Home / Welding technique
Back
Reading time: 2 min
0
1302
The preparatory stage is often more important than the work itself. Preparation for welding non-bending (non-rotating) seams is no exception.
Take a suitable tool and clean the welding area from all unnecessary debris, rust, paint residues. Then cut the pieces using a power tool or the thermal method, while keeping them together.
Based on the dimensions of our pipes, tacks are used to fix the workpieces, which resemble a welding seam.
- Introduction
- How to weld a horizontal joint
- How to weld a vertical joint
- How to weld a joint at a 45 degree angle
Safety regulations
When starting to connect rotary joints of pipes or non-rotary analogues, you need to know that work of this type has a high level of danger. Therefore, certain requirements must be met.
Butt jointing of pipe products by gas or electric welding must be performed on specially equipped sites that have special equipment, including various means of protection against electric arcs. These elements are distributed so that people present nearby are completely isolated.
To connect tubular products with a large diametrical cross-section and a weight of over 20 kg, it is recommended to use special lifts. The entrance to the site must be cleared; its width cannot be less than 1 m. Operating temperature values in the room must be maintained within +160C. A prerequisite is the presence of a ventilation system and free space.
According to the technology for carrying out work involving the use of welding equipment, all metal parts and elements must be grounded (pro
Errors in welded pipe processing
Since in practice, penetration welding of pipes is a difficult job, novice welders often reject parts. It is impossible to get rid of it without practice and personal experience.
An analysis of the theory of welding and standards for transmission welding can speed up learning.
The following will describe errors in pipe clearing and ways to prevent them.
And it is the accumulation of experience that will prevent the occurrence of incomplete welding in the future.
Experience and intuition are important in penetration welding, but studying the technical documentation for the task will greatly facilitate the work.
A couple more tips to prevent common mistakes:
- Despite the complexity, welding is performed with a short welding arc length. Even if you want to make the task easier, you cannot change the length of the arc. Welding already at a medium value will deteriorate the quality of the connection.
- During the welding process, the rod does not come off. The filler rod is torn off only when it is necessary to update it.
- From part to part you need to monitor the current settings.
- The preparatory stage should not be ignored. Proper stripping and trimming of edges makes the job easier.
- The work is carried out only with dry filler rods.
- You should not carry out the welding process in the light during bad weather.
- The quality of equipment and additional elements also plays a role in the reliability of the result.
Vertical welding of fixed joints
Applying seams vertically to the non-rotating ends of the pipes being welded is performed similarly to horizontal welding with one difference: a constant change in the inclination of the electrode relative to the perimeter of the seam.
The welding process involves the following steps:
- A joint is created, obtained during the pipe welding process, which relates to the root bead.
- Three rollers are formed that should fill the cut.
- A lock is created connecting the beginning and end of the roller.
- A decorative seam is made.
The first step is considered the most important, since this is the time when the joint is created, forming the base of the seam. The range of welding current is determined by the thickness of the metal and the gap between the joining parts. At the first stage, two main rollers are created.
To create a joint on the pipe, grab the base of each edge being connected, at the same time the second root layer is formed and the first layer is corrected.
Forming a reverse bead using electrodes with a diameter of 3 mm is carried out only in cases where the welded joint must be of high quality.
To perform the job, select the average or minimum current range, taking into account the following:
- Thickness of the metal blank.
- The distance between the edges of products.
- Blunt thickness.
The inclination of the electrode is determined by the direction of welding and depends on the penetration of the first layer of the seam.
The length of the arc also depends on the degree of penetration:
- A short arc is used when the main shaft is not sufficiently fused.
- Medium arc - with good penetration.
Welding speed performance largely depends on the volume of the weld pool. A roller of great height at the joints of metal parts leads to the fact that it does not harden for a long time. This can cause the formation of various defects. When selecting the welding speed, it is necessary to remember that only high-quality edge fusion ensures the normal condition of the bead.
Processing of metal of a certain thickness, as well as sampling and welding, is recommended to be done with electrodes with a diameter of 4 mm. In this case, the inclination of the electrode must be different from the inclination angle when working with the root roller. Here you should use a method called “back angle”. The speed in this case should be such that the roller remains normal.
Welding technology
After ignition of the arc, the process of melting metals immediately begins - electrode and base
Depending on the length of the arc, the productivity and quality of the seam are determined, so it is very important to choose the correct length of the arc. It is necessary to feed electrodes into the arc at the melting rate of the electrode
The more experience a specialist has, the better he copes with maintaining the length of the arc.
