Which welding is best to use?
Which welding will produce less smoke?
Which welding is best to use in an apartment when replacing a steel cold water riser with steel. The pipe is leaking
I myself work in a housing office, no one has ever suffered from smoke when welding, there are pros and cons everywhere regarding materials.
I recently encountered in one company that often does work for wealthy private owners that acetylene welding is considered a priority (heating radiators - the seam is visible). With acetylene, they say, if you weld it, then in any case the seam looks flawless, but with electric arc - maybe it will be beautiful, maybe not. Everyone has their own standard of what “beautiful” is. Well, if they want to use gas welding, that’s up to the owner; in this case, there is no ban on using gas welding.
In this case, gas welding is better
It is believed that gas welding is more effective than electric welding when welding thicknesses from 0.2 to 5 mm. In other cases, electric welding is more economical.
Welder Joe is considered to be the worst type of welding in terms of quality and performance, and was excluded as a subject of study for vocational schools and technical schools in 1988.
I entered training as a general electric welder in 1989 in the city of Chisinau, and I didn’t care whether there was gas welding there or not, because I was a city boy, and the road to the plant was prepared for me. But the kids who came from the village to study didn’t like this arrangement at all, and they were given this activity as an elective.
Welder Joe is still suitable for non-responsible structures, gas welding greatly overheats the metal, and now she is prohibited from performing most metal structures
Post edited by LekhaKolyma: 03 April 2022 19:46
It is still suitable for non-responsible structures, gas welding greatly overheats the metal, currently it is prohibited from performing most metal structures
It is believed that in terms of quality and performance this is the most unsuitable type of welding
All this is true, but try using any other type of welding to weld it to an old rusty pipe somewhere where neither your hands nor your eyes can really go. For example, in the ceiling, under the floor of a neighbor who, due to infection, does not let him in. When installing gravity heating, it will give any other type a head start. But that's probably all. Tinsmiths have already forgotten about it, but before they cooked cars? Gas welding. And they drove and didn’t fall apart.
But, in general, of course, this type of welding is becoming a thing of the past. Because those types of work where it is not replaceable are disappearing.
Post edited by SergDemin: 03 April 2022 20:16
Source
How to choose a welding machine for a beginner: what to look for
The selection algorithm is simple - first you decide on the main technical parameters, then on additional functions. A beginner should choose which welding machine to buy in exactly this order. At the first stage, you select a number of models that correspond to the purpose of the purchase; at the second, you weed out those that do not have the functions you need or, conversely, have unnecessary options.
Main parameters
Main characteristics - maximum welding current and electrode diameter, power consumption, mains voltage, operating time.
Maximum welding current
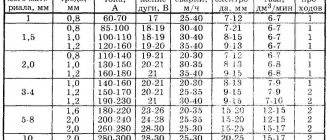
It depends on what thickness of metal you can weld and what diameter electrodes you will use. For example, if you plan to work with pipes or profiles up to 5 mm thick, then an inverter with a maximum output current of 160 A will be sufficient. There is no point in buying a device with higher performance if you will not weld thicker workpieces.
When choosing, you can refer to our table:
| Metal | Electrode diameter, mm | Workpiece thickness, mm | Maximum current, A |
| Carbon/stainless steel | 1,6-2,5 | up to 4 | 145 |
| 1,6-3,2 | up to 5 | 160 | |
| 1,6-4 | to 10 | 200 | |
| 1,6-5 | up to 15 | 250 | |
| 1,6-6 | up to 24 | 300 |
Power consumption
When assessing power consumption, you need to take into account the network capabilities at your dacha or garage. Currently, 15 kW is allocated to summer cottages. This is enough to work with an inverter up to 200 A, even if other equipment is turned on in the house. In older dachas and garages, the network can be designed for a lower load.
When buying a device, it is better to give preference to a model with a current and power reserve of about 20-30%. This will give you a little more options and allow you to solve non-standard problems if the need arises.
