A spring is an elastic element whose purpose is to accumulate and absorb mechanical energy. In technology, the most common springs are made of metal alloys: high-carbon and stainless steels, various types of bronze (beryllium, manganese, tin). But these parts can also be made from other non-metallic materials that have a high degree of strength and elasticity, such as plastic, wood or plywood.
Small springs are made by twisting small-diameter wire, while large ones are cast from annealed steel with further heat treatment.
- Classification
- Main characteristics
- Information from physics
Theory [edit | edit code]
From the point of view of classical physics, a spring can be considered as a device that accumulates potential energy by changing the distance between the atoms of an elastic material.
In the theory of elasticity, Hooke's law states that the tension of an elastic rod is proportional to the force applied to it, directed along its axis. In reality, this law is not fulfilled exactly, but only for small stretches and compressions. If the stress exceeds a certain limit (yield strength), irreversible damage to its structure occurs in the material, and the part collapses or receives irreversible deformation. It should be noted that many real materials do not have a clearly defined yield point, and Hooke's law does not apply to them. In this case, a conditional yield strength is established for the material.
Twisted metal springs convert the compression/tension deformation of the spring into torsional deformation of the material from which it is made, and vice versa, the torsional deformation of the spring into tensile and bending deformation of the metal, repeatedly increasing the elasticity coefficient by increasing the length of the wire resisting external influences. Wave compression springs are similar to many series/parallel connected springs that work in bending.
Stiffness coefficient [edit | edit code]
A twisted cylindrical compression or tension spring, wound from a cylindrical wire and elastically deformed along the axis, has a stiffness coefficient
k = G ⋅ d D 4 8 ⋅ d F 3 ⋅ n , >^<4>> <8cdot d_>^<3>cdot n>>,>
d
D—wire diameter;
d
F - winding diameter (measured from the wire axis);
n
is the number of turns;
G
- shear modulus (for ordinary steel
G
≈ 80 GPa, for copper
Functions of springs
All elastic components to which a load is applied are spring elements. However, springs, in a narrower sense, mean only those elastic elements that can absorb, store and release work over a relatively large distance. The stored energy can also be used to maintain strength. The most important applications of industrial springs:
- Absorption and damping of shock absorbers;
- Potential energy storage (spring motors);
- Application of force (clutch springs);
- Vibrating systems (vibrating table);
- Force measurement (spring scales).
Types of springs [edit | edit code]
By type of perceived load
:
- compression springs;
- extension springs;
- torsion springs;
- bending springs.
Extension springs
— designed to increase in length under load. In an unloaded state, they usually have closed turns. There are hooks or rings at the ends to secure the spring to the structure.
Compression springs
— designed to reduce length under load. The coils of such springs do not touch each other without load. The end coils are pressed against the adjacent ones and the ends of the spring are ground. To avoid loss of stability, long compression springs are placed on mandrels or cups, or smaller wave springs are used.
In tension-compression springs, under the influence of a constant force, the coils experience two types of stress: bending and torsion.
Bend spring
- used to transmit elastic deformations with minor changes in the geometric dimensions of a spring or spring package (springs, disc springs). They have a variety of simple shapes (torsion bars, retaining rings and washers, elastic clamps, relay elements, etc.)
Torsion springs
- can be of two types:
- torsion bar - a rod that exerts torsion (has a greater length than a coil spring)
- twisted springs that work for torsion (as in clothespins, mousetraps and stationery hole punches).
The Bourdon spring is known in instrument making
- a tubular spring in manometers for measuring pressure, playing the role of a sensitive element.
Notes
| : Incorrect or missing image | This article lacks links to sources of information. Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and deleted. You may edit this article to include links to authoritative sources. This mark is set May 7, 2015 . |
K:Wikipedia:Articles without sources (type: not specified)
| There is a more complete article in another language section Ressort (French). You can help the project by expanding the current article with translation. |
Material and manufacturing technology [edit | edit code]
The spring can be made of any material that has sufficiently high strength and elastic properties (steel, plastic, wood, plywood, even cardboard).
The material of various rubbers has elastic properties that do not require giving it a special shape and is often used in its direct form, however, due to less defined characteristics, it is used less often in precision machines.
General-purpose steel springs are made from high-carbon steels (U9A-U12A, 65, 70) alloyed with manganese, silicon, vanadium (65G, 60S2A, 65S2VA). For springs operating in aggressive environments, stainless steel (12Х18Н10Т), beryllium bronze (BrB-2), silicon-manganese bronze (BrKMts3-1), tin-zinc bronze (BrOTs-4-3), titanium (VT-16) and nickel alloys are used (A-286, INCONEL, ELGILOY).
Small springs can be wound from ready-made wire, while powerful ones are made from annealed steel and are hardened after molding.
Read also: The best electric saw for the garden rating
Kinds
Spring elements designed for torsion are used in various fields - from household to many types of industry (in mechanisms and units). Springs are divided into types and types based on different criteria:
- in the direction of winding - left and right;
- according to design features - torsion and coil springs;
- single and double.
Also, the variety of springs includes products made from different grades of elastic steels, coated with a layer of various metals to prevent corrosion and other damage.
The main types can be considered twisted and torsion springs; spiral and screw springs are used less frequently.
