Best selling pickling paste INOX D/GEL SUPER PLUS Paste for pickling the welding seam of stainless steel after welding
In stock Etching paste INOX D/P SUPER PLUS Intensive paste for etching stainless steel welding seam
Best seller Pickling gel ENERGY PICKLER GEL PLUS Gel paste for intensive pickling of stainless steel, odorless
In stock Pickling gel ENERGY PICKLER GEL Pickling gel for stainless steel, odorless
In stock Safe etching gel FUTUR DEK DBA Gel for etching stainless steel without nitric and hydrofluoric acids
In stock Etching paste INOX P 400 Etching paste for AISI 430 INOX P 400
In stock Etching gel INOX D/GEL SUPER PLUS SPRAY Means for etching large surfaces of stainless steel by spraying
Best seller Etching paste INOX D/GEL STRONG Fast-acting etching paste. Removes stubborn oxides in 3-5 minutes
In stock INOX D/GEL LIGHT SPRAY Gel spray for etching stainless steel without matting effect
In stock Pickling bath INOX D/L Liquid pickling agent for stainless steel by immersion
In stock Stainless steel passivator PASSINOX Stainless steel passivator for instant formation of a passive layer…
Best selling Passivator FUTUR PASS ADF GEL Stainless steel passivator. In stock.
In stock Passivator PASS OX Liquid passivator of stainless steel AISI 630, 304, 316, 321
In stock Pickling solution INOX D/L 400 Pickling liquid for stainless steel AISI 430
In stock Pickling agent ENERGY PICKLER GEL PLUS... Non-toxic means for pickling stainless steel by spraying. Without…
- 1
The high corrosion resistance of stainless steel is achieved through the formation of a chemically resistant passive layer of chromium oxide. To use stainless steel outdoors, in highly corrosive environments or for contact with chemicals, such a layer must evenly and completely cover the entire metal surface.
During the manufacture of stainless steel elements, the metal surface is subject to various deformations and damage due to thermal and mechanical treatment at all stages. Oxide layers on welds, dirt particles and other traces such as free iron can penetrate deep into the surface of the material during manufacturing processes. A protective layer cannot form in these areas, making stainless steel highly susceptible to rapid corrosion.
However, the process of etching and passivation of stainless steel removes and dissolves oxides located on the surface of stainless steel, including those formed during the welding process or during secondary heating, as well as corrosive particles and slag formations. After etching, a chemically clean metal surface is achieved, on which an optimal protective passive layer can be formed. For complete stainless steel pickling technology, FORSTEX offers a wide range of products for metal processing under different operating conditions.
Reasons why processing is important
During the manufacture of numerous structures using stainless steel as the main material, welding methods are actively used due to the functioning of an electric arc in an inert gas environment.
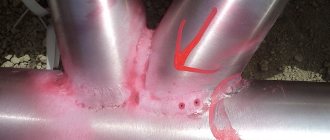
Despite the formation of relatively smooth and strong seams, they are characterized by the presence of an unattractive appearance, resulting in the need to treat stainless steel welds. Thus, the place of the welded joint is characterized by the presence of a mirror color, while the area near the seam is yellow and its many shades.
In the case of the formation of a pattern in the form of scales, the presence of small black stripes is noted in the resulting grooves. After a certain period of time, there may be a risk of rust forming in these areas.
Phenomena of this nature are a consequence of exposure to excessively high temperature conditions, which results in overheating in the welding area. When high temperatures are present, alloying elements burn out with simultaneous depletion, which results in a change in color and an increase in the degree of vulnerability to external factors.
At the end of the process, a film is formed, which is characterized by a low level of resistance to aggressive environmental influences, which leads to the gradual development of corrosion at the treatment site.
Pickling paste
The Salyut Association is a well-known supplier of certified products and materials for construction and industrial production. Having large, specially equipped warehouse facilities, we have accumulated large inventories of products to uninterruptedly satisfy customer requests. Constantly studying market conditions and demand, we are expanding the range of products and additional services.
Taking advantage of our offers, the customer can count on a personal approach and qualified assistance in the selection of materials, loyal prices and high quality materials.
