The issues of effective protection and decorative design of the surfaces of products made of various materials are quite relevant both for manufacturers and for many home craftsmen. Chemical metallization, which you can do yourself, allows you to effectively solve such problems.
Chemical metallization technology can be used on virtually any hard surface
DIY chemical metallization at home
If this is your first time performing chemical metallization at home, then you should study theoretical materials in advance and watch videos on this topic. Of course, you need to prepare equipment and supplies. In the process of chemical metallization, hazardous chemicals are used, which must be handled very carefully and comply with safety requirements. Chemical metallization itself, as mentioned above, is not a complicated method, and it can be easily carried out at home. Despite all the advantages of the method, we should not forget that even at home, chemical metallization is quite expensive. The price of a factory coating is even higher and will depend on the surface area covered.
Types of metallization
Metallization is the application of a thin metal layer to a surface. This way not only metal products can be processed, but also plastic, wood, glass and others. The most popular and well-known types of this process are chrome plating (that is, metallization with chromium) and galvanizing (when the surface of the product is coated with a layer of zinc). A lesser known type is aluminizing (applying a layer of aluminum to the surface).
Depending on the equipment and technology, there are several types of metallization:
- Galvanic. It is performed in a special electrolyte, which is poured into baths.
- Electric arc metallization. The coating here is applied in the following way: electric arc melting of a metal electrode is used.
- Gas plasma spraying technology is similar to electric arc metallization, when molten, finely dispersed metal is applied to the surface. Gas plasma spraying, like electric arc metallization, is a rather complex technological process, so it is used mainly in production.
- Cladding. In this method, a layer of metal is applied to the surface of the product, after which hot rolling is applied.
- Metallization is diffuse. High temperature causes atoms of the applied metal to penetrate the surface of the workpiece.
- Hot type of metallization. The coating is formed when the product is immersed in molten metal.
- Chemical metallization. This type is perfect for use at home.
Chrome plating of parts: step-by-step instructions
Chrome plating technology is not particularly complicated.
In order to prepare electrolyte for a small product, you need to take an ordinary glass jar of the required size or a plastic bucket and place it in a special tank. For these purposes, you can use a can. For electrolysis to be of high quality, it, the can, must be thermally insulated. Namely, take a wooden box or box, insulate it with fiberglass or polystyrene foam, as well as additional mineral or glass wool, sand and place the tank there.
Place a heating element and a thermometer inside the tank. Cover the top with a sheet of moisture-resistant plywood, which will act as a sealing cover, and attach the electrodes. Attach the cathode to the product, and immerse the anode (rod or plate) into a container with the sample.
The part in the can must be held with a bracket to ensure chrome plating on all sides.
Preparation of electrolyte solution
To carry out chrome plating of parts at home, you need to prepare a special solution consisting of chromium anhydride (250 g per liter of distilled water) and sulfuric acid (2.5 g per liter of water).
First you need to fill half the container with heated water (about sixty degrees Celsius). Add the required amount (based on the total displacement) of chromium anhydride, stir until completely dissolved, and add water to obtain the required volume. Then add sulfuric acid, stirring the liquid.
The resulting solution must be worked for three and a half hours, passing current energy through it (about 6 A per 1 liter). When the electrolyte turns dark brown, it will need to stand for at least a day.
Sample preparation procedure
Before preparing the part, you need to heat the electrolyte solution to sixty degrees Celsius and let it stand for three hours.
During this time it is necessary:
- Clean the part from dirt, rust, paint.
- Carry out degreasing using a special solution, for which there are several recipes. For example, it may consist of 150 g of sodium hydroxide, 5 g of silicate glue, 50 g of soda ash. Take everything per liter of water. Mix the ingredients, heat to ninety degrees Celsius, lower the product and leave for at least twenty minutes, and sometimes longer, depending on the size and degree of cleansing.
Direct chrome plating
During the chrome plating procedure, it is necessary to maintain the temperature of the electrolyte solution at an average of 53 C° (plus or minus two degrees). Place the product in the electrolyte and after a minute, apply voltage to equalize the temperatures of the sample and solution. Remove the part and dry for at least two and a half hours
Occurrence of defects
When chrome plating at home, defects such as:
- The surface shines unevenly. Occurs due to high current or low temperature of the electrolyte solution.
- Lack of shine - due to incorrect amount of chromium anhydride, excessive current, lack of sulfuric acid.
- The presence of brown spots means an excess of chromic anhydride and not enough acid.
- The layer is uneven. Excess current.
- Softening of the coating – high solution temperature, low current.
- Chrome plating falls off - unstable voltage, poorly carried out dehydration, low solution temperature.