Mains voltage
According to technical conditions, one or three phases can be allocated for the electrification of a site or garage. Depending on the model, welding machines can operate from a single-phase or three-phase network. There are inverters with a built-in automatic transformer that operate at any voltage. But their price is higher, and they are needed for professional use and travel.
As a rule, welders for household and semi-professional needs with an operating current of up to 250 A are connected to 220 V networks. If your network offers 380 V, then you can choose a device with a higher welding current.
Single-phase networks in dachas and garages are characterized by voltage sags. So that you can work in such conditions, it is better to buy an inverter, the characteristics of which indicate the ability to weld at 130-160 V. Otherwise, you will need a stabilizer. As well as for semi-automatic devices that do not like voltage dips.
Duration of continuous operation
The PV or PN indicator shows how long the device will work and rest. For example, for a given time period of 10 minutes, a model with a duty cycle of 60% in the maximum welding current mode works for 6 minutes and rests for 4 minutes. At low currents, welding can be performed for as long as necessary - 100% duty cycle.
Additional functions
To make the devices easier and more convenient to use, they are equipped with additional functions. In practice, not all may be needed. For a beginner in MMA the following may be useful:
- Hot start. Helps ignite the arc at the beginning of welding, especially useful when working with rusty metal, raw electrodes and electrodes with a basic coating, and eliminates the need to tap the ignition tip for a long time.
- Antistick. Reduces the current to minimum values when the electrode sticks and avoids its overheating, makes it easier to weld thin-walled metal and work in general - electrodes periodically stick even for experienced welders, and tearing them off is time-consuming and difficult.
- Adjustable arc force. Maintains stable combustion, needed if you do not have the skill to hold an arc and when welding at low currents - when the arc begins to die out, the working current increases automatically.
Additional useful functionality of semi-automatic devices includes inductance adjustment. It allows you to change the characteristics of the arc - make it more rigid for positional welding and deep penetration and softer with less spatter for face welds. The function of annealing the wire is also useful, ensuring its constant ejection after each cycle - this is convenient for the next start.
Modern machines may feature synergetic control for intelligent welding. You only need to set the diameter of the electrode or the thickness of the metal and the device itself optimizes the parameters and functions.
What is the difference between gas welding and electric welding?
Electric welding differs in many ways from gas welding. Scope of application, methods, process characteristics, economic feasibility, equipment, tools, efficiency, material to be welded, etc.
Electric arc welding is a process in which sections of metal to be joined are melted and then bonded together under the action of an electric arc. Welding is performed using an electrode, which melts or heats the surface.
Equipment
for electric welding :
Gas welding requires the following equipment:
The differences in the components for welding may not be so significant, but when it comes to performing work in places remote from sources of electrical energy, gas welding is most often used. In addition, gas is often used for welding when it comes to utility repairs (residential, non-residential premises, heating mains, etc.) That is, gas is more convenient in field conditions. Oxygen and acetylene cylinders are much cheaper than a diesel generator.
Characteristics of the gas and electric welding process
Gas welding has the following main properties:
Electric welding has the following features:
Economic efficiency of welding
This indicator strongly depends on the thickness of the metals being welded - gas welding will be effective and economically justified up to a metal thickness of 6 mm. Thicker plates will require an unreasonably large amount of gas. On the other hand, for welding small, thin metal surfaces, the use of expensive tools and expensive electricity is also not economically feasible.
Materials to be welded
Metals such as copper, brass, lead, cast iron, etc., are easier to gas weld than electric arc welding. In addition, their rapid heating can lead to a change in strength.
Conclusion
Based on the above, when choosing a welding method, it is necessary to take into account many factors in order to obtain the maximum technological and economic effect.
Source
In this article:
Thermal welding is used to connect:
- rail;
- pipes;
- grounding loops;
- metal surfacing;
- filling cracks.
Suitable for welding carbon steels and cast iron with a thickness of 10-15 cm. In a miniature version, cables and wires are fused using this method. The technology allows you to connect large cross-section metals in hard-to-reach places, saving time. But the seams are very rough and require sanding, so they are not suitable for the façade of products.