Application of springs [edit | edit code]
A spring is one of the most widely used elements of mechanisms, structures, and devices. Used to compensate for dimensional inaccuracies, wear, vibration removal, as an energy storage device, for simple measurement of pressure, weight, forces and accelerations; protection against shocks and overloads.
In stationery [edit | edit code]
- paper clips and stationery pins
- fountain pens and mechanical pencils
- staplers and hole punches
In construction [edit | edit code]
- The simplest door closers without dampers for gates and doors of intensive use, in cold climates for vestibules.
- In return mechanisms of manual blinds, roller shutters and heavy sectional doors.
- In directional valves in public places.
- In elevator buffers.
- In buildings and structures on unstable soils, in geologically active areas, as a seismic wave absorber.
In molds and dies [edit | edit code]
Compression springs with a rectangular wire cross-section are used in molds and dies; they are called tool springs. Thanks to the rectangular cross-section of the wire, the spring has more rigid spring properties with relatively small dimensions, which is very convenient for placing them in molds and dies.
In firearms [edit | edit code]
- Mainspring, recoil spring, magazine spring
- In gun simulation, an airsoft gun is a spring commonly used to push the projectile in spring-piston rifles.
In constant force mechanisms [edit | edit code]
The design of the mechanism or the spring itself ensures a constant force on the load-carrying element over a certain range of movement.
- Constant force supports for pipelines
- Constant force or torque roller springs
- Pipe fitting seals
- Specified load for floating bearings
Springs are elastic structural elements that serve to accumulate or dissipate mechanical energy. They surround us on all sides - under the keys of the computer keyboard, in the car suspension and in the lifting mechanism of the sofa. The most common are coil compression springs. There are several ways to make them.
Where are torsion springs used?
Torsion bars are widely used in various fields:
- Automotive industry (reinforced springs are often installed on SUV suspensions).
- Production of sectional doors (a lifting mechanism that balances the structure and facilitates its opening).
- Manufacturing of measuring instruments and pendulums.
- Manufacturing of multi-threaded gearboxes (evens out torques between parallel gears).
The variety of applications of torsion bars is due to their durability and design features. And in order for them to serve reliably throughout their entire service life, it is necessary to correctly calculate the spring stiffness and select the optimal length and diameter. What matters is the material of manufacture, the anti-corrosion coating, and where and by what technology they are produced.
Coil compression springs
Elastic elements can have different spatial forms. Historically, the first springs mastered by man were leaf springs. You can still see them today - these are springs on heavy-duty trucks. With the development of technology, people have learned to make more compact coil springs that work in compression. In addition to them, spatial elastic elements are also used.
Design Features
During operation, such springs take a load along their axis. In the initial position, there are gaps between their turns. The applied external force deforms the spring, its length decreases until the coils touch. From this moment on, the spring is an absolutely rigid body. As the external force decreases, the shape of the product begins to return to its original shape until it is completely restored when the load disappears.
The main characteristics describing the geometry of the part are:
- The diameter of the rod from which the spring is wound.
- Number of turns.
- Winding step.
- External diameter of the part.
The external shape may differ from cylindrical and represent one of the figures of rotation: cone, barrel (ellipsoid) and others
The winding pitch can be constant or variable. The winding direction is clockwise and counterclockwise.
The cross-section of the turns can be round, flat, square, etc.
The ends of the turns are ground down to a flat shape.
Operating area
Cylindrical coil springs of constant outer diameter and constant pitch are used more widely than others. They are used in areas such as
- Mechanical engineering.
- Instrumentation.
- Vehicles.
- Mining industry.
- Appliances .
and in other industries.
Use of springs in everyday life
Excerpt characterizing Spring
“Ma bonne amie, [My good friend,”] said the little princess on the morning of March 19th after breakfast, and her sponge with mustache rose according to an old habit; but just as in all not only smiles, but the sounds of speeches, even the gaits in this house since the day the terrible news was received, there was sadness, so now the smile of the little princess, who succumbed to the general mood, although she did not know its reason, was such that she reminded me even more of general sadness. – Ma bonne amie, je crains que le fruschtique (comme dit Foka – the cook) de ce matin ne m'aie pas fait du mal. [My friend, I’m afraid that the current frishtik (as cook Foka calls it) might make me sick.] - What’s the matter with you, my soul? You're pale. “Oh, you are very pale,” said Princess Marya in fear, running up to her daughter-in-law with her heavy, soft steps. - Your Excellency, should I send for Marya Bogdanovna? - said one of the maids who was here. (Marya Bogdanovna was a midwife from a district town who had been living in Bald Mountains for another week.) “And indeed,” Princess Marya picked up, “maybe, for sure.” I will go. Courage, mon ange! [Don't be afraid, my angel.] She kissed Lisa and wanted to leave the room. - Oh, no, no! - And besides the pallor, the little princess’s face expressed a childish fear of inevitable physical suffering. - Non, c'est l'estomac... dites que c'est l'estomac, dites, Marie, dites..., [No, this is the stomach... tell me, Masha, that this is the stomach...] - and the princess began to cry childishly, painfully, capriciously and even somewhat feignedly, wringing his little hands. The princess ran out of the room after Marya Bogdanovna. - Mon Dieu! Mon Dieu! [My God! Oh my God!] Oh! – she heard behind her. Rubbing her plump, small, white hands, the midwife was