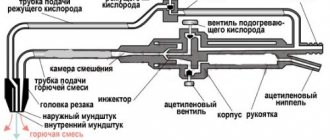
Device and design features
An oxy-fuel cutter is used to mix a mixture based on fuel (acetylene, propane) and cutting gases (oxygen) to produce a cutting jet.
Structurally, a gas cutter for cutting metal consists of the following elements:
- special head with two replaceable mouthpieces;
- tubes for supplying oxygen and gas;
- mixing chamber for forming a mixture of fuel and cutting gases;
- 3 valves – for flammable gas, supply and regulation of the amount of oxygen supplied;
- lever.
These are the main components of an oxy-fuel cutting tool as there are many other parts to its design.
Figure 1. Diagram of an oxy-fuel torch
Gas cutter for metal: types
The tool is classified according to various criteria, but the main ones are the type of combustible gas used and the principle of mixing the gas with oxygen. They are also divided by purpose (universal and special) and type of cutting (separation, surface, oxygen-flux).
According to the method of mixing gas and oxygen, cutters are of the following types:
- Injection - equipped with intra-nozzle mixing of gases, which ensures high reliability and safe operation of the devices. This is due to the fact that the gases pass separately along the entire length of the channels and are mixed into a combustible mixture in a special mixing chamber.
Photo 2. Appearance of an oxygen injection burner
- Injectorless - the design does not imply the presence of a mixing chamber. Oxygen is supplied through two tubes, gas through a third. They mix inside the head. Such a tool requires significantly higher hot gas pressure compared to an injection tool.
Photo 3. Appearance of a non-injector gas cutter
According to the flammable gas used, cutters are propane, acetylene and universal.
Acetylenic
Acetylene acts as the working gas, providing a high flame temperature (within 3300 °C). It is used for cutting thick metal workpieces and is equipped with additional valves for setting a high gas supply speed.
Propane
Designed for the use of propane as a cutting gas. They are characterized by higher reliability and long service life, and are safe to use.
Universal gas cutter
The universal tool provides the ability to use different types of flammable gas. Moreover, they are not much more expensive than a classic acetylene or propane cutter.
Gas burners and cutters
One of the types of equipment involved in metal processing is a propane gas cutter . Using cutters and torches, it is possible to cut sheets of metal into pieces. The PROFI Group company sells gas burners in a wide range, supplying only reliable production. As a leader in the production of equipment for processing metal products, we value our reputation and offer highly reliable equipment at reasonable prices. to buy a gas cutter for metal at very reasonable prices. A gas cutter (torch) is intended for cutting metal structures and cutting rolled products . The designs of gas burner models differ in individual parts and dimensions, but not in the principle of the device. The PROFI Group company offers users a cutting torch to buy from trusted manufacturers in America, Europe, and China. Having in their arsenal only high-quality equipment from the PROFI company, metal cutters can achieve flawless cutting of the material. The melting temperature should not be allowed to exceed combustion degrees. Otherwise, the metal will begin to melt before combustion begins. The cutting process is carried out due to the supply of oxygen to the combustion site. Before cutting metal, it must be heated. As a rule, the finished workpiece is cooled with water. Metal cutting with a gas cutter is carried out in the presence of a gas mixture, flammable and powerful equipment. The gas devices most used by craftsmen are injection-type cutters. Oxygen is supplied to them in two streams. Part of it is released through the central nozzle of the mouthpiece. The second part goes into the injector. A non-injector gas cutter for metal has a more complicated design The complexity of the injection-free design and the considerable price of the product are the disadvantages of this tool for cutting metal. An excellent device for off-grid operation is a portable cutting torch . This compact version of cutting equipment is always convenient to have on hand. To separate a certain part from a metal sheet, pipe or profile, it is enough to buy a gas cutter in Moscow from the PROFI Group company. Portable models are mostly represented by injection options. When working with such devices, oxygen cylinders are used. Portable portable devices with oxygen or propane cylinders are mobile and easy to use. To carry such equipment, you can use a container-type plastic suitcase. To use a gas cutter at home, it is not at all necessary to purchase professional equipment. a gas cutter for metal in a private household, of which is quite affordable for a wide range of users. To find out the price of a cutting torch , you need to contact the managers of the PROFI Group company, which sells similar equipment in a wide range. When choosing gas burners and cutters , you need to pay attention to their types, purpose and operating features. As a rule, a cutter for a gas burner is classified according to the following criteria: - cutting method; - to its purpose; — the presence of an injector; — manual or mechanical control; — power; - mouthpieces; - injection of low or high pressure oxygen. In the catalog of our gas equipment supplier company, the consumer will find many