Most often, railway tracks are repaired using thermite welding. Connections are made in accordance with GOST R 57179-2016, and the joints are designated by the abbreviation “SSR” - “butt joint of rails”.
What is the difference between argon welding and conventional welding?
Issues discussed in the material:
Not every novice welder knows how argon welding differs from conventional welding. First of all, it is necessary to understand the precise and free terminology. By “conventional” we most often mean the most common method of welding ferrous metals – electric arc. Argon, also known as argon-arc welding, is most often used when working with non-ferrous metal.
In addition to the working materials, both types of welding are fundamentally different in technological processes. From our material you will learn about the strengths and weaknesses of technologies, their main differences, and operating features.
Types of argon welding
Today, manual, mechanized, automatic and robotic technologies are used to join workpieces in a protective argon environment.
Is manual argon welding different from conventional welding? Apart from the difference mentioned above, there is no difference. In both cases, the process of joining the workpieces (moving the torch and feeding the filler wire) is performed manually. The technology is used both for welding simple parts and for working with complex structures. The disadvantage of manual welding (both argon and conventional) is low labor productivity. In addition, the welder needs quite a lot of experience to do the job well.
Otherwise, this technology is called semi-automatic, or semi-automatic welding. The welder operates the torch manually, and the filler wire is fed automatically. The productivity of this technology is three times higher than that of manual technology, and besides, a low-skilled specialist is enough to cope with the work. This type of joining of workpieces is widely used in shipbuilding.
Automatic argon welding is similar to conventional welding in that in both cases the parts are joined without the participation of a welder. Special equipment is used to weld workpieces. Its specificity directly affects the complexity of the work performed, the quality and configuration of the seam. The simplest seams are used to connect pipelines; automatic welding machines are used for their installation. This is the most productive technology with which it is possible to lay a pipeline even on the bottom of the sea.
Despite the fact that welders are not directly involved in the process of joining parts, highly qualified specialists set up the equipment, prepare it for work, and service and repair it.
Some time ago, another argon welding technology appeared - robotic, in which the connection of workpieces on conveyors is performed by robots. Its advantages include high productivity, as well as low cost.
The disadvantages of the technology are the high cost of equipment and the need to hire highly qualified specialists to configure and maintain robots. The installations are created by designers, and the software is developed by programmers. Both must have the highest qualifications. Robotic argon welding is used in the automotive industry. Economically, this technology is justified for large volumes of work.
Our top best welding machines for beginners
We can recommend several devices that are suitable for beginners. The characteristics and functionality of the models allow you to choose them for your home, cottage and garage.
The best inverter welding machines for a beginner
Svarog REAL ARC 200 BLACK with a welding current of 200 A for MMA is a good choice for beginners choosing an inverter for country tasks. The device is good for household use and allows you to work with electrodes up to 4 mm thick. This is enough for welding fences, gates, gates and canopies, including thick-walled pipes made of different types of steel. The device cooks stably at drops of up to 160 V and is equipped with an anti-stick function.
Slightly more expensive Svarog REALSMART ARC 200 is an inverter with synergetic control and a convenient digital panel. It offers anti-stick functions, hot start for easy ignition and arc force for improved welding performance. When choosing the electrode diameter, the welding current and the afterburner and hot start functions are adjusted automatically. The device is suitable for welding with electrodes up to 4 mm and working with steel up to 10 cm thick.
The best semi-automatic machines for beginners
The compact semi-automatic Aurora POLO 160 is a practical solution for beginners who plan to engage in MIG welding and work with wire up to 0.8 mm. The analog control panel allows the operator to easily set the thickness of the material being welded, after which the machine automatically sets the optimal current and voltage values. The model is lightweight and weighs only 8.6 kg, equipped with afterburning and inductance adjustment functions.
The polarity is easily changed, which makes it possible to use a self-shielding wire and eliminate the need to carry a gas cylinder, so the device is truly portable.
For those who want to purchase a device with advanced capabilities for a garage, country workshop and part-time work, we recommend AuroraPRO SPEEDWAY 180 SYNERGIC. This is a universal semi-professional semi-automatic machine, with which you can work with solid and flux-cored wire up to 1 mm, as well as piece electrodes up to 3 mm thick in MMA mode.