Mechanical grinding
Stainless steel is characterized by the presence of a high level of corrosive properties, which determine its active use in environments where liquids are often used. Although products made from such material are in active contact with water and are subject to preliminary welding, their appearance does not change significantly over time. This feature can be traced as a result of the use of certain processing principles.
Among the main processing options, it is customary to highlight mechanical grinding of stainless steel after welding. During this process, the top layer of the oxide component that forms at the welding site and represents a weak point in the entire structure is eliminated. Distinct color transitions and existing irregularities in the weld joint are also eliminated.
This process is characterized by the following sequence:
- eliminating waves in the area of the metal seam by using a thick grinding wheel and grinder, as well as leveling out any bulges present;
- using petal circles for the functioning of the grinder; the main goal of such elements is to carry out work more accurately, along with longer process times and consumption of materials, which is especially important for large-scale work;
- the use of a specially designed equipment complex in the form of a grinding machine, the result of which is a one-color matte coating;
- mandatory use of a respirator to reduce the risk of abrasive dust and metal particles entering the respiratory tract that are in the air during work.
Inverter welding on stainless steel - features of working with the material
Welding stainless steel is a process that requires certain skills. The peculiarities of the material can confuse even an experienced welder accustomed to working with traditional materials.
To weld on stainless steel with a good result, you need knowledge of the material.
Features of stainless steel affecting welding processes
To give steel anti-corrosion properties, the material is alloyed. As additional additives, a proven material is used that is 100% rust-resistant - chromium.
The mass fraction of this material in the alloy can reach 1/5.
In addition, high-quality stainless steel contains nickel, molybdenum and other materials that complicate the formation of a classic welding arc.
Examples of welding thin stainless steel with a simple MMA inverter
What factors complicate the welding process:
- Stainless steel has poor thermal conductivity. Compared to the usual composition, this figure is 50% lower. Therefore, the current should be reduced by 15%-25%. This is unusual for a welder.
- When heated, iron and chromium react chemically, resulting in the release of large amounts of carbide.
If the welding zone is not cooled, the iron part of the alloy completely loses its resistance to corrosion. Moreover, this is not a continuous surface covered with rust, but intercrystalline oxidation. Corrosion penetrates inside, completely destroying the product. - Excessive expansion when heated.
When welding thin stainless steel, the product becomes covered with waves that cannot be eliminated. Workpieces of great thickness can expand so much that the structure is deformed. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure a gap between the parts. - A welding filler wire made of stainless steel is recommended. If the gap is too large, voids may form inside the seam.
- With a high titanium content (as an alloying material), it is better to weld stainless steel with rutile electrodes. The coating contains titanium dioxide, which reduces metal spattering.
Welding stainless steel at home using an inverter
Since thin stainless steel sheets are the most difficult to weld, special technologies have been developed that take into account the characteristics of the material. Both methods operate in an inert gas environment, and the consumption of argon when welding stainless steel is no higher than when welding aluminum.
- Short arc welding. The most gentle mode for stainless steel sheets, however, requires a lot of experience
- Semi-automatic pulse welding. Each current pulse is accompanied by a discrete wire feed. One drop is formed per pulse. The edges of the sheet do not have time to warp due to temperature, and the seam turns out smooth and requires practically no welding treatment.
Even better weld quality is achieved by semi-automatic welding of stainless steel in a carbon dioxide environment.
You can do without various tricks, the only condition is the speed of the work. The wire feed should be accelerated and the seam should be carried out quickly and vigorously.
The principle is the same - the area around the weld does not have time to heat up and warp.
In general, a semi-automatic machine provides greater opportunities when working with such complex material.
By practicing on unnecessary scraps of stainless steel, you will quickly gain the necessary experience.
Another good way to weld stainless steel is semi-automatic welding in a carbon dioxide environment, see detailed video
Welding stainless steel with an electrode at home
Semi-automatic is quite an expensive pleasure for home use. Most often, a regular inexpensive inverter is used at home.
Sharing secrets or welding stainless steel with a standard inverter - video
The technology allows you to cook with high quality using special electrodes. However, inverter welding on stainless steel requires certain conditions:
- Do not under any circumstances overheat the seam area or the entire workpiece. We must try not to exceed the temperature of 200°C
- You can use thick copper plates for heat dissipation
- Welding is performed with low currents, a short arc and without oscillatory movements
- If you are working with thick material, with seam cutting, you need to cook in several short passes
- Thorough cleaning of workpieces with a steel brush before starting work
- The electrodes must be calcined in accordance with the instructions
- Immediately after cleaning the seam, it must be treated with etching paste. Otherwise, intercrystalline corrosion is inevitable.