modifications from various manufacturers. In terms of their appearance and application, cutting equipment has general similarities. The device may include a different number of internal mouthpieces, providing cutting of metal of various thicknesses. Before you start working with a cutter, you need to study the principle of operation of such a device. Depending on their purpose, autogens are either special or universal. As for gas burners, they are classified as oxygen injection units, kerosene, propane and acetylene. The most popular in work are universal ejector units. This gas cutter can cut metal in all directions. In addition, it is extremely easy to operate, which also explains the reason for its popularity. An important advantage of such a device is the ability to cut metals of various thicknesses. The essence of autogenous metal processing is that the metal burns in oxygen. The cutting device is quite simple and includes various elements that ensure its normal operation. The designs of various cutting equipment have their own distinctive features, but in general, they are not much different. The operation pattern of gas burners is also the same. You can increase the life of your nozzles and mouthpieces by cleaning them regularly. Autogen is equipped with special rubber seals and seals. Its ignition is carried out according to a special scheme. Before you start working with a gas burner, you need to watch the video instructions for its use. In addition, gas cutting torch must be treated with a special lubricant. All connections must be tightened tightly to prevent gas leakage while the torch is in use. The PROFI Group company guarantees its customers impeccable quality and safety of supplied metal cutting devices, as well as timely deliveries. The burner flame is also extinguished according to a certain pattern and in the required sequence. When work is carried out inside a building, it is necessary to ensure its ventilation. In addition, it is necessary to work with protective clothing that is resistant to fire. Even with a short break in work, the burner flame must be extinguished. Working with gas equipment requires performers to carefully follow safety regulations. The PROFI Group company is ready to equip its customers’ enterprises with the latest models of metalworking equipment.
Advantages and disadvantages
Any tool has its pros and cons, and a gas cutter is no exception. Among the advantages of modern devices with intra-nozzle gas mixing, the following should be noted:
- The relatively large thickness of the metal being cut is up to 300 mm, depending on the modification and operating parameters (gas used and oxygen pressure).
- Stable flame burning without pops or backfires.
- Possibility of cutting steel in any direction, regardless of thickness.
- High performance.
- Easy to maintain and long service life.
Photo 4. Oxygen gas cutting process
However, it has no less disadvantages:
- As a result of strong heating, the cut parts may become deformed (especially those made of thin sheet metal).
- The cutting width is quite large, which requires compliance with certain allowances during marking work.
- Low quality of cut - uneven edges with oxides and scale. Therefore, before welding or other work, pre-treatment of the edges is required.
- Quite a high cost of the oxy-fuel cutting process.
Product classification
Modern devices work by mixing oxygen and flammable gases. Fuel type is the first criterion for dividing into groups. The most common gas cutters are:
- Propane. It is very common because it is safe and has high efficiency. Used for cutting non-ferrous or ferrous metals, popular among amateurs and professionals. An example of a popular model is the Kord-05P-L340 propane cutter. It cuts metal from 3 to 500 mm thick, weighs only 0.9 kg, and costs about 1,500 rubles.
- Oxygen. It is an injection cutter, the working mixture of which is 85% oxygen and 15% flame. The first is supplied under high pressure, so the mixture ignites. The low cost of the oxygen gas cutter has allowed it to become popular among hobbyists. The cost is slightly lower than the propane analogue, since the considered device cuts not such thick metal (up to 300 mm).
- Acetylenic. This fuel is used when working with thick workpieces, as it gets very hot. The pipe through which acetylene is supplied has a valve that allows you to regulate the flow rate. The acetylene cutter is one of the few that has portable analogues. They become more popular every year because they are not inferior in quality to large products. An example is Redius P2A-01M, which costs about 1,600 rubles.
- Kerosene. Used for cutting carbon steels with a maximum thickness of 200 mm. It is not considered in demand, since it is more often found in the mining, coal industry, and mines. This is a kind of advantage of a kerosene cutter over propane and acetylene (they are not recommended for use underground).
- Petrol. The scope of application is the same as that of kerosene. It is considered a hand cutter, and the fuel is A-80, A-92, A-95 gasoline.
- Hydrogen. A mixture of oxygen and hydrogen has the highest combustion temperature among gases - 2800 degrees. Therefore, a hydrogen cutter is good for work that needs to be done quickly. The main advantage is that it is obtained by electrolysis from water, which is possible at home. Often used in jewelry making. There are larger and smaller specimens, with the latter being more popular. Adding water is the only maintenance requirement.
