The market for the production and sale of welding equipment offers a wide range of equipment of rectifier, transformer and inverter types. It is the latter type that is most widespread.
Inverters are easy to use, compact, mobile, easy to connect, affordable, and suitable for beginners and experienced professionals. The popularity of this equipment requires the correct choice of cable for it. The article will discuss which cable is best to use for an inverter welding machine.
Is it possible to extend the welding cable on the inverter?
To work effectively, welders have to constantly move around the site, and the socket is located in only one place, so in most cases it is simply impossible to do without an extension cord. The most popular cable length that can make your work comfortable is 20-40 m, generally speaking. And in special cases everything is selected individually.
Theory
No matter how many of us love physics at school, it is the school physics course that we will need to remember in order to theoretically calculate the length of our extension cord. Let's remember that the resistance of a copper conductor is calculated as follows: R= 0.017 *L/S. Also in our case, we can use Ohm’s law for an incomplete chain I=U/R.
Let's decipher the letters in our formulas, which can take on any meaning.
- 0.017 – resistivity of copper cable; Copper is taken a priori, since it has the lowest value.
- L - extension length, mm.
- S is the cross-sectional area of the conductor, mm2.
- U is the nominal voltage in the electrical network, V. However, the actual voltage should be measured, since the condition of most networks leaves much to be desired.
- I—maximum inverter current, A.
From the formula R= 0.017 *L/S a simple and obvious conclusion follows: the resistance increases with increasing cable length (at the same time a voltage drop is observed) and decreases with increasing its cross-section. Accordingly, the length and cross-section of the cable must be selected in such a way as not to provoke a voltage drop on this cable.
You should absolutely not use home extension cords to connect household appliances. Manufacturers save on the cross-section of the cores of such carriers; they will certainly flare up when the inverter is connected. You should also not use conductors with a cross section of 0.75 mm2 or less.
In general, it should be noted that a 2.5 mm2 cable is enough for reliable operation at a current of 160A, you just need to make a “note in the margin” that the wiring to the outlet must withstand such a load.
Those who like to wind the cable into a reel when welding should be warned. The phenomenon of Faraday electromagnetic induction, which inevitably arises around a conductor with alternating electric current, has not yet been canceled.
And even if the induction in the coil is too low to lead to undesirable consequences, during prolonged welding the wire will still heat up (heating up to 70 ° C is considered normal). In a tightly wound coil, the cable does not cool and an increase in temperature will inevitably lead to melting of the insulation with all the ensuing consequences. troubles.
The copper itself will most likely remain unharmed, since it has a high melting point of 1080 °C, but the insulation will stick together. Conclusion: work on an unwound cable or, if this is not possible, on a loosely wound one, so that heat dissipation is ensured due to natural air circulation.
Practice
Let's return to the question: what cross-section should I take the extension cord?
Previously, we would have said that if you have a good network at home and the maximum current of your welding machine does not exceed 160A, then you can take 1.5 mm2 - that’s enough.
It is faster for the circuit breaker to trip or for the inverter to go into overheat protection than for such a cable to burn out.
It is very simple to check this statement: it is enough to place a 160-amp device on a load ballast and turn it up to the maximum current.
A cable with a length of 10 m x 1.5 mm2 can last a long time. In our case, the exposure was made for 12 minutes (arbitrarily, this time could be longer or shorter).
During this holding time, the cable warmed up, but it was not so hot that it was impossible to grasp it with an unprotected hand (or it began to smoke).
That is, a cable with a cross-section of 1.5 mm2 carries a load of 160A, but this, of course, is the limit and it is better not to allow this.
However, if you are not going to “scald” the whole day with the “four”, this option is quite acceptable.
Why do we not recommend taking a cross section of 1.5 mm2 today? Very simple. Because they don't report! You take a 1.5 mm2 cable, and it turns out to be 1.1-1.2 mm2. Conclusion: even if you have a good network, take 2.5 mm2. They may not report it either, but in any case this will be enough for household needs.
What length?
