Which producing countries lead the global copper market? What role does Russia play in the global copper market? How is copper consumption distributed on the world market? What are copper prices in 2016? What will the global copper market look like in 2022?
The global copper market, like other markets of various metals, has recently been undergoing an increasingly active process of consolidation and acquisition of some companies, which ensures the rise and improvement of various areas of overall systematic work on financial and commercial issues. The global market demand for metal and the cost of copper on the world market is rising. Today, global demand in the mining industry of the largest Asian countries is growing very quickly. The increase in demand in the commodity market for metals and minerals is much more active in China, as well as in India, since the economic sectors in these countries require more materials and raw materials, compared to the economic demands of the advanced countries of the world. Extractive industries in such a situation should become the basis for the development of the world market over a fairly long term.
Global copper market: leading countries in production and extraction
Copper is the very first existing metal that became known to man. Over the centuries, it has become very deeply embedded in our everyday life. Today, however, copper is not as common, ranking third behind more well-known and widely used minerals such as aluminum and iron. Under natural conditions, this metal is not in its original state; it is obtained by mining ores of different compositions. The suitability of ore for beneficiation is determined if it contains 0.5-1% copper.
The types of copper ore found in a porphyry copper mine depend on the location and rock stock:
- The stratiform type includes sandstone and copper shale;
- A unique type of copper nugget belongs to the pyrite type;
- The hydrothermal type includes porphyry ore rocks;
- Copper-nickel ore belongs to the igneous type;
- The carbonate type includes a mixed composition of iron and copper.
In the natural environment there are rocks that include copper. This is bornite (the second name is copper purple, or variegated pyrite), which contains mainly iron, sulfur, and also copper; chalcopyrite (also known as copper pyrite or CuFeS2), it includes such chemical elements as sphalerite and galena; chalcocite - copper luster (formula CuS) is a very rare ore found in the natural environment.
There are secondary minerals in which copper can also be found:
- Ores such as cuprite contain native copper and malachite;
- A mineral such as covelin, or sulfur sulfide, contains 66% copper and 34% sulfur;
- Malachite contains copper dihydrocoxcarbonate, which can be found in Russia near Nizhny Tagil.
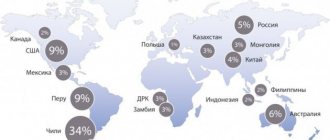
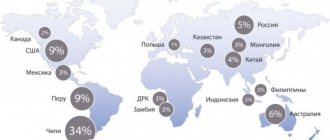
Latin America has the largest deposits of copper ore of any continent. For example, Chile produces 40% of the world's copper. The largest deposit of red metal in the state is located near the city of Rancagua. In this place, copper ore was found by the Indians before the arrival of European colonists. Industrial-scale mining of copper ore began at the end of the 19th century. Thus, the world market for copper was opened.
The largest mine in Chile, El Teniente, covers an area of up to 4 thousand hectares. The mine employs 6 thousand people with a minimum salary of $700 per month. The maximum depth of the mine reaches 80 meters, the length of mining is up to 2,400 kilometers. In one lift, the mining elevator brings approximately 350 workers out of the ground. The enrichment of the rock is determined by the presence of 1-4% copper. From the depths, ore is delivered by train along 10-kilometer-long rails; workers make 15 such shipments throughout the day. Ore is transported from the deepest mine in huge trucks seven meters high and eight meters wide.
The global copper market includes other mine locations in Chile:
- El Abra, where production is 150.4 thousand tons throughout the year;
- Cerro Colorado, where 89.5 thousand tons are mined;
- Los Pelambres, where 268.4 thousand tons are processed;
- Escondida, where they produce 1.34 million tons of copper ore per year.
It should be noted that in Chile copper ore is mined by nationalized enterprises, which indicates state control over their activities.
A lot of copper ores are found on the African continent. In Central Africa there is generally a kind of copper belt. This belt is located on the lands of the African countries of Zambia and Zaire.
