general information
Proper organization of the workplace (welding station) is a prerequisite for the productive work of a welder. The better the workplace is organized, the more convenient it is for the foreman to perform his duties.
The welding workplace has many variations. A welder can work alone or in a team; he can always perform work in one place or be mobile. And the organization of space will depend on each type of work.
The following requirements apply to any welding station:
- The area allocated for the work must be sufficient not only for work manipulations, but also for the free movement of the welder himself.
- The workplace must be equipped with all necessary tools and work surfaces.
- The workplace should provide places for convenient storage of work items.
- The workplace must be ventilated and must also have a sufficient number of light sources.
- The welding station must be safe and fireproof.
This is a brief description of a standard welding location. Subsequently, these points are supplemented with other requirements provided for the performance of certain works.
Other requirements
Also, do not forget about the following additional tools that make the welder’s work easier. This:
- screw clamps for tight contact with the product;
- wire brushes (manual and electric) - to remove slag and rust;
- narrow and wide steel brush for cleaning edges and seams;
- chisels, stamps and hammers - for cutting out places with defects, eliminating splashes, installing a stamp, etc.;
- a hammer with a pointed end for beating off slag;
- a set of templates for measuring the size of seams;
- canvas bags or glasses - for storing electrodes.
The welder should have easy access to consumables: electrodes, wire, flux, etc., so that he can easily change them during work. It is necessary to follow the labor protection instructions individually and generally.
If the welder works with a non-consumable electrode, then he must have a set of sharpened tungsten electrodes, pliers, wrenches, wire cutters, pliers, etc. The tool should be stored in a special box or bag.
Thus, the overall efficiency and safety of the work depends on how competently the workplace of a welder using the manual arc welding method was organized. The workplace is understood as an area assigned to the welder, which is equipped with equipment, tools and devices for welding. A properly organized place reduces injuries and accidents at work.
Types of welding spots
Any preparation of a welder’s workplace begins with defining the work. What kind of work will the master do? Will it be manual arc welding, will he weld on a semi-automatic machine or use other equipment? After all, the workplace of an electric and gas welder will definitely be different from the workplace of an electric welder.
In this article we will talk about a welding place for an electric welder. At the moment, two types of welding places are organized for such work: stationary and mobile. A stationary place is used in factories, workshops and workshops, and a mobile one is used at construction sites, field work, etc.
After the installation of a stationary post, it remains unchanged for a long time. Only welding equipment, components, and worn-out structures are replaced. Simply put, a stationary workplace is a kind of “skeleton” to which other equipment can later be added, but the post itself remains in the same place.
Mobile posts are more flexible. They can be changed and transported many times by changing the set of equipment. Let's take a closer look at what requirements apply to these jobs.
Stationary workplace
A standard stationary welding position for a welder is most often used in large and small industries. The stationary workplace has compact dimensions (on average about 4 sq.m.) and can be located in the open space of the workshop or be separated by special noise-absorbing partitions.
Such a workplace is located permanently at the enterprise; it is not disassembled or transported. Accordingly, all equipment remains directly at the workplace, no matter what shift the welder comes on. At a stationary station, relatively small parts can be welded, since their size is limited by the size of the working area itself.
At a stationary workplace, the welder must have a comfortable table, chair, and storage space. Consumables should be stored in close proximity to the welding table so that the technician can quickly replace them during the work.
If the workplace is enclosed by partitions, special attention should be paid to its lighting and ventilation.
Mobile workplace
The main characteristic of a mobile post is mobility. Having completed such a workplace, you can take it with you and perform work outside the workshop. A mobile workplace is many times more compact than a stationary one. In most cases, it is a cart on which welding equipment and consumables are placed.
Read also: How to correctly set dimensions on a GOST drawing
The mobile post does not have ventilation or special lighting, since it is often used outdoors, where there is natural exchange of air and sunlight.
The main disadvantage of a mobile post is the lack of protection from precipitation. If you have to work outside in the rain, you need to use a special canopy.
Create your own post
You can organize your workspace with your own hands. When creating a mobile welding station, additional components are required to carry tools and consumables.
Collection of tools and materials
When organizing a welder’s workspace you will need:
- Current supply devices. These include transformers or generators, often operating from a 380 V network.
- Cylinders with inert or active gas. Large capacity containers are installed at stationary posts.
- Set of fixing tools. These include vices and clamps.
- Means for pre-processing of metal parts - cold rolling and rolling devices, pipe benders.
- Inverters, semi-automatic welding machines for mobile posts.
- Electrodes, filler wire. It is recommended to purchase different types of materials.
We recommend reading: How to cut metal edges for welding
How to assemble
In the process of creating a welding booth with your own hands, follow the following rules:
- The recommended length of the working area is 2 m, width – 2.5 m. The ceiling height should be at least 2 m. The upper part of the office should not be closed.
- To assemble the walls, sheet steel or plywood treated with a non-flammable composition is used.
- For preliminary preparation and welding of metal parts, a convenient welding table is organized. It can be made stationary or foldable. For assembly, profile pipes and thick steel sheets are used. Tables must be equipped with metal holders that secure the current-carrying cable and grounding wire coming from the power source.
- Containers for storing electrodes and welding wire are placed on the side of the table. Drawers are installed in which small tools and technical documentation will be stored.
- Install single or multi-station arc power sources. The first option is preferable when organizing your workspace yourself. In the second case, the use of current-carrying busbars will be required.
- Install a switch to control the welding current.
Device in stages
A welding room can be set up in a garage, at a production site, or at a technical inspection station. In this case, the following scheme of work is used:
- Choose a place. It is recommended to locate the post away from flammable liquids, materials and gases.
- Assembling the cabin. From the floor to the bottom edge of the walls, leave gaps of 5 cm for ventilation. When working with inert gases, this distance is increased to 30 cm. Ventilation meshes are installed. A tarpaulin or plastic non-flammable screen is hung at the entrance.
- Mount a table with a tabletop. Provides the ability to adjust the height of the racks and the area of the tabletop.
- Install lighting fixtures.
- The cabin walls are painted with light gray paint that absorbs ultraviolet rays. Choose paint compositions based on titanium or zinc.
- Install a forced-type exhaust system. Connect the equipment to a centralized air exchange system.
- The floor is poured with concrete. Brick can be used to form flooring.
- Install a switch for emergency shutdown of welding machines.
At the last stage, connect the equipment to power sources.
More about ventilation
Ventilation is one of the most important elements that must be taken into account when organizing a stationary post. This is especially true for those workplaces where gas is planned to be used. Ventilation is necessary to remove vapors generated during work.
When working at a stationary workplace, a huge amount of dangerous vapors and fine dust is generated. They negatively affect the health of the welder and in some cases can ignite or explode.
To avoid this, an air duct with forced ventilation is mounted above the work station. It works throughout the entire welding operation, and helps not only get rid of dangerous fumes, but also cools the equipment.
When working outdoors, special ventilation is not needed. Natural air movement is more than enough.
Cabin
Organization of a workplace for an electric welder who works in a permanent place in the workshop begins with the arrangement of the cabin. This helps you carry out welding work calmly and protects others from sparks and flashes of light.
The cabin must have dimensions that allow products intended for welding to be brought into it. If the structures being produced are small, then the minimum area of the cabin should be 2 x 2 meters. This will allow you to place everything you need and move freely around the product. To prevent welding radiation from disturbing others, the height of the cabin walls is set to 1.8 m. Since most welding operations are performed at table level, this height will be sufficient. The cabin frame is made of profile pipes or corners. The posts are attached to the floor with anchors. It is possible to provide a door that will completely isolate the welder’s workspace around the perimeter.
To improve natural ventilation, a gap of 150 mm is set between the floor and the beginning of the booth wall. This promotes air flow and raises harmful gases from welding upward. The sides of the cabin can be made of slate sheets or thin iron. Options made of tarpaulin and even plywood are allowed, but these materials must be impregnated with fire-resistant compounds. It is advisable to paint the walls with zinc or titanium white. Yellow crown will do. These substances on the surface of the cabin will absorb ultraviolet radiation well. If you paint such a structure black or dark blue, the overall illumination will deteriorate, since the light coming from the lamp above the workplace will be absorbed.
Additional Information
Organization of the welding place is important, but the rules will only work in conjunction with the correct selection of equipment and welding tools. We will give a couple of recommendations regarding welding clothing, a helmet, wires and a holder. This is the minimum set of tools for a welder, not counting the welding machine, of course.
Protective clothing and mask
Protective clothing and footwear are essential for any welder. If you do not use protective equipment, not a single welding station will help you. Even well stocked.
The welder must wear a special work uniform (trousers and jacket), gloves, and shoes. Clothing must be made of non-flammable materials that are resistant to stains. Shoes should not conduct current. Also, clothing must be resistant to molten metal.
A mask is necessary to protect your eyes, hair and skin. Welding work without a mask is prohibited. The mask must be equipped with a light filter that protects the eyes from radiation. Its weight should not exceed half a kilogram, otherwise the master will quickly get tired of constantly wearing a mask on his head.
We have previously talked about masks, read about it here. We recommend choosing chameleon masks in the mid-price category or above. They are great for regular work and do the job well.
Welding wires
The welding wires also need to be chosen correctly so that they do not cause a short circuit or fire. The better the cable insulation, the higher its strength and reliability.
Pay attention to the workmanship and wire cross-section. If the cross-section is too small, the cable will not be able to withstand the load and will melt, which can lead to dire consequences. However, you should not choose cables with excess cross-section, since they are quite expensive and inconvenient to carry, store and use.
When organizing a welding workplace, make sure that it has a separate place for storing various cables. They should not constantly get tangled and dusty. They also need to be placed closer to the master, but away from explosive substances and materials.
Electrode holder
The correct organization of the workspace also depends on the “holder”. It must be easy to use so that the master can work productively. If you purchase a low-quality holder, all the convenience of the welding station will come to naught.
Any welding place must be equipped with several welding holders. Firstly, for their prompt replacement if necessary, and secondly, for performing various welding works.
When choosing a holder, make sure that its weight is not too heavy, but not too light. You should not experience constant arm fatigue from using a heavy holder. But at the same time, too light a holder can reduce the accuracy of the work. Select the tool individually.
The handle of the holder should be made of rubberized material. It should be easy to grip and not allow current or high temperatures to pass through. If the handle gets hot, the welder can feel it even through protective gloves.
The electrodes should be tightly attached to the holder and not “walk” from side to side.
For holders you need to provide a separate place in which they will be stored. It should also be close enough to the master’s hand so that he does not have to waste time searching for the right tool.
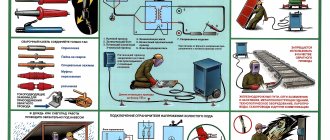
Electric welder station equipment
When equipping a welding station (stationary or mobile) for electric welding, the following conditions must be met:
- grounding is connected to the desktop and equipment housings;
- good illumination of the desktop surface (a combination of artificial light and natural light is allowed);
- floor made of fire-resistant material;
- table cover made of steel or cast iron, at least 20 mm thick, with a connected ground cable;
- drawers or pockets for storing tools, electrodes, technical documentation;
- stool with seat made of insulating material for welding while sitting;
- the presence of a rubber mat on the floor near the table.
When welding is carried out outdoors, the workplace is covered with a canopy or awning made of waterproof material to protect from rain, snow, and sun.
Stationary
Stationary welding stations are made in the form of booths without an upper ceiling.
Example of a stationary welding station
When arranging, take into account the requirements of regulatory documents:
- The area is not less than 3 m², the walls are 2 m high. A screen made of tarpaulin or non-flammable plastic is hung at the entrance.
- Ventilation gaps of at least 50 mm in size are left from the floor to the bottom edge of the walls. When working with inert gas, the gap is increased to 300 mm. The gaps are covered with a metal mesh with small cells.
- Install a table with a tabletop of at least 1 m². For working in a sitting position, its height is 60 - 70 cm, for welding standing from 85 cm.
- The walls are made of sheet iron, asbestos-cement slabs or non-combustible materials treated with a fire-resistant composition.
- A lamp is installed above the table.
- The walls are covered with light gray paint that has the ability to absorb ultraviolet radiation (zinc-based compositions or titanium white).
- An exhaust hood is installed or, when organizing a welding station in the workshop, it is connected to a centralized supply and exhaust air exchange system.
- The floor is poured with concrete or laid with bricks.
- A switch is installed inside the cabin to quickly turn off electrical equipment if an emergency occurs.
General view of a typical welding station
Mobile
When equipping mobile welding stations for manual welding, it is not necessary to organize air exchange or maintain the dimensions of the workplace. However, the safety requirements that apply to the stationary type must be observed. The trolley for moving equipment should have comfortable wheels that ensure transportation of the post without excessive effort.
Example of a mobile welding station
To carry out welding, a portable welding machine with a set of cables is used, which is moved along the object. To protect from bad weather, the mobile post is equipped with shields for installing a canopy. Tools and electrodes are stored in cabinets and holders. To protect nearby people from light radiation, the workplace is fenced with portable shields. When laying long pipelines, mobile welding stations are installed in small trailers on wheels from cars with an autonomous electric generator.
Purpose of equipping the welder's workplace
Organization of a welder’s workplace is a procedure that provides for the provision of the most favorable conditions for welding. One welder or a whole team can be responsible for a section. Among the features the following points can be noted:
- As a rule, a certain area located in a structure or at the site of construction and repair acts as a welder’s place.
- When considering the requirements for a workplace, most attention is paid to the fact that it must be equipped with the required tools and equipment.
- Preparing the work area also includes removing unnecessary items that could compromise welding safety.
- The organization is carried out taking into account the size and type of structure being processed. Particular attention is paid to ensuring that the welder or assistants do not have to fix the workpieces. This is prohibited by accepted safety precautions.
Schematic illustration of a welder's cabin
In general, we can say that only with proper organization of the workplace in accordance with safety precautions can welding be performed efficiently. This takes into account the welding location, environmental conditions and many other points.
Welding tables
Welding booths must be isolated from outsiders. They house a welding table and other work accessories, so they are quite spacious. The size of the cabins is 2*2 or 2*3 meters, and the height is up to 2 meters. To improve ventilation, the walls are mounted so that there is a gap of 20 cm from the floor.
Welding tables are used for welding and assembling parts. They are located inside the welding cabin at a height of 50-60 cm if the post involves welding in a sitting position, or at a height of 90 cm if the work is performed while standing.
The table area is at least one square meter. The requirement for the welder's workplace involves the use of special bolts to which the wires from the welding machine are attached. To suck dust from the welding arc, it is not allowed to place an exhaust hood, since otherwise the flow of gases and dust will pass through the welder’s respiratory tract.
There should be sockets for electrodes on the table. If the desk has a drawer, then documents and tools should be stored there. There is one more requirement: there must be a rubber mat under the welder’s feet.
If the table is equipped with local suction, it can be installed both on the table and outside the room. The fan built into the desk creates noise that reduces productivity. The optimal design for a welder's table is one with lower-side suction and installation of a fan outside the room: then dust and gas do not enter the welder's breathing zone.
Additional amenities may be provided in welding tables . For example, many welders practice stripping the end of the electrode by touching it to the surface of the table. As a result, after a certain period of time, metal growths form on the table, which interfere with the movement of products on the table and worsen its aesthetic properties. To prevent this from happening, the table surface is edged with copper plates at the edges. As a result, the table surface is not contaminated by the electrodes, since the metal does not stick to the copper.
Local lighting may be provided in the table . For welding small parts, when seams are applied around the perimeter, it is advisable to use a rotating table, which is adjustable in height with screws. This allows the parts to be raised and lowered to a comfortable position. During such work, the welder gets less tired and is less exposed to harmful emissions.
To eliminate the awkward position, you need to provide the welder with a seat that is height adjustable.
What are the locations for welding work?
Safety precautions and many other regulatory documents determine the classification of the workplace into several types. An example is the information below:
The first type is most often associated with special premises in workshops, the second - mobile ones, required for traveling to the site of an accident or construction. The welder's cabin is equipped only once in accordance with safety regulations, after which attention is paid only to the technical condition of critical mechanisms and structures.
Read also: How to harden a chainsaw chain
Electric welder station equipment
When equipping a welding station (stationary or mobile) for electric welding, the following conditions must be met:
- grounding is connected to the desktop and equipment housings;
- good illumination of the desktop surface (a combination of artificial light and natural light is allowed);
- floor made of fire-resistant material;
- table cover made of steel or cast iron, at least 20 mm thick, with a connected ground cable;
- drawers or pockets for storing tools, electrodes, technical documentation;
- stool with seat made of insulating material for welding while sitting;
- the presence of a rubber mat on the floor near the table.
When welding is carried out outdoors, the workplace is covered with a canopy or awning made of waterproof material to protect from rain, snow, and sun.
Stationary
Stationary welding stations are made in the form of booths without an upper ceiling.
Example of a stationary welding station
When arranging, take into account the requirements of regulatory documents:
- The area is not less than 3 m², the walls are 2 m high. A screen made of tarpaulin or non-flammable plastic is hung at the entrance.
- Ventilation gaps of at least 50 mm in size are left from the floor to the bottom edge of the walls. When working with inert gas, the gap is increased to 300 mm. The gaps are covered with a metal mesh with small cells.
- Install a table with a tabletop of at least 1 m². For working in a sitting position, its height is 60 - 70 cm, for welding standing from 85 cm.
- The walls are made of sheet iron, asbestos-cement slabs or non-combustible materials treated with a fire-resistant composition.
- A lamp is installed above the table.
- The walls are covered with light gray paint that has the ability to absorb ultraviolet radiation (zinc-based compositions or titanium white).
- An exhaust hood is installed or, when organizing a welding station in the workshop, it is connected to a centralized supply and exhaust air exchange system.
- The floor is poured with concrete or laid with bricks.
- A switch is installed inside the cabin to quickly turn off electrical equipment if an emergency occurs.
General view of a typical welding station
Mobile
When equipping mobile welding stations for manual welding, it is not necessary to organize air exchange or maintain the dimensions of the workplace. However, the safety requirements that apply to the stationary type must be observed. The trolley for moving equipment should have comfortable wheels that ensure transportation of the post without excessive effort.
Example of a mobile welding station
To carry out welding, a portable welding machine with a set of cables is used, which is moved along the object. To protect from bad weather, the mobile post is equipped with shields for installing a canopy. Tools and electrodes are stored in cabinets and holders. To protect nearby people from light radiation, the workplace is fenced with portable shields. When laying long pipelines, mobile welding stations are installed in small trailers on wheels from cars with an autonomous electric generator.
Stationary workplace
A stationary welder's position is found in various production workshops. They are suitable for welding small products. Among the features of equipping such premises, the following points can be noted:
- If the premises are properly equipped, unhindered access to workpieces is ensured.
- Explosive and flammable substances should not be located nearby.
- When using inverters that operate on flammable substances, cylinders should be located away from open flames.
- Unobstructed access should be provided to consumables, for example, electrodes and wire. This is due to the fact that during welding you need to quickly change some elements.
- The stationary location is prepared taking into account exactly which elements will be welded together. Safety precautions require that the welder's workplace ensures that the workpieces remain stationary during processing.
Stationary welding station
Training is carried out by following specific instructions, which are developed by an employee of the organization.
How to equip an electric welder's station
Regardless of the functionality (fixed or mobile), the place where the electric welder works must meet these requirements.
- Mandatory grounding of equipment.
- Sufficient illumination (it is best to combine natural and artificial light).
- Concrete or brick floors.
- A tabletop made of steel and cast iron, to which the ground cable is connected.
- The presence of drawers or pockets where you can put electrodes.
- To make it possible to work while sitting, the seat is made of dielectric material.
- A rubber mat to stand on.
Also, for outdoor work, a cover is installed to protect the area from precipitation.
Stationary post
Stationary posts must meet the following requirements.
- A fixed workplace is usually made in the form of a closed cabin without a roof. The area of such a post should not be less than 3 m². The height of the walls is 2 meters. The entrance to the cabin is covered with a tarpaulin screen.
- At the bottom of the cabin there should be a gap between the walls and the floor (250-300 millimeters).
- The work table is made of steel or cast iron. The countertop area is at least one square meter.
- The table itself can be adjusted in height so that the welder can work standing or sitting. For standing work, the tabletop is installed at a distance of 90 cm from the floor. For sedentary work - 50-60 cm.
- The surrounding walls of such a booth must be made of non-combustible material. They are painted in light gray tones. The white itself must absorb ultraviolet radiation.
- A good exhaust hood must be installed to remove smoke and other combustion products. Supply ventilation is also needed. At the same time, according to safety requirements, ventilation must ensure air exchange with a volume of at least 40 cubic meters. meters per hour.
- Lighting should be at least 60-80 lumens in brightness. It’s very good when such a post can combine street light with artificial lamp light.
Fixed posts are required to have all equipment grounded!
In addition, stationary welding equipment must be installed. It is necessary to have a switch that allows you to de-energize all devices in an emergency.
There are also additional drawers and mounts for consumables and tools.
Mobile post
Such posts are very convenient when welding in large spaces and working with structures with large parameters.
- All equipment for electric welding is located on a mobile cart.
- The length of the cables should ensure ease of movement during operation.
- When welding outdoors, do not provide additional ventilation. The combustion products released during the welding process themselves quickly spread.
- A portable welding station for outdoor work must have shields for quick assembly of the canopy in case of precipitation.
- To protect others from the effects of electric arc flashes, such posts must additionally be equipped with collapsible shields that can be easily moved around the territory.
- To make it convenient for the welder to work, mobile posts additionally have special stands and mounts for placing electrodes and tools.
Mobile post
A mobile place can be created for a gas and electronic inverter. It is worth considering that a welding cabin is required for its installation in case of high ambient humidity.
The fewest problems arise when using gas welding. This is because electrical equipment must be reliably powered.
Additional accessories and tools
Additional tools include: steel brush - necessary for cleaning the metal from dirt, rust before welding and slag upon completion of the weld; a hammer with a pointed end, which is used to knock off slag from the surface of the seam; chisel for cutting out a defective place in a weld - used to cut off drops of frozen metal from the surface of the product.
To carry out measuring work, the welder needs a tape measure, a ruler, a square, as well as a white marker for marking the product being prepared.
Welding wires: purpose, recommended cross-sections
The organization of the welding station involves the use of a cable of the most suitable cross-section. This indicator should be taken into account for the following reasons:
- If the cross-section is too small, the cable cannot withstand the load and begins to overheat. As a result, heat acts on the insulation, causing it to melt. If the damage is severe, a short circuit may occur.
- Large cables are expensive. At the same time, they are less practical to use; transportation and storage creates many problems.
Cable selection is carried out in accordance with regulatory documentation. The organization of the welder's workplace is carried out taking into account the fact that the cables should not be intertwined, all contacts should be fixed. Cable and other electrical equipment should not be located near flammable materials or water.
The optimal cross-sections of the welding wire are presented in the following table. As previously noted, the choice of wires is selected depending on the power of the equipment used by the welder. The optimal indicator is selected in accordance with the table.
Table of cable cross-sections depending on power
Using tabular data allows you to avoid quite a lot of problems. A high-quality cable has effective insulation, which eliminates the possibility of a short circuit.
Holder
The welder's main tool is the holder. Productivity and quality depend on its convenience and thoughtfulness. The holder can be of two types: to clamp the electrode like a clothespin, or to tighten it by twisting the handle. Regardless of the type, it should allow the electrode to be changed in 4 seconds.
The structure is well insulated to prevent electric shock. The cable and the holder itself constantly exert their weight on the welder’s hand. Therefore, the mass of these elements should be minimal so as not to overwork the welder and not limit movement.
If work is carried out at high current (from 500 A), then the holder is equipped with a protective pad that prevents the welder’s hand from being damaged by high arc temperatures. When the welding current exceeds 600 A, the cable is passed to the electric holder, bypassing the handle that the worker grasps. The sides that secure the electrode are subject to the adhesion of molten metal splashes, making it difficult to replace a new consumable element. This slows down the entire process and the welder gets tired faster. To prevent this effect, the surface of the holder on which drops of metal fly is lubricated with a scraper and cleaned at the end of the day with a needle file.
How to choose an electric holder
When organizing your workplace, you also need to choose the right electrical holder. How safe the workplace will be and what labor productivity will depend on its technical condition. The welding station can be equipped with several types of holders, it all depends on the type of work being carried out.
When choosing such a device, pay attention to the following points:
- Weight should not be more than 0.5 kilograms. Excessively heavy versions complicate the welder's task. When welding for a long time, your hands will get tired, which will ultimately reduce your productivity.
- Attention is paid to how comfortable the grip is. To prevent the handle from slipping, its surface is often grooved.
- During operation, the structure should not become very hot. Otherwise, problems may arise during prolonged welding. Although the welder must use special gloves, high heat causes significant discomfort.
- The surface must be insulated, since such an element should become a barrier to electricity in the event of a malfunction. When organizing the workplace, attention is paid to the quality and integrity of the insulation.
- The fastening of the electrodes must be strong, since at the moment of contact with the surface they are subject to mechanical stress.
It is recommended to purchase original electrical holders recommended by the manufacturer for organizing the workplace. Before each work, the condition of the structure is checked.
Types of ventilation systems and arrangement rules
An exhaust hood for a welding station, installed according to the rules, can significantly reduce the concentration of hazardous substances in the atmosphere and minimize harm to the environment. The type and power of fans, as well as the routing of air ducts, are selected taking into account the number and location of places for welders. Exhaust structures can be placed on the roofs of workshops or near them; the air intake should not be located in the area for the emission of polluted air.
Local
The welding shop or workshop has local and general exhaust
When creating a local type hood, the ventilation of the posts is selected taking into account the size of the elements being welded and the intensity of the work. The amount and composition of the gases formed depends on these nuances. Thanks to the simple design and design, the productivity of such a system reaches 5.5 thousand m3/hour. During welding and surfacing of large products on tables not equipped with devices, welding aerosols are removed using suction from mobile units with filtration ventilation. For some types of work, it is advisable to use lift-and-swivel hoods. Their design includes a flexible hose with a diameter of up to 200 mm, mounted on a console and directed to the desired area. The receiving pipe is placed at a distance of 7-8 meters from the worker.
General exchange
Exhaust fans at welding stations
The general exchange type system includes injection and exhaust fans, as well as air ducts equipped with filters and adjustable supply structures. Such ventilation is designed to provide fresh air to all areas of the workshop and reduce the content of harmful impurities in the atmosphere. It is worth choosing if more than 200 g/hour of electrodes per 1 m3 of the total volume of the room is used during the work. Otherwise, the influx of air masses will be provided naturally.
In winter, outside air is supplied to the workshop at a temperature not lower than +18 degrees. General ventilation for the welding station must be supplemented with filtration elements that purify the air before being released into the space. The performance of the devices is selected to ensure a 10-fold air exchange. The vertical speed of movement of air masses is maintained at no lower than 0.1 m/s. This value is sufficient for mixing media and eliminating welding aerosols from areas outside the posts.
Inside closed and semi-enclosed spaces
To organize a ventilation system inside a closed or semi-enclosed space, there are several available schemes.
In the workshop, you can create an organized air exchange in one container, where clean air will be supplied from outside. Next, the air masses are removed mechanically due to the combined action of inflow and exhaust. The second method involves removing contaminated masses near electric welding arcs; there is also a third option, which involves ventilating only the worker’s breathing zone by supplying clean air under the shield. The most common type of system is a tank ventilation scheme using a supply jet, which involves the installation of flexible hoses and high-pressure fans. The main advantage of this method is the supply of clean and heated air from the street during the cold season. Tanks in this arrangement are located in specially designated areas. To determine the volume of supplied air, its speed in the work area should not exceed 0.7-2.0 m/s for manual welding. You can avoid the entry of polluted air into the workshop by installing the mass supply from the opposite side.
Electric welder mask as a means of protection
Safety precautions for organizing a place for welders include the use of special shields and a helmet. When manufacturing them, the standards established in GOST 12.4035-78 must be taken into account. Among the main standards we note the following:
- The structure should not be heavier than 0.5 kilograms. Otherwise, it will be difficult to carry out the work.
- In order to protect the eyes, light filters are installed. They are divided into 13 classes, the choice is made depending on the power.
- When choosing a mask, attention is paid to ensuring that it fits comfortably. From time to time the welder has to open it for visual inspection of the seam.
There are a wide variety of protective masks available on the market. More expensive versions are characterized by greater efficiency. If you frequently carry out welding work, it is recommended to purchase a high-quality product, since ultraviolet and other radiation can be harmful to health.
Welder tools
The welder's tool is equipped taking into account the specifics of the upcoming welding work. However, there is a certain list of tools, the presence of which is strictly mandatory for a competent specialist. Without these elements, the welding process is impossible by definition.
Such tools include:
1. Electrode holder, on the quality and reliability of which the convenience of work and labor safety depend. The electrode holder cannot weigh more than 0.5 kg, must be in good working order, the electrode must not dangle in it, and the handle must be rubberized.
2. Welding electrodes. Electrodes are classified by brand, type, coating thickness, quality, purpose and permissible spatial positions. Of course, the electrode must match the type of metal being welded. Before work, you need to make sure that the electrode coating is uniform, dense, durable, without cracks or sagging. Among other things, a welder working with a non-consumable electrode must have with him a set of ground tungsten electrodes, a set of keys, pliers or wire cutters.
Ventilation requirements
It is necessary to pay attention to the efficiency of ventilation when organizing the place, especially when working with a gas apparatus. Its purpose is to remove warm air and supply cold air, which is required for cooling tools and equipment.
During operation, quite a large amount of toxic gases can be formed. At high concentrations there is a risk of poisoning. If the concentration of gases is high, then there is a possibility of their detonation.
As a rule, artificial ventilation is represented by air ducts that supply and discharge air. To improve operating efficiency, a fan is installed. Problems with equipment cooling and gas pollution practically do not arise when work is carried out outdoors.
Ventilation
When using gas in the welding process, it is necessary to ensure good ventilation of the room.
Ventilation is needed for several reasons:
- To reduce the concentration of toxic substances that may be released from the metals being welded . When carrying out welding work, various harmful impurities can be released into the air: carbon monoxide, nitrogen monoxide and fluoride inclusions.
- In order to remove gas contamination from the room , which can lead to detonation.
- To ensure cooling of working tools and equipment that overheats during operation.
Ventilation can be natural, which is carried out using air flow from the street, as well as artificial. For artificial ventilation, special hoods, fans and other means of air circulation are used.
Exhaust ventilation is designed to remove harmful gases from the room as much as possible, while supply ventilation is designed to compensate for organized exhaust by diluting substances to acceptable working concentrations for health.
The best option for a welder's workbench is one that is equipped with dust extraction directed downward or to the side. The effectiveness of the suction of harmful substances from the inhalation zone is ensured by the close location of the exhaust intakes to the arc site.
Requirements for special clothing
Special clothing can be considered personal protective equipment. It is manufactured taking into account the characteristics of metal processing, as well as the possible impact. The kit includes:
In most cases, they are made using tarpaulins to which asbestos is added. Due to this composition, the surface becomes much more resistant to the ingress of molten metal.
Welder clothing
The welder's suit is made from specialized fire-resistant fabric, which is designed to protect the specialist from sparks and splashes of molten metal and does not melt from contact with heated surfaces, which eliminates burns.
Moreover, the welder has no right to perform any type of fire welding work without a protective set of clothing, the list of which includes:
- Actually the welder's suit itself, which complies with the required GOST.
- Special shoes resistant to the thermal effects of sparks and steel splashes.
- Work mittens or gloves, mostly made of canvas.
Advantages of welding curtains
Special curtains are very popular. They make it possible to significantly simplify work and divide the site into several sectors. The features of such equipment include the following points:
- Fire-resistant fabric is used in production.
- The material used can also withstand minor mechanical stress.
Variety of welding curtains
There are several versions of such equipment, each characterized by its own characteristics.
Equipment for organizing a welding station
The welder's workplace (welding station) must be equipped in accordance with the requirements of SNiP and the technological process being carried out with certain equipment, tools, devices, etc. Depending on the work performed and the dimensions of the structures being welded, the welding station is located in special welding cabins. Cabins must be illuminated by daylight or artificial light, and also equipped with ventilation.
Safety fences
Universal metalworking workbench
The universal workbench is designed for metalworking and assembly, straightening, finishing, installation, adjustment, adjustment and other types of work.
Combination welder's table
A welder's table with a combined working surface is used as a stationary welding station. The table is designed for welding, as well as metalworking, assembly, finishing, straightening, cleaning, grinding and other works.
Solid standard curtain
Most often, a continuous curtain is installed. It is represented by a solid material that is attached to special load-bearing elements. Among the features we note:
- Visual protection and blocking ultraviolet radiation.
- Protects the environment from splashes and molten metal.
- The negative impact of side air flows is reduced.
Solid standard curtain
When choosing the most suitable curtain, attention is paid to the width of the seams, the thickness of the material and some other points.
Text of the book “Occupational safety during welding work”
3.3. Workplace of a gas welder and gas cutter
To perform gas welding work, you need cylinders with oxygen and flammable gases, an acetylene generator, gearboxes, rubber hoses (sleeves), safety valves, welding torches, cutters, etc.
The workplace of a gas welder and gas cutter is a welding station. Under the term "welding post"
understand the workplace where gas-flame processing of metals is carried out. Work stations can be mobile or stationary.
Mobile work station
used, as a rule, for manual welding work performed in the workshop, as well as during installation and on construction sites.
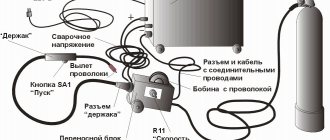
Gas supply to mobile work stations is carried out according to the diagrams shown in Fig. 3.1. Oxygen and flammable gas cylinders with appropriate pressure reducers are usually used as power sources. Gases are supplied to the working tool (burner or cutter) through a hose at least 10 m long (Fig. 3.1, a).
Instead of an acetylene cylinder, a mobile generator with a safety shutter is sometimes used (Fig. 3.1,
b).
For ease of moving the mobile post, it is allowed to install the equipment on one trolley. The acetylene mobile generator must be no closer than 5 m from the oxygen cylinder during operation. Transportation of the generator in a charged state is prohibited.
A gas welder (gas cutter) must have at his workplace pliers, a hammer, a metal brush for cleaning the metal surface, needles for cleaning mouthpieces and a small crowbar for turning the workpieces (parts), as well as tools (keys) for fastening gearboxes and opening (closing) valves cylinders and eliminating minor malfunctions of burners (cutters).
Rice. 3.1.
Gas supply diagram for a mobile welding station:
a -
from cylinders;
b -
from an acetylene generator;
1 —
oxygen cylinder;
2 —
oxygen reducer;
3 —
cylinder with acetylene;
4 —
sleeves;
5 -
burner;
6 -
mobile acetylene generator
Welders (gas cutters) are supplied with special clothing in accordance with established standards and safety glasses (with filter density C-3 when working with cutters and C-4 when welding with acetylene consumption up to 2500 l/h).
When using mobile posts in enclosed spaces, it is necessary to ensure natural or forced ventilation.
Stationary work station
(Fig. 3.2) is intended for performing manual and mechanized work in a workshop, site or workshop.
Gas supply (gas supply) to stationary posts is carried out centrally: gas is supplied through gas pipelines to places of consumption if the number of posts exceeds 10. With a smaller number of posts, when the installation of gas pipelines is irrational, gas supply from individual cylinders is allowed.
Oxygen is supplied to stationary work stations via a gas pipeline from an oxygen plant, gasifier or bypass ramp, and acetylene is supplied via a gas pipeline from an acetylene plant, stationary generator or bypass ramp. In the latter case, acetylene is supplied directly to the workshop gas pipeline.
Rice. 3.2.
Stationary work station for a gas welder:
1 -
welding table;
2 -
cover;
3 -
box for storing materials;
4 -
filler material;
5 —
reducer for supplying oxygen to the burner (cutter);
6 -
oxygen line;
7 – safety shutter; 8, 9 —
hoses for supplying acetylene and oxygen;
10 -
economizer;
11 -
burner;
12 -
water box;
13 —
swivel chair; ventilation with local air suction in the amount of 1700–2500 m3/h is not shown in the figure
When using other acetylene power sources, a central (group) safety liquid or dry shutter is installed at the entrance of the acetylene pipeline to the workshop, designed to protect the inter-shop gas pipeline from backfire. The type of valve is selected depending on the pressure and flow rate of acetylene.
Directly behind the valve (along the gas flow) at the gas inlet into the workshop, an acetylene input cabinet with a shut-off valve and a pressure gauge is installed, which should be located in an accessible and convenient place. Shut-off valves are located on branches of acetylene pipelines intended for supplying acetylene to individual sections of the workshop.
A pipeline for discharging purge gases into the atmosphere is connected to the acetylene line through a shut-off valve. This pipeline is located at least 1 m above the ridge of the ceiling. Similarly, a discharge pipeline is connected to the oxygen line through a shut-off valve.
At the entrance of the oxygen pipeline to the workshop, as well as at each branch of the intra-shop gas pipeline distribution, shut-off valves are installed.
The height of the acetylene pipeline above the floor must be at least 2.2 m, and the oxygen pipeline - at least 1.6–1.8 m. The oxygen pipeline is laid at least 250 mm below the acetylene pipeline (if parallel). The distance between gas pipelines when crossing them must be at least 100 mm.
In places where gases are consumed, gas dispensing stations are installed on acetylene and oxygen gas pipelines, which include appropriate shut-off, control and safety devices that ensure normal operation of gas welding equipment. It is supplied with oxygen from the gas disassembly station reducer if the oxygen pressure in the gas pipeline does not exceed 1.6 MPa (16 kgf/cm2).
When the oxygen pressure in the gas pipeline cannot be more than 1.6 MPa and the oxygen consumption does not exceed 10 m3/h, a gas dispensing station with a network reducer is used. In this case, connecting the equipment to the gas pipeline is allowed directly (without a gearbox) through a shut-off valve and the gas dispensing station does not have a regulating device.
In all cases, a tool (torch or cutter) must be connected to an acetylene gas pipeline through a safety device: a liquid or dry seal.
When supplying workshop gas pipelines for acetylene from bypass ramps, when the pressure in the network can exceed 0.12 MPa (1.2 kgf/cm2), a gas dispensing station with a dry seal is used. If the pressure in the acetylene pipeline cannot exceed 0.07 MPa (0.7 kgf/cm2), gas dispensing stations with a liquid or dry seal are used.
Safety valves must correspond to the maximum possible pressure in the acetylene line and gas flow. To connect equipment (burners, cutters) to gas distribution stations, hoses are used: for acetylene - class I, for oxygen - class III.
When using acetylene substitute gases with a gas pressure of up to 0.15 MPa (1.5 kgf/cm2), to protect the gas pipeline from the flow of oxygen into it, a check valve is installed at each gas dispensing station instead of a stationary safety liquid or dry valve. In the case when the pressure of flammable gas in the gas pipeline may exceed 0.15 MPa, a reducer is installed that reduces the gas pressure and protects the gas pipeline from oxygen entering it.
The propane-butane mixture is supplied to stationary work stations through gas pipelines from a dispensing station or from bypass (discharge) ramps. A typical gas supply scheme for stationary work stations using oxygen and propane-butane differs from typical schemes using other acetylene substitute gases only in the composition of the equipment. Moreover, the oxygen pipeline is laid above the gas pipeline for flammable gas at a distance of 250 mm. The choice of power sources, shut-off and reducing equipment, as well as safety devices depends on gas flow and pressure.
The stationary work station for manual work includes:
♦ gas dispensing station for supplying gases to burners or cutters;
♦ table with devices for fastening workpieces;
♦ local exhaust ventilation system to remove harmful emissions generated during gas-flame work;
♦ lifting device for moving processed products;
♦ fire-fighting inventory and equipment.
Gas dispensing stations included in the work station are built into the table or placed on gas consumption pipelines.
Work tables for welding are covered with a metal plate or brick. Equipping tables with a general or local ventilation device is carried out taking into account the type of work performed.
Each work station must have a tool (keys) for connecting equipment to power sources and troubleshooting possible problems with the operation of burners and cutters.
There should be a bucket of water next to the welding table to cool the torches during operation.
When gas welding cast iron, in addition to the listed equipment, heating devices (furnace, forge, etc.) are installed at the work station - at a distance of at least 5 m from the work site. Boxes with sand should also be located nearby to cool parts prone to cracking.
The equipment of a stationary post for mechanized work includes a mechanism for moving tools and products (or one of them).
When using oxygen-flux cutting, the flux feeder should be located at a distance of at least 5 m from the cutting site.
Causes of accidents during gas welding work.
The main causes of accidents when performing gas welding work are:
♦ explosion of mixtures of flammable gases with air and oxygen;
♦ explosion of acetylene generators due to backfire and oxygen entering them;
♦ explosion of carbide drums when they are opened due to the presence of an acetylene-air mixture in them;
♦ explosion of oxygen reducers when solid objects in the form of individual grains of sand enter them and the valve of the oxygen cylinder is suddenly opened;
♦ explosion of cylinders and other vessels that are under high pressure during operation due to heating, falls, impacts and other violations of the rules for using cylinders, as well as fire;
♦ ignition of oxygen hoses due to backfire;
♦ self-ignition and explosion when high-pressure oxygen combines with fuels and lubricants;
♦ ignition and explosion of tanks with fuel and liquids during cutting when they are placed near a fire source and the hose supplying flammable gas is incorrectly secured.
In addition, poisoning is possible with combustion products of flammable gases or vapors of the material being welded in the absence of ventilation or personal protective equipment (gas masks, respirators, etc.).
Performing work without appropriate protective clothing and footwear, as well as without safety glasses, leads to body burns and eye disease.
3.4. Gases for gas welding and cutting
Oxygen -
a colorless, odorless gas, heavier than air (the density of oxygen at a temperature of 0 °C is 1.429 kg/m3). Oxygen does not burn, but supports combustion by forming chemical compounds with almost all substances. In gas cutting, oxygen is used to produce a high temperature preheating flame and burn the metal at the cut site. Oil and fat in a stream of oxygen spontaneously ignite as a result of rapid oxidation.
Acetylene
-
a colorless flammable gas, lighter than air, with a weak ethereal odor - it is a chemical compound of carbon and hydrogen.
Technical acetylene, used for gas welding and cutting metals, contains impurities that give it a strong, unpleasant odor. When acetylene burns in oxygen, the flame temperature reaches 3200 °C. Mixtures of acetylene with air and oxygen are explosive if they contain 1.5–82% and 1.5–93.0% acetylene by volume, respectively. They can explode from a spark, open flame or extreme heat.
When heated to a temperature of 450–500 °C and a simultaneous increase in pressure to 153 kPa, acetylene explodes, forming a blast wave in which the gas pressure is 10 times greater than the initial pressure of acetylene.
The explosiveness of acetylene is reduced if it is in thin (capillary) vessels. This property of acetylene is used when filling cylinders under pressure. The density of acetylene in relation to air is 0.9, and in relation to oxygen – 0.8.
The causes of an acetylene explosion can be:
♦ formation of an explosive mixture in the presence of an ignition source; the presence of a catalyst (copper, brass, copper and iron oxides);
♦ temperature above 530 °C and pressure 0.3 MPa (3 kgf/cm2), at which polymerization of acetylene occurs, releasing a significant amount of heat;
♦ strong shocks or impacts from acetylene cylinders; prolonged contact of gas with copper or silver, as a result of which acetylene copper (acetylene silver) is formed, which explodes upon impact or increased temperature (the permissible copper content in the alloys from which acetylene equipment is made does not exceed 70%).
The auto-ignition temperature of acetylene depends on its pressure and the presence of impurities in it.
Propane-butane mixtures
consist of technical propane (C3H8) with an admixture (5-30%) of technical butane (C4H10). Propane, butane and their mixtures are formed during the processing of oil and petroleum products. These gaseous substances are heavier than air, colorless and have a specific odor. At low pressure they liquefy, while at normal pressure the propane-butane mixture turns into a liquid state at a temperature of about -40 °C.
Natural gases
-
these are all flammable gases that are extracted from the bowels of the earth.
They can be found in oil fields and accompany oil during its production. The main component of natural gas is methane (CH4), the volume content of which is 85–98%. The remaining 2-15% comes from nitrogen, ethane, propane, hydrogen sulfide, etc. Natural gas is light, colorless, odorless, non-toxic, but is an asphyxiating gas. To give it a characteristic sharp unpleasant odor, an odorant is added (16 g per 1000 m3 of gas). Natural gas is dangerous because when it burns incompletely, it releases colorless and very poisonous carbon monoxide. When its content in the air is 0.5%, death occurs within 20–30 minutes; at a content of 1%, after several breaths, loss of consciousness occurs, and after 1–2 minutes, death occurs.
Gas MAF
(methyl acetylene-allen fraction), belonging to the group of liquefied gases, began to be used in recent years for oxy-fuel welding and cutting of metals. MAF gas is produced according to TU 38.102.1267; grade A – for gas-flame processing, grade B – for organic synthesis.
The main flammable components that determine the properties of MAF gas are methyl acetylene and alley. Their content in the mixture is 70–75%, the remaining 25% is propane and propylene. In terms of fire and explosive properties, MAF gas is similar to propane.
The combustion temperatures of acetylene (3200 °C) and MAF (2927 °C) are close to each other.
A characteristic indicator of the combustion process is the amount of oxygen that must be supplied to the cutter (burner). For acetylene and MAF, the amount of heating oxygen supplied to the cutter (burner) per 10,000 kcal is approximately the same: 0.95 and 1.04 m3, respectively; for propane – 1.68 m3. Thus, when replacing propane-butane with MAF, the consumption of heating oxygen decreases by 1.6 times. When burning 1 m3 of MAF, 1.3 m3 of heating oxygen is saved compared to working with propane-butane.
Gases are prone to explosive self-disintegration, therefore, to obtain a stable combustion process, it is necessary to ensure good mixing of the combustible gas and preheating oxygen supplied to the cutter (burner).
If oxygen and gas are not mixed well, the flame becomes smoky and has a “whisker” appearance.
MAF gas has its own characteristics, so its use requires modification of equipment (welding torches and cutters). The number of tips for MAF is increased compared to similar tips for acetylene.
To replace 1 m3 of acetylene, 0.62 m3 of MAF gas is required, or 1.06 kg (density 1.7 kg/m3). Thus, 1 kg of MAF gas replaces 3.2 kg of calcium carbide. One cylinder of MAF gas weighing 21.2 kg replaces four cylinders of acetylene (acetylene cylinder capacity is 5.5–6.0 m3).
One cylinder of MAF gas replaces two cylinders of propane-butane, and the oxygen savings is 22 m3. When working in winter, there is no need to heat cylinders with MAF gas; complete evaporation of the gas occurs at a temperature not lower than minus 27 °C.
When oxy-fuel cutting of metal, two processes are combined: heating the metal to an ignition temperature of 1050 ° C and burning the heated metal in a stream of pure oxygen. Heat transfer to the metal and its heating to the melting temperature at the beginning of the cutting process are carried out according to the same laws as during welding.
It is known that when switching from acetylene to natural gas or propane-butane, the heating time of the metal when cutting into a sheet from the edge or when punching a hole in the sheet increases by 30%. When using MAF gas this time is reduced.
When the metal is heated with a high-temperature MAF-oxygen flame, it becomes possible to cut into the sheet “on the fly” without stopping to heat the edge of the sheet and pass through counter cuts without stopping. Using propane-butane does not allow cutting at such speeds.
According to TU 38.102.1267, empty cylinders for refilling provided to the MAF gas manufacturer must have a residual pressure of at least 0.05 MPa, regardless of the time of year.
3.5. Operation of cylinders
Operation of cylinders for compressed, liquefied and dissolved gases.
Cylinders are designed for storing and transporting relatively small quantities of a certain type of gas: compressed (air, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, etc.), liquefied (gaseous hydrocarbons, ammonia, chlorine) or dissolved (acetylene).
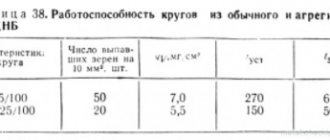
Data on cylinders for gases used in gas welding and cutting are given in table. 3.1.
Table 3.1.
Data on gas cylinders
The upper part of the cylinder has a neck into which a shut-off valve with a side outlet fitting is installed on the thread. If the cylinder is inoperative, then a plug is screwed onto the fitting. To protect the valve from damage, a metal or plastic cap is installed on the cylinder.
Strict labeling of cylinders has been introduced. The side fittings of valves for cylinders with flammable gases are made with a left-hand thread, and for cylinders with oxygen and other non-flammable gases - with a right-hand thread, in order to prevent misuse and the formation of explosive mixtures. Cylinders should be protected from impacts, as well as from high and low temperatures.
The maximum operating pressure in a cylinder at a temperature of 20 °C for compressed and dissolved gases is 15 MPa (150 kgf/cm2), and for liquefied gases – 3 MPa (30 kgf/cm2). If the cylinder temperature significantly exceeds the specified value, the gas pressure may exceed the permissible limit.
The following data is stamped on the upper, spherical part of each cylinder:
♦ trademark of the manufacturer;
♦ cylinder number;
♦ actual weight of an empty cylinder (for cylinders with a capacity of up to 12 liters inclusive - with an accuracy of 0.1 kg, from 12 to 55 liters inclusive - with an accuracy of 0.2 kg, over 55 liters - in accordance with the state standard or technical specifications for their manufacture) ;
♦ date (month and year) of manufacture and year of the next survey;
♦ working pressure;
♦ test hydraulic pressure;
♦ cylinder capacity (for cylinders with a capacity of up to 12 liters inclusive - nominal; from 12 to 55 liters inclusive - actual, with an accuracy of 0.3 liters; over 55 liters - in accordance with the state standard or technical conditions for their manufacture);
♦ the manufacturer’s quality control department stamp, round in shape with a diameter of 10 mm (except for standard cylinders with a capacity of over 55 liters); standard number for cylinders with a capacity of over 55 liters.
The height of signs on cylinders with a capacity of up to 55 liters inclusive must be at least 6 mm, and over 55 liters - at least 8 mm.
The weight of cylinders, with the exception of acetylene cylinders, is indicated taking into account the weight of the applied paint of the ring for the cap and shoe, if provided for by the design, but without the weight of the valve and cap.
The area on the cylinders where the passport data is stamped must be coated with colorless varnish and surrounded with distinctive paint in the form of a frame.
On cylinders with a capacity of up to 55 liters or with a wall thickness of less than 5 mm, passport data can be stamped on a plate soldered to the cylinder or applied with enamel (oil) paint.
Painting and marking of newly manufactured cylinders is carried out by manufacturing plants, and subsequently by filling plants, filling or testing stations.
The inscriptions on the cylinders are applied around the circumference, not less than 1/3 of it, and the stripes are drawn along the entire circumference, and the height of the letters on cylinders with a capacity of more than 12 liters should be 60 mm, and the width of the stripe should be 25 mm. The sizes of inscriptions and stripes on cylinders with a capacity of up to 12 liters depend on the area of the lateral surface of the cylinders.
It is prohibited to fill cylinders with gas if the periodic inspection period has expired, there are no established stamps, the valves are faulty, the body is damaged (cracks, severe corrosion, noticeable changes in shape), the cylinder is poorly painted, the coloring does not meet the standard, or the inscription on the cylinder is unclear.
Compressed gas cylinders are rejected if there is a weight loss of more than 20%, an increase in capacity of more than 3%, or the presence of other defects.
With a weight loss of 7.5–10% and an increase in capacity by 1.5–2.0%, the pressure in the cylinders is reduced by 15% compared to the originally set one.
With a weight loss of 10–15% and an increase in capacity by 2–2.5%, the pressure in the cylinders is reduced by at least 50%.
With a weight loss of 15–20% and an increase in capacity by 2.5–3%, the pressure in the cylinders should not exceed 600 kPa.
Cylinders in service are inspected at least once every 5 years. Cylinders intended for filling with gases that cause corrosion, as well as cylinders for compressed and liquefied gases used as fuel for cars and other vehicles, are subject to inspection at least once every 2 years.
Periodic inspection of cylinders is carried out by employees of filling plants, filling or testing stations.
If satisfactory results are obtained, each cylinder is marked with a stamp (round, 12 mm in diameter) of the filling plant where the survey was carried out, the date of the survey and the date of the next survey (on the same line with the manufacturer’s stamp).
The results of the cylinder inspection are recorded in the test log. Permission to inspect cylinders is issued to organizations by the local Promatomnadzor body.
Acetylene cylinders. Acetylene becomes explosive at a pressure of 200 kPa, therefore, for its safe storage and transportation at higher pressure, the internal cavity of the cylinder (2/3 of the volume) is filled with a porous mass - birch activated carbon, impregnated with acetone, which dissolves acetylene well. The cylinders are filled with porous mass and solvent in accordance with the state standard. Responsibility for the quality and quantity of the porous mass lies with the plant that fills the cylinders with it. Responsibility for the quality and quantity of the solvent lies with the plant that fills the cylinders with it.
After filling the cylinder with the porous mass and solvent, the mass of the container is knocked out on its neck (the mass of the cylinder without a cap, but with the porous mass and solvent, shoe, ring and valve).
To prevent solvent leakage (along with acetylene), filled cylinders must always be in a vertical position.
Inspection of acetylene cylinders must be carried out at the plant that fills them with acetylene at least once every 5 years. This includes external surface inspection, porous mass testing and pneumatic testing.
The condition of the porous mass in acetylene cylinders must be checked at the relevant filling plants at least once every 2 years. After checking the porous mass, each cylinder is marked with the year and month of the test, the mark of the filling plant and a mark (12 mm in diameter with the letters “Pm”) certifying the check.
During inspection, acetylene cylinders filled with a porous mass are tested with nitrogen under a pressure of 3.5 MPa, immersing them in water to a depth of at least 1 m. The purity of the nitrogen used for testing cylinders must be at least 97%.
In 1 liter of acetone at a pressure of 3 MPa (30 kgf/cm2) and a temperature of 20 ° C, 23 liters of acetylene are dissolved; With increasing pressure, the solubility of acetylene increases almost in direct proportion to the pressure.
Acetylene cylinders have a 1/2″ diameter valve with a left-hand thread. They are filled with gas under a pressure of 19 kgf/cm2. A cylinder with a capacity of 40 liters at this pressure contains 4–5 m3 of acetylene.
To store acetylene, cylinders with a diameter of 219 mm, a wall thickness of 7 mm, a capacity of 40 and 50 liters, a height of 1390 and 1700 mm, and a weight of 52 and 64 kg are used.
Oxygen cylinders.
A compressed gas cylinder consists of a cylindrical body with a convex bottom, an upper spherical part having a neck and a ring. A valve with a diameter of 3/4″ with a right-hand thread is screwed into the neck. To give the cylinder stability, a shoe is placed on the lower part of the body. A threaded ring is pressed onto the neck of the cylinder for screwing on a protective cap. Cylinders should be stored in an upright position, protected from shock and heat.
For oxygen, the most widely used cylinders are those with a capacity of 40 liters, having a body diameter of 219 mm, a height of 1390 mm and a wall thickness of 8 mm. The mass of such a cylinder is 67 kg. At a pressure of 15 MPa (150 kgf/cm2) and a temperature of 20 °C, it contains 6000 liters, or 6 m3, of oxygen. The cylinder is tested under a pressure of 22.5 MPa (225 kgf/cm2) once every 5 years.
The following requirements are imposed on oxygen cylinders: they must be in good working order, promptly inspected, painted blue and labeled “Oxygen.” The side fittings of cylinder valves with right-hand threads must be screwed in using foil or using liquid sodium glass, without using oiled parts and gaskets.
Storage and transportation of cylinders. IN
Under production conditions, compressed gas cylinders are stored with wrapped safety caps in special warehouses or under a canopy in a vertical position, in the nests of special racks. Due to the fact that compressed gas cylinders pose a great danger, no more than 50 cylinders are allowed to be stored together. The distance from the cylinder warehouse to buildings under construction and existing buildings must be at least 20 m.
Storing oxygen cylinders together with cylinders containing acetylene, propane, hydrogen and other flammable gases, as well as calcium carbide, paints and oils is strictly prohibited.
In the warehouse, the rules for the operation, storage and transportation of cylinders must be posted in a visible place. Storekeepers, loaders and other workers servicing cylinders must be trained in safety rules and instructed.
Warehouses for storing cylinders filled with gases must be one-story, with light-type coverings and without attics. Walls, partitions and coverings are made of fireproof materials of at least II degree of fire resistance; Windows and doors must open outwards. The height of storage areas (from the floor to the lower protruding parts of the roofing) must be at least 3.25 m.
The floors of warehouses must be level, with a non-slip surface, and the floors of warehouses for flammable gas cylinders must have a surface made of materials that prevent sparking when any objects hit them.
Lighting in warehouses for flammable gas cylinders must comply with the standards for hazardous areas.
The warehouse is divided by fireproof walls into compartments, in each of which it is allowed to store no more than 500 cylinders with flammable or poisonous gases and no more than 1000 cylinders with non-flammable and non-toxic gases (cylinder capacity 40 liters).
Compartments for storing cylinders with non-flammable and non-toxic gases can be separated by fireproof partitions at least 2.5 m high with open openings for the passage of people and mechanical equipment. Each compartment is equipped with an independent exit to the outside.
Cylinders are moved to gas filling and consumption points on special carts or using other devices. Cylinders filled with gas should be transported on spring vehicles or trucks in a horizontal position, with gaskets between the cylinders. Wooden blocks with cut-out sockets for cylinders, rope or rubber rings with a thickness of at least 25 mm (two rings per cylinder), etc. can be used as gaskets. All cylinders during transportation must be laid with valves in one direction.
When loading, unloading, transporting and storing cylinders, measures must be taken to prevent falling, damage and contamination of cylinders.
Standard cylinders with a capacity of more than 12 liters should be transported and stored with the caps screwed on. Filled cylinders can be stored at the filling plant until they are released to consumers without safety caps. When transporting and storing cylinders with poisonous and flammable gases, plugs are placed on the side fittings of the cylinder valves. Cylinders filled with gases must be protected from sunlight during transportation.
Strip welding curtain
The protective curtain is selected taking into account various parameters. The main ones can be called:
- Thickness and type of material. Some fabrics are characterized by increased resistance to temperature.
- High-quality versions are stitched.
- Type of supporting structure.
Strip welding curtain
Such protection can be installed quickly; after the process is completed, it is quickly assembled. The supporting element is made of corrosion-resistant metal.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Table
For convenient welding operations, it is practical to place the product on the table. This increases the speed of welding and the convenience of welding in hard-to-reach places. The welder's table is made to individual sizes, based on the dimensions of future products. The legs must be height adjustable to accommodate workers of different heights.
The table should include devices for:
- safe placement of the holder during the process of rearranging the product;
- quick access to consumables and easy electrode change;
- location of tools (hammer, file, flashlight, slag separator, metal brush);
- ignition of the electrode on the rough surface;
- installation of non-standard structures with protrusions in special holes.
TEST Preparation for work and maintenance of the electric welder's workplace test on the topic
TEST
Preparation for work and maintenance of the electric welder's workplace
MDK 02.01. Equipment, technology and technology of electric welding
PM.02. Welding and cutting of parts made of various steels, non-ferrous metals and their alloys, cast iron in all spatial positions
by profession 150709.02 Welder (electric welding and gas welding work).
Testing is a softer instrument; they place all students on equal terms, using a single procedure and uniform assessment criteria, which leads to a reduction in pre-exam nervous tension.
Download:
| The attachment | Size |
| podgotovka_k_rabote_i_obsluzhivanie_rabochego_mesta_elektrosvarshchika.docx | 18.65 KB |
Preview:
budgetary educational institution of the Omsk region
primary vocational education
"Vocational School No. 65."
Preparation for work and maintenance of the electric welder's workplace
MDK 02.01. Equipment, technology and technology of electric welding
PM.02. Welding and cutting of parts made of various steels, non-ferrous metals and their alloys, cast iron in all spatial positions
by profession 150709.02 Welder (electric welding and gas welding work)
Compiled by: Baranov Vladimir Ilyich master of industrial training
Sedelnikovo, Omsk region, 2013
Preparation for work and maintenance of the electric welder's workplace.
Each question has one or more correct answers. Choose the correct answer.
- Welding post:
a) this is a welder’s workplace that has an electrical supply and is equipped with the necessary welding equipment and accessories;
b) this is a section of the production area where welding of parts or assemblies is carried out.
- A stationary post is usually installed:
a) in the form of a separate site on the construction site;
b) in the form of a workplace on the structure being welded;
c) in the form of a separate cabin measuring 2x2.5 m.
- Stationary post includes:
a) welding current source;
b) welding table;
c) local ventilation.
- To protect people working closely in other professions, mobile welding stations are equipped with:
a) additional ventilation;
b) portable shields (fences), screens;
c) sound alarm.
- When welding large-sized structures, the welder's workplace must be equipped with:
a) a lifting platform or ladder;
b) additional fencing or screens;
c) additional ventilation.
- Preparing the workplace for work includes:
a) cleaning the workplace and clearing passages to the welding table;
b) selection of tools, equipment and personal protective equipment;
c) assembly of the welding chain.
- The length of welding wires should not exceed:
- During work you must:
a) protect the wires from possible damage;
b) place finished parts in appropriate containers;
c) comply with fire and electrical safety rules.
- If a malfunction is detected, you need to:
a) fix the problem yourself;
b) stop working and wait for the instructor;
c) report the malfunction to the instructor.
- Fire extinguishing means include:
a) a container with sand and a shovel;
c) a box with rags.
Test assessment criteria:
Score “excellent” 9-10 correct answers or 90-100% of 10 proposed questions;
Score “good” 7-8 correct answers or 70-89% of 10 proposed questions;
Rating “satisfactory” 5-6 correct answers or 50-69% of 10 proposed questions;
Rating unsatisfactory” 0-4 correct answers or 0-49% of 10 proposed questions.
List of used literature
- Galushkina V.N. Technology of production of welded structures: a textbook for beginners. prof. education. – M.: Publishing House, 2012;
- Ovchinnikov V.V. Technology of manual arc and plasma welding and cutting of metals: a textbook for beginners. prof. education. – M.: Publishing House, 2010;
- Maslov V.I. Welding work6 Textbook. for the beginning prof. education - M.: Publishing House, 2009;
- Ovchinnikov V.V. Equipment, technology and technology for welding and cutting metals: textbook - M.: KNORUS, 2010;
- Kulikov O.N. Occupational safety during welding work: textbook. guide for beginners prof. education - M.: Publishing House, 2006;
- Vinogradov V.S. Electric arc welding: a textbook for beginners. prof. Education - M.: Publishing House, 2010.