Popular: Inverter welding lessons for beginners - video
If you work with an inverter, be sure to practice before starting important work. Master thick stainless steel workpieces with medium welding currents.
When you feel the pace of the seam passing through a short arc, gradually move to thinner sheets, reducing the current value.
It is quite difficult to work with 3 mm electrodes and low currents on stainless steel. Don’t start cooking “finish” until you realize that you have mastered the technology.
Grinding after welding
If you are making a utilitarian product (water tank, canister, pipeline), giving it a “marketable appearance” after welding is not necessary.
It is enough to remove black slag and carry out basic grinding.
Slags are removed using pickling paste or acid. To prevent the acid from flowing over the surface that does not need treatment, it must be thickened.
For example, wood sawdust. Then the dissolved slag is washed abundantly with running water, and the welding site is wiped dry.
Grinding is carried out using standard means - abrasive wheels. There is no technology, you just clean the surface to an even layer.
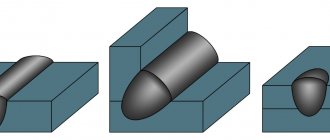
Pay special attention to the absence of small shells on the surface of the seam.
Polishing stainless steel after welding
The next step in the complex of processing carried out in relation to the area of welding work is polishing the stainless steel after welding. It should be noted that not only individual areas of the product are subjected to such a process, but also the entire surface of the product as a whole, which guarantees a shiny final look.
Polishing provides an even greater level of cleaning of the surface being treated by obtaining a solid and smooth area, which subsequently results in the ability to withstand the external influence of aggressive liquids.
Initially, the area of the welds is exposed to a disk of vulcanite, the purpose of which is to give the weld the required shape and depth by forming the structure of the concave sample.
The next step is considered to be the application of a special paste intended for polishing. In most cases, GOI paste is used. The main objective of the polishing process is to achieve a mirror-like surface with the immediate absence of previously present matte spots.
Gels and acids for processing
In order to eliminate the presence of color transitions resulting from the welding process, as well as to neutralize the formation of an oxide layer that promotes the corrosion process, etching of stainless steel welds is widely used. This method falls into the category of acid exposure for the purpose of processing the material.
The best option is to use hydrochloric and sulfuric acid to treat stainless steel welds. If it is not possible to use the above compounds, nitric or hydrofluoric acid can be used. These substances are intended to be produced in the form of a gel and paste for etching welds on stainless steel.
It is also currently considered possible to purchase specially designed aerosols for such purposes.
Application of etching
The etching process is widely used in production during the cleaning of the upper layers of steel from welds, scale, oxides and rust. It is used when searching for internal defects by removing the top layer of the workpiece or to study the structure of the metal.
This procedure cleans the material, thereby increasing the adhesion of the top layer. This is necessary for the successful connection of a metal workpiece with another surface, after which a paint, enamel, galvanic layer or other protective coating is applied.
This type of processing not only ensures quick cleaning of the workpiece, but also creates a specified pattern on the top layer of metal. Using etching, you can cut out a channel of any thickness or create a complex image. Processing of large workpieces and rolled products is also possible. You can easily adjust the processing depth down to microns, making it possible to process surfaces with complex areas and small grooves. The procedure is used to carry out analysis that determines the formation of intercrystalline corrosion in stainless steel.
In addition, this process is widely used during the processing of carbon, low-alloy and high-alloy steels, non-ferrous metals and titanium. This technology is indispensable when processing small metal parts, watch gears. It is used to manufacture semiconductor chips and printed circuit boards in electronics. This processing method ensures the formation of a conductive channel on the microcircuits. In aircraft manufacturing, etching plays an important role, since through this process the thickness of metal sheets is reduced, thereby reducing the weight of the aircraft. This operation also plays a big role in applying drawings and inscriptions. Etching produces a relief image created by destroying a metal surface according to specific patterns. In everyday life, the operation helps clean the pipeline.