This strip of ore deposits stretches 50 kilometers wide by 160 kilometers. African ore deposits are very rich in metal. They contain 3.3-4% red metal, which is found in pyrites, chalcopyrites, bornites and chalcocites. Rock on the “black” continent is mined in mines only 60 meters deep, which makes its extraction very easy.
The largest ore-bearing reserves of copper are located in Zambia near such villages as Chililabombwe, Nkana, Nchanga, Mufulira, Ron Antelop, as well as on the lands of Zaire within Kambowe, Ruwe, Kipushi, Musonoi, Dikuluwe, Musoshn.
Recently, due to the tense political situation, copper ore production on the African continent has noticeably decreased - by as much as 3.5%. The world copper market reacted immediately, prices began to rise at a very fast pace.
The Republic of Congo and South Africa hold the leadership in copper mining on the African continent. These countries are not located within the so-called “copper belt”, but, nevertheless, supply a very large amount of the red metal to the world copper market.
Since deposits of ore containing copper are located almost on the surface, copper-containing ore is mined in most cases by open-pit mining. On the African continent, most of the rock is obtained from the ground by hand; here labor is practically not mechanized. Even small children earn money by mining ore, and the work is very hard, there are no normal conditions at all. In this regard, there is always a high probability of injury and even death. By the way, it is worth noting that in Chilean mines, the owner of the mining enterprise is not responsible for safety precautions and conditions that threaten the life of the employee. The miners sign an agreement with the enterprise, which states that they go into the mine passages voluntarily and at their own responsibility. Government agencies pretend not to notice anything. Only the international association that defends human rights is concerned about human life.
According to Transparency International, huge deposits of copper were discovered on the territory of the Afghan Republic, which brought the country to the world copper market, placing it in second place. But a large number of deposits have not yet been explored, so industrial production is not yet fully carried out.
The Ainak copper ore deposit is recognized as the largest, not only in the country, but throughout the world. The main contradictions regarding its development appeared in the process of a dispute between an ore mining company and an archaeological organization. It so happened that on a honey vein, archaeologists discovered the old city of Mes Aynak, once built by Buddhists and representing an invaluable historical find. And after that, ore mining at this place was prohibited.
State plans include organizing the development of an ore deposit in Ainak, in the amount of 300 thousand tons per year, with a gradual increase in production rates in order to enter the world copper market.
The Ainak deposit is characterized by an area of 5 km2, as well as copper reserves, according to experts, in the central part - 9.8 million tons, in the western part - 9.9 million tons. Planned investment investments in copper mining amount to $4.4 billion. The Chinese company MCC was attracted as an investor.
Active development on the territory of the Ainak field was planned in 2011. In 2015, production was supposed to be 200 thousand tons of copper. Now these plans have been postponed to 2022. There is hope that the Aynak field will eventually be launched at full capacity and will significantly improve the economic condition of Afghanistan. The country's dream of entering the global copper market will come true, but at the same time preserving the remains of the old Buddhist settlement as a cultural historical heritage.
- Customs clearance in international trade
Copper production centers
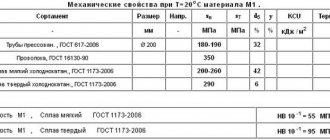
Copper production centers are present in different regions of Russia. Kazakhstan boasts the richest ore deposits. There are also deposits in the Urals. According to the latest data, Russia ranks first in the world in copper ore mining. Copper plants are being built in close proximity to the mines. The raw material factor is the determining component, due to the low content of concentrates in the feedstock. There are 11 copper complexes in the Urals, producing 43% of the country’s copper. In addition to our own raw materials, production also uses those imported from Kazakhstan. There are also waste recycling plants. For example, sulfur dioxide gases, as a byproduct of copper mining, are used to create sulfuric acid, which is then used to make fertilizers.
World copper market: metal production from 1900 to 2015.