already walking towards her, with a significantly calm face. - Marya Bogdanovna! It seems it has begun,” said Princess Marya, looking at her grandmother with frightened, open eyes. “Well, thank God, princess,” said Marya Bogdanovna without increasing her pace. “You girls shouldn’t know about this.” - But how come the doctor hasn’t arrived from Moscow yet? - said the princess. (At the request of Lisa and Prince Andrey, an obstetrician was sent to Moscow on time, and they were waiting for him every minute.) “Nothing, princess, don’t worry,” said Marya Bogdanovna, “and without the doctor everything will be fine.” Five minutes later, the princess heard from her room that they were carrying something heavy. She looked out - the waiters were carrying a leather sofa that was in Prince Andrei's office into the bedroom for some reason. There was something solemn and quiet on the faces of the people carrying them. Princess Marya sat alone in her room, listening to the sounds of the house, occasionally opening the door when they passed by, and looking closely at what was happening in the corridor. Several women walked in and out with quiet steps, looked at the princess and turned away from her. She did not dare to ask, she closed the door, returned to her room, and then sat down in her chair, then took up her prayer book, then knelt down in front of the icon case. Unfortunately and to her surprise, she felt that prayer did not calm her anxiety. Suddenly the door of her room quietly opened and her old nanny Praskovya Savishna, tied with a scarf, appeared on the threshold; almost never, due to the prince’s prohibition, did not enter her room. “I came to sit with you, Mashenka,” said the nanny, “but I brought the prince’s wedding candles to light in front of the saint, my angel,” she said with a sigh. - Oh, I'm so glad, nanny. - God is merciful, my dear. - The nanny lit candles entwined with gold in front of the icon case and sat down with the stocking by the door. Princess Marya took the book and began to read. Only when steps or voices were heard, the princess looked at each other in fear, questioningly, and the nanny. In all parts of the house the same feeling that Princess Marya experienced while sitting in her room was poured out and possessed everyone. According to the belief that the fewer people know about the suffering of a woman in labor, the less she suffers, everyone tried to pretend not to know; no one spoke about this, but in all the people, in addition to the usual sedateness and respect for good manners that reigned in the prince’s house, one could see one common concern, a softness of heart and an awareness of something great, incomprehensible, taking place at that moment. No laughter could be heard in the big maid's room. In the waitress all the people sat and were silent, ready to do something. The servants burned torches and candles and did not sleep. The old prince, stepping on his heel, walked around the office and sent Tikhon to Marya Bogdanovna to ask: what? - Just tell me: the prince ordered me to ask what? and come tell me what she says. “Report to the prince that labor has begun,” said Marya Bogdanovna, looking significantly at the messenger. Tikhon went and reported to the prince. “Okay,” said the prince, closing the door behind him, and Tikhon no longer heard the slightest sound in the office. A little later, Tikhon entered the office, as if to adjust the candles. Seeing that the prince was lying on the sofa, Tikhon looked at the prince, at his upset face, shook his head, silently approached him and, kissing him on the shoulder, left without adjusting the candles or saying why he had come. The most solemn sacrament in the world continued to be performed. Evening passed, night came. And the feeling of expectation and softening of the heart in the face of the incomprehensible did not fall, but rose. Nobody was sleeping. It was one of those March nights when winter seems to want to take its toll and pours out its last snows and storms with desperate anger. To meet the German doctor from Moscow, who was expected every minute and for whom a support was sent to the main road, to the turn to the country road, horsemen with lanterns were sent to guide him through the potholes and jams. Princess Marya had left the book long ago: she sat silently, fixing her radiant eyes on the wrinkled face of the nanny, familiar to the smallest detail: on a strand of gray hair that had escaped from under a scarf, on the hanging pouch of skin under her chin. Nanny Savishna, with a stocking in her hands, in a quiet voice told, without hearing or understanding her own words, what had been told hundreds of times about how the late princess in Chisinau gave birth to Princess Marya, with a Moldavian peasant woman instead of her grandmother. “God have mercy, you never need a doctor,” she said. Suddenly a gust of wind hit one of the exposed frames of the room (by the will of the prince, one frame was always displayed with larks in each room) and, knocking off the poorly closed bolt, fluttered the damask curtain, and, smelling cold and snow, blew out the candle. Princess Marya shuddered; The nanny, having put down the stocking, went to the window and leaned out and began to catch the folded frame. The cold wind ruffled the ends of her scarf and the gray, stray strands of hair.
Spring requirements
The following properties are required for the work to function effectively:
- high strength;
- plastic;
- elasticity;
- wear resistance.
To ensure the design values of these parameters, it is necessary to correctly select the material, accurately calculate the dimensions, develop and follow the manufacturing technology.
State standards determine the requirements for the manufacture of springs. According to permissible deviations, they belong to one of the accuracy groups:
Schematic representation of a spring
Strict requirements are imposed on the accuracy of geometry and surface cleanliness.
Products with scratches and other external defects that reduce the resource of the product and its service life do not meet the standard
Tips for choosing a mattress
To choose a mattress with an independent spring block and not make a mistake, it is recommended not to rush into the purchase. Customer reviews may not always reflect the real picture. It is known that opinions regarding the parameters of a product may not always coincide.