Chrome plating at home is a process that requires a certain skill and strict adherence to the rules and instructions. Any violation can lead to poor-quality chrome plating. Therefore, it is worth studying the technology of this process in detail and only then proceeding with its implementation.
Chemical chrome plating
Chrome plating methods
Galvanization technology consists of applying a surface metal layer to a part for a specific purpose - decorative or protective through the use of an electrolyte.
Consequently, electroplating - chrome plating at home suggests that a layer of chromium from an electrolyte of a certain composition will be deposited on the surface being treated when exposed to electric current. This process can be carried out in different ways.
- Carrying out chrome plating using a bath filled with a solution. The technology is accessible for DIY, but is more often used when working with small parts.
- Spraying the coating using a galvanic brush. This technique does not limit the dimensions of the workpiece; it is also optimal for non-removable elements. During the work process, the master has the opportunity to control the thickness of the applied layer and visually assess the quality of the spraying. But this process is more labor-intensive, as it may require up to 20 movements in one place.
Galvanic chrome plating method
Galvanic chrome plating of parts is the most popular method, because all the steps can be done with your own hands. Electroplating involves placing parts in a special solution with a certain composition, from where, under the influence of waves (solitons) of electric current, chromium atoms will be deposited on the surface. Having the right set of tools for chrome plating, you can create a high-quality coating yourself by galvanizing.
Electrolytic chrome plating method
One of the types of galvanizing. When electrolysis is used, tri- or hexavalent chromium gives the product the desired “metallic” appearance. When using a trivalent element, the main substance of the solution is chromic anhydride. The use of hexavalent chromium differs from the previous method by the presence of chromium sulfate in the solution.
When carrying out electrolytic chrome plating of disks or other parts, it is important to strictly observe the proportions of the components. Otherwise, the protective layer will quickly peel off or there will be stains, uneven dullness and insufficient gloss.
Diffusion chromium plating method
Chromium coating is done using a galvanic brush. At home, this method is more preferable, because the master does not need to use a bath. It is especially recommended to perform the technique for parts made of aluminum, carbon steel, and alloys with silicon.
Chemical metallization of surfaces and parts
In the process of this work, chemical reagents, a compressor and a spray gun are used. Almost the same operations are performed as when painting surfaces with acrylic varnish or enamel. When chrome plating in this way, not a protective polymer film is applied to parts and structures, but a mirror-like thin layer of metal. Its thickness is in the range of 0.075-0.25 millimeters. The chemical and physical characteristics of such a coating are comparable to those obtained by vacuum deposition.
Catalytic chrome plating method
A subtype of chemical chrome plating of ferrous or non-ferrous metals, which involves applying a liquid without acids to the part. The technology is safe for humans and helps create original, unusual effects.
Catalytic chrome plating can be used for conventional and flexible products (with electrolysis, the latter is impossible; the coating will peel off).
Typically, silver is used as a reagent in an alkaline ammonia solution, and formaldehyde or hydrazine is used as a reducing agent. The use of silver makes the piece look milky with a mirror surface.
Chrome plating using chemical metallization
The chemical metallization method is most suitable for chrome plating parts at home. There are also special reagents here, but no other complex equipment is required except a spray gun and a compressor.
In many ways, the chrome plating process is reminiscent of conventional painting of products with enamel or acrylic colored varnish, only the result is different. Instead of a polymer protective film, a thin (0.075 - 0.0) is formed on the surface.
25 mm) a metal layer with a mirror shine, not inferior in physical and chemical characteristics to vacuum deposition.
There are two methods of chemical metallization:
- recovery of chromium from salts during chemical reactions;
- coating with specially selected chemicals, as a result of the interaction of which a durable monomolecular layer of silver or other metal is deposited on the surface.
To work with chromium salts, you will need sodium hyposophyte, chromyl fluoride, chromium phosphate, chromium chloride or acetate, caustic soda, acetic acid and other chemicals.
Most of them are unsafe for health, some are very poisonous. If you intend to chrome parts using this method, you need to repeat the chemistry course.
Even with carefully written instructions, it is difficult to achieve the desired result.
Vacuum chrome plating
The technology belongs to chemical metallization and has another name - the PVD process. Gives condensation of chromium vapor on the surface of the part after placing it in a special vacuum chamber. In this installation, under negative pressure, chromium is heated to the evaporation temperature, then settling like fog on the product.
Calculation of pressure and chrome plating period will depend on the degree of wear of the part and the type of material. After vacuum chrome plating, the thickness of the metal layer is minimal, so the part on top is coated with special spray paint or varnished.