For MIG welding, inductance settings for adjusting arc characteristics and constant wire annealing are available. For MMA, a full set of useful functions - anti-sticking, arc force and hot start. The control is synergetic - this simplifies setup.
Two methods of argon welding
How does argon welding with a consumable electrode differ from conventional welding? In this case, the welder, in addition to the current strength and electrode, selects the additive supply rate and the type of inert gas. The use of protective gases supplied to the work area from high-pressure cylinders increases the cost of work. The shielding gas is most often a mixture of 75% argon and 25% carbon dioxide. The wire wound on a coil acts as a consumable electrode.
Despite the difficulties that lie in the need to simultaneously control the supply of wire, gas, and current strength, the welds obtained in this case are characterized by high quality. In addition, the speed of work is higher than when using MMA.
It is easy for novice welders to work with semi-automatic MIG inverters, since during the welding process there is almost no spatter of molten metal, no slag is formed in the weld, and a small amount of smoke is generated. MIG technology is simpler than MMA when comparing labor costs and the quality of the resulting welds.
The additive gun design makes the job faster. MIG is optimal for welding thin sheet metals. It should be borne in mind that the surface of the workpieces must be thoroughly cleaned; this is why argon welding differs from conventional and MMA welding.
Argon welding differs from conventional welding in that it is difficult to use in open areas. This is due to the risk of wind blowing shielding gas out of the working area, which will negatively affect the quality of the seam. A special welding wire with a flux core allows you to cope with this disadvantage. Its properties are similar to a consumable electrode in a coating. This wire can be used instead of liquefied gas.
Argon TIG welding differs from conventional, MMA and MIG welding in a large number of conditions and elements used. This is a universal technology that allows you to work with almost any metal, including aluminum. However, it requires a higher qualification from the welder. In addition, the cost of work is also higher than with other types. Argon TIG welding is optimal for body work; it is also used to connect elements of artistic forging, and is used where, after completion of the welding work, the seams should not be visible. The seams obtained using TIG are distinguished by their visual appeal, especially for fans of the dieselpunk style.
Argon welding with a non-consumable electrode is performed using both alternating and direct current; the electrode itself does not burn out. This is due to the tungsten contained in it. Since the size of the electrode does not change during operation, it is easier for the welder to control the position of his hand. The current intensity is adjusted using a foot pedal, so the specialist needs to precisely coordinate his movements.
This technology allows you to work with low current values, which guarantees the safety of even very thin workpieces. When choosing low current settings, you must thoroughly clean the surfaces of the parts to be welded, and also be prepared for the fact that the work itself will take longer. Argon TIG welding is suitable for joining aluminum products that cannot be welded using other technologies.
The nuances of working with argon welding
Argon welding is similar to conventional welding in that both technologies, in addition to theoretical knowledge, require practical skills. And before you start practicing, it’s worth learning about the nuances of working in a protective environment of inert gases in order to avoid mistakes during the welding process that negatively affect the quality of the welded joint.
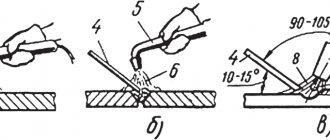
First of all, it is necessary to thoroughly clean and degrease the edges of the workpieces to be joined. In this regard, argon welding is also no different from conventional welding. Cleaning is necessary even if the metal surface does not visually contain any traces of dirt or corrosion. It is better to perform the welding itself with a short arc, since with a long arc the weld will be wide and shallow and, as a result, of low quality.
The arc when using argon welding should be short, the electrode rod should be as close as possible to the metal surface. To obtain a narrow, deep seam, the electrode should be moved longitudinally without sideways deviations and without transverse movements. Otherwise, the quality of the seam will be worse.
Both the filler wire and the electrode must be placed exclusively in the working area, otherwise the protective properties of argon will be impaired, resulting in oxygen entering the weld pool. The additive must be supplied smoothly and evenly, without jerking. Violation of this requirement will lead to severe spattering of the metal and a decrease in the quality of the weld.