It is recommended to consult with the store manager and personally check the product for hardness. If the sellers allow you to lie on the mattress, you should take advantage of the offer and see for yourself how comfortable the mattress is specifically for you.
Only after making sure that this is a mattress that you would like to sleep on can you make a purchase.
Material requirements
The strength parameters and fault tolerance of a product are largely determined by the material from which it was decided to be made. Metallurgists distinguish special spring steels in the classification of steels. They have a specific crystal structure, determined both by the chemical composition and the heat treatment of the products. Highly alloyed alloys of increased purity and high metallurgical quality provide high elasticity and ductility, and are able to retain their physical and mechanical properties after repeated deformations.
Spring alloys 60S2A, 50HFA and stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т have gained popularity among mechanism designers.
Classification of blocks and their differences
Depending on the number of springs, their shape and quantity per 1 m2, several types of blocks are distinguished. Their characteristics determine how comfortable a person lying on the mattress will feel.
Pocket Spring or TFK
One of the most popular independent spring blocks. It has good orthopedic characteristics and provides optimal support for the spine.
Spring characteristics:
- diameter - about 6 cm;
- barrel-shaped;
- six turns;
- 220–300 pcs/m2.
Multipocket
Block with excellent anatomical and orthopedic properties. Characterized by high elasticity and the ability to support the body in its natural position.
Spring characteristics:
- diameter no more than 4 cm;
- cylindrical shape;
- number of turns - 10–12;
- 500–1000 pcs/m2, depending on the model.
Micropocket
Elastic block designed for very high loads. Recommended not only for heavier customers, but also for those who prefer hard sleeping surfaces.
Spring characteristics:
- diameter - about 2.5 cm;
- wire thickness - about 1mm;
- number of turns 12–14;
- the spring shape is cylindrical;
- 500–1000 pcs/m2.
The block is in little demand due to its high price.
Hour Glass
The spring block is characterized by moderate elasticity, excellent orthopedic and anatomical properties, which are obtained thanks to the original shape of the spirals.
Spring characteristics:
- diameter - about 6 cm;
- number of turns 7.5;
- the shape of the springs is “hourglass”;
- no more than 300 pcs/m2.
Dual Spring
Spring block with double springs. The name literally translates as “spring within a spring.” Ideal for people with a large weight difference, since the outer coils are designed for a 100 kg load, and the inner ones for 150 kg.
Spring characteristics:
- 256 pcs/m2, internal - 128;
- diameter - about 6 cm;
- cylindrical shape.
Copper Coil
The block is an improved analogue of TFK. It differs in the location of the springs, which allows you to increase their number to 300 pcs. per 1 m2. This characteristic allows you to increase the rigidity of the mattress.
Reinforced
A special category of models designed for loads up to 200 kg. They use more elastic wire for springs, increasing the number of turns and the number of spirals per 1 m2.
With hard zones
Special models containing springs with different characteristics. They are distributed zonally in the block, which allows for different body support, depending on the pressure applied in a particular area. This support allows you to completely relax and maintain the correct body position during sleep.
Features of the technology
The technological process for manufacturing elastic elements depends on the technical requirements for the design. Making a spring is not as easy as an ordinary part, which should not have special elastic properties. This requires special equipment and equipment.
Winding of springs with a round coil section is carried out using the following methods:
- Cold. Suitable for small and medium sizes (wire diameter up to 8 mm).
- Hot. For large diameters.
Spring coiling technology
After winding, the elastic elements are subjected to various types of heat treatment. During this process, the product acquires the specified properties.
Calculation
When making springs, the first step is to make a calculation. If the calculations are made incorrectly, the element will not cope with the load or will fail prematurely.
Read also: Men's three-piece suit (92 photos)
The following values are used for calculation:
- highest torque;
- twist angle;
- diameter of wire and spring;
- material strength – nominal and ultimate.
If you are not an engineer, you should not carry out independent calculations of torsion springs - the probability of error is too high. But to facilitate calculation work, you can find special calculators on websites.
Most often, for the manufacture of springs, standard designs are used, drawings for which are already available, but if it is necessary to make a batch according to an individual order, specialists come into play and develop new documentation.
Read also: Avocado - what is a fruit or vegetable?
The torsion spring drawing includes the following information:
- winding direction (in technical requirements);
- dependence of load on deformation and vice versa;
- hardness value (for products with further heat treatment).
If the number of turns is more than 4, then they may not be fully displayed on the drawings; all necessary information is in the accompanying documentation and technical requirements.
Read also: Why do you need flux when soldering?
Cold coiling technology without hardening
First you need to do preparatory operations. Before a workpiece is wound from wire, it is subjected to a patenting procedure. It consists in heating the material to the plasticity temperature. This operation prepares the wire for the upcoming change in shape.
Read also: How to ring a DC motor
During the winding operation the following parameters must be maintained:
- External diameter of the product (for some parts the internal diameter is standardized).
- Number of turns.
- Winding pitch.
- The total length of the part, taking into account subsequent operations.
- Compliance with the geometry of the end turns.
Cold coiling without tempering
Next, the end turns are ground down to a flat state. This must be done to ensure high-quality support for other structural parts, to prevent their destruction and the spring from slipping out.
The next stage of the technological process is heat treatment. Cold coiling of springs involves only tempering at low temperatures. It allows you to increase elasticity and relieve mechanical stresses that arise during winding.