Thermochemical chromium plating
Powdered products consisting of fireclay and ferrochrome are used. The technique is similar to that for chemical chrome plating, only the product will be subject to heating during the process.
Spray processing
Sputtering of elements with chromium (catalytic metal working) is performed using the “silver mirror” reaction, in which complex silver layers located in alkaline ammonia solutions act as reagents. The function of a reducing agent is assigned to a formaldehyde or hydrazine solution, or inverted sugar syrup. When silver and a reducing agent are simultaneously sprayed, the steel product acquires a boiling white surface with a mirror shine. Such products are characterized by excellent reflective characteristics. The next stage involves applying a varnish coating to the product to protect it from scratches with the addition of a light-fast coloring toner. To obtain the latter, three pigments are mixed - black, blue and violet in a ratio of 1: 1: 3. Processing using a “silver mirror” is divided into a number of successive steps :
- Analysis and preparation. First, the surface of the product is thoroughly cleaned by rinsing with a specialized composition. To increase adhesion, the surface is sanded with sandpaper with an abrasiveness level of P500−600.
- Application of a glossy base. A glossy black substance is applied to the prepared material, which eliminates the risk of yellowness in the final mirror coating. Then the varnish coating is dried at room temperature from 20°C to 25°C, without the use of specialized equipment, and drying lasts 8 hours. If drying is carried out at a temperature of 60°C, the process duration is reduced to 45 minutes.
- Drying.
- Etching the surface of the product to increase its adhesion to silver, followed by cleaning with distilled water.
- Sensitization or specialized surface treatment using an activator. This allows you to protect the surface with a special film.
- Metallization using silver.
- Application of a protective varnish coating to the product, which reliably protects it from tarnishing and loss of original qualities during long-term use, mechanical stress, or due to the destructive influence of aggressive environments.
Adhesive primer and pigments in decorative chrome plating
I want to tell you about such an important tool for decorative chrome plating, such as adhesive primer-varnish and pigments for imparting color to the mirror, for example, gold and other colors. I’ll show you the composition of the soil I use and how to use it.
So why is this adhesive primer-varnish with such a long exotic name needed? Everything is clear from the name: adhesive, which means the varnish sticks well to the surface, which means transparent primer, which means it is not used as a finishing coat, but before it. We figured out the name. After metallization, the primer is applied to the mirror as the first layer, and the finishing varnish is applied to it. But what exactly is the problem, you can simply apply the finishing varnish to the mirror and that’s the end of the matter. You can just use auto varnish without primer... but it won’t hold up well, somehow, and here’s why. Conventional car varnishes are two-component, are not designed for metal and therefore will begin to chip over time.
Usage
The use of chromium in ferrous metallurgy is large - it is about 2/3 of the total metal smelting. The production of chrome-plated alloys is profitable - even small additions of alloys give the alloy the best qualities of a resistant metal.
We recommend: COPPER - the foundation of civilization
The remaining third is mainly used for chrome plating. Chrome plating can be functional, decorative, or combine both qualities.
Chrome wheels
Plumbing products are simply designed for chrome plating. Heat, moisture, and chemicals will not damage the faucet, shower, or bathroom accessories.
Informative: often the protective layer is applied to a previously created “primer” of copper and nickel.
A layer of functional chrome plating protects parts from corrosion; its thickness reaches several millimeters.
Decorative chrome plating is for beauty; its layer is thin, only 0.2-0.7 microns.
Chrome plating happens:
- electrolytic;
- chemical;
- vacuum;
- diffuse.
Interesting: a gas plasma spraying method has been developed that makes the chrome plating process safe.
Benefits of technology
Chemical metallization is a very simple process. Applying the coating is technologically simple. To do this, it is enough to have standard sprayers. This allows you to coat any product: from a phone case to a car hood or a statue. Any materials can be chrome-plated: plastic, ceramics, wood, plaster, etc. The degree of reflection of the coating depends on the number of layers applied.
Chemical metallization gives the product additional strength and hardness. Moreover, the coating has high wear resistance. The strength here is ensured by a protective varnish that can withstand any operational wear. For the chrome plating process, dimensions do not matter. Any surface area can be sprayed in a short time. This is one of the main differences from the vacuum metallization process or galvanic electrodeposition.
Recommendations
To obtain a high-quality metal layer on products and in order not to harm your health, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Before the procedure begins, all electrical contacts are checked for reliability;
- During the metallization process, it is imperative to use rubber gloves to protect your hands from burns;
- The room must be ventilated, as this process releases gases that irritate the mucous membrane of the respiratory system.