An arc measuring 0.5 to 1.1 times the electrode diameter is normal. In order to more accurately calculate the exact arc length, you need to find out what brand and type of electrodes are used. The position and significance of the welding site is also of considerable importance. If the arc is longer than normal in size, then combustion stability decreases, waste losses increase, the penetration depth becomes uneven, and the seam becomes uneven.
In order to make a quality seam, you should pay attention to the angle of inclination of the electrode. For working from below, the electrode angle is usually 10 to 30 degrees back
Often the arc is directed in the direction where the electrodes are pointing. The correct slope, in addition to a reliable seam, also gives a lower cooling rate of the substance.
To obtain a metal roller of the required size, you need to vibrate the electrode in a perpendicular direction. Using oscillatory movements, seams with a bead size from 1.5 to 4 electrode diameters. Such seams are used most often.
Obtaining a reliably boiled root is achieved using the movement of triangles. This movement is carried out with the execution of fillet welds with seam legs over 6 millimeters and butt edges with a bevel.
Seams can be divided according to the method of filling them into multi-layer, single-layer, multi-pass, single-pass.
A multilayer seam is such if the number of layers corresponds to the number of arc passes. Such seams are often used on problem areas and joints.
Multi-pass welds are used in T-joints and corners.
To increase the strength indicator, seams are made in sections, cascades or blocks. All these seams are produced using reverse-stage welding technology.
Rules for filling pipe seals
You need to start filling the seal from the bottom of the edge, which is the platform. This is necessary to select the optimal welding method. The horizontal roller should be performed in high mode. Also, the welding method is determined by the location of the slag, “backward angle” or “right angle”.
To obtain a bead, reinforcement or a “hump” is necessary, which is formed when welding in a position from below to create a shelf, thanks to which the next bead is welded at an increased mode. The second treatment should be carried out with gentle movements, adhering to the lower edge.
Before starting welding of the third bead, its level of completeness is determined. It is important that the gap left between the connecting seam and the top edge is not very large for the fourth roller and not very narrow for the two rollers. The third roller along the top edge should have the smallest width to the top edge. The optimal size may coincide with the diameter of the electrode.
Filling the groove is carried out by forming 3 more beads, which make it possible to fill the base of the weld and strengthen the joint. When carrying out work, it is important to maintain a right angle and fill the groove at high welding speed. This is the only way to achieve strong bonding of the layers to each other.
Preparation for work
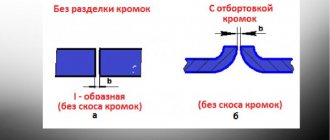
The technology for preparing for the start of welding work includes the following stages: initially it is necessary to prepare the metal, that is, mark it, assemble and cut pipes. To do this, it is necessary to install parts of the pipes in their original position and clean each joint from rust, putty, dirt, paint and other deposits. Then you need to mark using a square, tape measure and scriber to transfer the dimensions of the structure to the metal from the drawing. For this purpose, you can use a metal template. It is worth remembering that parts of the pipes are slightly shortened during welding, so during work you need to leave an allowance based on an error of 1 millimeter per transverse joint, and 0.1-0.2 per 1 millimeter of a longitudinal seam.
Due to the fact that most pipes have a round cross-section, thermal cutting is most often used when preparing pipe parts.
Approximately 30% of the total process time is spent assembling parts for welding. During assembly, product manufacturer, pipe diameter, product series and other factors must be taken into account. Welding tacks are used for assembly. They are lightweight seams with a cross-section of up to 1/3 of a full-fledged seam. The tack size depends on the pipe diameter and wall thickness and ranges from 20 to 120 millimeters. Tack welding is used to reduce the likelihood of sections of the structure moving, which can cause cracks during cooling. When welding pipes with large diameter and thickness with electricity or gas, or welding in an inconvenient location, mechanical equipment is used during assembly.
If you need to ignite an arc, you need to short-circuit the pipe with the end of the electrode and tear the electrode off the surface of the structure. The distance is approximately equal to the diameter of the coated electrode. This is necessary to heat the metal to a certain temperature at the cathode spot. When heated, primary electrons are released.
To ignite the arc, sliding or butt technology is used.
During back-to-back ignition, the metal heats up at the point of the short circuit. When an arc is ignited using sliding technology, the metal is heated in several places on the welding surface of the product. The first method is most often used, the second is usually used when welding small pipes with difficult locations.
Making locks
The stage of making the locks involves the final work on the formation of the rollers. In this case, the welding of each bead is accompanied by a 2 mm offset on the main seam. The finished lock represents the starting point of the roller, offset by 5 mm relative to the previous layer.
A decorative seam completes the welding of pipes in a fixed position. When surfacing is carried out in a horizontal position, narrow beads are formed. The last one should be completely flat. Welding is performed in high speed mode.
When fully welding a joint, the entire perimeter without breaking must be taken into account. The displacement of the locks relative to each other is allowed no more than 50 mm.
The multi-pass type of welding of rotary and fixed pipes with thick walls involves spiral guidance. In this case, the number of locks is reduced and, as a result, the number of defects is reduced. Welding should be stopped at a distance of about 20 mm from the beginning of the bead in order to align the weld seams in height. The larger roller can be hemmed and also ground off.
Hemming the bead can be done in a practical way, allowing you to reduce the number of locks and make a better connection. This method starts from the edge of the roller, which is melted by holding the arc. Then they approach the roller with an active electric arc and move on to the next layer, taking into account the previous one. As a result, the end of one layer becomes a continuation of another roller.
Introduction
Be sure to ground metal parts such as the welding table, transformer base and other non-insulated devices.
Use electrical wires and cables with insulated coating. After welding the fixed pipe joints, take a hammer and chisel and remove any remaining slag. Then, if necessary, the seam can be smoothed with a grinder.
At the moment, 3 main methods of welding metal fixed fragments are used, which fundamentally determine the concept of operation of each of them:
- In a horizontal position;
- In a vertical position;
- At an angle of 45 degrees.
The choice of a specific method for welding fixed pipe joints must be based on:
- wall thickness;
- pipeline location;
- placement angle during welding.
Combining pipes using a three-layer seam is used if the thickness is 12 mm. Each seam should be no more than 4 mm high, and the width of the seam bead should be no more than three diameters of the conductor.
As the name suggests, rotary pipes can be rotated in the desired direction, making the welding process of non-rotating pipe joints easier and there will be no need to create complex seams (for example, ceiling ones).
Horizontal surfacing
Welding of horizontally positioned butt pipes is considered a rather complex technology. Only a professional welder with certain skills and experience can perform such work. The most difficult thing is the constant adjustment of the electrode to change the angle of inclination.
Welding is performed in three consecutive positions:
- Ceiling.
- Vertical.
- Bottom.
Each seam is made with an individual current value. The ceiling position allows welding at a high power level. All stages involve continuous welding; at the beginning it is best to use the “backward angle” method, and complete the work with the “forward angle”.
Types of pipelines and welding
Welding of pipelines is carried out taking into account their type:
- main lines;
- water;
- technological and industrial;
- sewer;
- gas supply structures.
The following types of welding are distinguished:
- mechanical (due to friction);
- thermal (melting using plasma, gas or electro-beam method);
- thermomechanical (magnetically controlled arc obtained using the butt contact method).
The use of a certain type of connection also depends on the pipe material:
| Material | Welding type |
| Copper | Electric arc, gas or contact. The first connection method using a tungsten non-consumable electrode and filler wire is more effective. Argon or nitrogen is recommended as shielding gas |
| Steel | Semi-automatic machines are used, as well as electric and gas welding |
| Galvanized pipes | Any type of connection can be used, but flux is considered a mandatory component, protecting the product from fading of the coating |
| Profile structures | Welding is performed using gas or arc methods. The experience of the welder is important here |
How to solder a copper pipe yourself In a modern apartment there are many copper pipelines. They can be found in heating radiators, some sections of water supply, air conditioners, and refrigeration units. When full or...
Welding pipes at an angle of 45 degrees
Welding pipe products located at an angle of 450 has some peculiarities. In particular, we are talking about the spatial position of the seam, taking into account a certain angle. This type of work can be performed by general craftsmen with a variety of welding skills. The first roller is created using an electrode at a right angle.
The seam is formed by continuously filling the second layer. After this, they immediately proceed to melting the first layer. After welding with the constant use of an electrode, it is necessary to fix the pipe to create horizontal and vertical seams. In this case, the welding layer on the front side is not flat when compared with the rest of the beads.
The vertical connection of metal pipes by means of manual arc welding is carried out similarly to welding in a horizontal position. A distinctive feature of the first method is the use of a method, the implementation of which involves the use of translational movement of the electrodes. Consequently, it is necessary to constantly adjust the angle of inclination of the electrodes relative to the seam, which runs along the entire perimeter of the welded tubular product.
Method of working with a horizontal joint
The method of dealing with fixed pipeline joints in a horizontal position differs in that it is not necessary to completely cut the edges. These actions must be carried out using medium arc welding. You can only maintain an insignificant 10-degree cut. Such actions ensure an improvement in the process of joining metal parts and maintaining their quality at the same level. It is better to weld horizontal pipeline joints in separate, narrow layers. The root of the seam is welded with the first roller, using electrodes 4 millimeters in diameter. The force limit according to Ohm's law should be set in the range from 160 to 190 A. The electrode receives a characteristic reciprocating movement, while a thread-like roller 1-1.5 mm high should appear inside the joint. The coating of layer No. 1 must be thoroughly cleaned. Layer No. 2 is made in such a way that it covers the previous layer when the electrode moves in a reciprocating manner and when it swings almost imperceptibly between the edges of the upper and lower edges.
Table of the ratio of welding currents depending on various indicators
The direction of the second layer is no different from the first. Before performing the third layer, the current must be increased to 250-300 A. To make the process of joining metal elements more productive, you need to use electrodes with a diameter of 5 millimeters. The direction of cooking of the third layer is opposite to the directions of the previous two layers. The third roller is recommended to be performed at higher settings. The speed must be chosen so that the roller is convex. It is necessary to cook at a “back angle” or at a right angle. The third roller should fill two-thirds of the width of roller #2. The fourth roller should be performed in the same modes as the third roller. The inclination angle of the electrode is 80-90 degrees from the surface of the pipe, which is located vertically. The direction of the fourth roller remains the same.
The technology for performing electric welding with horizontal joints in the presence of more than 3 layers has its own peculiarity: the third layer with all subsequent ones are performed in directions, each of which is opposite to the previous one. Pipes reaching a diameter of 200 mm, as a rule, must be welded with continuous seams. The reverse-step method is typical for the welding process of pipeline joints with a diameter of more than 200 mm. It is recommended that each section be approximately 150-300mm long.
Types of pipelines and welding
There are a huge number of pipelines that are used to move different materials and working fluids. Based on their purpose, there is the following classification:
- technological;
- main lines;
- industrial;
- gas supply pipelines;
- water;
- sewer.
Read also: Machine for tightening car strut springs
In the manufacture of pipelines, various materials are used - ceramics, plastic, concrete and various types of metals.
Modern welders use three main methods for joining pipes:
- Mechanical is carried out due to explosions as a result of friction.
- Thermal, which is carried out by melting, for example by gas welding, plasma or electric beam.
- Thermo-mechanical is produced by a magnetically controlled arc using the butt contact method.
There are many types of welding, which are divided into many classifications. Before you weld pipes, you need to figure out what is the best way to do it. Theoretically, each type is suitable for welding pipes of small and large diameters. It can be carried out by melting and pressure. Melting methods include electric arc and gas welding, and pressure methods include gas press, cold, ultrasonic and contact. The most common methods for connecting communications are manual electric arc and mechanized.
Various arc welding techniques
Welding of pipelines can be performed in several technological ways:
Welding with joint rotation
First, three potholders are made at 4, 8 and 12 o'clock. Then two main stitches are made from approximately 1 to 5 o'clock and from 11 to 7 o'clock. After this, the pipe is rotated 90 degrees and finishing seams are applied, which completely seal the connection of the two seams.
To prevent burns, it is recommended to use a 4-mm electrode of the SM-11, VSC-1 or UONI-11/45(55) brands for the first layer, and to create an electric arc, set the current to 130 A (±10 A). To perform the second and third layers, you need to take 5-6 mm electrodes, and the current should be increased to 200-250 A.
Welding without joint rotation
This technology is used when working with stationary pipelines that cannot be moved. The first layer is performed from the bottom up, and the second and third layers can be performed both from top to bottom and from bottom to top.
Welding hard-to-reach places, for example, a part of a pipeline pressed against a concrete pad or a brick wall, must be done through a tie-in - a technological hole on top of the pipe. When the welding work is completed, the technological hole is also welded.
Welding pipes in winter conditions
At negative temperatures, the welding zone rapidly cools, and the removal of hot gases from the molten metal, on the contrary, becomes difficult. Because of this, pipe steel becomes brittle, which sharply increases the risk of thermal destruction of the steel, the appearance of hot cracks extending from the weld, as well as hardening structures.
To avoid these defects, it is necessary, firstly, to connect the pipeline elements as tightly as possible to each other, secondly, it is necessary to heat the surface of the metal to a light red tint, and finally, thirdly, the current strength must be increased by 10-20%. This will allow you to achieve a tough and ductile weld that reliably seals the gap between the pipes even in severe frost.