- By purpose
- By structure
- By surface type
- According to welded metals and composition
- Steel welding wire
- Copper-plated welding wire
- Stainless steel welding wire
- Aluminum wire
- Cored wire
- What to choose – welding electrodes or wire?
Welding wire is one of the main welding materials used in high-tech semi-automatic arc welding in MIG/MAG shielding gases. It is also used as a filler rod using a non-consumable TIG electrode, as well as a base material for the manufacture of coated stick electrodes for manual MMA arc welding.
When working with an automatic welding machine, all welding processes: wire feeding, ignition, maintaining the welding mode, its completion are mechanized. When using a semi-automatic machine, only the supply of filler material is mechanized; the welding torch is moved manually.
By purpose
Welding wire is classified according to a number of parameters, the main ones being structural features, chemical composition, and specific use.
According to purpose, it is divided into products of general and special use. The first is used when welding all grades of steel (the letters Sv are present in the marking), as well as in surfacing (Np). The second is used when welding special alloys, cast iron, when performing welding work under water, as well as when welding with forced formation of a seam.
In the second case, the chemical composition of the filler material is, as a rule, completely identical to the composition of the base metal.
Surfacing wire
Surfacing is the technological process of applying a layer of metal to the surface of a product by fusion welding. It is used to restore the original dimensions of parts and to give the surface layers of the part special properties required for its successful operation.
When surfacing by fusion welding, a pool of liquid metal is formed, which includes part of the molten metal of the product and the deposited electrode metal. Thus, the metal of the electrode turns out to be diluted with the metal of the product. When restoring worn parts, unless it is necessary to increase their wear resistance or other properties, electrodes and filler wire of a composition are used that ensures the production of deposited metal that is similar or close to the composition of the metal of the product. If, according to operational requirements, it is necessary to increase wear resistance, heat resistance and other properties, a variety of alloyed electrodes and wires are used, which, taking into account the partial dilution of the deposited metal, ensure the formation of a surface layer of the required quality. In addition to increased alloying, technological methods are used to reduce the proportion of the base metal in the surfacing, in particular, they reduce the welding energy (surfacing at low currents), increase the transverse vibrations of the electrode, etc.
The main raw material for arc surfacing of metal on worn parts is steel surfacing wire. They produce 19 grades of surfacing wire, including: 8 grades - from carbon steel Np-25, Np-30, Np-35, Np-40, Np-45, Yp-50, Np-65, Np- 80); 8 grades—alloy steel (Np-40G, Np-50G, Np-65G, Np-ZOGSA, Np-30Kh5, Np-40Kh2G2M, Np-5KhNM, Np-50KhFA); 3 grades - made of high-alloy steel (Np-30X13, Np-40X13, Np-PZA).
Steel surfacing wire is produced in the following diameters, mm: 0.3; 0.5, 0.8; 1; 1.2; 1.4; 1.6; 1.8; 2; 2.5; 3; 4; 5, 6; 6.5; 8. The hardness and purpose of the surfacing wire are shown in the table below.