Removing poor-quality coating
There are two ways to remove low-quality chrome. The first is chemical dissolution, carried out in a 50% solution of sulfuric acid. The products are placed in a container with sulfuric acid and kept until the coating is completely dissolved. The second is the anodic dissolution method, carried out in a galvanic bath. Products are immersed in a bath of 20% caustic soda solution and connected as an anode; steel sheets or parts are used as a cathode. The process takes place at a temperature of 70-80C and an anodic current density of 20-25 A/dm2 until chromium is completely dissolved. Before repeated chrome plating, the products are heated for 1.5 hours at a temperature of 150-200C to remove hydrogen.
Required Equipment
Electroplating (chrome plating) at home is possible if you have the following type of equipment:
- power supply: it should show 1A at the output and be equipped with a voltage regulator; for small volumes of work, a current rectifier is sufficient; the wiring cross-section depends on the size of the workpiece (minimum 6.25 mm);
- wires: the positive one will be immersed in the electrolyte, the negative one, with an alligator holder, will be located at the end towards the workpiece;
- anodes made of tin, lead or antimony alloys;
- containers of suitable size made of chemically resistant, non-conductive material; the ideal option is a plastic bath; for chrome plating of small parts, a glass jar is sufficient;
- a wooden box with thermal insulation made of glass or mineral wool in which the container will be placed; Ordinary sand can also be used as insulation;
- sealed lid: it can be made from a piece of plywood or wooden boards;
- heating element, the power of which is sufficient to heat the liquid in the selected container to a temperature of 60-80°C;
- contact thermometer or thermostat;
- a hollow mold for pouring electrolyte with a tap or brush at the end; to make it, a bundle of copper wire is used, secured and tied with lead wire.
Compositions of chemical copper plating solutions
Many recipes for chemical copper plating solutions with formaldehyde as a reducing agent have been developed. In general, the composition of these solutions is as follows:
- copper (II) salt - 2-600 (usually 20-150) mmol/l;
- ligand donor - 1-4 times more than Cu(II) content; CH20 - 30-400 mol/l;
- alkali - up to pH = 11-14;
- concentration ratio CH20/Cu (II) - 1-50 (usually 3-12);
- stabilizer and other additives.
Of the copper salts, copper sulfate is most often used, but nitrate, chloride, carbonate, tartrate, and gluconate can be used.
Tartrates (sodium potassium tartrate, the so-called Rochelle salt, or Rochelle salt), ethylene diamine tetraacetate (EDTA, or Trilon B) are used as ligand donors. Ligands bind copper(II) into complexes and thus hold them in an alkaline solution.
Formaldehyde is usually introduced into a solution of chemical copper plating in the form of an aqueous solution - formalin. In copper plating solutions, you can use paraform, trioxane, and polyoxymethylene glycols, which decompose in alkaline solutions to form CH20.
Preparing the part for metallization
While the electrolyte is settling, it's time to do this.
Removing contaminants
In order for chrome plating to be of high quality and inexpensive, the layer covering the part must be uniform and thin. This can be achieved if the surface is cleaned down to the very base. How to remove foreign fractions and degrease is up to you to decide. For samples with smooth edges, as a rule, “sandpaper” is sufficient. In other cases, you will have to think about how and with what to remove dirt and rust.
Degreasing
This is the second preparatory stage. Limiting yourself only to traditional means - gasoline, white spirit, solvent “666” or something similar - means you will not achieve high-quality metallization. Chrome plating on such a surface will not last long.
Additional processing is carried out in a solution that is specially prepared for these purposes. There are many recipes, but the most popular for metallization at home is the following:
150 (caustic soda) + 50 (soda ash) + 5 (silicate glue).
*Based on g/l of water.
The pre-treated workpiece is immersed in this solution, which must be brought to a temperature of 85 (±5) ºС. The exposure time depends on the relief of the part and the degree of its residual contamination (from ⅓ to 1.5 hours).
Features of the chrome plating process
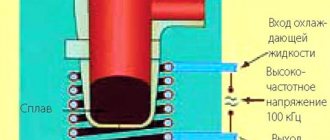
The “installation” diagram with the voltage switching polarity is shown in the figure (see above).
- The current is supplied after the sample is immersed in the electrolyte with some delay. Why? High-quality metallization will occur only if the temperatures of the part and the solution are equal. So you'll have to wait a little. This time can be reduced if the sample is preheated to 40 - 50 degrees. For example, in front of the reflector.
- Recommended current is within 55 ºС.
- After the entire part is covered with a layer of chrome, without “bald spots” (determined visually), it must be dried in an electric cabinet (at least 2.5 - 3 hours).
