One of the most difficult and time-consuming tasks of modern welding production is the connection of cast iron products, especially when it comes to large-sized structures. Today, for high-quality welding of cast iron products, TsCh-4 electrodes are mainly used.
Electrodes TsCh-4 are intended for cold welding of ordinary and high-strength cast iron.
General characteristics of TsCh4 type electrodes
Structurally, elements of this type are rods on which the main coating is applied. They are used for working on high-strength cast iron (with spherical graphite in its composition), as well as for welding products made of gray cast iron (with plate-type graphite).
The functional purpose of these electrodes includes high-quality connection of objects made of dissimilar metals, welding of damaged structural elements, formation of new welds and correction (welding) of various defects that arise during the casting process, special surfacing of initial layers of metal on cast iron parts.
Welding consumable parameters
For high-quality welding work, it is important that all electrode parameters are optimally selected.
This or that practical application influences the choice of the diameter of the specified element - it can vary from 3 to 5 mm. Depending on the upcoming welding operation, it is necessary to set the correct current mode - 65-80, 90-120 or 130-150 amperes.
For high-quality welding work, you need to choose the right electrodes.
For effective operation, the electrodes should be pre-heated. To achieve the best results, it is recommended to do this at a temperature of +170...+200°C.
Chemical composition of the deposited metal
The TsCh-4 model contains the following chemical components:
- carbon (C) – 0.25%;
- manganese (Mn) – 0.5/2.5%;
- phosphorus (P) – 0.07%;
- sulfur (S) – 0.04%;
- silicon (Si) – 0.10/0.80%;
- vanadium (V) – 8.5/10.5%.
The electrode rod has an iron base.
This metal allows you to work efficiently with the material from which the object being welded is made and ensures a high-strength weld.
Features of cast iron
Unlike steel, cast iron contains a significant amount of carbon - from 2 to 6%, while CO2 is in a free state - in the form of graphite. This determines its unique characteristics - it is extremely hard, but at the same time fragile, has low ductility and viscosity. These properties affect the processing and welding of metal. If the parameters, materials and welding techniques are incorrectly selected, the following risks exist:
- due to the presence of graphite in the metal, cracks may form;
- carbon burns out, which leads to the formation of pores in the weld;
- Refractory oxides are formed, whose melting point is higher than that of cast iron.
In addition, difficulties during welding can be caused by such a property as high fluidity, which prevents the formation of a high-quality seam.
Rapid cooling of gray cast iron after a heating temperature of more than 750°C leads to the transformation of graphite into iron carbide - cementite. The cast iron itself turns from gray to white. Such cast iron cannot be welded.
Classifications and approvals
Welding electrodes TsCh-4 meet the technical specifications of TU U 28.7-34142621-006:2012 and are approved by:
- TUV – Association of audit companies of the Union of Technical Supervision of Boiler Equipment Facilities (Germany);
- STB – Gosstandart (Republic of Belarus);
- KZ-standard – GOST 9466 (Republic of Kazakhstan);
- MD-standard – GOST 9466 (Republic of Moldova).
We recommend reading Characteristics of LB 52U electrodes
Welding electrodes TsCh-4 are approved by TUV, STB.
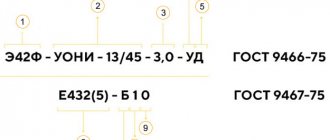
Explanation of markings
The marking on the electrodes, regulated by GOST, contains information about the components included in the composition. The base of most brands consists of iron, but there are other options. For example, MNC-2 contains:
- M – about 30% copper;
- N – nickel 65%;
- Ch – indication of purpose “for cast iron”;
- 2 – serial number indicating the ratio of components.
Advantages of the elements
Electrodes of the TsCh-4 brand have a number of functional advantages, among which the following can be distinguished:
- They allow you to weld objects/structures made of cast iron, as well as together – from cast iron and steel, which is impossible with the help of many other brands of electrodes.
- They are characterized by simplified ignition and stable combustion of the welding arc, which results in a uniform, strong connection of the parts being welded.
- The chemical composition is selected in such a way that it is possible to work with different types of cast iron.
- Versatile. They are used equally effectively in both the down and corner positions, both for cold welding (without heating) and for hot welding (at temperatures above 250°C).
- They perfectly eliminate defects and do an excellent job with preparatory deposition on parts from the 1st to the 2nd layer.
- During the welding process, metal is formed in the seam with virtually no metal spattering.
- Available for purchase.
When used correctly, these electrodes guarantee a strong welded connection with an even and durable seam. Moreover, they are suitable for both industrial use and home use.
Electrodes of this brand perform well in combination with modern welding machines.
TsCh-4
Basic coated electrodes designed for both hot and cold welding of ductile, ductile and gray cast irons. The main purpose is welding of defective castings, surfacing when repairing cast iron parts. These are also electrodes for cast iron and stainless steel; they allow high-quality welding of these two alloys with different structures. Often, to obtain a more effective result, they are used only for surfacing the first layers, after which it is performed with other, special electrodes.