Hardness and purpose of surfacing wire
| Wire grade | Approximate hardness of deposited metal | Welded products |
| Np-25 | NV 160…220 | Axes, spindles, shafts |
| Np-30 | ||
| Np-35 | ||
| Np-40 | NV 170…230 | |
| Np-45 | ||
| Np-50 | NV 180…240 | Tension wheels, trolley ramps, support |
| Np-65 | NV 220…300 | Support rollers, axles |
| Np-80 | NV 260…340 | Crankshafts, cardan shaft crosspieces |
| Np-40G | NV 180…240 | Axes, spindles, rollers, shafts |
| Np-50G | NV 200…270 | Tension wheels, support rollers for tracked vehicles |
| Np-65G | NV 230…310 | Crane wheels, support roller axles |
| NP-ZOHGSA | NV 220…300 | Crimping rolls, crane wheels |
| N l-30X5 | HRC3 37.. 42 | Rolling rolls of section rolling mills |
| NP-40ХЗГ2МФ | HRC3 38…44 | Parts exposed to impact and abrasive HOCV |
| Np-40Х2Г2М | HRC3 54…56 (after hardening) | Machine parts working with dynamic loads (crankshafts, steering knuckles: axles of road wheels) |
| Np-55ХНМ 60 | HRC3 40…50 | Forging and punching dies, forging machine rolls |
| NP-50HFA | HRC3 43…50 | Splined shafts, crankshafts of internal combustion engines |
| NP-30Х13 | HRC3 38…45 | Hydraulic press plungers, crankshaft journals, dies |
| NP-40X13 | HRC, 45…52 | Support rollers for tractors and excavators, conveyor parts |
| Np-GIZA | NV 220…280 | Railway crosspieces, crusher jaws, bucket teeth |
By structure
In terms of mechanical structure, products are divided into three main types.
Solid (solid section) . The classic and most common option. This is the same wire, which is a solid calibrated metal core obtained by cold rolling. It is from such a workpiece that electrode rods are obtained during the production of electrodes. As an independent filler material it is used in automatic and semi-automatic welding in shielding gases.
Powder . In the marking it is designated by the letter P. It is made in the form of a thin tube, inside of which there is pure flux or flux mixed with metal powder. The share of the latter is 15–40% of the mass of the entire product. When the arc is ignited, thanks to flux and metal powder, a zone of carbon dioxide and slag is formed in the welding area - it protects the deposited metal from oxidation. The weld pool is formed by drops of molten metal wire, covered with a thin layer of slag. The latter is easily removed after welding.
Activated . It also has a tubular shape, but there are significantly fewer powdery substances in it - up to 7%. The role of “activators” during ignition is performed by deoxidizers: titanium, magnesium, silicon oxide; calcium fluoride; alkali metal carbonates. They not only create a protective environment, but also ensure fast ignition and stable burning of the electric arc. Low carbon steel Sv-08G2S is usually used for manufacturing.
Powder
The sheath of flux-cored welding wire can be flat, have one or more bends, or two layers. The composition of the powder mixture is varied.
Most often, such a filler material is used when welding steel alloys with a low carbon content and a low degree of alloying. It can also weld non-ferrous metals, cast iron, and other alloys.
There are two main types of flux cored welding wire. The first type is called self-protective. The name speaks for itself. No additional protection is needed when working with such an additive. The use of the second type requires protecting the site of the seam being formed with fluxes or a gaseous environment.
Compound
The powder mixture is divided into 5 groups according to its composition.
The first group includes a mixture of titanium dioxide of mineral origin (rutile) and aluminosilicates in the form of feldspar, granite, and mica. For deoxidation, a complex compound of iron and manganese is introduced into the composition, and a protective cloud of gases is formed by cellulose or starch.
Calling the welding wire “rutile-organic” reflects its composition. It is a self-protective type that provides a low-porosity joint and is widely used in construction.
The second is the rutile group. The filler contains similar powders in a different proportion and without the addition of organic matter. Therefore, the welding process with rutile wire is carried out in a carbon dioxide environment.
The third group represents a carbonate-fluorite mixture. It contains carbonates, titanium oxide, aluminosilicates, and oxides of alkaline earth metals. A mixture of iron compounds with manganese or silicon is deoxidized.
Sometimes titanium and aluminum are added to them. This type of welding wire can be used both without protection and with protection through a gaseous environment.
The fourth group is a mixture of rutile and fluorites, supplemented with oxides of alkaline earth metals and aluminosilicates. The deoxidizing additive is a compound of iron with manganese, silicon (ferromanganese, ferrosilicon). The use of this wire requires gas protection.
The fifth group includes fluorite powder with a small amount of oxides and deoxidizers. As the latter, not only ferromanganese was added, but also aluminum and magnesium. Welding with fluorite wire does not require protection.