Before finishing the article, the author with great regret must add a couple of “flies in the ointment”. Those who are not afraid of the listed difficulties need to take into account a number of other problems that they will have to face.
Some - for example, ensuring high quality polishing, maintaining the absolute accuracy of the recipe, the difficulty of determining the optimal dimensions and shape of the electrodes, maintaining a constant current regime - will seem insignificant against the background of just one.
Where can I get anhydride and “pure” acid? The first one is on sale, but only for legal entities, with the preparation of the relevant documents. Store-bought H2SO4, which is purchased for the purpose of preparing electrolyte for batteries, is not suitable. It is not “clean” enough, so it will not provide high-quality chrome plating.
The article turned out to be quite complete. Whether or not to engage in metallization at home is up to you, dear reader, to decide.
Procedure for preparing electrolyte
There are quite a lot of methods, as well as the reagents used. For chrome plating at home, the most common electrolyte option is based on sulfuric acid and chromic anhydride. Component ratio: 2.5 g H2SO4 + 250 g CrO3 per 1 liter of clean water.
- First, the bath is filled. Water (distilled is the best) is poured in approximately ½ full. Its optimal temperature is 60 – 65 ºС. Under such conditions, the dissolution of the chromium compound will occur faster.
- Load CrO3 and mix thoroughly until all grains disappear.
- If necessary, add a certain amount of water (to the required volume), then add sulfuric acid.
After mixing the resulting solution, it is subjected to “processing”. It consists in passing a direct current through it. Its strength is calculated from the ratio: 1 liter - 6.5 A. Visually, the readiness of the electrolyte can be determined by its shade. It should turn dark brown in color. After this, the solution settles in a dark and cool place for at least 24 hours.
When choosing a capacity by volume, you need to focus on the power of the power supply. Accordingly, it should be selected based on the dimensions of the parts to be metallized. This is another reason why chrome plating of large samples at home is impractical and difficult.
The main problems with chrome plating and methods for solving them
- Lack of coating in recessed areas of the product - occurs due to low current density in recessed areas and excess sulfuric acid in the electrolyte.
Solution: use shaped anodes, start the chrome plating process (1-2 minutes) at twice the current density - give a boost to the current, reduce the sulfuric acid content - add water or chromic anhydride to the electrolyte.
- The coating is matte or burnt (usually on protruding parts of products) - occurs due to high current density at a given temperature, passivation of anodes or insufficient heating of parts before the process.
Solution: adjust the ratio of current density and temperature, increase the distance between the anodes and cathodes, clean the anodes, control the heating of the parts before immersing them in the chrome plating bath.
- Dark stains, stripes, dots on the surface of products - insufficient concentration of sulfuric acid in the electrolyte solution
Solution: add sulfuric acid to the solution.
- The dark color of the coating means a high content of trivalent chromium, a lack of acid, and a low temperature of the electrolyte during the chrome plating process.
Solution: in addition to heating the electrolyte and adding sulfuric acid, the electrolyte should be treated with current.
- The coating peels off - poor-quality degreasing of the product surface, a sharp increase in current density with decreasing temperature.
Solution: adjust the temperature regime of chrome plating, improve the preparation of the surface of the product.
- Graininess or swelling - the presence of solid particles in the electrolyte and (or) poor preparation of the product for galvanic processing.
Solution: electrolyte filtration and quality control of parts preparation.
Course of action
To do chrome plating at home using a special galvanic brush, you can use the following procedure:
- The fibers are tightly wrapped with lead wire.
- The wrapped bristles are placed in a transparent cylinder (preferably made of plexiglass). The top of the container is covered with a lid equipped with a filling hole and a metal contact. One of the ends of the lead winding made is soldered to this contact.
- Small through holes need to be made in the foam plastic membrane located above the bristles.
- A 12-watt transformer is used as a rectifier. The plus is supplied to the contact, which is attached to the cover, the minus is fixed on the element being processed.
- The electrolyte contained in the cylinder penetrates the bristles through holes made in the membrane.
When using any method, a compressor or a good vacuum cleaner will be useful to remove dust.
Electrolyte preparation
To calculate the volume of electrolyte ingredients, you should adhere to the following ratios, measured in grams, per liter of pure water:
- Chromium anhydride - 250 g;
- Sulfuric acid - 2.5 g.
A glass vessel is filled halfway with settled and boiled water, the temperature of which should be approximately 60 degrees. Chromic anhydride is then placed into the container. The solution is stirred until the substance dissolves, after which sulfuric acid is carefully poured into it.
Then the composition must be kept under current for three and a half hours. If the calculations are made correctly, the electrolyte will turn dark brown. Having de-energized the composition, it must be left for one day in some cool and dark place.