The world copper market at the beginning of the 20th century offered only 495 thousand tons of copper. Almost 100 years later, 11,526 thousand tons were mined; by 2015, copper production reached 22,848 thousand tons. Thus, over 60 years, starting from 1900, global production of the red metal increased by 3.2% annually, over 10 years since 1960, annual global production growth amounted to 3.4%, in the 70s it increased by 2.4%, in the 80s - increased by 2.2%, in the 90s - increased by 3.1%, since the beginning of the 21st century - increased annually by 2.3%.
Traditionally, the world's leading producer of copper and other minerals, Chile, has increased its share of production annually, starting from 13% in 1978, 29% in 1997 and reaching 30% in 2015.
Last year, the world copper market received 5,700 thousand tons of copper ore and various concentrates from Chile. In African states during this period, on the contrary, copper production decreased sharply.
Obtaining copper metal
. Smelting is a pyrometallurgical high-tech process that is carried out to obtain a special metallic type of copper. Enterprises involved in copper smelting at the first stage take copper concentrate as raw material. Downstream copper producers use copper in the form of scrap metal. Approximately 50% of the copper that the world copper market receives is produced by virtually four countries: among Latin American countries - Chile, in the east - China and Japan, and among them also the United States of America.
Refined copper production
. The share of refined copper produced using the unique SX-EW technology ("solvent extraction - electrical extraction") in the total composition of the global production of this type of copper is planned to increase and today has already reached almost 20%. However, the main method for obtaining refined copper, as before, is the production of copper cathodes using the electrolysis method. By the way, the largest manufacturer of red metal in the Russian Federation, the Norilsk Nickel mining and metallurgical plant, is developing its production using a similar methodology.
In recent years, the global copper market has given a special place next to the United States to the countries of Chile and Southeast Asia. Over the past 30 years, Chile has entered the world copper market as the most active producer of refined copper. Supplies of this type of copper to the world market in this country in 2012 increased, compared to 1960 figures, by as much as 1858%, amounting to 177 thousand tons. The output of such copper in the Asian region increased by almost 2000% over the same period, mainly due to the expansion of Japanese and Chinese production.
Refined copper production volumes by region, thousand tons
Experts on the global copper market suggest that global copper production will increase in the near future. They emphasize that almost all the world's copper production companies have a goal of taking advantage of today's very strong market conditions. In the near future, this fact (plus the measures that Chinese officials are taking to stop the massive export of non-ferrous metal outside the state) may lead to increased supply, and the cost of copper on the world market will decrease.
Metal Bulletin data for 2012 identified the main reasons influencing the increase in risks in the metal market:
- A noticeable deterioration in the quality of copper ore mined and supplied to the world market;
- An increase in the number of mines as opposed to copper mining in open pits, which led to increased costs of organizing production;
- The impact of global political instability, since new mines and mines are in most cases located on the lands of those countries in which not everything is stable;
- The backward infrastructure of the country, where new deposits of the red metal are located;
- Short-term force majeure circumstances, for example, workers protesting or bad weather forecasts.
The global copper market and copper prices were in this state sometime before the beginning of 2014. At the same time, if you look at the data from the International Copper Study Group (ICSG), then, starting in 2015, the situation has been changing. Additional supplies of metal are being made to the world market of copper made from copper concentrate, which is reflected in the effective outcome, because in this way the shortage of copper in sale is restored and the cost falls. This direction continues to exist at the beginning and first half of 2016. The decline in supply to the market persists only in the SX-EW sector, but it cannot fully replace the upward trend in copper production capacity using established technologies.
Methods for obtaining pure metal from ore
Today, copper production is carried out by the most common method - pyrometallurgical. Globally, it is used by 90% of processing companies.
Scheme for obtaining copper from ore
- preparatory – receiving raw materials from mining enterprises, sorting them;
- blowing in a converter - the output is blister copper;
- refining.
melting for matte;
Enrichment of the resulting raw materials occurs using flotation. The ore is placed in a container of water, then compressed air is added there. As a result, foam is formed, copper particles stick to the bubbles, and waste rock settles to the bottom.