It all depends on your network and device. Example from practice. Carrying length is 120-130 m, welding with a Forsazh 161 machine from a shield and a good network: with a “troika” you can weld, but it’s quite difficult, but with an electrode ø2.5 mm you can weld freely and even cut something!
Which plug and socket should I use?
An ordinary 16A socket and simple high-quality plugs burn and melt at currents above 160A (but these are like consumables). When you buy, be sure to take a magnet with you to the store and “feel” the plug with it (the socket, however, no one will let you take it apart) - is it magnetic or not? Nowadays there are a lot of low-quality goods painted to look like copper or brass.
Characteristics and types of welding cables
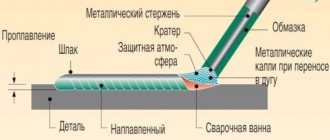
and the only function of the welding cable is to deliver electricity uninterruptedly and without losses to the welding site, where it is converted into heat, which will lead to the melting of the metal and subsequent welding.
The cable consists of two conductors, at one end of which an electrode holder or ground clamp is mounted, at the other ends there are terminals or plugs, as on household welding inverters.
Requirements
The welding cable must pass the operating welding current with minimal losses. Of the available materials, copper has the highest conductivity. So that the wire itself does not heat up, that is, there is no noticeable voltage drop on it, it must be thick enough (large cross-section).
The structures being welded have a complex shape, and welding has to be done in different positions. The electrode must freely reach any place in the structure being welded. Therefore, the welding wire must have maximum flexibility and not interfere with the work.
Since there are often metal conductive structures around the parts being welded, the wire must have reliable insulation. In addition, the insulation must allow cooking in difficult natural and industrial conditions.
It must withstand exposure to heat, cold, spilled oil or other lubricants. The conductor and insulation must be resistant to shock, jerking and chemically aggressive environments.
Since during operation the welding wire has to be wound and wrapped many times, it must withstand this. These requirements are met by large cross-section stranded copper wire in a soft, oil-resistant rubber sheath.
Characteristics
Today, they do not produce a universal welding cable that could work in all climatic and production conditions. But they produce a fairly large line of wires that meet the main conditions of a welding cable: minimal resistance and flexibility.
For domestic manufacturers, the KG brand means that the flexible cable is made of copper. It is intended for connecting power elements of non-stationary equipment and can be used as a welding cable. In addition, there is a special welding cable KS. In terms of technical characteristics, they are almost identical.
If the wire is marked KG 1x16, this means a flexible single-core power cable with a cross-section of 16 mm2. Permissible operating current 189 A.
The first number indicates the number of wires, the next two or three numbers indicate the cross-section of the wire. The letters HL indicate that the cable can be used at low operating temperatures down to -60 ⁰C. The additional coating prevents cracking in the cold.
The letter T indicates the ability of the wire to work in conditions of high humidity and temperatures up to + 85 ⁰C. In addition, the letter T says that the wire has antiseptic properties and is not afraid of fungus and mold, which is typical for a tropical climate.
The abbreviation KOG indicates that the strands of the welding conductor are especially flexible and allow it to be used in any of the most inconvenient and hard-to-reach places without causing harm to its working qualities.
This cable provides maximum comfort for the welder. In the KS welding cable, the letter P means polymer coating, HF means high frequency voltage. Choosing such a cable for the inverter will be an ideal solution.
When carrying out welding work in areas of increased fire danger, it is necessary to use an appropriate welding cable.
The KGN marking means non-flammability. All KG cables, regardless of climatic version, are completely sealed and can be used underwater. The only thing that needs to be done is to ensure tightness at the junction of the conductor with the device and the electrode holder.
Types of conductors used
The main types of cables used in welding devices are:
- single-core conductors with a copper current-carrying core made of many thin wires are mainly used for inverters;
- two-core conductors, representing an anode and a cathode, which provide the use of high-frequency current for pulsed welding and alternating current for cutting metal;
- Three-core conductors are used in automatic welding machines used in the installation of pipelines and other products where an even and high-quality seam is required.