Part preparation
Before you do chrome plating yourself at home, you need to prepare it. Rust, varnish, dirt and paint must first be removed from surfaces to be treated. Once the cleaning is complete, you can begin degreasing.
Experts point out that it is undesirable to use gasoline and white spirit for this purpose, because these compounds will negatively affect processing. It is better to use a special mixture based on caustic soda, soda ash and silicate glue
The solution must be heated to 90 degrees Celsius and the part should be immersed in it for about half an hour. If the element has a complex configuration, then the holding time can be increased.
Three parts of the galvanic process
Electroplating at home, chrome plating is an electroplating process. Therefore, to carry it out, it is necessary to have three components: a cathode, an anode and an electrolytic medium in which the transfer of charged metal particles will occur.
- Cathode. A plate of pure lead or an alloy of lead and tin. It must be remembered that the cathode area must be larger than the anode area. The cathode is connected to the positive output of the rectifier.
- Anode. This is the chrome-plated part itself. It should hang in the electrolyte medium so as not to touch the walls and bottom of the container. In addition, the anode must never touch the cathode.
- Electrolyte. Chromium plating requires particularly careful preparation of the electrolyte.
Electrolyte preparation
The electrolytic fluid kit for chrome plating includes the following components:
- Chromic anhydride: 250 g/l.
- Sulfuric acid: 2−3 g/l. Chemically pure, concentrated. Technical sulfuric acid is not suitable.
- Distilled water.
The water is heated to a temperature of 60−80 degrees. After this, the anhydride dissolves in it. The solution is cooled slightly and then the required amount of sulfuric acid is added to it in a thin stream.
Preparing the surface of a chrome-plated product
Consists of three stages:
- Mechanical cleaning, grinding and polishing.
- Degreasing.
- Nickel plating.
The peculiarity of chrome plating is that, on the contrary, it emphasizes all existing irregularities, chips and cracks on the surface of the product. Therefore, traces of old paint, rust, chips, cracks and other defects must first be removed from the surface of the chrome-plated part. Preparation of the chrome surface consists of the following steps:
- Sandblasting.
- Polishing with fine sandpaper.
- Sanding with soft materials and polishing paste.
Do not use gasoline or White Spirit for degreasing. Otherwise there will be problems with the quality of chrome plating. The best option is to prepare a special solution:
- Caustic soda: 150 g/l;
- Soda ash: 50 g/l;
- Silicate glue: 5 g/l.
The solution is heated to 90 degrees. After that, the part is lowered into it and kept for 20-40 minutes, depending on the area and surface relief of the part.
Nickel plating is the last stage of preparing a part for chrome plating. The nickel plating process is carried out in a special galvanic bath. The cathode in this case is metallic nickel, and the electrolyte is a solution of sulfuric acid and nickel salts.
Preparation of surfaces for chemical metallization
Before starting the metallization procedure, it is necessary to prepare the surface of the product. Initially, it is cleaned, and then the remaining fat is removed. The more responsibly you approach these procedures, the stronger and more durable the future metallized coating will be. To perform these procedures, you need to select the right equipment. You can effectively remove unnecessary layers of paintwork, rust, and various contaminants using a functional sandblasting machine.
If the case is not so advanced, then coarse sandpaper will help clean the surface. This whole procedure is not at all complicated and can be easily done at home. The main thing is to approach this responsibly.
Application area
The electric arc metallization method in combination with subsequent painting of metal structures is a hybrid coating, the service life of which significantly exceeds the sum of the service life of each layer separately due to the synergy effect. Such coatings are used for long-term anti-corrosion protection of products operated under conditions of exposure to aggressive factors inside and outside structures, in liquids. Coatings formed as a result of electric arc metallization are used to protect:
- metal structures;
- reinforced concrete supports of overpasses, bridges;
- fuel and oil storage facilities;
- pipelines;
- equipment for petrochemical industry enterprises, heating networks.
Basic principles of the chemical copper plating process
For the reduction reaction to occur, a sufficiently strong and active reducing agent must be present in the solution. The more positive the standard potential of the metal, the wider the choice of possible reducing agents. The autocatalytic nature of the reduction reaction is also necessary, that is, the ability of the resulting metal to catalyze reduction. This ensures preferential deposition of metal on the required surface and obtaining a compact coating of significant thickness.
The degree of autocatalysis depends on both the nature of the metal and the nature of the reducing agent. In the absence of autocatalysis, the reduction reaction proceeds throughout the entire volume of the solution and leads to the formation of powdered metal.
The driving force of the autocatalytic reduction process is the oxidation of the reducing agent, the effectiveness of which can be assessed by its redox potential.
