a weld correctly
You can cook it at an angle “back” and “forward”, that is, towards yourself and away from you. In the first case, the heating of the alloy is stronger, and in the second, less. That is, you should make a choice depending on the material. The angle of inclination is selected in accordance with the formed weld pool. The length of the electric arc should always be the same - about 2-3 mm. Depending on the required strength of the structure and the alloy used, you can choose one of the types of electric arc welding motion, the diagrams of which are presented in the article.
What is electric arc welding - classification and methods
Electric arc welding is one of the methods of joining metal parts, which is characterized by its own operating principle. Within the framework of this technology, to obtain seams, a high current is simultaneously applied to the electrode. As a result of this interaction, an electric arc is formed.
This definition gave the name to this type of welding. Another name is fusion welding. The second name is due to the fact that when a high current is applied, the metal in the affected area takes on a liquid form.
There are several types of arc welding, each of which has its own characteristics.
Types of arc welding
Depending on what devices and technology are used to produce seams, arc welding is divided into the following types:
Manual.
As part of this technological process, the workpieces are moved and welded by a technician. The advantages of this method include the ability to connect metal parts in any conditions.
Disadvantage - the risks of getting a poor-quality seam due to specialist errors increase.
Mechanized.
As part of this technological process, workpieces are fed to the machine using appropriate equipment. But the parts are welded by a person.
A number of sources distinguish semi-automatic electric arc welding technology as a type of mechanical welding. In this process, the torch is moved by the worker himself, while the wire feeding, arc ignition process, and connection formation are performed by specialized equipment.
Automatic.
The process in this case is completely automated. That is, special equipment is involved in feeding and welding workpieces. These devices independently (according to a previously entered program) determine the intensity of the flame, regulate the supply of consumables, and more.
Depending on the technology used to protect the seam obtained under this influence, arc welding is classified into the following types:
- without protection - the process takes place in the open air (typical for manual electric arc welding technology);
- in a vacuum - the process occurs automatically in an environment in which there is no air;
- using gas mixtures that prevent oxidation of the compound;
- submerged - the metal is protected by slag, which is formed during melting.
Combined methods are also used. To protect the welded joint, the following gases are used:
- helium;
- carbon dioxide;
- argon.
Shielding (active or inert) gas is supplied through a special device - a welding torch nozzle, which is equipped with welding machines.
Depending on the nature of the impact, this technology is classified into the following types:
- In a bun. This technique uses a bundle of electrodes that are connected to each other to pass a direct electrical charge. The method allows the use of currents in a wide range of values.
- Lying electrode. The method involves laying with a coating 50-120 cm long in a corner or a pre-cut joint. Next, a copper bar is installed, under which an electric arc is applied.
- Inclined electrode. This technique is used to improve productivity.
Taking into account the nature of combustion, electric arc welding is divided into the following types:
- Open arc. The method is used for manual welding and shielding gases.
- Closed. With this technology, the arc is present in the molten material, remaining invisible to the welder.
- Half open. Part of the arc in this case is visible above the metal. Electric arc welding of this type is used to join aluminum workpieces using automated equipment.
If you want to know what silumin is and where it is used, read our article.
Depending on the type of equipment and the characteristics that need to be given to the future seam, electric arc welding is carried out using a consumable or non-consumable electrode. In the first case, copper, aluminum, cast iron or steel rods are used. Consumable electrodes are used as filler material.
If you want to learn more about welding with a non-consumable electrode - tig welding, then follow the link and study.
Safety in MMA
Always wear a protective suit and shoes with strong toes and thick soles. Never start working in flip-flops or with any parts of your body exposed. You should also wear special welding gloves - quite sensitive to movement, but well protective. Be careful with your eyes and always wear welding goggles or a visor. Prepare your work area thoroughly and remove flammable items. Always have a fire extinguisher and a first aid kit nearby, as the activity is associated with risks.
Consumable electrodes used in the manual arc welding process
All conductors on sale can be divided into:
- Fusible. Their core melts and is added to the molten metal of the two workpieces and remains in the weld. It is coated with flux powder that is effective for creating a gas atmosphere.
- Infusible. Made from tungsten and used exclusively to supply current. Gas for the bath is supplied by a special hose.
Another difference is the cross-section diameter. The larger it is, the higher the current strength and the wider the maximum seam. More details in the video:
Filler wire - what is it?
Another variety. In essence, this is a large coil of material (aluminum, copper), which performs the same functions as a fusible electrode, that is, it conducts current and at the same time is a material for forming a connection between structural elements. The difference is the absence of sprinkling, so gas must be supplied from the outside. The second option is to sprinkle flux powder along the seam formation.