Classification
There are two main varieties, which differ both in appearance and in purpose. In any case, they serve to conduct current. The first extension cord for a welding machine is an ordinary network connection device that helps increase the distance from a stationary power source. The second type of extension cord allows you to increase the size of the wire for the welding machine, which is responsible for conducting the output voltage current, which is obtained after processing by the transformer. This is especially true if the apparatus itself is located permanently at the post, and it is necessary to carry out welding further than is provided for by the dimensions of the post.
Is it possible to extend the welding cable on the inverter? — Metals, equipment, instructions
The inverter welding machine has gained wide popularity among home craftsmen and small repair shops. To obtain a strong and durable seam, a powerful and serviceable machine is not enough. High-quality wires for the welding inverter of suitable cross-section, type and length are also required.
Device
Of the available metals, copper serves as the best conductor . Combined with its flexibility, this makes it an ideal material for making the base of welding wire - conductors.
The structure consists of the following main parts:
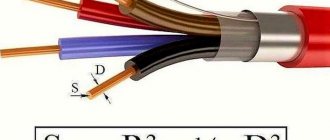
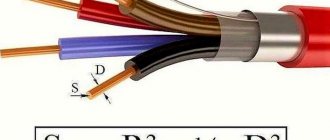
- copper core, twisted from a large number of copper wires with a diameter of up to 0.5 mm;
- separating layer - a thin shell that prevents the core and the insulation layer from sticking together, can be supplemented with talc or other powder;
- an insulating coating consisting of rubber, rubber or other polymer.
The ends are provided with contacts to connect to the inverter and holder. They are crimped and soldered to ensure the best contact.
Kinds
With household and semi-professional class inverters, the most common in home workshops, single-core wires of the KG brand are mainly used.
Depending on their purpose and characteristics, they are:
- KG-HL , insulation is made of frost-resistant rubber, they work in the cold;
- KG-T , insulation impregnated with substances that prevent the growth of fungus and mold, used in humid climates
- KOG , highly flexible wires, for welding in hard-to-reach places, for example, in shipbuilding.
According to the number of cores they are divided into:
Single-core
Most of the inverter wires are single-core.
One wire connects the device terminals to the electrode holder, the other to the ground clamp on the workpiece.
Twin-core
Used for high frequency welding and alternating current operation . Two cores have their own insulation; the outside is covered with another insulating layer. Alloys of copper and other non-ferrous metals are used as materials.
Three-core
Such wires are used to connect automatic welding systems connecting pipelines and large containers.
Each core also has its own insulation.
Section selection
The correctly selected welding cable cross-section for the inverter will allow you to work safely and with the expected performance.
If the wire cross-section is insufficient, the resistance of the wire will cause loss of current due to its heating; as a result, the machine will not be able to develop the required welding current and the quality of the seam will deteriorate sharply.
In this case, the indicator on the inverter will blink , indicating an overload.
In order to connect low-power portable inverters operating from a 220V network, light and flexible wires with a cross-section of up to 16 mm2 are used.
For more productive devices, a cross-section of up to 50 mm2 will be required.
Correct connection
Proper connection ensures the welder productive and safe work.
Connecting wires to a welding machine requires compliance with a number of rules:
- there must be a terminal at the end, crimped or soldered;
- The wire cross-section must correspond to the maximum operating current of the device plus a margin of 20%
- You should carefully monitor the polarity of the connection and observe it;
- The cable must lie freely in the work area, without tension or loops.
How to connect a welding machine if there is not enough wire to the welding zone? You can increase its length.
Is it possible to extend the welding cable on the inverter?
When increasing the length, you need to understand that the longer the cable for connecting the welding inverter, the greater the losses and the lower the resulting current strength.
If it is necessary to weld at a great distance from the machine, wires of a larger cross-section should be connected to compensate for losses.
When splicing 380V cables equipped with terminals with a hole into a single circuit, they should be cleaned and securely connected with a bolt and nut, not forgetting to install large diameter washers. The connection point must be carefully insulated, taking into account the fact that the wire will be repeatedly pulled through metal and concrete.
How to connect an inverter if there is no crimped terminal on the cable? Wires are spliced by repeatedly interweaving the wires that make up the core . Then the connection point should be soldered and crimped.