Semi-automatic or inverter: which is better for a beginner
Some devices are only suitable for working with thin metal, while others are suitable for working with thick metal. Some have high deposition productivity, while others have relatively low ones. There is equipment that is convenient to use outdoors and in hard-to-reach places, and models that are not intended for “fields”. Therefore, when choosing a welding machine for a beginner, it is important to start not from the amount he is willing to spend, but from the purpose of the purchase and operating conditions.
Manual arc welding inverters
Manual or MMA welding with a coated electrode is the most common. The method is simple - the electrode core is melted and transferred to the weld pool. An external supply of shielding gas is not required. It is provided by coating the electrode, which forms gas and slag. They protect the bath from air: oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen.
Piece electrodes need to be replaced frequently due to their short length. Welding performance is sufficient for everyday tasks and part-time work. There is no need to carry a protective gas cylinder with you. Thanks to this, inverters are convenient when you need to load the device into the trunk and go from the garage to the country house, as well as when you need to weld on the street or in a confined space.
There are dozens of types of electrodes. This allows you to work with different alloys and expands the possibilities. But you need to remember that the electrodes do not burn out entirely - the cinders are thrown away, so their utilization rate is no more than 70% per 1 kg.
Semi-automatic machines for welding in shielding gases
For semi-automatic or MIG welding, you need a spool of wire, a gas cylinder and a torch. The arc and weld pool are protected by the gas in which you work.
Semi-automatic welding is faster and more productive than MMA. Therefore, it is more suitable for garage repairs, starting a small business and making money. This is an appropriate choice when welding work needs to be done quite actively and frequently, and it is possible to transport both the apparatus itself with a spool of wire and a cylinder with hoses to sites.
Welding wire utilization rate up to 90%. There is no need to change it often and constantly throw away leftovers.
There is no point in comparing inverters for MMA and semi-automatic machines for MIG from the point of view of which welding machine is easier for a beginner to weld. To develop any skill you need practice.
An inverter can be recommended for home, garden and minor repair work because of its practicality: mobility, compactness and versatility. If your plans include garage repairs and earning money, it’s better to choose a semi-automatic.
The essence of electric arc (conventional) welding
It will take time to learn how to properly perform argon welding. The welder will have to not only study the essence of the welding process, but also become familiar with its features and, of course, develop practical skills. It is important to understand the difference in the properties of various metals, understand welding machines, choosing the one that best meets the needs of a specialist, appropriately equip a workshop for the work, establish and justify their cost. After all, regardless of whether argon welding differs from conventional welding, both can bring profit to the welder. Of course, if he decides to do it professionally.
Let's take a closer look at the nuances of TIG, MIG and STICK technologies - knowing the features, advantages and disadvantages of each of them, it is easier to choose the most suitable option.
Argon welding differs from conventional welding in that in any case it uses an electrode, filler wire and inert gas, which performs a protective function and improves the quality of the weld. But these elements will vary depending on the technology used. Thus, in different versions of argon welding, consumable and non-consumable electrodes are used, the filler wire is made of different materials, and in addition, the inert gases used differ.
Electroslag welding
The essence of electroslag welding is to connect two sides of the metal using the heat generated by the slag pool. To do this, the joining area is filled with conductive flux. A welding electrode (wire) is connected to it, which heats the flux, forming liquid slag. The electrode continues to conduct current while immersed in the welding slag pool. Arcless method. The temperature rises and the edges of the metal melt together.
The thickness range of metals welded using this method is 20-3000 mm. Slag welding can be used to connect:
Technology is used in the chemical industry, mechanical engineering, shipbuilding, and the aviation industry.
Types and nuances of electric arc welding
The simplest type is welding using a consumable electrode. In addition to simplicity, this is also the most affordable option from a financial point of view.
The simplicity of the process lies in the fact that it only requires the welder to select a suitable electrode and the required amperage. An electric arc melts the metal of the electrode, and a protective gas environment protects the weld pool from the penetration of oxygen formed during the combustion of the flux that covers the electrode. Protection is necessary, since oxygen, when reacting with the metal of the workpiece, causes its oxidation, which negatively affects the quality of the weld.
