Hi all. I’ll start keeping my logbook of the submitted article, because... all my subsequent topics will refer to it in one way or another. I installed a bunch of things on my car. And while installing additional wiring on my car, I encountered a big problem, namely, the inability to purchase ready-made shielded wires needed (for example, with a cross-section of 0.85 mm2 and the number of 4 or more pieces in one screen). Well, someone will say, yes, you can take a USB or interconnect cable and make the one you need from them - I DO NOT agree. The cores of the USB cable have in some cases an insufficient cross-sectional area (0.3 mm2 maximum) and are only suitable for transmitting audio and video via digital (rear view mirror with a parking screen or transmitting sound between the MMSS and the amplifier and between the amplifier and the ceiling via a DIN cable) . And the interconnects are so huge and take up so much space that when using them, it becomes impossible to reinstall the decorative plastic of the interior in its original place or to wire them in narrow spaces behind the front instrument panel (dashboard). I didn’t find the necessary shielded cables on the Ukrainian market (I don’t know about Russia or other countries). Who found it and where, share it in the comments. Therefore, I made all the necessary shielded cables myself. As practice has shown, the result exceeded all expectations. Below is my version of the “production” of a shielded cable. To create, you need the following components: 1. Aluminum tape. Moreover, it is VERY important that the composition (written on the label) contains ALUMINUM. Adhesive tapes of the type “for gluing aluminum/silver surfaces of your car” are not suitable - they only contain plastic painted in aluminum color. You can buy it at a construction supermarket 100%. If you are not sure about the conductivity of the tape, take a resistance tester with you and test it locally.
Next, we take the required number of wires, add a wire free from insulation to them and connect them into a braid. After this, we slowly wrap the wires with aluminum tape, with the conductive side facing in and the adhesive side facing out. This will enable the wire free from insulation to become an active screen and ensure continuous conductivity of all sections of the screen from one plug to another, because You are unlikely to be able to continuously apply the screen (adhesive tape). It will also ensure a tight fit of the screen with the adhesive side to the future insulation after shrink procedures. It will look something like this:
That's all, I hope it helps everyone.
How to make a shielded cable for a crankshaft sensor or a knock sensor? We do not consider the question “why shield.” Read relevant literature.
1. Buy ready-made, thermo-oil-gasoline resistant. For example, MGTFE is an excellent cable of the highest quality.
2. Braid the wires.
3. Foil. This solution has been personally tested and works on multiple machines. I have also seen a crankshaft or knock sensor foil wire in the stock wiring of one of the modern cars. I think it was a Mitsubishi.
Any foil is needed. I found regular food in the kitchen. You can also use aluminum tape (not aluminized shiny film, but real aluminum)
We tear off the foil in strips and carefully wrap the wires
Place the next piece with an overlap of several centimeters
We clear the wire to a length of 5-10 cm and spread out the copper wires. This will be the shield ground wire. Grounding is connected only on one side of the cable. That's what cable science says.
Here in the photo the copper wire is not tinned. This is a mistake; the wire needs to be tinned to prevent the creation of a galvanic copper-aluminum pair, which will destroy the connection.
We wrap the spreader mixed with layers of foil into the last centimeters of shielding.
We wrap our cable with electrical tape
Don't forget to connect the ground wire to ground.
Recommendations
Comments 59
Instead of electrical tape, you can use heat shrink.
A cable like this costs 20 rubles per meter
Sorry for my ignorance, but why a shielded cable for DPKV? What are the advantages of it?
Usually it is necessary for dpkv and dd for protection against interference
I guessed this myself, that the screen is anti-interference, but what kind of interference can affect the DPKV? And how can they influence?
A car has almost the worst conditions for electronics in terms of the level of interference and interference. Well, for example, the ECU will begin to see detonation where there is none, and make mistakes in counting the pulley teeth
Isolation of wires from interference | High frequency measurements
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) is an external or internal electromagnetic phenomenon that can have a negative impact on the quality of operation of technical equipment (TE).
Vehicles are subject to certain requirements regarding both their noise immunity and noise emissions. Read about the quality criteria for the functioning of a technical device and EMC testing in the article “EMC testing”.
Currently, against the backdrop of constant consolidation (growth) of electronic components and an increase in the speed of signal processing, failures of devices and systems often occur due to electromagnetic influences.