To obtain a metal deposit in the form of a continuous layer, the difference between the potentials of the reducing agent and the metal being reduced should not be too great, since otherwise a rapid, sometimes almost instantaneous, formation of a highly dispersed reduction product occurs. To prevent the rapid occurrence of the reaction, ligands are introduced into the solutions, forming fairly strong complexes with the ions of the metal being reduced and leading to a decrease in the potential difference due to a shift in the redox potential of the metal ion-metal pair to a more negative region (Table 1). Ligands also perform another function: they prevent the formation of metal hydroxides in an alkaline environment.
Table 1. Normal redox potentials of some metals in aqueous solutions at a temperature of 25 ° C
Almost the only reducing agent used in chemical copper plating solutions is formaldehyde. It is available, cheap and allows you to produce copper coatings at room temperature. The reduction of copper by formaldehyde is an autocatalytic process. The potential-forming reaction for formaldehyde is as follows:
The magnitude of the potential as a function of pH under standard conditions is described by the equation
The formaldehyde oxidation potential values at various pH values are presented in Table 2.
Table 2. Dependence of formaldehyde oxidation potential on pH
The catalytic reaction on the copper surface occurs at room temperature at pH > 10.0-10.5. To initiate this reaction on the activated dielectric surface, higher pH values are usually required: 11-11.5 at 1-2 mol/l CH20 and 12.0-12.5 at 0.1-0.5 mol/l CH20.
Sequence of actions in the process of chemical metallization
Despite the fact that this process is simple, it is important to perform all steps in strict sequence:
- First, the surface to be treated is thoroughly cleaned.
- Then degreasing is carried out. This is a very important stage, since the quality of the result depends on it.
- The degreased surface is washed with water.
- If not the entire product is metalized, then those areas that should remain uncoated must be insulated with lead (it is resistant to electrolytic solution).
- The product is attached to a wire through which electric current is supplied and lowered into an electrolytic solution. Here it needs to be maintained for a certain time.
- After time, the product must be taken out, dried, cooled and polished.
Surface degreasing
Degreasing is a very important stage in preparing the surface for metallization. How thoroughly the surface is degreased, the quality of the metal layer will be formed.
For example, let's cover a glass glass from Ikea with a mirror. First you need to degrease it.
The degreasing composition is simple: water 50-60 ° C and sodium hydroxide, a tablespoon per liter. Stir thoroughly.
We take a regular dishwashing sponge and very carefully wipe the surface with a degreasing solution. Next, wash off with water. You can water it with a garden sprayer and wipe the part with another clean sponge to remove all the degreaser.
It is important that the surface is completely wetted with water. If dry “islands” are formed during wetting, then the silver will not stick to this place.
Basic reagents
All reagents for chemical metallization must be prepared using specially filtered water. This ensures high light resistance and minimal coating thickness (up to 0.4 microns)
It is important that the solution contains the maximum concentration of the reagent. Reagents for chemical metallization must not contain carcinogens or substances that irritate the respiratory tract
Set for 20 sq. m should contain reagents in the following volume: binder primer - 3.3 l, protective varnish - 1.6 l, modifier - 1 l, activator - 1 l, reducing agent - 1 l, hardener - 0.5 l, pigment toners - 40 ml. The cost of such a set will be about 20 thousand rubles.
How to determine steel grade
There are simply a huge number of different steel options, each grade is characterized by its own specific features. If the manufacturer has not carried out markings, then you can find out the characteristics of the metal only by independently conducting various tests. We'll talk about this in more detail later.
How to determine steel grade
Methods for determining steel grade
A fairly common question is how to determine the grade of steel. There are several common methods:
- The first involves removing chips from the surface, for which a chisel can be used. At high carbon concentrations it will be short and brittle. A decrease in the indicator causes an increase in plasticity. However, it is not possible to accurately determine the brand using this method.
- The second method involves hardening the product, after which it is necessary to make cuts. If the material is simply sawed before and after hardening, then it contains a small amount of carbon. Due to the increase in carbon concentration after treatment, the surface becomes too hard.
- Determining the steel grade by spark is based on a visual inspection of the sparks that are formed when processing the surface with a grinding wheel. With an increase in the size of the sparks and their number, the hardness index increases, which depends directly on the carbon concentration. Such a test does not give an accurate result, since the main characteristics of the flying chips depend on the force of pressing and some other points. You can find tables that decipher the qualities of a material based on chips.
Spark test methodDevice for determining steel grade
You can also determine the brand by the color of the sparks produced. For this purpose, special tables were compiled. The test can be carried out at home only if the lighting is correct.