When developing certain skills, a welder can perform various types of welding work using a consumable electrode in a coating. It is suitable even for uncleaned surfaces or metals showing signs of oxidation. The main thing that a specialist must do is to choose the right electrode. The welding process can use both alternating and direct current.
Argon welding differs from conventional welding in that it is more difficult to control the process in this case. During operation, sparks are formed, the seam becomes clogged with slag, which reduces the strength of the welded joint. It takes a lot of effort to do a good weld. Also, this technology is not applicable when working with aluminum, sheet metals and thick massive workpieces.
Electric arc characteristics
An electric arc, which is formed using a welding machine, is, in fact, an electrical discharge flowing in a gas environment. The electric current that moves in it receives this opportunity due to the presence of an electric field in it. For the purpose of streamlining terminology, such an arc is usually called a welding arc.
The welding arc, which is the main element of the formed electrical circuit, is characterized by a decrease in voltage. If the welding electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the welding machine, it is called an anode, if it is connected to the negative terminal, it is called a cathode. When performing electric arc welding using alternating current, the cathodes and anodes alternate places.
The most important parameter of the welding arc is the distance between the interacting electrodes. Such a gap through which electric current flows is called an arc. The flow of electric current through such a gap is possible only if it contains charged particles - electrons and ions. Initially, naturally, such particles do not exist in this interval. For them to appear, the ionization process must be started.
Arc Welding Structure
Ionization of the arc gap occurs as follows: electrons begin to be emitted from the surface of the cathode, which charge the vapors and gases formed above the weld pool. The welding arc is:
- compressed type (its cross-section can be changed using the nozzle of the welding machine, the magnitude of the electromagnetic field, and gas flow parameters);
- free (it is also called a direct arc - the parameters of an arc of this type are not adjustable, they are unchanged).
Why should you contact us?
We treat all clients with respect and carry out tasks of any size equally scrupulously.
Our production facilities allow us to process various materials:
When completing an order, our specialists use all known methods of metal machining. Modern equipment of the latest generation makes it possible to achieve maximum compliance with the original drawings.
In order to bring the workpiece closer to the sketch submitted by the customer, our specialists use universal equipment designed for jewelry sharpening of tools for particularly complex operations. In our production workshops, metal becomes a plastic material from which any workpiece can be made.
The advantage of contacting our specialists is their compliance with GOST and all technological standards. Strict quality control is carried out at every stage of work, so we guarantee our customers a conscientiously completed product.
Thanks to the experience of our craftsmen, the output is an exemplary product that meets the most demanding requirements. At the same time, we start from a strong material base and focus on innovative technological developments.
We work with customers from all regions of Russia. If you want to place an order for metalworking, our managers are ready to listen to all the conditions. If necessary, the client is provided with free specialized consultation.
Source
What is the difference between gas welding and electric welding?
Gas welding requires the following equipment:
- a special gas burner; - flexible communication tubes; - a special filler wire (sometimes they do without it).
Electric welding requires the following components:
— electrical power source;
The differences in the components for welding may not be so significant, but when it comes to performing work in the steppe, forest, and places remote from sources of electrical energy, gas welding is most often used. In addition, gas is often used for welding when it comes to utility repairs (residential, non-residential premises, heating mains, etc.) That is, gas is more convenient in field conditions. Oxygen and acetylene cylinders are much cheaper than a diesel generator.
Characteristics of the gas and electric welding process
Gas welding has the following main properties:
— a large area is heated;
- automation of gas welding is difficult; - gradual heating of the metal; - with increasing metal thickness, the productivity of gas welding decreases.
Electric welding has the following features:
— a small area is heated;
- full automation of the electric welding process is possible; - the metal being welded heats up almost instantly; - productivity during electric welding practically does not depend on the thickness of the metal.
Economic efficiency of welding
Lead, copper, cast iron, brass, etc. Metals can be welded more easily by gas welding than by electric arc welding. In addition, their rapid heating can lead to deterioration in properties, for example, to a change in strength.