Technological features and properties
Welding using TsCh-4 is carried out using short rollers (25-30 mm long) with roller cooling in the open air (to a temperature of +60°C and below). If parts are welded, the basis of which is malleable or high-strength cast iron, it is allowed to increase the length of the roller to 80-100 mm.
Welding using TsCh-4 is carried out in the open air.
To achieve the required quality of welding work, each technical parameter is important, therefore it is necessary to pay attention to the following characteristics of the described electrodes:
- diameter – 3-5 mm;
- length – 35 cm;
- type of coating – basic;
- pre-calcination temperature – +170…+200°C (for an hour);
- overheat protection – no;
- electrode consumption (average) – 1.8 kg/1 kg of deposited metal;
- productivity during surfacing – up to 1.1 kg/hour (with a diameter of 4 mm);
- quantity in a pack – 30 pcs.;
- standard packaging weight is 0.8-1 kg.
We recommend reading Description of rutile-coated electrodes
How much do electrodes cost for cast iron?
The main factors that determine the cost of this consumable are the brand and country of origin, the type of electrodes, their brand and coating composition. Traditionally, high-quality European and American analogues are considered more expensive - for example, products from such well-known brands as ASPIK or UTP. Excellent consumer properties when working with cast iron are demonstrated by the German-made UTP 86 FN electrode and also by German Capilla brand products. Russian analogues are cheaper, while the quality of modern domestic products is at a high level.
Nuances and conditions of use
In the process of welding parts made of low-plasticity cast iron with free graphite in its composition, a worker, especially if he is just learning a new job, can get a connection whose quality cannot be called optimal. To prevent such a result, TsCh-4 rods must be operated at a constant current of reverse polarity.
The functional parameters of the connection will be improved by preheating the raw edges of the base metal to a temperature of +650°C for an hour. After welding, it is necessary to allow the surface to cool for some time. It is better to do this in special ovens for cooling or by wrapping the joint with heat-insulating material.
To eliminate the risk of shedding of the electrode coating, TsCh-4 elements can be dried no more than 2 times.
Special properties of electrodes
- TsCh 4 electrodes are characterized by good welding and technological characteristics: ease of arc ignition, stable combustion, easy separation of the slag crust, insignificant metal losses due to spattering, as well as good formation of metal in the weld when welding in the lower position.
- Vanadium, a strong carbide former, is introduced into the weld metal welded with TsCh 4 electrodes during the welding process. Carbides of this element, formed during the welding process, do not dissolve in the iron mass and form non-solid, finely dispersed inclusions. In this case, the metal base turns out to be quite plastic and decarbonized. After welding, it is possible to process it with a cutting tool.
Storage rules
Electrodes are supplied to customers in packages with film thermal protection. Inadequate storage can minimize this security. Therefore, these products must be stored in rooms with a temperature not lower than +15°C and a minimum level of humidity.
It is necessary to provide reliable protection against accidental falls of other objects onto stored rods or from falling off warehouse shelves. Mechanical damage compromises the integrity of the coating, which can negatively affect the quality of welding.
Where can I buy electrodes for cast iron?
You should buy such products only from well-known manufacturers and trusted suppliers - this is a guarantee of high factory quality and brand reputation. This is precisely the high quality of cast iron electrodes produced by one of the oldest specialized enterprises in Russia – the Magnitogorsk Electrode Plant.
On our website you can buy products at the manufacturer's price. Depending on the brand, the material is perfect for both welding and restoration surfacing. The products have GOST R and sanitary-epidemiological examination certificates.
Electrode selection criteria
The quality of welding work depends on the correct choice of electrode brand according to the main criteria:
- Compliance of the electrode grade with cast iron in the repair part;
- Thickness of the welded wall;
- Type of technology used;
- Requirements for the weld according to physical and mechanical parameters;
- The need for subsequent machining of the joint;
- The outer coating – basic or acidic, has a different reaction to operating conditions;
- For old, low-quality cast iron and in the presence of contamination, the cross-section of the rod should be larger;
- Welding of thin-walled parts is carried out using electrodes whose cross-section is close to the wall thickness.
If you have no experience and have difficulty choosing, it is recommended to take electrodes of the MNCh-2, TsCh-4 or OZCh brands with a cross section of 3-6 mm. In case of preference in favor of foreign manufacturers, the universal UTP brand is recommended.
Important Tips
It must be remembered that electrodes for steel workpieces are not suitable for welding cast iron due to other physical properties and structure of the material. Residual stresses and fatigue phenomena can cause destruction of the weld during further operation. Electrodes for cast iron are much thicker than consumables for steel, which is determined by the massiveness of the material.
The electrodes used must correspond to the cooling time with the base metal, which is very long for cast iron. The percentage of carbon content in cast iron and filler material must be the same. Compliance with the basic conditions will help avoid carbon burnout and the occurrence of excessive internal stress.
More often, rods with a basic type of coating are used. Acid spraying is less common.