Anyone who regularly welds metals sooner or later begins to ask questions - how to choose a welding machine, which brands to look for? If a powerful welding machine is needed for production needs, construction, repairs at service stations, then a budget welding inverter is suitable for welding in domestic conditions. However, it is not enough to take into account only the volume of work to be done. Before choosing welding equipment, pay attention to its technical characteristics, find detailed information about the manufacturer, and read reviews of the model of interest. To ensure that you purchase a truly high-quality item, we suggest reading a review of the most popular welding equipment and recommendations on choosing welding machines for the home.
Types of welding machines
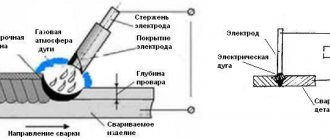
Welding machines are necessary to generate very high temperatures, under the influence of which metals form strong interatomic compounds. The required temperature regime is achieved thanks to an electric arc. An arc is a short circuit that can form between two electrodes, but is most often struck between the electrode and the surface being welded.
The quality of the connection depends on the arc, more specifically on its stability. For both a novice welder and a professional, it is important that the seam has no defects, is evenly fused and subsequently withstands environmental influences well. A good welding machine should provide optimal current characteristics for the intended job. Both an advanced welder and a household welding device perform a series of transformations of electrical energy that was obtained from the network. First of all, its voltage decreases, while the current increases. Some models convert alternating current to direct current or change the frequency of the current. Depending on the method of energy conversion, welding devices are:
- Transformer;
- Inverter;
- Rectifier;
- Semi-automatic.
Welding machine design
Homemade welding device.
The rectifier of the device is a kind of shelf made of aluminum plates, which is tightened with pins. Each pair of diodes included in the rectifier design is clamped between plates 1 mm thick and measuring 44 x 42 mm.
The transistor, capacitors, thyristors, zener diodes, diodes and resistors are mounted on a fiberglass board.
The design of the welding unit includes the following elements:
- package switch, rated for 16 amperes or more;
- fan;
- diodes designed to operate at currents of 16 amperes or more;
- capacitors designed to operate at voltages of 400 volts or more;
- capacitors designed to operate at voltages of 1000 volts or more;
- thyristors KU221 A, installed on a radiator for cooling;
- KD13A or KD2997A diodes mounted on radiators with thyristors;
- resistors brand C5-16 or more powerful;
- screws, washers necessary for assembling the device;
- aluminum plates.
Read also: Comparator on lm358 circuit
For installation work you will need the following tools:
- soldering iron;
- pliers;
- screwdriver, knife, hacksaw;
- hammer;
- drill.
A welding unit made using these elements can be used for welding work in the household. It easily welds most metal products.
If you need to perform some simple welding work for domestic needs, it is not at all necessary to purchase an expensive factory unit. After all, if you know some subtleties, you can easily assemble a welding machine with your own hands, which will be discussed below.
Pros and cons of MMA transformers
Such devices are still very popular today because they are low cost and easy to use. Electricity in this device is converted by a power transformer operating at a frequency of 50 Hz. The electric current first flows to the stationary primary winding, which is represented by an insulated wire. After the magnetic flux is formed, the voltage passes to the secondary winding, which has no insulation and moves. A magnetic field arises. Since the windings have different numbers of turns, it becomes possible to obtain the necessary voltage and current indicators: the more turns there are in the secondary winding, the higher the outgoing current. You can increase the welding current in another way - by bringing the coils closer to each other.
The advantages of transformers include:
- Affordable prices;
- Simple design;
- Reliability.
Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting the significant weight of most transformer models, high noise levels, and relatively low efficiency - no more than 80%. In addition, transformers consume a lot of electricity, so it is not recommended to connect them to a stationary power supply.
Transformers (with or without rectifier)
The heart of a transformer is the core. It is assembled from transformer steel plates, which are quite problematic to make by hand. By hook or by crook, the source material is extracted at factories, construction teams, and scrap metal collection points. The resulting structure (usually in the form of a rectangle) must have a cross-section of no less than 55 cm². This is a rather heavy structure, especially after laying the windings.
During assembly, it is imperative to provide an adjusting screw, with which you can move the secondary winding relative to the stationary primary.
In order not to go into the complexity of calculating the cross-section of wires, we will take typical parameters:
- secondary current 100–150 A;
- open circuit voltage 60–65 volts;
- operating voltage when welding 18–25 volts;
- current on the primary winding is up to 25 A.
Read also: How to use a stapler or stapler correctly
Based on this, the cross-section of the primary wire should be at least 5 mm²; if you do it with a margin, you can take a wire of 6–7 mm². The insulation must be heat-resistant and made from a material that does not support combustion.
The secondary winding is made of wire (or better yet, a copper busbar) with a cross-section of 30 mm². The insulation is rag. Don't let the thickness scare you, the number of turns on the secondary is small.
The number of turns of the primary winding is determined by a coefficient of 0.9–1 turns per volt (for our parameters).
The formula looks like this:
W(number of turns) = U(voltage) / coefficient.
That is, with a network voltage of 200–210 volts, it will be about 230–250 turns.
Accordingly, if the secondary voltage is 60–65 volts, the number of its turns will be 67–70.
From a technical point of view, the transformer is ready. For ease of use, it is recommended to make a small margin on the secondary winding, with several branches (at 65, 70, 80 turns). This will allow you to work confidently in places with low network voltage.
Hiding the unit in the housing or leaving it open is a matter of safety of use. A typical DIY welding transformer looks like this:
The optimal material for the case is 10–15 mm textolite.
Adding a rectifier
A homemade powerful welding transformer from a circuit design point of view is a regular power supply. Accordingly, the rectifier is designed as simply as in a network charger for a mobile phone. Only the element base will look several orders of magnitude more massive.
As a rule, a pair of capacitors are added to a simple diode bridge circuit to dampen rectified current pulses.
You can assemble a rectifier without them, but the smoother the current, the better the quality of the weld. To assemble the bridge itself, powerful diodes of the D161–250(320) type are used. Since a lot of heat is generated on the elements when loaded, it must be dissipated using radiators. The diodes are attached to them using a bolt connection and thermal paste.
Of course, the radiator fins must either be blown by a fan or protrude above the case. Otherwise, instead of cooling, they will heat the transformer.
Mini welding transformer
If you do not need to weld rails or channels from 4–5 mm steel, you can assemble a compact welder for soldering steel wire (making frames for homemade products) or welding thin sheet metal. To do this, you can take a ready-made transformer from a powerful household appliance (the ideal option is a microwave) and rewind the secondary winding. Wire cross-section 15–20 mm², power consumption no more than 2–3 kW.
The calculation of the circuit is carried out in the same way as for more powerful units. When assembling the rectifier, you can use less powerful diodes.
Micro welder
If the scope of application is limited to soldering copper wires (for example, when installing distribution boxes), you can limit yourself to a design the size of a pair of matchboxes.
Performed on transistor KT835 (837). The transformer is manufactured independently. In fact, it is a high-frequency boost converter.
Unlike traditional welders, this circuit uses high voltage, up to 30 kV. Therefore, care should be taken when working.
We wind the transformer on a ferrite rod. Two primary windings: collector (20 turns 1 mm), base (5 turns 0.5 mm). Secondary (boost) winding - 500 turns of 0.15 wire.
We assemble the circuit, solder the resistor circuit according to the circuit (so that the transformer does not overheat at idle), the device is ready. Power supply from 12 to 24 volts, with the help of such a device you can weld wire harnesses, cut thin steel, and join metals up to 1 mm thick.
A thick sewing needle can be used as welding electrodes.
Features of MMA inverters
Among the best welding machines there are many inverter-type models. This technique produces welding by changing the electrical characteristics several times. First, a current with a frequency of 50 Hz enters the rectifier, where it becomes constant. Then the transistors convert the current back into alternating current, but its frequency increases to 20-50 kHz. Next, using a transformer, the current is given a voltage of 70-90 V and the current increases to 100 -200 A. The last stage is a rectifier and a high-frequency filter, thanks to which the electric current becomes constant and in this form is supplied to the place where the arc is formed.
Despite the fact that inverters began to be mass produced only in the 80s. twentieth century, they are very popular at the present stage. The reason for this is their following advantages:
- Welding current is adjustable over a wide range.
- Can be connected to a household electrical outlet.
- Low energy consumption with high performance (efficiency - 85% and above).
- Smooth voltage and current regulation.
- Possibility to weld for a long period of time without turning off the device.
- Welding is carried out in all positions, with almost no metal spattering.
- Arc stability.
When planning to choose an inverter-type welding machine, please note that it still has disadvantages:
- High cost of the device and its components.
- It is necessary to protect the device from exposure to dust and moisture, periodically clean it with a soft brush and an air stream.
- Despite the fact that the best manufacturers declare that their welding devices are frost-resistant, inverters are more likely to fail at temperatures of -15 degrees Celsius and below.
How to choose a welding inverter can be found here.
Why are rectifiers needed?
A home welding machine may not change the frequency of the electric current, but provide a stable arc in a different way. When using a rectifier, the current first enters the transformer, where the current increases and the voltage decreases. Then the voltage is applied to the semiconductor, which is silicon or selenium diodes. The resulting direct current is supplied to the electrodes.
It is difficult to imagine the rating of the best welding devices without rectifier-type devices, because they:
- Guarantees a stable arc;
- Minimize metal splashing during operation;
- Allows you to save consumables;
- Form a neat seam with a fine pattern;
- Excellent for joining alloyed and non-ferrous metals.
Choosing a welding machine-rectifier is not advisable if:
- Are you interested in budget models?
- There is no possibility to transport the device,
- It is not possible to inspect the device before each use for the quality of insulation, cleanliness and reliability of the terminals.
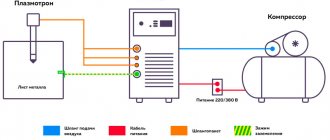
Advantages of semi-automatic welding
Among household welding machines, semi-automatic machines have gained great popularity. Welding can be carried out using self-shielding wire without the use of gas, or with wire in a shielding gas environment. The latter can be used helium, carbon dioxide, argon, which displace air from the place where the weld is formed. Thanks to this, the connection is strong and free of defects. Arc movements during semi-automatic welding are carried out manually, the wire ejection is controlled by special programs. Thanks to this, the semi-automatic machine is easy to use and ideal for beginners. The operating mode of the device depends on the wire feed speed, its type, type of gas and current strength.
A home welding machine operating in semi-automatic mode has the following advantages:
- You can correct the work directly during the welding process.
- High speed of work (up to 18 m/min) and high-quality connections as a result.
- The welding speed is smoothly adjustable.
- Guarantees strong seams when welding thin metal.
- Has many settings and additional modes.
- You can weld either spot or continuous seam. Welding is carried out in all spatial positions.
The disadvantages of a semi-automatic machine include:
- High cost of the device and consumables.
- The connection is not to a household power supply.
- Problems arise when working in an open space: the protective gas is blown away by the wind, and the connection may become unstable.
Types and methods
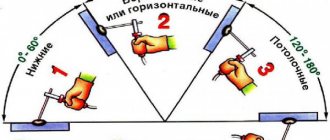
Electric arc welding has several varieties. Each of them has some distinctive features that affect the quality and type of welded joint. The following types of electric arc welding are distinguished:
- Manual electric arc welding. During it, only human manual power is used without mechanisms;
- Mechanized type. During the process, mechanization is used to feed wire into the welding area, and part of the work is done by manual force;
- Automatic type. Welding is carried out automatically. Special equipment independently feeds the arc, regulates its length and movement.
The technological process of electric arc welding is also divided into methods:
- In a bun . During welding, several electrodes are bundled together, their ends are welded and installed in a holder. A larger range of currents is used and you can independently increase performance indicators.
- Welding with a lying electrode . During this process, laying can be done with a length of 50 to 120 cm with coating in a cut joint or corner. A copper bar with a longitudinal groove is placed on it. After this, the workpiece and electrode are connected to a current source. The carbon rod ignites an arc that goes under the bar area. It moves along the joint, melts the working element and welds the edge. The result is a welded joint.
- Welding with an inclined electrode . This method is carried out to improve productivity. During this process, the electrode is fixed in a clamp with a holder, which moves under its weight along the stand. At the moment the arc is ignited, the electrode melts and the holder falls down.
Choosing the right model
How to choose a welding machine that, with intensive use, will last for many years without breakdowns? First of all, you need to decide what brand the device will be and what technical characteristics it will have.
Imported devices are most often represented by Chinese-made models - Aurora, Svarog, Foxweld, etc. You should not be afraid for the quality of such a product, since these are fairly well-known brands that control products at all stages of production. Those who prefer European brands can opt for welders from ESAB, Fubag and some models from Elitech. For adherents of Russian technology, models from the Kedr, Resanta or Interskol brands are suitable.
Pay attention to the supply voltage: a household welding machine can be connected to a regular electrical network, but an advanced welder will only work with three-phase voltage. The no-load voltage is also important, which allows you to quickly ignite an electric arc and ensure its uniform combustion. Devices using direct current for welding have HCV up to 90 V, devices for alternating current - up to 80 V.
The power of a welding machine depends on the amount of current it can produce. Devices intended for use at home, on a construction site, in small production, produce a current of 200 - 250 A. A welding inverter for large industrial work produces a current of 250 - 500 A.
The functionality of the device is also indicated by the duration of the operating time - the time period during which the equipment is able to work without shutting down. Please note that European manufacturers calculate this indicator at a temperature of + 40 degrees Celsius, Chinese - at a temperature of +20 degrees Celsius.
The best welding inverter will have a high degree of protection from environmental influences. The most popular models are with degrees of protection from IP21 to IP23, the housing of which cannot accommodate objects with a diameter exceeding 12 mm. The most protected from moisture are devices with an IP23 index: water will not enter their housing even when it enters at an angle of 60 degrees.
DIY welding transformer
The assembly of the transformer version will be slightly different from the previous one. This unit operates on alternating current, but for welding with direct current you need to assemble a simple attachment for it.
To work, you will need transformer iron for the core, as well as several tens of meters of thick wire or thick copper busbar. All this can be found at the metal collection point. The core is best made U-shaped, toroidal or round. Many also take the stator from an old electric motor.
The assembly instructions for the U-shaped core look like this:
- Take transformer iron with a cross-section from 30 to 55 cm2. If the figure is higher, the device will be too heavy. And if the cross section is less than 30, the device will not be able to work correctly.
- Take a copper winding wire with a cross-section of about 5 mm 2, equipped with heat-resistant fiberglass or cotton insulation. Insulation is important because during operation the winding can heat up to 100 degrees or more. The winding wire has a square or rectangular cross-section. However, such an option is difficult to find. An ordinary one with a similar cross-section will do, but you will only need to remove the insulation from it, wrap it in fiberglass and thoroughly soak it with electrical varnish, and then dry it. The primary winding has 200 turns.
- The secondary winding will require about 50 turns. There is no need to cut the wire. Connect the primary winding to the network, and on the secondary wires find a place where the voltage is about 60 V. To find such a point, unwind or wind additional turns. The wire can be aluminum, but the cross-section must be 1.7 times larger than for the primary winding.
- Install the finished transformer into the housing.
- To bring out the secondary winding, copper terminals are required. Take a tube with a diameter of 10 mm and a length of about 4 cm. Rivet its end and drill a hole with a diameter of 10 mm, and insert the end of the wire, previously cleared of insulation, into the other end. Next, crimp it with light hammer blows. To strengthen the contact of the wire with the terminal tube, apply notches to it with a core. Screw homemade terminals to the body with nuts and bolts. It is best to use copper parts. When winding the secondary winding, it is advisable to make taps every 5-10 turns, they will allow you to change the voltage on the electrode in steps;
- To make an electrical holder, take a pipe with a diameter of about 20 mm and a length of about 20 cm. At the ends, about 4 cm from the end part, cut out recesses to half the diameter. Insert the electrode into the recess and press it with a spring based on a welded bush of steel wire with a diameter of 5 mm. Attach the same wire that was used for the secondary winding to the second terminal using a nut and screw. Place a rubber tube with a suitable inner diameter onto the holder.
Read also: Milling wood with a manual router video
It is best to connect the finished device to the network using wires with a cross-section of 1.5 cm2 or more, as well as a switch. The current in the primary winding usually does not exceed 25 A, and in the secondary winding it fluctuates between 6-120 A. When working with electrodes with a diameter of 3 mm, stop every 10-15 to allow the transformer to cool down . If the electrodes are thinner, this is not necessary. More frequent breaks are needed if you are working in cutting mode.
Do-it-yourself mini-welding
To assemble a miniature welding machine yourself, you will only need a few hours and the following materials:
- graphite rod from an old battery;
- side cutters or pliers;
- knife;
- dry rag;
- sandpaper;
- gloves;
- 20 cm of wire with a diameter of 5 mm made of aluminum or copper;
- 6 cm of PEV 0.5 copper wire;
- insulating tape;
- stranded wire;
- any metal clamp;
- a transformer from a microwave power supply with a rectifier, or an old TV or receiver.
First, carefully disassemble the old battery and remove the graphite rod from it. Sharpen the end with sandpaper and wipe with a dry cloth. Clean a piece of thick wire 4-5 cm from the end from the insulation and use pliers or side cutters to bend a loop. Insert a carbon electrode into it.
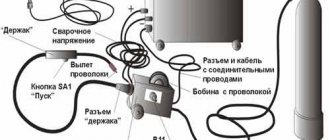
Remove the secondary winding from the transformer and wind 12-16 turns of thick wire in its place. Now all this is inserted into a suitable housing - and the device is ready.
Its wires are connected to the terminals of the secondary winding, the carbon rod is inserted into the loop and crimped well. Connect the positive terminal to the electrode holder, and the negative terminal to the twist of the working parts. The holder handle can be adapted for an electrode.
You can use a soldering iron handle or something similar. Connect the device to a household network and connect the parts using graphite . A flame should appear, and a spherical weld seam will form at the end of the parts.
For a home workshop, having a welding machine is very important. Such devices have different designs and modifications . Both beginners and experienced craftsmen often prefer not factory-made, but home-made devices that can be modified in their own way.
Welding work at home has long become commonplace. Availability of equipment and consumables, the opportunity to inexpensively attend welding courses, various training manuals for acquiring independent skills. All these factors make it possible to save on the labor costs of a professional welder and increase the efficiency of work.
However, if you carefully study the welding machine market, unpleasant aspects become clear:
- High-quality welders have a high cost; it is more profitable to hire a specialist several times (unless, of course, you do this work constantly).
- Affordable units have a number of disadvantages: low reliability, poor seam quality, dependence on the supply voltage and type of consumables.
Hence the conclusion: if you need high quality equipment at an affordable price, you will have to make a welding machine from available materials with your own hands.