The next stage is firing. As a result, they try to reduce the sulfur content in the ore as much as possible. The composition is heated to 800°C - sulfides are oxidized, and the amount of sulfur is reduced by 2 times.
Next, the resulting mass is sent to special furnaces - the smelting stage for matte. Here the temperature rises to 1450°C. The iron and remaining sulfides are finally oxidized and blown off in converters. The result is blister copper, which is cast into ingots, and slag.
Copper production ends with refining. It involves the final purification of the metal from impurities.
Electrolytic refining (purification) of copper
The method is as follows:
- blister copper ingots are placed in a bath with an electrolyte (sulfuric acid);
- Thin sheets of pure copper are placed in the container - the cathode;
- connect electric current;
- As a result, all copper particles collect at the cathode, and impurities settle at the bottom - they are called sludge.
Often the sludge contains precious metals - gold, platinum.
What place does Russia occupy in the global copper market?
Russia has always occupied not the first place in the world copper market for the production of red metal, even in the past Soviet years. Today our state is developing the global copper market and produces approximately 5% of copper concentrates, as well as refined copper.
Almost 2/3 of the mined copper is sold for export and enters the world copper market. Of course, we have a number of competitive privileges - the close location of production facilities of various technological stages on the same territory, inexpensive energy resources and rock enriched with associated elements. All this allows our manufacturer to feel confident in exploring the global copper market. This confirms a fact specific to the leading sectors of the domestic economy: in terms of the best copper production indicators, we surpassed Soviet times 10 years ago. Russia now has every opportunity to increase the amount of copper produced: quite large reserves, a rapidly developing market within the state, available financial opportunities for creating new production capacities. But, starting in 2001, copper production began to slow down and sometimes even decrease. And the problem is not that there is an unfavorable price for copper on the world market - and in the worst times, our producers increased production growth, and in the 2000s, which were favorable in terms of pricing policy, they, on the contrary, began to reduce export supplies. To understand what has become an obstacle to the development of the state copper industry, it is necessary to analyze the history of the development of the industry, as well as the features of the structure of our production.
Nowadays, the copper market in Russia is divided between three players - MMC Norilsk Nickel, Ural MMC, and the Russian Copper Company. The largest enterprise is the diversified non-ferrous metallurgy enterprise Norilsk Nickel, which in its structure resembles some of its partners from Western countries. Copper mining is not the first place in business for this manufacturer (the company receives its main income by selling nickel and platinum group metals), so over the past 15 years, the share of the largest producer in Russia in global copper production has almost halved - starting from 5. 8%, dropped to 3%. Thus, if the copper industry of our state continues to develop, it will be, first of all, thanks to the Ural copper holdings - the Ural MMC and the Russian MK. For these giants, the development of ore deposits, as well as the smelting of copper from it, is not even the main, but the only direction in business, and therefore their attitude towards it is especially reverent. But these enterprises have recently been hit by a number of problems that have prevented them from developing production and becoming leaders in order to enter the global copper market.
Existing problems include indicators such as obsolescence and physical deterioration of production lines at those metallurgical enterprises that are part of holdings. The Kyshtym Copper Electrolytic Plant, which is part of the Russian Copper Company, was built in the 18th century, reconstruction took place in 1992, and modernization took place at the enterprises only nine years ago. Uralelectromed, which is the parent enterprise of the Ural MMC, underwent its last major renovation back in 1999. Today, Russian copper industry enterprises are very different in their productivity from Western ones, and in 1999 the city of Karabash was “awarded” by the UN Commission on Ecology the title of “the most polluted city on earth.” A couple of years ago, copper holdings became very active, investing in fixed assets of enterprises, but the situation has not yet changed dramatically. Moreover, having surpassed the production indicators of Soviet times, Ural enterprises have practically used all inexpensive opportunities on the path to intensification and have approached full 100% utilization of production capacity. In the end, they were faced with a choice: either take the path of extensive development and expand production, or begin a deep reconstruction with unforeseen terms for the return of expenses for such projects and the same unforeseen social upheavals (very often “reconstruction” could lead to the complete liquidation of the enterprise and building a new one, but somewhere else, and maybe in a remote area). It is clear that these areas require huge investments. Meanwhile, both the first and the second holdings were forced to direct material and human resources to perform completely different tasks.