An interesting video about this was prepared by the Welding Center company:
Also, a gas cutter for metal has a different design; this is the second classification criterion. This includes dimensions, number of tubes, method of ignition of the mixture, and more. Highlight:
- industrial cutters (for large volumes of work; also known as gas metal cutting machines);
- compact, portable, mini-cutters (conventional names, since the product is no larger in size than a blowtorch; used, for example, when lighting a fire);
- tourist (similar to the previously named one, but has a preheating function and works properly at any angle of inclination);
- cutter with piezo ignition (does not contain valves; the mixture is ignited by pressing one button).
Some products for cutting metal with gas are divided into separate groups. Below are more details about them.
- Air arc cutters. Purpose: cutting non-ferrous or ferrous metals in production conditions. They are small-sized (for example, the domestic air-arc cutter RVDm-315 weighs 500 g and is 315 mm long), highly productive, but only works with a power source and a compressor. Buying it for household needs will be a waste of money. In addition, to operate an air-arc cutter you will need electrodes, cathodes and nozzles, which will have to be purchased regularly.
- Three-pipe devices. Also known as in-nozzle mixing cutters. Unlike most gas welding cutters, they have not two channels (tubes), but three. The first carries cutting gas - oxygen, the second - flammable gas (propane, acetylene, etc.), the third - heating gas. For normal operation of a three-pipe device, increased working gas pressure (minimum 20 kPa) is required.
Three-pipe gas cutter
The design allows you to use any flammable gas; you just need to select suitable mouthpieces for the cutter. They are among the safest products, since the mixing of elements occurs not at the base of the product, but at the head. However, this increases the price of a three-pipe cutter by 1.5-2 times.
Equipment for gas cutting is divided into injection and ejector. The latter have two separated channels - for heating and combustible gases. In injection systems they are combined. An ordinary cutter, which is used to work in factories, most often an injection one; This type also includes devices for manual oxygen cutting, compact and mini-products. Ejector equipment for oxygen cutting is a three-pipe apparatus.
Next - a few words about regular investments in work.
Features of choice
To avoid mistakes, before purchasing a gas cutter, it is important to familiarize yourself with some of the design features of the device. This will allow you to understand what primary factors you need to pay attention to when choosing it.
Selection rules:
- Nipples - made of brass and aluminum, the former are considered more durable.
- Mouthpieces - the outer one is usually made of chrome bronze or pure copper (distinguished by a reddish tint). For acetylene devices, it is also desirable for the internal one to be copper; for others, the use of brass analogues is allowed.
- Connecting tubes are made of brass. At the same time, they should not have a decorative coating that can hide minor defects.
- Valve spindles are made of stainless steel; brass spindles have a short service life.
- Handle – aluminum is considered the best material, plastic is less wear-resistant. Its size must be at least 40 mm to have a comfortable girth.
- Cutter length – for cutting thick metal, as well as painted or oily materials, it is better to choose devices up to 1000 mm in size. In other cases, you can buy 500 mm burners.
Photo 5. Basic consumables for gas cutters
Also, when purchasing, it is recommended to take the tool in your hands and check it for ease of use. The productivity and time the master can work with a cutter without fatigue directly depends on this.
Correct setting of the cutting torch
Before you start working with a new gas cutter for metal, you need to properly connect and check the functionality of the tool. The device is directly configured by the manufacturer in the factory and is the final stage of its assembly. Individual intervention in the burner design is prohibited.
Sequence of work:
- Study the operating instructions and follow all steps according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Connect the device to cylinders with flammable and cutting gases. At the same time, they must be equipped with gearboxes: oxygen – blue, propane – red. Rubber gas supply hoses are screwed onto the threads of the gearboxes and tightened with clamps.
- Check the integrity of the tool, the presence of all gaskets, and the absence of oil traces near the oxygen valve.
- Adjust the gas and oxygen supply, blow out the hoses. When working with acetylene, open the supply valve 1 turn, and the pressure of the substance should be up to 1 atm, but it is better to set it to 0.54 atm. To purge, you need to open the valve on the cutter, and after the sound changes, close it. When setting up the oxygen supply, the pressure is set to 2 atm. Then the hoses are purged using valves on the gearbox and cutter.
You should also remember that it is forbidden to change the hoses for supplying oxygen and propane (acetylene) with each other, or to blow the hose for propane (acetylene) with oxygen.
