Representatives of the older generation probably remember how they woke up and fell asleep to the sound of a bugle in the pioneer camps, where most of the city children spent their summer holidays. The bugle is also known to the guys as a mandatory attribute of all training camps, rallies, and military-patriotic games. But few people know that this simple, well-known musical instrument is one of the oldest, which laid the foundation for the emergence of other brass instruments. The forges themselves originate from signaling instruments that were made in ancient times from the bone horns of animals. The material for the forge is copper, brass. Translated from German, horn means horn.
In Dahl's dictionary
m. and mining avg. (see goryat, burn, rake), a type of furnace with a wide brow (tent), with a bellows, a blower or draft, for heating and partly smelting work; own that part of the working furnace where the fire is, for heating, melting, etc. A forge forge, in which iron is heated or boiled for forging; it can be, depending on the work: welded, laid, wedge, oblique, etc. The forge is loud, large, for making iron from cast iron. G. blast furnace, and in a smaller form, cupola, iron-smelting. G. extractive (mining), where silver is smelted; G. separation (purification), where silver is purified. | Ur.-Kaz. forge, rod chuvala, butt, on which food is cooked, milk for kaymak; blmr. galley, carbass stove. Forge, pertaining to a forge. Forge casing, frame, arch above the forge, with a pipe. Forge window, an opening in the wall of the forge for setting up a tuyere. Forge stone, fire-resistant, used. when calcining forges. Crucible Wed. forge, a place for heating, melting, cleaning by fire. Crucible, belonging to or relating to the crucible. Gornovishche Wed. remains or ruins of an abandoned forge. Miner m. worker at the forge, to support the fire, etc. Miner m. church. pot; Little Russian Belarusian garnok, garnushka. There will be a merchant for a holey miner. In wedding The song remembers mountaineers, at feasts, mugs, glasses; Isn’t that why the proud guests are wrong? proud? Gornatik m. Kaz. clay or fashionable vessel. Gornushka eastern a corner with a hole, to the left of the hearth of a Russian stove, where the heat is raked; grandma, baburka, stove, zagnetka, zharotok, porsk, ash pan. BURN m. music. German a special type of clarinet, in military music, a type of trumpet, horn. Bugler m. musician who plays the bugle. Gornistov, which belongs to him.
Types and design of blacksmith hearths
For thousands of years, blacksmiths have worked with one type of furnace that burns solid fuel. As a rule, the source of fire was charcoal, and later - stone.
Today, modern types of furnaces operate using gas fuel, or generally using electricity (induction furnaces).
However, no matter what fuel is used for the forge, there are uniform principles of its design.
The design may differ depending on the type of fuel consumed.
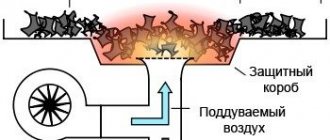
The forge consists of the following parts.
- Table made of fireproof material.
- A furnace nest or hearth with a grate.
- Lance.
- Tent and umbrella.
- Chimney.
Table
The purpose of this part of the furnace is to place on it the hearth, tuyere and other individual structural parts.
The table is made depending on the type of forge. Portable options are usually made from steel, while stationary ones are made from refractory bricks.
However, for example, open furnaces can be made from either wall materials or steel, while closed types, for the most part, can only be made from refractory bricks.
Steel table with forge nest (hearth)
Hearth and grate
This is the part of the forge where fuel combustion and heating of workpieces actually occurs.
The grate is the part of the furnace that provides access to the fuel from additional forced air. This part can be made in any form: from a cast iron plate with holes to grates made of a similar heat-resistant material. The main thing is that the grate provides access to a sufficient amount of air from the tuyere into the fireplace.
Hearth and grate
Moreover, this part must have properties that allow it to withstand very high temperatures reached during the combustion and heating of workpieces.
Another feature of the grate that blacksmiths can use is the shape of the holes, which contribute to the formation of the flame necessary when heating various workpieces and materials.
Lance
The purpose of this part is to supply air to the furnace. The supplied oxygen from the device that provides air supply for the forge (forge bellows, compressor or fan) enters the tuyere body and from there through the grate into the hearth itself to the burning fuel.
Forge with umbrella and tuyere under the table
The second function is to collect the remains of burnt fuel (in solid fuel stoves).
Tent and umbrella
These parts of the hearth are usually present in closed or semi-closed designs of stationary furnaces.
The tent closes the hearth from the outside space, as a result of which a stable temperature is maintained inside the oven. In addition, this part of the forge makes the cooling of the furnace gradual and uniform, which is used by blacksmiths when stabilizing a forged product.
An umbrella is the upper part located above the fireplace. Its task is to remove smoke and vapors generated during combustion, as well as to ensure normal draft. This makes fuel combustion more high-temperature and stable.
Chimney
Essentially, this is a regular chimney for exhausting and removing smoke. Properly made, it provides the normal draft necessary for combustion.
These are the main parts of the structure, the appearance and presence of which may differ depending on the type of forge itself and the fuel it consumes. Let's take a closer look at how some of these elements are structured and what their normal functioning depends on.
In Vasmer Max's dictionary
I I. “melting furnace”, folk. Goron (Shakhmatov, IORYAS 7, 1, 299), Ukrainian. mining, other Russian gurn, tslav. gran "lebes", bul. garne, Serbohorv. Grne, b. p. -eta, Slovenian. gŕnǝc, Czech, Slavic hrnec, Polish garnek "pot", v.-pud. hornc, nj.-luzh. gjarńc. Related to Lat. fornus “oven”, Old Indian ghr̥ṇás “heat, heat”, Old Prussian. goro “Feuerstand”, further, to burn; see Bernecker 1, 371; Trautman, BSW 102; Bezzenberger VV 12, 79; Osten – Saken, IF 22, 318; Walde - Gofm. 1, 533 et seq. Wed. also garnets. II •• (II. “musical instrument, trumpet” from German Norn “horn.” - T.)