There are also special extension cables that have crimped and insulated connectors. Their type must match the connector of your device.
Manufacturers do not specify any restrictions on cable length. In each case, the welder himself decides what is better - to lengthen or drag the inverter and gas generator more often .
Marking of welding cables
The welding wire marking consists of several groups of letters and numbers. From it you can understand which model is in front of us.
First there are several letters indicating the type of cable.
After the type, a dash may indicate the climate class of the wire:
Next comes a number indicating the number of cores - 1, 2 or more. The designation is completed by the cable cross-section in mm2.
Safety requirements
When welding work, the following requirements must be observed:
- Do not work with wires with damaged insulation or insufficient cross-section;
- the wire in the working area should be placed freely, without clinging to the welder’s hands or feet;
- there must be enough light in the working area for the welder to move confidently;
- When connecting to the device, polarity must be observed.
Safety precautions when working
- "A" is the class to which it belongs. As mentioned above, there are several of them - KS, CG and there is also its version KOG (especially flexible)
- “B” - this place indicates the operating temperature range. If they are in the range from -40 to +50 degrees, then nothing is written, if from -60 , then the marking is CL (cold-resistant); if there are special antifungal and moisture-resistant additives, it is considered tropical and is designated as “T”. It can withstand up to +50 heat. When it does not burn at all, it is marked as non-flammable - “NG”.
- “B” - a number equal to the number of working cores from 1 to 3 .
- “G” - this last position indicates the cross-sectional area of the cable for the welding machine in square millimeters.
Useful tips Connection diagrams Principles of operation of devices Main concepts Meters from Energomer Precautions Incandescent lamps Video instructions for the master Testing with a multimeter
Is it possible to lengthen the welding cable on an inverter - Metalworker's Handbook
Reading time: ≈4 minutes
Included with any inverter is a welding cable. Its length, as a rule, is no more than two or two and a half meters. If you are a beginner, then extending the wires will not be a big problem for you. But for practicing craftsmen, the question is “is it possible to lengthen the welding cable on the inverter?” more relevant than ever.
Choosing an extension cord for a welding inverter is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. It is necessary to take into account the cross-section of the cable for the welding machine, what kind of cables there are, and what features need to be taken into account.
Types of extension cords
To figure out which extension cord is needed for a welding inverter, you need to know what you can buy in the store. Manufacturers offer two types of extension cords.
This is a standard welding inverter extension cord that simply allows you to be more mobile. The second type is extension cords, which not only increase the length of the welding cable, but also increase the size of the wire for the welding machine.
This type of extension cord is needed when your cables are not designed to carry the input voltage current when welded with a transformer.
Based on these features, you should start your choice.
Calculations
What else should you consider if you need to choose an extension cord for a reel welding machine? First of all, resistance. After all, the extension cord is the same current conductor as the welding cable itself. And it is designed for certain loads. Simply put, you need to know how much current the extension cable can handle.
To determine the resistance we need to know two formulas: R=ρ×L/S and I=U/R . Thanks to them, we will be able to accurately calculate what loads the extension cord must withstand.
S is the cross-sectional area of the cable (usually measured in square millimeters and indicated on the cable itself), L is the length of the extension cable, and ρ is the resistivity (depending on the metal the cable cores are made of).
Now the second formula. Here I is the value of the maximum current with which we can cook using an extension cable. U is the network voltage. It is important to indicate the actual DC voltage, and it is often less than 220V. This way the calculations will be more accurate.
Based on these formulas, it can be understood that the voltage on the welding machine largely depends on the resistance of the extension cable. The greater the resistance, the more the voltage drops.
Ideally, extension cables and welding leads should not significantly affect your electrical voltage. It is better to purchase high-quality ready-made extension cords in the store, they are the safest. In addition, before purchasing such cables it is easier to select the wire cross-section.
Application
So, you have selected and purchased extension cables. It would seem that it’s time to connect them and start welding. At this stage, many beginners make a number of mistakes, due to which the cables are not effective enough or do not work at all.
First, always straighten the inverter extension cord before use. Don't let it twist into knots or break. This applies to cables of any length.
Decide in advance what maximum length is optimal for you and do not buy too long cables, which will be wound into a reel for most of the welding. This is an irrational use.
In addition, when coiled, cables can cause increased induction. This is fraught with melting of the wires and failure of the inverter itself.
Also ensure that extension cables do not overheat during operation. Check the wires periodically and pick them up. If you can hold it calmly for a few seconds, then the temperature is not higher than normal. And if the cable gets so hot that you cannot handle it without gloves, then you need to stop welding and check the integrity of the cable.
Excessive heating of the cable also leads to failure of the welding machine and destruction of the cable itself.
As for storage, you need to be careful here too. Do not wrap the wires tightly, as this will deprive them of natural ventilation. Try to store cords in a dry, clean place and do not leave them outside or expose them to direct sunlight. Make sure that the connecting contacts and the cable plug do not become dirty or rusty.
Instead of a conclusion
You may need a welding cable extension in many situations. Welding a greenhouse or garage door, for example.
And if for some a plot of 6 acres allows them to reach the standard cable to the welding site, then owners of large plots immediately face additional problems.
We recommend that you purchase an extension cord anyway, even if you have never needed one. This way you will significantly expand your capabilities. We wish you good luck in your work!
[Total: 0 Average: 0/5]
Welding cable for inverter, connection to inverter welding machine, can it be extended, brand
page » Articles about welding » Welding station » Equipment » Cable » Welding cable for inverter
The market for the production and sale of welding equipment offers a wide range of equipment of rectifier, transformer and inverter types. It is the latter type that is most widespread.
Inverters are easy to use, compact, mobile, easy to connect, affordable, and suitable for beginners and experienced professionals. The popularity of this equipment requires the correct choice of cable for it. The article will discuss which cable is best to use for an inverter welding machine.
Welding cable design
To ensure the normal functioning of the inverter, wires with a copper base should be used. Copper is the best conductor of electric current. You should also use cords that are highly flexible. They simplify the work process and guarantee freedom of action for the performer.
The cable design includes the following elements :
- conductive copper core consists of many wires, the cross-section of which does not exceed 0.2 mm;
- covering can be made of rubber or rubber (natural or butadiene);
- The separating layer is made of a special transparent film that prevents the coating and core from sticking together.
Characteristics of welding cables
As noted earlier, the cable for the inverter must be highly flexible . In addition to this important property, electrical conductors are required to meet the following characteristics :
- Strength , i.e. resistance to mechanical stress: shocks and tears.
- Resistance to temperature fluctuations, the ability to use the conductor in conditions of very low or fairly high temperatures.
- Resistant to sunlight and moisture .
- Immunity to mold and mildew .
- Elasticity - minimal likelihood of bending.
Welding cable for inverter: types
There are few brands of conductors designed specifically for welding work. And there are only two types of cables that meet the above characteristics: KG and KOG.
Among craftsmen, the first type is in particular demand - flexible cable (KG). It should be used to connect mobile mechanisms to networks with alternating voltage up to 660 V with a frequency of 400 Hz . DC voltages up to 1000 V .
KOG is a particularly flexible cable, analogous to KG, indispensable when working in hard-to-reach places, ensures quick changes in the position of equipment and guarantees freedom of action for the performer.
It is recommended to use it for connecting electrode holders, automatic and semi-automatic installations to networks with alternating voltage up to 220 V with a frequency of 50 Hz or constant - up to 700 V.
If the performer is thinking about which brand of cable for the remote control of the welding inverter is more suitable, then you can choose KOG.
Each of these brands has the following varieties, which are clearly distinguishable if you look at the markings:
- KOG-HL/KG-HL - cold-resistant , resistant to extremely low temperatures, down to -60°C;
- KOG-T/KG-T - tropical , resistant to various types of mold formations, operating temperature should not exceed +55°C.
You should also pay special attention to the following varieties:
- KGn has non-flammable insulation and should be used in fire hazardous conditions.