Thus, the choice of welding method depends on many factors that must be taken into account in order to obtain the maximum economic and technological effect.
Gas or electric welding?
Today we want to figure out what the features of each method are. And is it possible to answer the question, which one is better? They differ significantly in operating principles, tools, scope of application and other parameters. Let's take a closer look at each type.
Electric
It is also called electric arc. It joins metals by melting and bonding parts under the influence of an electric arc. A special electrode helps with this, which, when melted, acts as glue.
When working with the popular argon, a tungsten electrode is used. Argon displaces oxygen from the working bath, that is, it protects the welding site from unwanted impurities and gases. Oxygen has a bad effect on the quality of the seam. Therefore, argon arc welding is used, since this gas is 38% heavier than air.
Electric welding can occur under the influence of alternating or direct currents. To work with alternating current, you need a welding transformer. It produces a powerful electric current to stabilize the arc.
Gas
Unlike electric welding, gas welding occurs due to a jet of burning gas from a special torch or cutter. To start cooking, connect 2 cylinders with different gases to the burner: the one that will burn (can be propane, butane or methane) and the oxidizer (oxygen). And sometimes it is better to use acetylene, which “works alone”.
Pros and cons of welding methods
Both options have their advantages and disadvantages. The features of electric welding include the following points:
To summarize, we can say that it is simply impossible to objectively determine which welding is better - gas or electric. They are both unsafe and require a highly qualified performer. Depending on the situation and the composition of the material being joined, one or another method is better.
Content
- Semi-automatic or inverter: which is better for a beginner
- How to choose a welding machine for a beginner: what to look for
- Our top best welding machines for beginners
You can weld a frame for a canopy, greenhouse or gate, install bars on the windows of a country house, and carry out minor repairs in the garage yourself.
To do this, you need to understand the welding process and select a welding machine. There are models on sale for household, semi-professional and professional purposes with different characteristics, functionality, capabilities and prices. We share tips on which welding machine to choose and buy for a beginner for a summer house or home, based on the upcoming tasks.
Gas and electric welding
Most connections of metal elements and parts are made by welding. The two most common types are gas and electric. In any case, welding is the process of forming a strong connection between metal surfaces as a result of heating their edges to a high temperature and forming interatomic bonds along the joint line.
In order to understand what gas and electric welding is, we will consider the main features and principles of their operation.
Operating principle of electric welding
If metal welding is carried out using an electric arc, then it is classified as electric arc. The metal parts are connected by means of an electrode, which can either melt to form a bonding seam, or be used solely to heat the contact surface, while remaining inert.
Electric arc welding with alternating current requires a welding transformer that provides high currents of 200-500 amperes on the secondary winding, which is necessary to stabilize the arc discharge. When welding on direct current, you will need a rectifier unit that ensures a uniform load on the electrical network.
Operating principle of gas welding
When gas welding a metal, its surface is heated by a hot stream of burning gas flowing from the torch nozzle. As a rule, the co-combustion of two different gases is required - the original fuel (propane, methane or butane), mixed with an oxidizer, which is most often oxygen. However, when acetylene is used, a sufficient amount of oxidizing agent is already contained in the surrounding air.
Electric arc welding is used in places with a reliable power supply, where the network is able to withstand its starting and operating currents. It is lighter and more compact than gas analogues. Gas welding is preferable in field conditions, away from electrical networks.
Source
Plasma welding
Plasma is used to melt the edges and filler metal. The equipment consists of a direct current source, an argon gas cylinder, and a plasma torch. To remove excess heat from the plasma torch nozzle (torch), water cooling is often provided.
The gas is supplied to the plasmatron and heated by an electric arc. Thanks to this, it increases in volume up to 100 times. Due to thermal expansion, it begins to flow out of the nozzle at high speed. This is plasma. Its temperature is 30,000º C, which exceeds the characteristics of other welding methods.
There are two options for implementing the technology:
Using plasma welding, metals up to 9 mm thick are connected in all spatial positions. The method is suitable for welding: