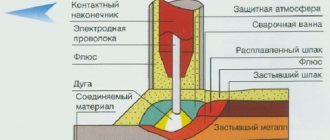
Argon-arc welding received this name because of the specifics of its action: an arc discharge occurs in an inert gas-argon environment, which leads to the formation of a melting pool and the connection of metal surfaces with each other. Electrodes for argon arc welding can be of two types.
Welding surfaces using this method can be carried out using a melt electrode or a tungsten electrode, which remains intact and melts the edges being joined.
In the technical nomenclature, argon arc welding machines are designated by the following abbreviations:
- RAD – manual argon arc welding using a tungsten electrode;
- AMA - argon welding in automatic mode, when the gas torch is supplied to the welded edges automatically using a special support;
- AADP - the additional “P” means that this device uses consumable electrodes.
The international standard uses the following abbreviations, usually in devices with non-consumable electrodes:
- TIG – welding is performed using tungsten in an inert environment;
- GTAW – gas tungsten welding.
Independent, without the participation of professionals, but high-quality and fast assembly of metal structures during repair work, soldering of seams, as well as cutting of various metal products is possible with the help of a good welding machine for the home. How to choose an easy-to-use welding machine for your home?
Among the many metal processing technologies, laser cutting stands out for its cost-effectiveness and efficiency. Read more about laser cutting of metal here.
Technical characteristics of argon arc welding
Argon is used primarily to displace air from the welding environment and reduce to zero the interaction of the molten edges with air, the ingress of which can lead to treachery.
Initially, this technique was used for welding aluminum surfaces (argon arc welding of aluminum). All welding is done using droplets of molten metal (large droplet and drip).
Manual arc surfacing of metal: diagram
It looks like this:
And in it:
1 – part with base metal;
2 – bath in which operations are carried out;
3 – electric arc of a certain length (preferably stable);
4 – fused layer;
5 – restorative coating;
6 and 7 – solidified and liquid slag, respectively;
8 and 9 – rod, already melted (8) and not yet (9);
10 – holder.
Scope of argon arc welding
The most basic area of application is the joining of non-ferrous metals and alloy steels, especially of low thickness. Otherwise, additives are used.
Additives for argon-arc welding are metals of higher density and lower melting point, which are sprayed by surfacing and act as a connecting “layer”.
In this case, welding is only possible in an environment of inert gases or carbon dioxide, since the entry of air will lead to spattering of soft molten metals.
Certification Center NAKS "Center for Welding Production Bridges"
Regulatory documents for steel bridge construction determine the list of welding equipment permitted for use in the manufacture and installation of metal structures of steel bridges.
The use of unspecified brands of welding equipment, both domestic and foreign manufacturers, for automatic welding methods is possible only after a comprehensive study of this equipment for compliance with the requirements of regulatory documents for steel bridge construction of the Russian Federation. Research of new welding equipment is carried out at the industry research institute of steel bridge construction - Branch of JSC TsNIIS "National Research Center "Mosty".
Below is a list of welding equipment approved for use in steel bridge construction in the Russian Federation.
| № | Name of welding equipment |
| RD welding method* | |
| 1 | VD-306D, VD-306DK. |
| 2 | VD-313. |
| 3 | VD-306S1. |
| 4 | KSU-320 is a universal welding converter for use with VDM-1202S. |
| 5 | Inverter type: Fast and Furious, STICK 350 CEL, etc. |
| Welding method MF* | |
| 1 | PDGO-601 (connector A-1231) with VDU-511 with burner A-1231-5F2. |
| 2 | PDGO-601 (connector A-1231) with VS-600 with burner A-1231-5F2. |
| 3 | Inverter type: FLEX-400, Megatronik, etc. |
| Welding methods MP, MPG, MPS* | |
| 1 | PDGO-511 with VD-506DK with a torch for welding with metal cored wire with a diameter of up to 1.6 mm. |
| 2 | PDGO-511 with VDU-511 with a torch for welding with metal cored wire and solid wire with a diameter of up to 1.6 mm. |
| 3 | PDGO-510 with VDU-511 with a torch for welding with metal cored wire and solid wire with a diameter of up to 1.6 mm. |
| 4 | PDGO-601 with VS-600 with a torch for welding with solid wire with a diameter of up to 2.0 mm. |
| 5 | A-681M (“shorty”) with VDU-505, VDU-506, VDU-601. |
| 6 | Inverter type: Origomig-500, FALTIG-400. |
| Method of welding AF in the lower position (H1, H2) | |
| 1 | TS-16 with VDU-1250. |
| 2 | ADF-1250 with VDU-1250. |
| 3 | TS-30 with VDU-1250. |
| 4 | TS-17MU with VDU-1250. |
| 5 | ADF-1002 with VDU-1250. |
| 6 | TS-16 with VDU-1204K (Kaliningrad Electric Welding Equipment Plant - “ESVA”). |
| 7 | TS-30 with VDM-1201 (VDM-1601) and 6RB306. |
| 8 | TS-17MU with VDM-1201 (VDM-1601) and 6RB306. |
| 9 | ADF-1002 with VDM-1201 (VDM-1601) and 6RB306. |
| 10 | TSF-101 with VDU-1204. |
| Welding methods AF, APS, APPG in a vertical position (B1) | |
| 1 | Device A-1150U with VDU-505, VDU-506, VDU-601. |
| 2 | Device A-1150U-2 with VDU-505, VDU-506, VDU-601. |
| 3 | The device "Voskhod" with VD-506DK. |
| 4 | Carriage "KAT 200ZhLS" with NB-500. |
| 5 | VelTrac carriage with VelSmart 400. |
* It is allowed to use similar welding equipment indicated in the table, which has been certified by NAKS in the “KSM” group, only for welding methods RD, MF, MP, MPG, MPS.
Up-to-date information on welding equipment approved for use in the manufacture and installation of steel bridge spans can be obtained by contacting the Mosty State Center directly.
Tig welding technology
In general, technological standards can be divided into two types:
- manual mode, when a torch with a tungsten electrode and a filler rod are manually fed by a specialist to the place of connection and surfacing;
- automatic mode, when everything is served automatically. Argon arc welding of pipes is the clearest example, since when connecting pipelines, the seam must meet the requirements for standard sizes. Installation of argon arc welding in this case is carried out on special frames-spars, which provide movement relative to their plane and axis.
A weld seam is usually called a permanent connection, which is formed during the process of solidification of the weld pool from the melting of metal edges with an electrode. Read more about welding seams.
Extremely similar to argon, plasma welding occurs using a plasma arc flow. More details here.
An argon burner contains a hard tungsten electrode, to which a high-frequency current is supplied from an oscillator. This current ignites the “jet”.
What is NAKS
The National Welding Control Agency is an organization that functions to conduct certification of welding production specialists. A welder of the NAKS category has the right to work with particularly critical structures. Such work is paid higher, but the requirements for the professionalism of certified welders are much greater.
In addition to conducting exams, the NAKS institution conducts training for welders, produces teaching aids and improves prescriptive documents, and also provides consulting services during critical projects.
Types of welder certification are distinguished based on the order in which the welder or organization undergoes the procedure; exam levels; main groups of technical devices, the maintenance of which requires highly qualified specialists; applied technologies.
Advantages and disadvantages of argon arc welding
Pros:
- reliable isolation from the environment, improved quality and no disruption of the crystal lattice in the connected surface;
- indicative thermal power of the arc discharge, which has a positive effect on the quality and speed of welding;
- argon arc welding allows you to join dissimilar metals;
- the entire process can be carried out under supervision.
Minuses:
- protection by argon from ambient air can be impaired when working in wind or draft, since the gas can simply “blow away”;
- the torch must be periodically cooled when welding with a high-current arc;
- strong ultraviolet radiation, especially when using helium as an inert gas.
Since hot and welding work requires special skills from the work manufacturer, compliance with technical and industrial safety standards, as well as approvals, periodic certification is carried out in order to extend or obtain permission and admission to hot work of various categories.
Information about the welding pencil can be found here.
Who should be certified
NAKS certification can be carried out for:
- Working personnel. Employees can improve their qualifications voluntarily, hoping for a better position or with an eye to another job. In addition, enterprise employees may be required to undergo certification before being involved in work on a large, responsible project. In order to receive documents confirming qualifications after NAKS certification, the welder must successfully pass practical, theoretical and special exams.
- Technologies. Technologies that are used in the installation, repair, and assembly of structures used at hazardous production facilities are subject to mandatory certification. Control welded joints (as a rule, products from various metals are welded) are subject to examination in the laboratory, after which the NAKS commission issues its verdict.
- Equipment and tools. When certifying equipment, the compliance of the actual technical characteristics of the devices with those specified in the passports is carefully checked, the degree of wear of the equipment and its completeness are studied. The tests also include analysis of welds made in the presence of a commission.
- Welding materials. As in the case of equipment, the characteristics specified in the technical passport must correspond to the real ones. As a rule, NAKS certificates for small-scale batches of consumables have a shorter validity period than those intended for serial batches.
Possible problems
Even despite strictly following the instructions, a beginner may encounter some problems, the cause of which is unknown to him. The most striking example is the appearance of pores on the seam, indicating that there was gas under the flux that should not have been there. In most cases, porosity is caused by the presence of hydrogen or carbon dioxide, less often the root of evil is nitrogen. Nitrogen pores are only possible when working with micro-alloyed steel if the material has nitride hardening.
The same problem occurs if the workpiece was cut with a plasma cutter. Carbon dioxide falls under the flux if there are not enough deoxidizing agents in the weld pool. To prevent the formation of pores, at least 0.2% silicon is added to the liquid bath. Also, the deoxidation reaction occurs when the temperature decreases, and vice versa - there will be more carbon dioxide when it increases. The most common root cause of pores is hydrogen, often caused by insufficient cleaning of the edges to remove dirt or rust.
In addition, wet flux may be the source of hydrogen pores in the welded seam.
In the next video you will see automatic submerged arc welding of an I-beam at a factory.
Disadvantages of seams
Defects in welding seams occur due to:
- differential heating of a metal product;
- shrinkage of the molten substance;
- structural changes in a chemical element.
To prevent welding imperfections, parts are secured in special tools. This option is ideal for viscous compounds that do not cause cracking.
Some welders use the reverse strain method or the method of complete (partial) elimination of internal stresses.
State regulation of technology, connection types, characteristics
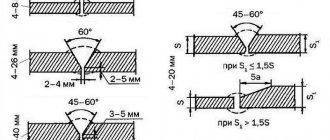
GOST 8713-79 classifies and marks with letter designations the subtypes of the submerged arc joining method:
- AF - on weight . Produced without means to prevent metal from leaking into the gaps between the edges being joined. If you need to weld to full depth, then this is done in two steps on both sides of the seam.
- AFf - on a flux bed . The name of the method illustrates the essence: flux is placed under the joint to be welded, and a rubberized hose is pressed against the joint through a fireproof lining. Air is supplied into the tube under pressure - the powder is pressed tightly against the products in the seam area.
- AFm – on a flux-copper lining . It is used to prevent burnout of metal edges, connecting corner, butt and T-joints with flux-copper backings that form the reverse side of the seam.
- AFo – on the remaining lining . It is used for one-sided welding, when it is impossible to weld on a flux pad. Steel backings guarantee complete weld penetration of the seams.
- AFP – on a copper slider . Its design provides a cored wire connection with forced formation of a fillet weld. Liquid slag is formed as the arc burns and then floats to the surface.
- AFsh - with preliminary application of a welding seam . It is used less frequently due to significant labor costs. Simplifies the product assembly process.
- AFk - with preliminary welding of the weld root . Performed with a coated or consumable electrode in a protective gas. The penetration depth reaches 1/3 of the thickness of the part.
Types of fluxes and their features
According to the manufacturing method, fluxes are:
- fused;
- ceramic.
Fused fluxes are made from slag-forming manganese ores and quartz sand by grinding, mixing and melting, followed by granulation. Such fluxes are economical and well suited for welding low-alloy steel parts.
Ceramic (unmelted) fluxes are made from oxidizing agents and salts of amphoteric metals, which are crushed, mixed with liquid glass until homogeneous, then granulated and calcined.
Approximate cost of ceramic fluxes on Yandex.market
Ceramic fluxes have a fine powder structure; they are used for welding complex high-alloy steel alloys, and the composition of the flux is selected for the specific grade of steel being welded.
According to the chemical composition, fluxes are:
- saline;
- oxide;
- mixed.
Salt fluxes contain fluoride and chloride salts and are used for electric welding of titanium and steel alloyed with nickel and chromium. Oxide fluxes contain oxides of active metals and silicon and are used for welding low-carbon steel. Mixed fluxes contain metal oxides and salts in various proportions and are used for welding multicomponent alloys or parts made of different metals.
welding equipment
The production of welds is carried out using automatic and semi-automatic devices.
The automatic device includes:
- gas reducer;
- acid cylinder;
- heater;
- dehumidifier.
The main element of the machine is the welding head. The speed of melting depends on the speed at which it feeds the electrode wire (constant or variable).
The semi-automatic machine provides wire feeding mechanically. The movement of the arc in the direction of the seam is carried out manually.
Semi-automatic equipment includes:
- electric holder;
- cassette;
- control cabinet;
- welding torch;
- power supply;
- the wire.
Approximate cost of machines for semi-automatic welding on Yandex.market
The main element of the mechanism is the electric holder. It keeps the electrode in a certain position and provides current to the welding area. The arc is activated by a short circuit or a trigger button located on the handle of the holder.
How to choose the right mode
The quality of your work depends on the correct choice of electrode thickness and current strength. Remember: the thicker the metal being connected, the larger the diameter of the tungsten electrodes used, and accordingly, the higher the current. In the operating instructions that come with the device, you can find all the data on the current strength and diameter of the electrodes, depending on the thickness of the parts being connected.
The most popular today are AMA and RAD welding. But professionals who need to perform a large amount of work use powerful, fully automatic units.
The most popular welding methods in Poland
Let’s say from our own experience, since we are an agency that employs on average 20 welders for work in Poland every month directly to the employer and to our agency. According to the welding method in Poland, the most popular method is 135. We already wrote this in our previous article “Welder in Poland. What do employers offer and for what? Interview".
You can see this with a clear example by going to our vacancies section for welders. Most of them are based on the 135 method.
We advise welders to also master other methods. This makes you a rarer specialist, allowing you to negotiate the best rate for yourself. Why are we sure of this? Since the employer spends time and money looking for a welder. Plus the fear that a good specialist might come, but he drinks. We wrote this for a reason. Employers, when they give us an order to recruit workers, emphasize that the welder does not drink or appear drunk at work.