It is extremely important to strictly adhere to the design heat treatment schedule, carefully controlling temperature and holding time.
After heat treatment, it is necessary to carry out test and control operations.
Further, if necessary, protective coatings can be applied to prevent corrosion. If they were applied by galvanic method, the products are reheated to reduce the hydrogen content in the surface layer.
Research part
As a first example, I explored Newton's first law. This example effectively demonstrates the operation of the law of inertia - Newton's first law.
Next I will demonstrate how I performed it. I inserted a piece of thin steel strip into the horizontal stand to act as a spring. Nearby, on a stand, I installed a short steel tube, on it there was a rectangular piece of cardboard (it should lie strictly horizontally) and a steel ball with a diameter slightly smaller than the hole in the tube. Place the ball on the cardboard so that its center lies above the hole. He bent the spring with his finger and released it.
Returning to its original position, the steel strip hits the edge of the cardboard, it flies away, and the ball falls inside the tube. The example is explained quite simply. The rolling friction force of steel on cardboard is very small, and it is not enough to move a heavy steel ball. According to the law of inertia, a ball in a state of equilibrium strives to maintain a state of rest, and it succeeds perfectly in this.
Example of Newton's first law
As a second example, I studied Newton's third law. I took two identical books. I tied a string around each of two books of equal weight and connected the two strings with several rubber bands put together. Next, I placed the books on a smooth surface and spread them apart so that the elastic bands were taut, and placed the pencil exactly in the middle.
Then I released both books at the same time, and each of them was pulled by the rubber band to the pencil at the same distance.
This example confirms the law that action and reaction are equal. If one book is heavier than the other, then the heavier book will move a smaller distance, but the amounts of motion imparted to both books will not change. They are the same.
Example of Newton's third law
As a third example, I examined springs in toys. I figured this out by familiarizing myself with the structure of some of them. There is a spring inside these toys. A compressed spring has potential energy, due to which the body can do work. Next I set up an experiment. I placed the spring on a metal rod from a tripod. He squeezed it and tied it with thread. I set the thread on fire and the spring flew high up. The spring acquired speed as its potential energy turned into kinetic energy.
Another example was when I started the toy by turning the key, the spring inside the toy compressed and its potential energy increased. The more turns of the key I make, the more the spring will compress, the greater the supply of potential energy the spring will receive. Then I let go of the toy. The spring inside the toy began to unwind, thereby turning the potential energy of the spring into the kinetic energy of the toy. The operation of these toys is based on the law of conservation of mechanical energy.
At home I found spring pistols with suction cup bullets. When I inserted the bullet into the gun, the spring inside compressed. A deformed spring has a reserve of potential energy, due to which, when the trigger is pulled, the bullet begins to move. In accordance with the law of conservation of mechanical energy, the potential energy of the spring is converted into the kinetic energy of the suction cup bullet.
The phenomenon of bullet suction to the surface that follows a shot can also be explained. This phenomenon can be explained by the existence of atmospheric pressure. When the suction cup hits a surface, some air is forced out from underneath the suction cup due to the impact. As a result, atmospheric pressure forces press the suction cup bullet to the surface, because atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure under the suction cup.
Conclusion
While doing this research work on the physics of spring, I learned a lot of new things, became interested in studying physics and began to understand it better. This work is accessible to people of all ages, because to explain the work, I provided enough knowledge of a school physics course.
From the point of view of classical physics, a spring can be considered as a device that accumulates potential energy by changing the distance between the atoms of an elastic material. In the theory of elasticity, Hooke's law states that the tension of an elastic rod is proportional to the force applied to it, directed along its axis. In reality, this law is not fulfilled exactly, but only for small stretches and compressions. If the stress exceeds a certain limit (yield strength), irreversible damage to its structure occurs in the material, and the part collapses or receives irreversible deformation.
As part of my research project on the physics of springs, I became convinced that, according to the law of inertia, a ball in a state of equilibrium tends to maintain its state of rest. Also in the second example, it became clearly clear to me that action and reaction are equal. When completing example 3 and subsequent ones, I began to better understand the designs of toys and the use of springs in them.
I am not going to stop there and plan to continue my work in the next physics project, because there is still so much interesting stuff ahead.
List of sources used
- A.V. Peryshkina - Newton's Laws;
- E. N. Sokolov “To the young physicist” - movement by inertia;
- Elena Tyan - Hooke's Law. Pioneer stories;
- I. Ya. Lanina “Extracurricular work in physics” - dividing toys into groups;
- Savelyev I.V. General physics course - the law of conservation of energy;
- Susskind L., Grabowski D - theoretical minimum;
- Toys whose action is based on Archimedean force.
- History of springs (based on Wikipedia).
- Inertia. Newton's first law.
- Types of springs.
If you liked the page, share it on social networks:
Cold coiling technology with quenching and tempering
The first stages of the technology coincide with the previous process. Changes begin at the heat treatment stage. It is carried out in several stages:
- Hardening. The workpiece is heated to a given temperature and held for 2 to 3 hours. Next, it is subjected to rapid cooling by immersing it in a container with mineral oil or saline solution. During the hardening stage, the workpieces must be in a horizontal position. This will avoid deformation
- Vacation. The workpiece is heated to 200-300° and kept for several hours to relieve internal stresses and improve elastic properties.
Further measuring and control operations are also carried out. The workpieces that have passed the inspection are sent for sandblasting to remove scale. If necessary, shot blasting should also be done to increase the strength of the surface layer of the metal.
The process is completed by applying a protective coating.
Hot coiling technology with quenching and tempering
Before winding, the workpiece is heated to plasticity temperature using one of the following methods
- muffle furnace;
- gas-burner;
- high frequency heating.
Next, the workpiece is supplied to the coiling equipment. The geometry is adjusted and flat ends are formed.
Heat treatment includes hardening and low-temperature tempering.
Heat treatment schedules are constructed based on the properties of the material and the dimensions of the workpiece.
Operating mode of the quenching and tempering furnace line
Next comes the control and measuring stage. Manufacturing is completed by applying anti-corrosion protection.
Equipment and fixtures used
To make an elastic element, specialized equipment is required. These are winding machines. You can make a part on a regular lathe, but it will require additional equipment with special equipment. Medium and large series are produced on semi-automatic machines that operate with minimal operator intervention. You can also make a spring from wire by hand. This will also require special equipment.
At the next stage of machining, the ends are ground on face grinding machines. For single production or small series, this can be done with a grinding wheel.
Heat treatment is carried out using mandrels that prevent product deformation in specialized furnaces for hardening and tempering. Both operations can be done in a universal oven.
Equipment and fixtures used
For quality control, load installations and measuring systems are used. In case of single production, measurements can be made with a universal tool.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Spring manufacturing technology plays an important role and is of great importance for their trouble-free long-term operation. Elastic elements are high-tech products that require qualifications and experience from design engineers and technologists, as well as a good fleet of equipment at the manufacturing enterprise.
The operation of the entire unit, where this part will be a component, depends on how correct the calculations of the spring were, the selection of material taking into account the required characteristics and features of its application, as well as the technologies used and manufacturing accuracy.
How to choose the right one
The first question that needs to be answered is how the furniture will be used.
If this is a folding sofa for sleeping, you should pay attention to orthopedic options with independent blocks. Sleeping on them is much more comfortable, the body will feel rested
Store managers will help you choose a sofa.
It is also important to choose the “right” filler. Foam sofas are not as reliable and durable
After a few years, it will begin to sag, and the springs may dig into people sitting or lying on the sofa
It is better to pay attention to coconut coir - it is tougher and more reliable than foam rubber
The material of its production is high-carbon spring wire of different thicknesses.
For most, the cost of the product plays a significant role. Sofas with dependent spring blocks are the cheapest, but if you plan to use the product for a long time, you should not buy the cheapest models
It is better to pay attention to the average price category, since such sofas will last longer and will not require repairs after a few months
Prices for different springs may vary.
Twisted compression springs: design and operation features
During operation, this type of spring absorbs loads applied in the longitudinal-axial direction. Compression springs initially have gaps between the coils; the application of external force leads to deformation, characterized by a decrease in the length of the product, and is limited to the moment when the coils touch. When the impact is canceled, the spring must restore its shape and geometric dimensions to what they were before the load was applied.
The main dimensions that determine the type of individual part are:
- – Diameter of wire (rods).
- – Number of turns.
- – Winding pitch.
- – Product diameter.
The most common are cylindrical helical compression springs, in which the diameter of the product is the same along the entire length. These parts are widely used in various industries: instrument and mechanical engineering, mining, gas and oil production, and others.
In general, compression springs can have not only a cylindrical shape, but also a conical, barrel-shaped, or more complex one. The pitch of the turns can be constant or variable, and the winding can be clockwise or counterclockwise.
This introduces features into the generally accepted technology of their manufacture.
Spring characteristics
For twisted cylindrical and conical:
- number of turns
- coil pitch
- The diameter of the wire
- maximum load capacity
- linear relationship between the deformation (settlement) of a spring and the load applied to it
For wave:
- tape section
- number of turns
- number of waves per turn
- stiffness coefficient
- ultimate load
also fatigue characteristics of materials.
Spring requirements
To do their job effectively and correctly, these elements must have good strength, ductility, elasticity, endurance and relaxation resistance.
Achieving these qualities is possible subject to many factors, including:
- – Correct choice of material.
- – Competently carried out calculations.
- – Compliance with manufacturing technology.
Read also: Stationary welder workplace
High-quality springs must meet the requirements of GOST and the technical specifications of a specific customer.
According to the standard, there are three accuracy groups for controlled deformations:
- – With permissible deviations up to 5% (+/-).
- - To 10%.
- – Up to 20%.
In accordance with this, three groups of accuracy according to geometric parameters are defined.
An important requirement for these parts is a clean surface; scratches and other defects are not allowed here, as they lead to a decrease in strength and reliability.
Conical springs
As previously noted, to significantly increase stability, a conical spring has recently been often used. It is characterized by the following features:
- In general, we can say that the product as a whole resembles a cylindrical version.
- Each subsequent turn has a diameter smaller than the previous one. That is why this type of spring is characterized by a large diameter of the first turn, since the rest are inserted inside.
- Another important point is the increased resistance of the product to displacement. This is due to the fact that the turns fit into each other, and the distance between them is significantly reduced. Increased stability is something that is required quite often.
- This version is installed in the case when a minimum length of the product in a compressed state is required.
This type of spring is characterized by difficulty in production. This is why the cost of the product increases significantly.
Material requirements
Springs for operation in certain conditions are selected according to standard sizes, taking into account the nature and magnitude of loads characteristic of operating conditions. The reliability of the operation of these parts is determined by many factors, including the quality and structural state of the metal/alloy after heat treatment, and the presence of residual internal stresses. In addition, the metallurgical quality of the steel/alloy is important. So long-term, trouble-free operation begins with choosing a material with a certain set of properties.
Helical compression springs, depending on the size, work performed and other factors, are made of various steels/alloys, including structural spring-spring, stainless steel, and others.
The most widely used materials are steel 60S2A GOST 14959-79, as well as 50KhFA, 51KhFA, 60S2KhFA and similar alloys. Of the stainless steels, the most widely used steel is 12Х18Н10Т.
Types and advantages of mechanisms
The methods of fastening and the location of the springs in the block depend on its type. Let's look at all the options for the mechanism, tell you what a spring snake is in a sofa, and how it differs from a multi-pack.
Choosing a quality sofa is not so easy.
Independent
One of the most reliable and modern blocks. Each spring is in an individual fabric case; the elements are not connected to each other. The mechanical load is distributed only over the springs involved: if there is no pressure on some area, it will not sag under the weight.
Independent springs are considered the best option in sofas for daily sleep.
Due to this feature, blocks with independent springs are considered the most reliable. If one spring fails, you do not have to repair the whole unit. The sofa will not sag and lose elasticity. Most often, sofas with independent blocks have small springs made of thin steel wire.
For springless filling, foam rubber or polyurethane is used.
Bonnell
This system uses double-cone springs, which consist of 4-5 turns. They are connected by a steel frame. The design is impressive and durable. Bonnel has several frames, due to which the rigidity of the base is achieved. This system is reliable and durable.
Dependent springs Bonnel (Bonnel) are an economical option for filling for upholstered furniture.
Bonnell systems are very popular due to their features:
- springs are made of high carbon steel, environmentally friendly;
- The block can be laid on a base made of any material, including plywood or MDF.
The production of Bonnell blocks is simple, so basic mattresses with them are inexpensive.
In corner sofas, the sides are lined with polyurethane foam boxes, and the top is covered with batting or felt. Used for sofas with various folding mechanisms, found in accordions and books. The service life is several years, but with careful use it can last longer.
Multi-package
In appearance and manufacturing pattern they resemble independent springs. Each item is also placed in an individual case. The difference between these blocks is the size of the springs. If in standard independent systems the elements are larger, then in a multi-package a large number of small springs are used.
Smaller springs respond more “sensitively” to pressure - they adapt very well to the user.
At the same time, sofas with such blocks are very durable and can withstand significant weight.
Advantages:
- weight is distributed evenly;
- the springs are not connected; if one fails, the system does not fail;
- due to the cover, the broken spring is not visible through the upholstery;
- have a supporting effect;
- Suitable for most models.
MicroPocket – for sleep, load up to 150 kg.
When purchasing a sofa with a multiblock, you need to pay attention to the number of springs. There must be at least 435 of them
Snake
What does a snake spring look like in a sofa: the elements inside the frame are connected by steel brackets, they are interdependent and resemble a snake in appearance.
Spring snakes are familiar to us from Soviet furniture and in fact are not a block.
Such blocks are made from galvanized steel under high temperatures. The most reliable bases are those with a large number of bends.
Such a sofa “gives up” most quickly under the weight of the human body, is pressed deeply and begins to resemble a hammock.
The main advantage of the mechanism is that it is cheap. However, sofas with a spring snake are not suitable for upholstered furniture for frequent use.
This is the cheapest, but also the most creaky option.
Features of the technology
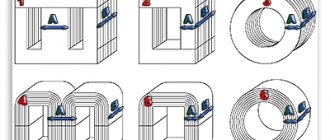
Depending on the intended purpose of such parts and their specifications, it is appropriate to talk about the features of their production technology. The manufacture of products from materials with a round cross-section can be done by cold or hot winding. The first method usually produces small/medium springs (from wire up to 8 mm in diameter), and the second - large ones.
In addition, the difference is determined by the use of different types of heat treatment, which is associated with the need to give the products certain characteristics.
Technology of cold coiling of springs without hardening
The coiling of the blanks is made from wire, which was previously patented by the manufacturer. This process involves heating to a temperature above the transformation range, which perfectly prepares the material for subsequent cold plastic deformation.
The blanks formed by coiling ensure compliance with such mandatory parameters as:
- Diameter (this parameter can be internal, middle or external).
- Number of turns provided (working and general).
- Step and height dimension of the manufactured part (changes possible as a result of subsequent processing are taken into account).
- The correctness of the compression of the outer turns.
The next stage is mechanical finishing (facing), during which the end turns (non-working) are processed until a surface is formed perpendicular to the axis. After this, heat treatment is carried out - in this case - only low-temperature tempering. This imparts permanent elastic properties and eliminates the stresses created during winding. An important technological point is to correctly determine the temperature and exposure time, focusing on the diameter of the selected material and the requirements of the standards. Heat-treated springs are subject to control and testing to ensure that the parameters comply with the requirements of the drawings.