Isolating wires from interference: types of EMI
Let's consider the issue of shielding the cable (wires) as part of the functioning of servo systems. If the wires are not insulated from interference, the stability of these systems is disrupted, which leads to signal transmission errors and sometimes switching devices on/off. The electromagnetic interference itself can propagate through the cable or be emitted by the cable itself. The range of the former is usually up to 30 MHz, while the latter (radiative) is over 30 MHz.
Types of EMF
You need to start understanding the principles of shielding by understanding the principles of EMF transmission through connections. This is necessary because wire shielding that is effective for some types of connections may be completely ineffective for other types. Moreover, if the shield is not properly connected (grounded), you can get even worse results than without shielding.
Four types of interference can degrade signal quality in circuits:
- capacitive;
- inductive (magnetic);
- internal;
- radiative.
Capacitive interference. On the one hand, such interference is among the most easily suppressed, and therefore causes fewer problems. On the other hand, such interference may result in distortion of RF signals in conductors with high output resistance. To suppress this type of interference, wires with grounded shielding should be used.
Inductive interference. The cause of this type of electromagnetic interference is the influence of a strong magnetic field, which operates on the principle of a generator. This can cause a relatively low impedance current to flow through the conductor, which can disrupt signal transmission. These interferences, as well as the consequences of their impact, can be quite powerful to disable/enable technical equipment. An effective way to suppress inductive noise is to use twisted pair cables that have a grounded braided shield. Shielding wires with foil is not as effective due to magnetic eddy currents.
Read more about this type of interference in the article “Inductive interference”.
Internal interference. Such interference includes EMI, which occurs when the source is directly connected to the system. For example, when the power supply creates impulse noise on the AC line. Methods for suppressing internal noise include isolation, filtering, or other impedance matching techniques. When suppressed, shielding is ineffective, but it can be used to prevent interference from leaving the system. For strong internal impulse noise in an unshielded system, it is possible for it to become inductive.
Radiative interference. This type of interference is the most complex and has a number of limitations related to frequencies. To suppress such interference, shielding the wires with foil is not enough. Braided shielding can be effective, although there are additional requirements for its use in this case. These include, for example, the following:
- the screen inside the shielded wires must not be interrupted;
- screening must be complete, from all directions, etc.
Isolating wires from interference: types of shielding
There are three types of cable shielding:
- braided;
- spiral winding;
- foil.
Shielding wires with braid. This type of wire insulation against interference consists of copper threads woven into a network. These threads can cover both individual conductors and twisted pairs, and simultaneously all the cores in the cable. The percentage of coverage is determined by the density of the copper threads in the braid: the higher it is, the better the protection against EMF and the lower the radio emission. The flexibility of such a braid, as well as its service life, is directly affected by the diameter of the threads.
Shielding of wires with a spiral winding. This type of shielding provides greater flexibility and bending life than with braid. A spiral winding is a bare or tinned wire that is twisted in a spiral around a conductor. This type of braid is most effective for low frequencies, coverage is more than 95%. Spiral winding as shielding is used in the most flexible cables that are resistant to deformation (twisting, etc.). In such cables, other types of shielding (braid and foil) can be damaged during the cable twisting process.
Shielding wires with foil. This is usually aluminum foil on a polyester backing. This substrate provides mechanical strength. Aluminum provides effective protection against capacitive-type RFI.
Methods for applying a foil screen to a conductor:
- foil to the conductor;
- foil out;
- with the edges of the wound strip of foil being folded into a Z shape.
We recommend
For electromagnetic interference measurements, we recommend TDEMI systems from GAUSS INSTRUMENTS.
The concept of speaker cable
Shielded speaker wires
Before moving on to the main topic, let's take a closer look at the topic of speaker cable. Today, customers are offered a sea of assortment, the choice of which is not so easy. In any case, you must proceed on the basis of your own budget, taking into account information and knowledge about the types of cable. “Average,” so to speak, motorists, as a rule, don’t bother too much with wiring. They think that there is not much difference, but they are deeply mistaken.
Note. Naturally, if the owner of a budget acoustics system with simple speakers thinks so, then there are no questions. But the owner of an expensive speaker system, on which, as they say, no expense was spared, is obliged to pay attention to the speaker wires, since a considerable percentage of high-quality music reproduction depends on them.
Shielded acoustic wires
The following is important information about the speaker cable:
- Without going too much into the jungle of physical and technical details, let us note one obvious pattern. It concerns sound distortion, which is less, the better the quality of the speaker cable;
- Resistance is considered a decisive value, a parameter of any cable that determines its quality. So, the lower this resistance, the better for the transmitted signal.
Note. In turn, the resistance is directly affected by the material from which the cable is made. In addition, the diameter and length of the wiring are equally important.
- If we proceed from the opinion that an acoustic cable consists of two metal conductors isolated from each other, then today the most popular is copper wiring, which consists of 20 conductors;
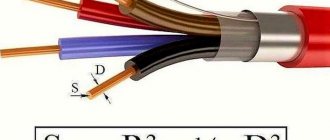
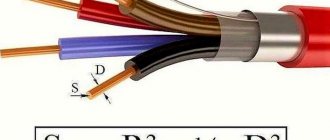
- As for the diameter of the wire or its cross-section, the standard size is 2-4 square meters. mm is considered popular. For example, the signal transmission speed in such a cable, provided that the length is appropriate, is approximately equal to the speed of light.
Wires for acoustics
Note. The ideal wiring resistance is zero when the cable length is 3 meters and the cross-section is 2.5 square meters. mm.
- All interconnect cables are called shielded (see Shielded acoustic cable: how to choose). In this case, the screen is a kind of protection of the conductor from EM interference. It is more correct to call protection in a particular case an external screen, which can be made of different materials: metal, plastic, etc. The type of protection also varies: braiding, foil, etc.
Note. It is believed that such a shielded cable, which requires a mandatory connection to ground (to protect against interference), is not ideal.
Acoustic shielded wire
- For this very reason, the balanced cable was invented. So, in an unbalanced cable there is one internal rod responsible for the main signal. As for the external screen, it is doubled due to the returned path signal;
- A balanced cable already implies the presence of 2 conductors, called hot and cold. Both outputs carry the same signal, but the difference is determined by their similarity. The effectiveness of such wiring is determined precisely by the balance of both conductors;
- In addition to balanced and unbalanced cables, another type of wire is known, called Star Quad. It is specially designed to improve interference immunity. This wire operates with 2 pairs of internal cables that are connected in parallel (of course, they are insulated).
Classification of shielded wires
There are different types of how you can shield a wire. It depends on the purpose of the cable. Therefore, there are the following types of purpose of shielded cable with copper or aluminum conductors:
- Power cables
. Designed for different voltage levels - from low to high. Thanks to the built-in screen, the cable does not spread electromagnetic interference into the environment and neighboring sources of electricity. It can be applied both to conductive conductors and after insulating them. - Combined
- power and control cable in one mechanism, distinguished by its flexibility. Typically, this type of purpose is used in the operation of mobile electrical mechanisms. For example, excavators. In this case, the shielded wire is insulated with rubber. Does not allow interference to spread to control mechanisms. - Signal cable type
- usually used when high accuracy in data protection during operation is required. This list includes fire, security, and measuring equipment. For example, a protective screen in a fire alarm can maintain high performance even when in a burning room. In addition, it usually has a minimal level of combustion product emissions. - Control and data transmission cables
– used in telemechanical or telephone networks. The screen is made of aluminum or polyethylene foil. This type of protective screen is also used in computer communications. Can be used for both external and internal installation. - Single-core shielded wire
is used for audio or video recording devices.
CI Properties Table
| EC type | Composition of protection | Notes |
| Foil | Copper/aluminum | The foil completely protects the conductors and also provides complete coverage. Disadvantage: susceptibility to mechanical damage, bending and turning. |
| Mesh braid | Copper, other metals | The most reliable form of shielding, but quite difficult to produce. Conductors are not covered 100 percent, as with foil protection, but 60-85 percent (rarely 95%). They cost significantly more. |
| Spiral braid | Copper, other metal | Provides higher performance in terms of flexibility compared to other types of EC. There are no advantages in other parameters. Covers up to 80% of conductor area. |
| Dual screen | Copper, aluminum, other metals | It is a combination of braid and foil |
Use of metal mesh for shielding
Figure 1. Metal braid When installing various radio-electronic and electrical devices, it is important to pay attention to the problem of their noise immunity. Incorrect selection of the connection diagram, unsuccessful method of cable routing, incorrect grounding and shielding scheme - all this can lead to malfunctions and even complete failure of the devices. Typically, to eliminate the influence of extraneous electromagnetic fields on devices, electrical mechanisms and equipment when performing installation work or connecting to power networks, as well as laying cable lines, a shielded cable is used.
Methods for getting out of this situation
To solve the problem, it is not necessary to completely replace the cables; it is enough to arrange additional shielding, which will significantly reduce the influence of electromagnetic fields. Structurally, it can be done in the following ways:
• installing an enclosing metal screen;
• spray conductive materials onto the inner surface of the equipment body.
However, there are designs and situations where the use of such screens is impossible or impractical. In this case, you can do the shielding yourself, thus localizing the source of electromagnetic interference. The essence of shielding is the limitation in space of electromagnetic energy that is generated by the field source. Very often in electrical appliances, protection from the mutual influence of wires and cables is carried out using a screen in the form of a braid of copper wires or a winding with metallized foil. These screens are divided into 2 types:
• magnetostatic;
• electromagnetic.
The most optimal method for properly shielding wires with your own hands is to use metal shielding mesh, which reduces the energy of electromagnetic waves by reflecting energy or absorbing energy by a conductive medium. The material from which it is made must provide the maximum possible protection and reduce interference generated by the electromagnetic field. The type of material in this case is selected depending on the nature of the interference field - magnetic or electrical.
Metal braiding and its types
However, there are designs and situations where the use of such screens is impossible or impractical. In this case, a metal braid is used (shielding braid). It reduces the energy of electromagnetic waves by reflecting energy or absorbing energy by a conductive medium. The material from which it is made must provide the maximum possible protection and reduce interference generated by the electromagnetic field. The type of material in this case is selected depending on the nature of the interference field - magnetic or electrical.
Shielding braid - brands and materials
Depending on the nature of the interference and the operating conditions of the cable, the metal shielding braid for the cable is available in various designs. Some of them:
• PML copper braiding, tinned with POS-40 tin-lead solder for temperate climates (PML UZ) and tin for tropical climates (PML T2);
• PMLOO made of copper wire tinned with tin;
• PMVLOS made of copper, silver-plated wire;
• PMLON made of nickel-plated copper wire;
• PBAMO made of bimetallic Al-Cu (aluminum-copper) wire coated with tin;
• PBAMS made of Al-Cu (aluminum-copper) bimetallic wire coated with silver;
• PBAMN made of Al-Cu (aluminum-copper) bimetallic wire with nickel coating.
When using braided cables, please note that:
• such protection requires more space in the housing compared to conventional wires;
• the braid must be connected to the body to create a shielding effect;
• installation of shielded wires is more difficult than unprotected ones.
PML braid and PSO braid
Tinned copper braiding PML is used for shielding wires and cables to prevent the negative influence of electromagnetic interference on the operation of various devices used in the national economy. Wires can also be used to ground various types of devices. The braid has the following dimensions:
| Braid sizes | Smallest diameter of the shielded (armored) product, mm | The largest diameter of the shielded (armored) product, mm |
| 3x6 | 3 | 6 |
| 6x10 | 6 | 10 |
| 10x16 | 10 | 16 |
| 16x24 | 16 | 24 |
| 24x30 | 24 | 30 |
| 30x40 | 30 | 40 |
| 40x55 | 40 | 55 |
Features of EC
When constructing an AC circuit using EC, knowledge of the features of this cable is very important. Let us note an interesting fact. The word "shielded" is borrowed from the English language, where it means not only "screen" but also "protection." To be precise, in Western terminology it is customary to distinguish between Screened wire and Shielded wire, which is a combined type of EC (foil/braid).
Note. In addition, if the screen is laid on top of the wire in one layer, then it is designated by the letter F. If there are two layers on top of the conductor - S.
Design differences between screens
In addition to the main differences, the screens also differ structurally:
- The foil film is laid with the metal side inward and lengthwise. This implies laying a drainage conductor;
- The metal layer is turned outward (used with two layers of protection);
- The foil is laid overlapping and has a longitudinal seam.
Note. The drainage wire, which is provided in the design of the EC, is very important. It allows you to achieve greater reliability of the screen (additional protection is provided in case of accidental rupture of the foil).
How to shield a cable
It is almost impossible to make a protective screen for a cable on your own; moreover, it is better not to do this without experience or at least specialized education. It is better to trust factory cable wires, of which there are a huge number in stores. The protection is placed under the main sheath of the wire. Self-cladding of the wire requires care and precision so that the fabric remains intact and without damage.