Photo 6. The process of separation cutting of thick rolled metal with a gas cutter
Gas cutting VS plasma cutting
application and differences
Plasma cutting has become widespread due to the accuracy and quality of the cut, but traditional gas cutting is still used in various technological processes. Oxygen cutting is still widely used for jobs that require a high degree of mobility and maneuverability, especially cutting thick steel workpieces.
Both processes have their advantages and limitations: material thickness, cut quality, maneuverability and component cost are just a few things to consider when making your choice. Below we will consider the advantages and features of each.
What is oxygen cutting?
In oxyfuel cutting, the flame of the oxygen-fuel mixture preheats the steel to its ignition temperature.
A stream of oxygen is directed at the metal, creating a chemical reaction to form iron oxide, also known as slag. A powerful flow of oxygen removes slag from the cut.
When using oxy-fuel torches, cut quality, preheat time and metal thickness depend on the type of fuel gas. The process uses one of four fuel gases in combination with oxygen: acetylene, propane, propylene and natural gas.
What is oxygen cutting used for?
Manual oxygen cutting is common in low-volume projects when the use of expensive units is not economically justified. For example, preparing parts for subsequent forging and stamping, in foundries, cutting pipes. Oxygen cutting is effective when working with thick steel and ferrous metals.
There are oxy-fuel torches that can be used for several processes such as cutting, welding and soldering.
Advantages of oxygen cutting:
- The undeniable advantage of this process is the low initial costs and portability of components compared to plasma cutting machines.
- The ability to quickly cut thicker steel, in addition to the versatility of the system.
What is plasma cutting?
At a basic level, plasma cutting is a process in which a high-velocity jet of ionized gas is delivered from the orifice of a constriction nozzle. High-speed ionized gas, plasma, conducts electricity from the torch of the plasma cutter to the workpiece. The plasma heats the workpiece, melting the material. Different gases are used for different types of metal: Ferrous metals and alloys are cut using active gases - oxygen. Inactive, inert gases: nitrogen, argon, are used when cutting non-ferrous metals and alloys.
A high-speed plasma flow created by a built-in or separately connected compressor mechanically blows away the molten metal, separating the material.
What is plasma cutting used for?
Plasma cutting is performed on any type of conductive metal, such as: non-ferrous metals, mild steel, aluminum and stainless steel. Using a plasma cutter, mild steel is cut faster than alloys.
Plasma cutting is ideal for cutting workpieces less than 25mm thick. Plasma cutting is great for unusual tasks, such as cutting metal foam: a metal with a cellular structure that is almost impossible to cut using oxyfuel cutting. Compared to mechanical means, plasma cutting is generally much faster and easier to perform non-linear cutting.
Advantages of plasma cutting:
- Pros of plasma cutting include ease of use, better edge quality, and faster moving speeds.
- Plasma cutting does not rely on oxidation, so it can cut aluminum, stainless steel and any other conductive metal.
- Work with any metals: ferrous, non-ferrous, refractory.
- Productivity when cutting metal of small and medium thickness is 3 times higher than manual oxygen cutting.
- Point, local heating of the surface, without unnecessary deformation and overheating of all parts.
- Safety because there are no flammable gas cylinders.
- Possibility of cutting complex shapes.
Needed for periodic repairs, maintenance or projects that require large volumes of cutting.
Preparing the tool for work
Before work, it is necessary to properly prepare the gas cutter. The preparation process consists of several stages that minimize the risks of tool failure and injury:
- Inspection of cylinders, rubber hoses for supplying fuel and cutting gases, connecting and fastening elements, burners for defects or damage.
- Check all connections for gas leaks.
- Inspect the condition of the seals - if there are cracks, they change shape and require immediate replacement.
When working with injection cutters, you also need to check that they are working correctly. This is done until the flammable gas supply hose is connected. Initially, an oxygen hose is connected to the corresponding fitting on the burner, and the valve on the reducer of the oxygen cylinder is opened. Then the oxygen and flammable gas supply valves on the cutter open - if you put your finger against the flammable gas fitting, you will “suck it in.” In this case, the injection is OK.
Burners, cutters, reducers, cylinders, electrodes
Gas welding is used to heat metal with a high-temperature flame resulting from the combustion of flammable acetylene gas mixed with oxygen.
In some cases, instead of acetylene, its substitutes can be used: propane-butane, methane, gasoline or kerosene vapor, MAF (methyl acetylene-allen fraction). The main advantage of gas welding is that it does not require a source of electricity or additional expensive equipment. Welding can be done even in the field. Gas welding is especially convenient when welding small-diameter pipes in hard-to-reach places.
An acetylene torch is the main tool for manual gas welding. In the burner, oxygen and flammable gas (acetylene, propane) are mixed in the required proportions. The resulting mixture flows out of the torch mouthpiece channel and burns, producing a stable flame that melts the base and filler metal at the welding site.
Welding torches , brought to your attention, allow you to perform not only manual welding, but also soldering, heating ferrous and non-ferrous metals and alloys using a gas flame. The burners have a simple and repairable design and are equipped with replaceable tips for different thicknesses of metals. Certified, reliable and safe to operate, subject to basic operating rules.
Instructions for use
The cutting technology involves initially setting the ratio of oxygen and propane at 1 to 10 – i.e. at an oxygen pressure of 6 atm. The flammable gas pressure is set to 0.6 atm.
Opening and closing the gas supply is carried out in a strict sequence:
- The oxygen and flammable gas valves open 0.5 turns (strictly in that order).
- The flammable mixture is ignited.
- The torch is brought to the metal being cut and by opening the valve, the supply of oxygen is added until a cutting jet appears.
- After completion of the work, the supply of flammable gas is initially shut off, and then oxygen.
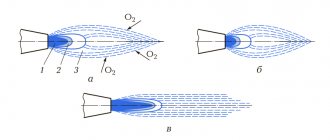
Figure 7. Scheme of the process of oxygen cutting of metal
The cutting technique after igniting the torch involves the need to heat up the metal area in the cutting area. If the heated area becomes red, the oxygen supply can be increased a little more. After completely cutting through the workpiece, the torch moves along the cutting line. The speed of movement of the cutter depends on the thickness of the rolled metal being cut, the operating characteristics of the process, and therefore is determined individually.
The following video shows how to properly use a gas cutter:
Oxygen cutting of thick metal
Oxygen cutting of thick metal is often mechanized using portable equipment and gas cutting machines. You need to understand that during such processing, acetylene is used, as well as a number of other flammable gases: natural, petroleum, hydrogen, in addition, fuels such as kerosene and gasoline are used.
In terms of quality and productivity, this cutting technology is superior to most others, which is why it is often used in production.
We recommend articles on metalworking
- Steel grades: classification and interpretation
- Aluminum grades and areas of their application
- Defects in metal products: causes and search methods
It is important to mention the method of processing thick materials with an oxygen lance. It is necessary for sawing through thick metal in metallurgical furnaces, creating holes in concrete products, etc. To do this, a tube made of steel with a low carbon content is pressed to the cutting site, directing gas through it. Let's make a reservation that the treated area and the end of the tube are preheated using a soldering iron, and only after that the gas supply is opened. As soon as the end of the tube lights up, it comes into contact with the metal - the cutting itself occurs through the combustion of the materials of the tube and the workpiece.
Do-it-yourself cutting torch
You can make a mini-torch for small jobs (for example, melting and cutting copper wires) yourself. For this you will need:
- 2 large droppers;
- a can of gas for refilling conventional lighters;
- a needle used to inflate balls;
- nipple;
- compressor;
- aquarium pump;
- copper wire;
- soldering iron with consumables;
- needle file
Assembly instructions:
- The needle from the dropper is bent at an angle of approximately 60°, the sharp end is sharpened.
- A hole is made in the side of the ball needle, into which a bent needle from a dropper is passed with the end protruding by about 2 mm.
- The remaining hole is wrapped with copper wire and sealed well.
- Tubes from droppers are attached to the ends of the needles.
- A gas cartridge is connected to the thick needle, and a compressor is connected to the thin one.
Photo. Appearance of a homemade mini-cutter
The gas supply is regulated by plastic jumpers installed on the tubes from the droppers.
Gas cutter Kovea - a compact and powerful burner for home use
Gas gear and equipment from the South Korean brand Kovea enjoys considerable popularity in the domestic market, where it has occupied a leading position in recent years.
1 Information about Covea cutters
The Kovea gas cutter of any model is a multifunctional pistol torch powered by a compact gas cylinder. Such devices are intended for household use. With their help you can:
- warm up metal surfaces;
- light coals in a fireplace, barbecue, fire;
- burn out the nests of ants and other insects;
- carry out simple heat-shrinking work;
- repair pipes of household pipelines;
- weld the seams.
The Kovea gas cutter is not used for cutting metal, since its power is simply not enough to carry out such activities.
All models of such gas equipment are characterized by approximately the same flame temperature.
One Kovea gas cutter differs from another only in the power and size of the flame, as well as the recommended purpose (some installations are prohibited from being used for repairing pipes, others are not suitable for welding seams, and so on).
Covey cutters are conventionally divided into three groups:
- Low-power. They are aimed at the needs of aircraft modellers, radio amateurs, and professional jewelers who need a very thin flame to work. In essence, the Kovea low-power gas cutter is a modern soldering iron with a small-volume gas cartridge, which is enough for a maximum of 12–15 minutes of operation;
- Medium power. Universal devices with the ability to regulate the shape and power of the flame. They are suitable for heating up a car lock or a soured nut on any structure, and for quickly lighting a fire in camp conditions;
- High power. Such devices are most often used in everyday life. They make it possible to perform any work that we listed at the beginning of the article.
So that you can wisely choose a Kovea gas cutter for use at home, we provide a description of several of the most popular models of such equipment these days.
2 Key Features of Kovea KT Models
The KT 2104 cutter is a powerful gas device made in the form of a blowtorch. This model allows you to perform a variety of work. Gas cylinders equipped with a standard thread cannot be connected to the KT 2104 (the cutter does not have a corresponding adapter). The equipment works in tandem with high collet cylinders (for example, with KGF-0220).
The KT 2104 is characterized by a fairly large firepower, so this Kovea gas cutter is optimally used to solve various technical problems. Device power – 1.64 kW, weight – 125 g, highest flame temperature – 1300 °C. KT 2104 consumes about 120 grams of gas per hour.
A more modern model is the high-power soldering iron KT 2408. The temperature of the flame it produces is also 1300°. It guarantees a flame stream of increased stability. KT 2408 is equipped with a special mechanism designed to preheat the fuel. Due to this, it is very convenient to use for complex activities (soldering seams, pipes). The flame power of this device is 4.12 kW, the connection is made to a collet cartridge.
Another popular model is the KT 2511. Medium in power and compact in size (15.5x5.5x20.6 centimeters), the Kovea gas cutter weighs 153 grams. Model 2511 is ideal for ordinary household work, the comfort of which is ensured by the presence of a piezo ignition system. The power of the 2511 is only 1.08 kW, but it is enough to produce a flame flow with a temperature of about 1300 degrees.
3 Burner TKT 9607 – tourists’ best friend
This Kovea gas cutter can be recommended to fans of picnics and overnight stays in nature during hiking trips. With its help, you can easily light a fire even in very bad weather conditions (light rain, gusts of wind). In addition, TKT 9607 can be used as a full-fledged burner on which you can heat and cook food. This opportunity is especially important when you spend your outdoor recreation in protected areas where it is prohibited to make fires.
It only takes a few seconds to start the TKT 9607; operating the gas device does not cause problems for inexperienced tourists (anyone can learn to operate a gas cutter very quickly). Its undoubted advantages also include:
- low explosion hazard;
- compactness (dimensions - 20x4x9.5 centimeters, weight - 129 grams);
- high reliability;
- Possibility of use in closed temporary shelters and premises (campsites, tents).
The described Kovea gas cutter has a flame power of 1.09 kW, gas consumption per hour of operation is no more than 80 grams. TKT 9607 will become a reliable assistant for anyone who wants to spend a couple of days in nature, away from civilization. The main thing is not to forget to take with you enough gas cans so that the cutter can perform its tasks.
Tips from experts on working with a cutter
Experienced carvers advise always using high-quality personal protective equipment:
- special glasses;
- gloves (mittens), jacket and pants with fire-resistant properties;
- special work shoes.
The workplace must also be properly equipped. The location of gas cylinders is at a distance of 5 m from hot work. The workshop should be well ventilated, the floor should be concrete or earthen. The flame of the gas-oxygen burner should be located frontally relative to the gas supply hoses. Hoses must not interfere with work.
It is also important to have auxiliary tools and devices for marking work - pencil (chalk), tape measure, square, ruler. To ignite the flame, you will need a special lighter, which the carver should always have at hand.
At the end of the work, you need to carefully inspect the workplace so as not to accidentally step on a piece of molten metal, which can burn through even the thick sole of your shoes. The cut metal blanks are usually left to cool in natural conditions, but if necessary, forced cooling with water is allowed - this must be done carefully so that hot splashes do not get on the skin.