The thing is that Ural holdings are fundamentally different from global copper production companies due to their internal characteristics. The main part of the income of copper industry companies is created at the very first stage, directly during the extraction and enrichment of the rock. That is why most of the enterprises producing crude and refined copper for the market are not purely metallurgical, but are mining, i.e. enterprises that extract raw materials. The creation of such in those places where there were large active copper deposits, as well as mines, with a further transition to the creation of direct metallurgical production. These enterprises have a sufficient raw material base and can offer surplus of their products even to the world copper market. Companies do not want to produce rolled products or finished goods for the world market. The basis of copper holdings in the Urals are not mining and processing plants, but, first of all, copper-electrolyte enterprises, such as Uralelectromed in UMMC, Kyshtym copper-electrolyte plant in RMK, which, due to their huge size, play a leading role in the holding: the flow of goods from most of the company's small enterprises involved in the long copper manufacturing process chain.
- International franchising - as a form of product promotion in other countries
Copper production enterprises in the Urals developed at a slow pace; their owners had to buy out assets gradually. The unifying and absorbing wave covered two directions - in the field of obtaining raw materials assets, and in the field of buying out enterprises of higher processing. In this process, the Ural MMC and several companies led by the general director of the Kyshtym copper-electrolyte plant, Alexander Volkhin, who created the basis of the RMC, found themselves in serious confrontation with each other. It ended recently, when Volkhin combined his assets with enterprises led by the former manager of the Ural Mining and Metallurgical Plant, Igor Altushkin. In conclusion, in recent years, these holding companies in the Urals, instead of successfully implementing strategic plans for sovereign business development, must constantly divide property among themselves.
It is impossible to accurately determine whether UMMC or RMK were able to create a real promising copper production holding. In each of the companies there is a certain imbalance, which, based on the situation, they must address today. Having a strong production unit for the production of the final product and rolled products, they have a rather weak raw material base. With the available concentrates, the Ural MMC covers approximately 55%, and the Russian Copper Company approximately a third of what it needs, which leads to serious problems in the supply of raw materials and threatens to disrupt the sequence of all links in the business chain.
World copper market: consumption from 1900 to 2015.
At the beginning of the last century, the industry increased its order for refined copper, starting from 494 thousand tons per year and already in 2015 to almost 23 million tons per year. In pre-war times, orders for copper production grew by an average of 3.1% every year. After the end of World War II, from 1945 to 1973, the copper market began to grow at almost 4.5% per year. Since 1974, when the first crisis in the oil industry began, demand for the red metal began to decline to 2.4% annually, but in the 90s there was a new increase of approximately 2.9%. Already at the beginning of the 21st century the growth was approximately 3%.
Today, the main customers of refined copper are mainly those at the forefront of industrial development, as well as Asian countries that are beginning to develop their market. These are China, India, Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Thailand, as well as the states of the European Union - Germany, Italy, France and, of course, by tradition - the United States of America. With all this, the use of refined copper is concentrated in large production capacities of countries around the world, and the global copper market is expanding, primarily thanks to countries such as China, India, and Japan.
In general, the global copper market over the past few years has been oriented towards the needs of the Chinese, but their growth has decreased, although it remains significantly higher than the world market in terms of indicators. Since global copper use in 2015, compared to 2014, did not actually increase, in China these figures reached 5.3% - 9.18 million tons. In 2016, copper consumption in China, according to Antaike, could increase by somewhere between 4-4.5%, compared with the results of 2015, when overall global demand increased by only 3%.