All fillers contain iron powder.
Mechanical properties
In addition to classification by composition, flux-cored wire is divided according to mechanical qualities. An important characteristic is impact strength. The designation encodes the minimum temperature value at which the welding seam can withstand a standard load of 35 J/cm2.
The numbers range from 0 to 6. In some cases, letters are indicated. Thus, the value of the minimum temperature of +20 °C at which the seam can withstand the specified load corresponds to the letter K.
The higher the number, the lower the permissible temperature. The number 6 corresponds to a temperature of -60 °C. In the marking of a powder additive, an additional letter indicates the recommended location in space. Standard characteristics and marking features of flux-cored wire for arc welding are reflected in GOST 26271-84.
By surface type
The surface of the products can be copper-plated (denoted in the marking by the letter O) or uncoated. Both options, depending on the task, allow you to obtain a high-quality, even seam. Copper-plated wire is used when welding carbon and low-alloy steels in a protective gas environment (more details below). Copper plating provides:
- improved current supply due to the excellent properties of copper as a conductor;
- reduced resistance when pushing the wire through the feed tip hole;
- more stable arc burning;
- necessary alloying of the weld metal.
Also in this case, the volume of sprayed metal is reduced by 30–40%.
Advantages
- The wire is excellent for use with automatic systems as they are set to feed at a speed equal to the melting speed;
- The skeins are several meters long, making them convenient to use in production;
- The lack of coating reduces the likelihood of defects due to insufficient drying, inclusions in the composition and other negative factors;
- There are many models that differ only in thickness, which helps to conveniently select a brand for working with a particular thickness of the workpiece;
- Here there is a minimum percentage of slag formation, which not only improves the quality of the connection, but also eliminates many subsequent procedures for cleaning the finished result, and so on.
For welded metals
This is the most extensive classification, which is based on the division of this welding material into types depending on the composition of the metals and alloys themselves.
Steel welding wire
Includes the largest number of brands - more than 50. The diameter of the products varies from 0.3 to 12 mm. Brands form three main groups:
- for medium-alloy and low-alloy steels, wire alloyed with manganese and silicon of the Sv-18KhGS, Sv-08G2S, Sv-08GS grades is used;
- for high-alloy materials, grades Sv-08Kh14GNT, Sv-12Kh13 are used;
- for welding low-carbon steels, wire of a similar composition is used (grades Sv-08, Sv-YUGL, Sv-10G2).
When alloyed with nickel, manganese and chromium, it is possible to join parts made of high-carbon steels. Welding can be performed under submerged arc and in a gas environment (argon, carbon dioxide).
Copper-plated welding wire
Its key advantages were mentioned above: thanks to the copper coating, the product provides good ignition and stable arc burning. Diameter – from 0.6 to 2 mm. Welding is performed in a gas-protected environment; the steels being joined are high-alloy and carbon.
Among Russian analogues, the most often used is the already mentioned steel wire Sv-08G2S with a copper-plated surface (that is, in the marking - Sv-08G2S-O). Copper-plated wires are popular and in demand for low-carbon (grades Sv-08-O, Sv-08A-O) and low-alloy (Sv-08GA-O, Sv-08GS-O, Sv-08ХМ-O) steels.
Due to their high qualities, Esab brand products are widely used (OK PRO 51C, OK Autrod 12.64 and other brands). The product on which such a welding wire is wound is a plastic cassette, which is very convenient for mechanized welding, since the material is fed automatically.
Stainless steel welding wire
Welding on stainless steel involves the use of two types of products - solid section and tubular (powder). In the first case, a protective gas environment is created from the outside (flux is poured into the joint area), in the second, this environment at high temperature is created by minerals, ores, slags and other components of the flux, which is located in the cavity of the tube. Hence another name for tubular wires – self-protecting.
Products are produced with increased (marked with the letter P) and normal accuracy according to GOST 18143-72, diameter - 0.13... 6.0 mm. Thus, the abbreviation PP means “high precision powder”.