- KOG-U is used only in temperate climates , in the temperature range from -45 to +40°C.
general information
First, let's figure out why cables are needed at all and why connect them to the welding machine.
In simple terms, welding wires connected to a power source (welding machine) are designed to conduct the resulting current to the holder and to the workpiece. One cable is connected to the holder, and the second is connected to ground (to the part). Due to this connection, an electrical circuit is formed during welding, which precisely allows the welding process to be carried out.
Also don't forget about humidity. A cable for a welding machine that is not designed to work in very humid conditions may simply become moldy and deteriorate. It is necessary to choose cables with antiseptic properties. Such wires not only withstand high humidity and high temperatures, but also generally have a long service life.
If you still have cables in the kit, but they are too short, you can connect them. Below is a video on how to connect welding cables.
Cable for a welding machine: brand, cross-section, length - All about construction
There is a renovation technology that involves removing worn insulation and applying a new layer of it. This allows you to bring welding wires back to life and extend their service life.
Expert opinion
Viktor Pavlovich Strebizh, lighting and electrical expert
Any questions ask me, I will help!
They have excellent resistance to high and low ambient temperatures with a wide range from -50 C to 50 C, they are resistant to moisture and other aggressive external factors. If there is something you don’t understand, write to me!
Is it possible to lengthen the welding cable on the inverter - Machine tools, welding, metalworking
We are talking about cables for welding machines. Its structure and, most importantly, the choice of a specific type for specific metal welding work is much more important than it might seem at first glance. Let's start with its functional purpose. and the only function is to efficiently supply electrical current to the electrode.
You know that we always prioritize the efficiency of welding work, which is determined by many parameters. One of the most important parameters of this kind relates to the characteristics of a special wire - its cross-sectional area.
This indicator must be kept in mind when choosing a suitable option without fail, as well as several other parameters: total length, characteristics of the local network in terms of possible voltage drop, and much more, which we will talk about now.
Types of cables
Naturally, the main determining factors in choosing a welding cable will be the properties of the machine itself for which it is purchased. The first thing is the current strength in the device. If, for example, it is 189A as close as possible, then the correct choice of wire to the inverter will be a KG 1x16 cable.
Types of welding cables KG.
It should be noted that all cables that are suitable for welding equipment are not cheap. Therefore, it makes a lot of sense to stop and think about what exactly you are going to do, and what kind of product you will need. There are a great variety of them on offer.
The structural varieties are as follows:
Selecting the cross-section of the welding cable
The cross-sectional area of the wire for welding is one of the most important parameters for the efficient operation of the entire device: such key indicators as the maximum maximum current strength and conductivity will depend on the cross-sectional area.
The quality of overall welding work depends on these key indicators - the strength and aesthetics of the formed seam and the speed of operational work.
Wire brand and permissible load.
The cross-sectional area, which refers to small calibers, is approximately 7 mm². These products are designed for inverter devices of compact dimensions, which operate when connected to household electrical networks with a voltage level of 220V.
If you are dealing with industrial automatic welding equipment, you will have to deal with conductive cables with large cross-sectional areas - about 47 - 49 mm².
The line of this kind of products with a wide variety of cross-sections and braids is presented in numerous catalogs and tables that will help you choose the most suitable cable cross-section accurate to the millimeter.
In such catalogs, additional markings and maximum current strength with voltage, cord length and calculated weight of the equipment are indicated.
What happens if the cross-sectional area of your wire is smaller than the required size and does not fit the programmed power of the equipment in any way: the electric current will be generated in excess, as a result it will begin to concentrate on the fuse of the device.
You will not be able to work in such conditions, because at the slightest ignition of an electric arc, the device will instantly turn off to relieve the voltage.
Rules for connection and use
When connecting cables to inverter devices, there are a number of rules that you need to know and follow without fail:
- To connect the device, at its end there are welding connectors and special tips attached by soldering - plugs for the welding cable. The product should only be connected through them.
- The wires can be connected to each other. This should only be done using special crimping. The main rule here is the mandatory isolation of connections between each other.
- The cable is connected to power type connectors and electrodes through their holders. In this case, it is necessary to remember the polarity, which cannot be changed, except in cases where all current parameters are changed.
- The welding cable for the inverter cannot be used for any other purposes - to pull the device towards you, for example.
- A mandatory requirement is full technical compliance of the cable and the corresponding equipment in terms of rated power and all other parameters.
Cable extension: yes or no
This question most surprisingly continues to excite the minds of professionals and has been a hot topic of discussion for a long time.
Some believe that extension should never be carried out, because too long wires with connectors for the welding cable will lead to a decrease in the efficiency and quality of work.
On the other hand, if the wire is too long, voltage loss may occur. In this case, the arc will become shorter, it will be much more difficult to control, and the overall quality of welding will decrease significantly.
Criteria for selecting a cable for welding
The main criterion for selection is the stability of the welding process. This stability is influenced by many things - not only the indicators of the current and the mains voltage source, but also many parameters of the welding and mains wire.
Therefore, when choosing, we think about the correct length, the correct cross-sectional area and braid material - all three parameters are of serious importance. If, for example, the welding current reaches high values, the wire must be selected according to a certain type and material.
We have already said that all wires for welding machines have their own electrical resistance values. It can be calculated using tables, this is not a problem. For example, an aluminum conductor has a higher resistance coefficient than a copper conductor.
Section selection
Choosing the right wire cross-section is the main task. The conductivity depends on the cross-section, which, in turn, has a direct impact on the speed of work and the quality of the formed connection. The cable must comply with the technical specifications of the inverter.
Conductors with a small cross-section (up to 7 mm2) will be a suitable option for small devices that operate from a household electrical network of 220 V.
Also for inverter-type units, cables with a cross-sectional area of 10 are suitable;
16 and 25 mm2. More detailed information about the characteristics of conductors and COGs is provided in the linked articles. Important! Use of unsuitable wire may result in overheating, fire and/or short circuit, which may cause equipment failure or fire.
Extension cord without switch
For more powerful loads, you can choose models without built-in switches. Protection in this case must be provided by automatic devices in the panel.
Choose such models for garages and cottages with a wire cross-section of at least 2.5 mm2, since socket groups are often protected by 25A circuit breakers.
And if an extension cord made with a 0.75mm2 cable is overloaded, no machine in the switchboard will work. The extension cord will start to melt first.
They also have brass contact plates inside them. Sometimes they are attached to a base made of non-combustible material. This is directly responsible for the fire safety of the entire block.
One such material is polyamide. In general, all manufacturers must make the extension cord housing from non-flammable plastic, but not all “Chinese” comply with this.
The power wires can be either soldered or resistance welded (the best option), or simply tightened with screws in special terminal connectors.
It is more reliable when the clamping occurs with a plate, because very often these screws crush the tip of the wire, worsening the contact area and the contact itself.
If your carrier is made in this way, then it would be more advisable to crimp such wiring with an NShV tip.
Soldering may fall off at high currents and heat, but nothing will happen to the welding. Even during short circuits.
In addition to the contact brass plates, do not forget to check the plug itself with a magnet. It should also be made of non-ferrous metal and not be magnetized.
Protection
Strive to choose models with built-in surge protection and protection from dust and moisture. Moisture resistance is indicated by the Latin letters IP. Household extension cords most often come with IP20 numbers.
They can only be used in dry and dust-free rooms, but not in the bathroom or garage. Models with IP44 protection already have dust and splash protection.
Do not confuse models of surge protectors and simple carriers with a shutdown button. The latter have a built-in switch designed to manually turn off the power.
It in no way protects the equipment from voltage surges and imbalances. To do this, there must be at least a varistor inside the case. What this is will be discussed below.
By the way, the switches themselves are different:
- bipolar
- four-pole
It is better to choose 4-pole networks. It's quite easy to distinguish them.
Four-pole is twice as wide. It is he who breaks both phase and zero.
With a two-pole connection, you can only disconnect the neutral conductor, and the phase will still be supplied to sockets and devices when the plug is plugged in.
Be careful!