Volumes of copper consumption by region, thousand tons
At the same time, the world copper market, like the world market of non-ferrous metals, is generally subject to periodic changes. Since the mid-1990s, changes in demand for non-ferrous metals have been determined mainly by changes in the demands of Asian countries. But, since, from 1998 to 2002, the economies of Asian countries were gripped by a deep economic crisis, manufacturing companies began to freeze their projects to create modern production lines and develop large rock deposits, most manufacturers sharply reduced production on the world market.
In 2002, this happened for the first time in 12 years; the production of refined copper decreased compared to the previous year. Starting from the end of 2002 - beginning of 2003, the recession was replaced by a revival in the economic development of the advanced countries of the world, the global copper market increased copper consumption, and active demand appeared in China. But frozen production could not be launched instantly, and the increase in ore production was generally designed for a long period. Thus, the global copper market was left with a large shortage, which grew to enormous proportions last year, and copper stocks in warehouses, on the contrary, decreased to critical levels.
Company owners are beginning to intensify the process of creating favorable conditions for production and are making statements about the reproduction of outdated lines and the launch of new production lines. But the process of introducing new large investment plans in 2004-2006 took too long, so the ratio of supply and demand in the copper market did not change in the direction of demand, and in addition, the cost of copper on the world market increased. Already, starting from 2011 to 2015, there has been a shortage of 100-140 thousand tons on the copper market. In 2016, due to the rapid development of production and only a slight increase in demand, excess copper again appeared on the market.
Copper reserves in the world
The largest amount of copper, approximately 65%, occurs in North and South America. European states have 15% of resources, Asian states - 11%, African states - 4.5%. The largest confirmed copper reserves are recorded in Chile. Almost 20% of the world's reserves are located there. And in the USA - 12.7%. In addition to these countries, there is a lot of copper in Poland, Indonesia, Iran, Kazakhstan, China, Uzbekistan, the Philippines, as well as in Zaire, Zambia, Brazil, Canada, Mexico, Panama, Peru and Australia. In each of these states, according to experts, there are about 10 million tons.
Global copper market: prices in March 2016
At the beginning of spring, the global copper market changed; prices on the London Metal Exchange increased by almost 2.7%, that is, by 129.5 USD/t, changing from 4,726 USD/t, as of March 1, 2016, to 4,855. 5 USD/t., as of March 31. The world copper market recorded the highest prices on March 18, they amounted to 5,103 USD/t, the minimum price was on March 1 and was 4,726 USD/t. The difference in cost in March fluctuated and amounted to $377, and the average price for the month was $4,947.55/t. The price increase, compared to the previous month, was 7.7%, 352.07 USD/t.
Copper stockpiles at LME warehouses fell by 25% in early spring, down 48,725 tonnes, from 193,475 tonnes on 1 March to 144,750 tonnes at the end of the month.
The main events taking place in the global copper market at the beginning of 2016:
- According to the customs service in China, the supply of copper and semi-finished products to the world copper market in February amounted to 420 thousand tons. The drop compared to January was 4.5%, less by 20 thousand tons.
- Avanco Resources in Brazil announced the release for the first time of an entire batch of copper concentrate from the Antas ore reserves. The planned unloading begins in April.
- Boliden has announced that it is buying the Kevitsa copper-nickel mine in Finland, which is owned by First Quantum, for $712 million. The amount of nickel smelted last year was 8,805 tons, and 17,204 tons of copper were produced.
- The company Minas do Alentejo (Almina) (Portugal) plans to increase the production of copper concentrate this year by 22% compared to 2015, i.e. from 109 thousand tons to 133 thousand tons. At the same time, the manufacturer plans to reduce the cost of mining one ton of copper by 9.6%, in fact to $3,100 per ton.
- Peru's copper production is expected to increase this year, driven by the rise in commercial opportunities at MMG's Las Bambas mine in the second half of 2016. It is expected that the amount of copper concentrate produced at the enterprise will reach 250-300 thousand tons this year, while a maximum of 400 thousand tons can be produced per year. Already on March 20, the first part of copper ore with a volume of 11.33 thousand tons was delivered to the port of Nanjing (China).
- International franchising - as a form of product promotion in other countries