Cable with screen
Typically, wires are shielded using two types of materials: either a braid or a solid foil covering is created. Foil has its pros and cons. Simply put, it is a thin layer of aluminum. Using the wire braiding method, a high level of grounding is ensured. It is considered one of the most reliable methods, but the disadvantage is that minimal gaps may form in the surface. Their size depends on the thickness and length of the wire.
Shielding Signal Wires
Shielding is the protection of a signal wire from noise or unwanted signals.
Signal wires have high quality signal transmission due to their shielding and twisted pair construction to ensure better matching of their longitudinal impedance and ground impedance. At high frequencies, common-mode interference can occur due to the difference between the length of the wires and the frequency characteristics of their impedances.
Signal wire shielding methods take into account the path of interference.
To completely eliminate the adverse effects of parasitic capacitive coupling, an electrostatic screen made in the form of a conductive tube is used. In this case, it is correct to ground the electrostatic shield only from the side of the signal source. In Fig. Figure 1 shows how to improperly ground an electrostatic shield.
In Fig. Figure 2 shows hybrid grounding, which is the most popular method when transmitting a broadband signal from a distant source with high resistance.
Making a screen that will reliably protect against parasitic inductive couplings is much more difficult than a classic electrostatic screen. For manufacturing, you need a material with increased magnetic permeability. In addition, the thickness of such a screen should significantly exceed the thickness of electrostatic screens.
For frequencies less than 100 kHz, it is possible to use steel screens or screens made of permalloy (an alloy of iron and nickel). For higher frequencies, screens made of copper or aluminum are suitable.
Since shielding the magnetic component of interference is difficult, special attention must be paid to reducing the inductance of the signal cable and selecting suitable receiver and transmitter circuitry. In Fig. 3, 4, 5 and 6 show connection diagrams for the amplifier and screen, providing different rms noise amplitudes.
For most, for example, temperature sensors, the signal sources do not have a protective ground, and therefore an electrostatic shield is used along with a differential amplifier and output resistors. The screen grounding diagram in this case is shown in Fig. 3.
Double shielding of long cable
A double shield (Fig. 7) is used to improve the quality of shielding over a wide frequency spectrum. The internal screen is grounded on one side (the signal source) to prevent the passage of capacitive interference, while the second, external screen, is used to reduce high-frequency interference.
In any case, to prevent accidental contact of the screen with metal objects and the ground, it must be insulated.
In the case of a long cable, even with proper grounding, interference still passes through the screen, and therefore it is better to transmit the signal over a significant distance or with serious requirements for measurement accuracy either in digital form or via a fiber-optic cable. For this purpose, analog input modules with a digital RS-485 interface or fiber-optic converters of the RS-485 interface can be used.
Subscribe to the newsletter
Quite often, at industrial facilities, in production workshops, office buildings, etc., there is a need to jointly lay cables for various purposes in one trench, tray, cable channel, etc. The insulation of current-carrying conductors and the cable sheath do not provide effective protection against electrical noise and parasitic electromagnetic radiation arising due to currents flowing through the cable and negatively affecting the operation of the equipment. For such installation conditions, a cable with shielded cores will be required.
Shielded cable diagram
The properties of a shielded cable directly depend on its intended purpose, therefore the design of cables of different types differs from each other. For power cables with a rated voltage of up to 3 kV, a screen is usually applied to the twisted conductors using a common screen made of foil material or braided copper wire, and for data cables, in addition to the general screen, individual pairs can be protected from the effects of electromagnetic fields. The marking of shielded cables differs from other types of cable by the presence of the letter “E” in the letter abbreviation. However, for power cables with voltages above 6 kV, the presence of a screen in the design is mandatory, therefore the letter “E” may not be included in the designation of a screened cable.
How to Comply with Electrical Safety and EMC Standards
An electronic device can only be placed on the market if it is certified to meet international electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards. The article discusses the features of certification of electronic products, in particular medical devices, and examines the main international standards for electrical safety and EMC. Considering that in many cases Russian GOSTs, in fact, repeat international standards, the article will be useful to Russian developers.
Connecting multiple TVs
To connect several devices to one antenna at once, splitters are used, which are otherwise called “crabs”.
How to connect multiple TVs to one antenna via a video splitter:
Crabs are recommended for use in areas with strong television signals, i.e. close to television towers, since when a crab is connected, the signal strength decreases sharply. For example, if you connect 2 TVs to one antenna, the signal loss will be about 30%. The number of outputs on the crab must strictly equal the number of connected devices. If there is a free exit on the crab, the signal quality will still drop.