Advantages and disadvantages
Pros:
- ease of use, it is not necessary to fix the part to the floor, you can even work in weight;
- installation does not take up much space;
- it is possible to combine different alloys;
- can be moved to another place, taken with you in the car;
- ease of use - you can easily teach the basics of electric arc welding technology.
Minuses:
- Contact with gas and bright flashes of light negatively affect the health of the welder.
- A good, even seam will only be achieved after long experience and the ability to work with various materials.
- Quite a labor-intensive and lengthy process.
Let us conclude that the RDS for welders is a device that is more suitable for work at home and in small industries.
Areas of use of arc welding with electrodes
In the case when electric arc technology is used, the metal parts of the parts are connected using an electrode that is completely treated with hot silicate coating. The latter melts the electrode and firmly binds the metal edges of the products.
Electric arc welding is used in the following cases:
- For creating reinforcement meshes in spatial blocks, as well as flat frame elements.
- In the process of assembling block structures to combine them.
- In the manufacture of meshes and frames from reinforcing bars.
- During the installation of prefabricated reinforced concrete structures for connecting reinforcing bars and embedded parts.
- If it is impossible to use connecting contact equipment in specialized companies, for the preparation of reinforcement products.
- For tying rods whose diameter exceeds 10 mm. Welding is not used to connect frames with rod thicknesses less than 8 mm due to the high complexity of the welding technology for such structures, as well as the likelihood of burnout of the workpieces.
- At construction sites, joint resistance welding is used to connect reinforcing bars.
Methods of manual arc welding of metal: welding work in different positions
This is one of the biggest advantages of installing an RDS because the worker can be in any relationship with the surfaces being welded. You will get a good connection if you adhere to certain technical standards.
Bottom position
The most common one. The workpiece lies on the floor or a low table, the person is on top. Fasten the parts well and ensure that the bath forms smoothly and evenly.
Vertical
Due to attraction, the molten metal will tend to drain, and smudges may form. It is easier to work from top to bottom, but it is better the other way around, since drops of hot material will cover the finished, hardened seam.
Ceiling
Work must be done very slowly, making periodic intervals. This way the alloy will have time to cool and crystallize so as not to drip down. This also contributes to additional heating.
Preparation of the metal surface for welding and requirements for the assembly of metal parts before welding
Preparation of parts for welding consists of straightening, marking, cutting, preparing edges for welding, cold or hot bending.
Metal straightening is performed on machines. Sheet and strip metal are straightened on various sheet-straightening rollers. Angular steel is straightened on roller machines. I-beams and channels are straightened on cam-type straightening presses.
Marking is an operation that determines the configuration of a future part. The use of marking and marking machines with a pneumatic punch ensures a marking speed of up to ±1 mm and allows the use of software control. The use of gas-cutting machines with a large-scale photocopying control system or program control allows you to do without marking.
Mechanical cutting is used for straight cutting of sheets, and sometimes for curved cutting of sheets when using roller shears with circular knives for this purpose. Carbon steels are cut by oxygen and plasma arc cutting. In terms of mechanization, these methods can be manual or mechanized. For cutting alloy steels and non-ferrous metals, oxygen-flux or flame-arc cutting can be used.
The form of preparation of metal edges for welding depends on the thickness of the sheets. Before welding, the base metal and filler material must be thoroughly cleaned of rust, oil, scale, moisture and various types of non-metallic contaminants. The presence of these contaminants leads to the formation of pores, cracks, and slag inclusions in welds, which leads to a decrease in the strength and density of the welded joint.
Requirements for the assembly of metal parts before welding. The assembly and welding devices used must ensure accessibility to the installation sites of parts, handles of fixing and clamping devices, as well as tack and welding areas. These devices must also be sufficiently strong and rigid, ensure precise fastening of the parts in the desired position and prevent them from deforming during the welding process. In addition, assembly and welding fixtures must ensure optimal assembly and welding order:
— the smallest number of turns when applying tacks and welds;
— free access to check the dimensions of products and their easy removal after production;
— safety of assembly and welding works.
Any assembly operation should not impede the next operation. Parts received for assembly must be carefully checked. All geometric dimensions of the part and the prepared shape of the edges for welding are subject to verification.
As a rule, the assembly of welded structures is carried out either according to markings or with the help of templates, stops, clamps, clamping mechanisms, stands or special jig devices that facilitate assembly operations. The assembly accuracy is controlled with templates, probes (Figure 36), as well as measuring instruments.