If, according to operational requirements, an anti-corrosion coating is provided, its application becomes the last stage in the production of such parts. Only if galvanization was used are the parts heated to dehydrate them.
Technology of cold coiling of springs with quenching and tempering
The difference between this technology and the previously described one begins only at the heat treatment stage. Previous steps: winding and the necessary mechanical processing are performed in exactly the same way.
The first stage of heat treatment is hardening: heating to a certain temperature (depending on the material used), holding the part for a specified time and forced (rapid) cooling in a special environment, mainly in oil (sometimes in water, saline solution, etc.). Important: to heat the springs for hardening, they are placed horizontally to avoid subsidence under their own weight.
The heat treatment is completed by tempering - heating to a relatively low temperature and holding for a strictly defined time to impart the necessary qualities.
After this, parameters such as hardness and correct compression/recovery are monitored. If provided for by the manufacturing technology of a specific part, sandblasting, shot hardening, and application of a corrosion-preventing protective coating are used.
Technology of hot coiling of springs with quenching and tempering
Hot winding involves preheating the material in an electric or gas oven (a possible option is the use of high-frequency currents).
The workpiece prepared in this way is subjected to winding according to the requirements of the technical specifications, layout, as well as trimming and finishing of geometric values using tools. After this, the part is submitted for hardening, the parameters of which are determined by the material used, and then for tempering.
At the end of the heat treatment, parameters are monitored and, if necessary, crimping, capping, other additional operations and surface treatment are carried out. The production process ends with dyeing and drying.
Pros and cons of using sofas equipped with spring blocks
As a rule, the mechanism we are interested in is built into those pieces of upholstered furniture that are intended for sleeping, that is, folding ones. After transformation, such sofas turn into the most comfortable sleeping place, comfortable and sized for relaxing rest.
This mechanism is universal and very convenient, however, in addition to this, it also has a lot of advantages that need to be taken into account before purchasing.
Let's consider the advantages of the pieces of furniture that interest us, equipped with spring blocks.
Table 1. Advantages of using sofas equipped with spring blocks
| Dignity | Description |
| Long service life | If you choose a high-quality product of the type that interests us in the store, then you will be able to use it for many years after, even if the sofa becomes not a place for evening relaxation, but an intensively and constantly used place for sleeping |
| Ability to withstand heavy weights | Spring blocks are designed to withstand heavy loads, therefore, they can be used as a sleeping place even for people who are prone to obesity or who are obviously overweight. In this case, none of the mentioned persons will experience any discomfort, for example, from squeezing. |
| Adjustment to body features | Spring blocks help the base of the sofa create a body memory effect. In other words, they adapt to your size and other body parameters, and create the most comfortable conditions for rest and sleep. |
| Resistance to deformation | High-quality spring struts do not deform even after prolonged use. In addition, they also show a certain resistance to falls, shocks and other “attacks” on your part, therefore, their properties are preserved for as long as possible. |
| Versatility of use | These mechanisms can be built into sofas of various types, equipped with all sorts of transformation mechanisms, for example, into book sofas, therefore, you can choose a product to your liking without giving up the desired model just because you want a built-in spring block. |
| Acceptable cost | Surprisingly, these spring blocks built into the sofa do not increase the price of the structure too much. Although, definitely, the cost of furniture equipped with them cannot be called low, nevertheless, it is available to almost every buyer, which, of course, cannot but please us. |
Of course, it is almost impossible to independently design such a complex system for comfortable relaxation, since it requires a large number of various production equipment
However, we cannot say that the spring blocks we are interested in have only advantages, since this is fundamentally wrong. In fact, they are not without some disadvantages. Let's take a look at them too.
Table 2. Disadvantages of sofas with built-in spring blocks
Disadvantage Description
Low quality foam rubber
Unfortunately, it often happens that low-quality foam rubber is used as padding for sofas equipped with spring blocks. Of course, this reduces the overall cost of the piece of furniture, however, it ultimately leads to a rapid loss of elasticity and shape. As a result, after a short amount of time it becomes simply impossible to sit or sleep on such a sofa.
Poor spring quality
It also happens that manufacturers decide to save on the quality of the spring block and produce it from materials unsuitable for this. As a result, the main “skeleton” of an upholstered piece of furniture has minimal shock-absorbing characteristics, which leads to sagging of the springs, and subsequently to breakage again.
Excessively high cost
Some manufacturers, taking advantage of the ignorance of customers visiting their store, charge huge prices for sofas, arguing that they are equipped with a high-quality spring block. Unfortunately, the spring block is different from the spring block, and not each of them requires you to pay fabulous sums
Fortunately, there are not many such unscrupulous sellers and manufacturers today, but it is still better to be careful and go to trusted companies.
Equipment and fixtures used
Making springs requires a variety of equipment to best suit the requirements of each step of the process.
Winding is carried out either on special spring-coiling machines, or on turning equipment converted for these purposes. It is also possible to use manual equipment or specialized semi-automatic machines. Further processing - mechanical - is carried out by face grinding machines, and thermal - in hardening and tempering furnaces. Important: to prevent warping during heat treatment, special mandrels are used. For small parts they are used during tempering, while large parts are hardened on a mandrel.
Quality control is also carried out on special equipment designed specifically for this process.