However, it is impossible to accurately identify the material in this way.
The option with alloying elements can also be identified by other performance characteristics, for example, resistance to high humidity or strong magnetism.
In the CIS, the applied designation standards are characterized by the fact that they can be used to indicate the main elements. When considering the issue of decoding the brand, we note the following points:
- The abbreviation “St” is often used. In other cases, no abbreviations are used at all, only numbers.
- In most cases, the first number indicates the carbon concentration. The following can be used to indicate the amount of alloying components.
- The composition may include alloying components that significantly change the properties of the material. An example is the inclusion of chromium, which increases resistance to high humidity.
Classification of steels by purpose
Labeling is deciphered using tables that indicate the designation of the chemical element.
Marking of steels according to international and CIS standards
In order to decipher a brand, you can use a variety of standards. Some alloys are designated by certain symbols that indicate the purpose of the metal.
An example is the following points:
- The letter “Ш” is used to designate metals that are used to make bearings. They are characterized by increased wear resistance.
- High-quality alloyed workpieces are designated by the letter “L”. Often the symbol is indicated at the end.
- “T” is used to designate heat-strengthened rolled products.
- High corrosion resistance of the workpiece is determined by the letter “K”.
- If copper is included in the composition, then the symbol “D” is used when indicating the brand.
- Instrumental can be identified by the letter “U”. They are often used in the manufacture of various tools that are characterized by high wear resistance.
- The symbol “P” is indicated to designate alloys that contain tungsten. Such a substance significantly increases the heat resistance of the structure.
By deciphering the brand, you can determine which chemical elements are included in the alloy. The numbers in most cases indicate the concentration, symbols, type of alloy and specific chemical elements.
European steel marking system Carbon steel grades according to GOST and ISO international standards
In conclusion, we note that there is simply a huge number of products on sale; in many cases, the brand is affixed by the manufacturer. It is almost impossible to independently determine the composition without the use of special equipment.
, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Chemical reagents used
Chemical metallization technology involves the use of various substances that bind together to form a protective coating after undergoing a chemical reaction. Using an activator and reagents for chemical metallization, you can do without special equipment, but the method is not suitable for large parts.
To carry out the processing in question you will need:
- The reducing agent is the main component. Chemical metallization reagents should be stored according to the recommendations provided by the manufacturers.
- The activator is also an important reagent that determines the performance of the surface. Chemical metallization reagents have labels that indicate the name of the metal. Let's take gold, mel and chrome as an example.
- The primer is applied to the surface to ensure the most favorable processing conditions. It significantly increases the adhesion of the applied metal.
- The varnish protects the applied coating from chemical and mechanical influence.
- In order to give the surface a certain color, special toners are used. The specific shade is indicated on the toner packaging.
Reagents for chemical metallization
It is worth considering that when doing the work yourself, it is quite difficult to ensure high quality surfaces. In some cases, you have to use special cleaning compounds.
Considering the disadvantages of chemical metallization, we note that when carrying out this procedure, harmful chemicals are used, work with which must be carried out in strict compliance with safety precautions. This technology is quite simple to implement and resembles the method of coating a surface with a paint and varnish substance.
Chrome plating at home
I would like to share my experience of decorative chrome plating in real home conditions. This can be done using this starting set of reagents for creating a mirror in chrome, gold, copper and any other shade on any surface. The kit contains reagents that are not available in regular stores. These are silver nitrate, stannous chloride, sodium hydroxide, glucose and sodium thiosulfate. Everything else can be bought in regular stores and is available to everyone, this is acetic acid 70% (in grocery stores), ammonia or ammonia 10% (in a pharmacy), distilled water (in auto parts). You will also need scales up to 300 g. (radio parts stores), measuring cups (also suitable for food products), disposable cups, spoons, syringes and hand sprayers. To obtain a chrome-look mirror, you need to go through 4 stages: preparing solutions degreasing the surface activating the surface metallization I’ll start with the recipe for decorative chrome plating, which is so carefully guarded in the depths of their workshops by people who are fluent in the art of chrome plating.
Safety conditions
Chemical metallization (chrome plating) is a process hazardous to health, so it is important to comply with safety requirements. The process itself should take place in a well-ventilated room. It is good if high-quality forced ventilation is installed in this room. When starting chemical metallization at home, it is important to take care of protective equipment for the respiratory system, vision, and skin, that is, special glasses, a respirator, closed clothing, an apron, and gloves.
To prepare the necessary solutions, only distilled water is used. It is also worth thinking about the reagents - they must be pure, of high quality, and marked “C”. Dishes for reagents are also important - containers should be glass or enameled.