Figure 36 — Inspection of assembly for welding
The preparation and assembly of products for welding is carried out in compliance with the following basic mandatory rules:
— the blunting of the edges and the gaps between them must be uniform along the entire length;
- the edges of the elements to be welded and the adjacent areas 25 - 30 mm wide from the end of the edge must be dried, cleaned of burrs after cutting, oil, rust and other contaminants;
— in order to avoid deformations, tack welding should be performed with high-quality electrodes at intervals of no more than 500 mm with a length of one tack welding of 50 - 80 mm;
- to ensure normal and high-quality formation of the seam, it is necessary to grab the lead strips at the beginning and at the end of the product.
Electric arc
This term refers to a prolonged discharge of current that creates high temperatures. In fact, this is the combustion of gases, which under normal conditions do not transfer electrons and ions so intensively. It is triggered by electron emission - the release of a negatively charged particle at the moment of contact between the electrode and the metal.
The influence of welding arc welding on the quality of the seam
The shorter the distance, the smoother the connection - without drops or leaks. But it is very difficult to hold a few millimeters. Also, a short electric arc with the correct manual arc welding process leads to:
- uniform melting of the coating;
- an even beam of sparks;
- sufficient penetration depth;
- lack of oxidation.
The parameter can be determined by the sound - if it is uniform, without clicks or glitches, then you should strive to maintain this distance.
Influence of the mode on the seam
When working with different surfaces, you should arrange the elements differently and weld the ends, straight cuts, sections, etc. But this should not force you to change hardware settings. The choice of mode depends solely on the width and depth of penetration you need. The table will help you choose:
| Metal thickness, mm | Current strength, A | Electrode diameter, mm |
| 3 | 175 — 185 | 3 |
| 5 | 200 — 225 | 4 |
| 7 | 250 — 270 | 5 |
| 10 | 300 — 330 | 6 |
Impact of current
The higher the indicator, the deeper the metal melts, the stronger the connection. But at the same time its breadth decreases. The type of equipment used also matters, whether it operates on alternating or direct electricity. In the first case, the connecting section will be narrower.
Manual welding technique - creating an arc
When working with consumable electrode arc welding, the arc is fired after the technician touches the work area with the rod. This process is started in two ways:
- touch and lift - the arc is formed after the rod is slowly withdrawn from the metal surface;
- by striking (like a match) - an arc is formed by quickly striking the end of the rod along the surface.
The second option is considered more preferable. However, when working in hard-to-reach places, the first method is used.
How to cook correctly is written in detail in our article. Come in!
Manual arc welding basics training
To become a professional manual arc welder, you must undergo training at a technical school. A professional worker has a rank that characterizes his ability to work with various materials and complex structures. But for home use, just read our article and watch the video:
On the site you can learn about other properties of metals, as well as find a wide range of equipment for band sawing. Go to our catalog to find out more. To clarify the information you are interested in, contact our managers by phone;; 8. They will answer all your questions.
Classification of gas-shielded arc welding methods
Recently, joining metal parts in a protective gas environment has become very popular. It includes the following methods of manual arc welding: atomic-hydrogen, argon-arc, and also in a carbon dioxide environment.
Argon-arc welding is characterized by the creation of a protective environment of argon (an inert gas), which is supplied to the working area through a special nozzle. The gas protects the melt from the air environment, in which nitrogen and oxygen are particularly active. The electrode can be used either consumable (welding wire) or non-consumable (tungsten). Whether or not to use additives when working with a non-consumable electrode is up to the master to decide. This depends on the type of weld. Argon-arc welding is preferred for joining thin-walled products made of non-ferrous metals and alloys, as well as special steels. The arc is powered by direct or alternating current from conventional welding equipment.
Automatic and semi-automatic welding using a consumable metal electrode in a carbon dioxide environment, which is much cheaper than argon, is gaining increasing popularity. This makes it easier to monitor the welding process and increases its productivity, which is often not inferior to the speed of submerged arc welding. However, there is also a drawback. Carbon dioxide cannot be used for welding non-ferrous metals and alloys because it has a high oxidizing ability. Therefore, it is used to connect structures made of stainless, low-alloy and carbon steels. The arc is most often fed from direct current of reverse polarity.
To join copper workpieces, nitrogen is sometimes used instead of argon (nitrogen-arc welding). Sometimes semi-automatic welding is carried out in a water vapor environment.
In addition to the methods described, atomic-hydrogen welding is used to join non-ferrous metals, as well as special steels. In this case, the arc burns between two tungsten electrodes in a nitrogen-hydrogen mixture (obtained from the decomposition of ammonia) or hydrogen.