Blowing
A certain volume of air must be supplied to a forge, especially one operating on solid fuel, otherwise the required temperature of 1100-1300 degrees will not be achieved.
Previously, blowing through the tuyere was provided using blacksmith bellows, pumping oxygen into the hearth. Today they have been replaced by fans and compressors.
Blowing can be arranged from below, from the side or from above. With bottom supply, air is initially pumped into the chamber in front of the grate - a lance, on top of which a grate with fuel is located.
Bottom air injection device
In small portable furnaces, air injection can be achieved using a small fan, but large stationary furnaces will require a larger volume of oxygen.
In the simplest homemade devices, airflow is provided by installing computer fans or even hair dryers.
In the Encyclopedia Dictionary
(from German Horn - horn), a wind-copper mouthpiece musical instrument without valves, with a conical barrel. Used for signaling.—(Cabo de Hornos, Hoorn), cape on the island. Horn, in the Tierra del Fuego archipelago, the southernmost point of the South. America (55°59′ S, 67°16′ W).—1) a small furnace with an open shallow shaft, used for melting metals in crucibles and heating blanks before forging. 2) The lower part of the shaft melting furnace. 3) The simplest metallurgical furnace (hearth) at the early stage of development of metallurgy.—A. B., see Hoorn A. B.—(Horn, Hoorn) Philippe de Montmorency (Montmorency) (c. 1524-68), count, one of the leaders of the anti-Spanish noble opposition on the eve and at the beginning of the Dutch Revolution. Executed.
Varieties of forge
The forge reached its heyday, perhaps, in the 19th century; it was then that many of its variations appeared using valves and taps. Thus, at the beginning of the century, a keyboard horn or a horn with valves was invented in England, which almost immediately became a fairly popular instrument. A large bugle with valves, called an ophicleide, was used in symphony and brass bands. Its popularity lasted until the middle of the century. Later it was replaced by another instrument - the tuba, which pushed the forge with keys far into the shadows. The valve horn or flugelhorn is used in brass bands and jazz ensembles.
In the dictionary Dictionary of foreign words
a, m.
A brass wind signal instrument in the form of a straight tube with a bell. Bugler - a musician who gives a signal on a bugle.||Cf. FORNISH" title='French horn, French horn is, what is French horn, French horn interpretation'>French horn, HELIKON" title='HELIKON, HELIKON is, what is HELIKON, HELIKON interpretation'>HELIKON II, CLARNET" title='CLARNET, CLARNET is , what is CLARNET, CLARNET interpretation'>CLARNET, SAXOPHONE" title='SAXOPHONE, SAXOPHONE is, what is SAXOPHONE, SAXOPHONE interpretation'>SAXOPHONE, TROMBONE" title='TROMBONE, TROMBONE is, what is TROMBONE, TROMBONE interpretation'>TROMBONE , TUBA" title='TUBA, TUBA is, what is TUBA, TUBA interpretation'>TUBA, BASSON, FANFARA, FLAGEOLET, FLUTE.
Share the meaning of the word:
Grate bars
This part of the furnace is used in the construction of a solid fuel furnace.
Most often, it is a massive cast-iron stove with holes or slots that allow air to penetrate to the burning fuel and holds the coal. The area of the grate may vary. It all depends on the size of the fire and the type of fuel.
The grate can also be made of refractory bricks or a steel plate.
Grate
In professional devices, the shape of the holes plays a role. By changing their configuration, the blacksmith gets the flame he needs, which is used to heat the part.
The placement of the grate can vary depending on the side of the air supply: from below (classic version), from the side or from above.
The main task of the grate is to provide the forging forge with a sufficient volume of forced air, hold fuel (coal) and withstand high temperatures.
Grate bars are used in all types of solid fuel stoves.
Stages of making a homemade forge
Making a forge for forging yourself is a step-by-step process. To manufacture the equipment, it is necessary to prepare consumables:
- thick sheets of heat-resistant steel;
- refractory clay for external coating of the structure;
- fireclay bricks;
- metal corners, channels;
- metal pipe for the chimney;
- a metal grate that acts as a grate;
- construction sand;
- metal door with hinges;
- old vacuum cleaner to create air flow.
If the heating device will operate on fuel oil, you need to consider a combustible mixture supply system. Stages of making a homemade heating device:
- Draw a drawing with exact dimensions marked with holes.
- Assemble a support structure from metal channels. To connect individual elements you need to use a welding machine. The seams are cleaned and covered with an anti-corrosion coating.
- Assemble a chamber with a door for filling solid fuel. Air must be supplied through it for the coals to produce heat. Install the grate.
- Build a chamber from fireclay bricks to heat the workpieces. Make a hole on the top and secure the chimney pipe.
- Connect an old vacuum cleaner that can blow out to the air supply system. Install the door on the window used for feeding workpieces.
- Coat the outside of the bricks with refractory clay so that the heat is retained in the heating chamber.
After assembling the structure, you need to check its functionality. To do this, you need to conduct a test run and light the fireplace.
DIY horn
Selection principles
When choosing purchased equipment for a blacksmith shop, you need to consider a number of factors:
- The size of the heated surface. The possible size of the processed workpieces will depend on this.
- Type of fuel used. It is necessary to take into account the characteristics of the consumable material.
- Air supply option. Equipment with an electric compressor allows you to work faster and more productively.
- Dimensions of the forge.
It is necessary to remember about the reliability of removing combustion products from the structure. To do this, you need to check the chimney and the holes that create draft.