The most important parameter by which welding wire for stainless steel is selected is strict compliance with the chemical composition of the metals - filler and base. Among the most commonly used wire grades are SV01Х18Н10, where the proportion of Cr in the composition is <20%, Ni <12%; SV06Х20Н11М3 – they are used for joining austenitic chromium-nickel steels (12Х18Н10Т, 08Х18Н10, 08Х18Н12Б, 03Х18Н11 and other grades).
Aluminum wire
The standard according to which aluminum welding wire is produced is GOST 7871-75. An important detail: the vast majority of welded products are made not from pure aluminum, but from alloys based on it. Alloying additives add strength, ductility to this metal, improve anti-corrosion and other properties. The most commonly used wire grades:
- Sv1201 – used for welding alloys with the addition of copper (up to 5%);
- SvAK5 – used for joining parts made of aluminum-silicon alloys (Si content up to 3%);
- SvA85T, SvA99 – these grades are used to weld alloys containing magnesium (up to 5%).
Welding is carried out in protective gas environments.
When working with aluminum alloys, the chemical composition of the wire must be identical to the composition of the parts being welded. The exception is an alloy of aluminum and magnesium. Due to the active evaporation of Mg during welding, it should be 10-20% more in the consumable material to replenish the required volume in the weld metal.
Cored wire
And once again to the tubular, self-protected wire. We have already talked about the principle of its operation during welding. We will indicate the brands and features of the composition of the flux that is used in such welding tubes.
- PP-AN8, PP-AN10 – the main part of the flux is rutile filler (titanium dioxide). Allows you to obtain a high-quality seam when working with medium-carbon steels.
- PP-AN4, PP-AN9, PP-AN20 (titanium dioxide plus fluorite - fluorspar). Welding is carried out on low-alloy steels.
- PP-AN1 (titanium dioxide plus carbon compounds). Used for welding parts made of low carbon steels.
- PP-2DSK – with fluorite filler (fluorspar mineral), for low-alloy and low-carbon steels.
Brands PP-AN11, PP-AN17 are also used (carbonate compounds are added to fluorite - salts of carbonic acid). They are used for connecting critical structures made of low-alloy and low-carbon steels.
Types of welding wire for semi-automatic machines
Typically, for semi-automatic machines, wire is supplied in three packaging options: in a coil, in a coil and in a skein. The first type of packaging is the heaviest, can reach 1.3 tons. The reel has a mass of 15 to 120 kg. The last package weighs from 5 to 18 kg.
Most often, the wire is packaged in boxes or polyethylene bags; if it does not have packaging, then before starting work the wire must be dried at a temperature of +200 °C.
Copper-plated
Copper-plated welding wire is used when working with carbon and low-carbon steels. It is coated with a specialized copper compound and is used for welding metal in shielding gas.
This wire provides a strong and high-quality metal connection, characterized by neatness and evenness of the seam.
neatness and evenness of the seam.
This welding wire is actively used in:
- construction and construction production;
- automotive industry;
- aircraft and shipbuilding.
This product has fairly high surfacing characteristics and is best suited for applications such as:
- formation of a bead on the weld seam;
- filling the gap in the middle of the edges of the connected structure.
Copper-clad wire has a constant chemical composition, high strength and low cost.
We recommend articles:
- Types of welds: we understand the classification and features
- Fusion welding: where it is used and how it is produced
- Welding modes and parameters for different equipment
Alloyed
This steel welding wire is used for additive in manual and semi-automatic welding. It is divided into:
- highly alloyed - with a high content of additives in its composition;
- low-alloy – with a small proportion of additives;
- carbonaceous - which contain more than 0.2% carbon elements.
Due to the fact that the wire restores the alloying compounds of the metal, it is very ductile and resistant to deformation, in addition, it is particularly resistant to corrosion.
This wire is usually used when welding large parts and pipes with large diameters. It helps to form tight seams and works in several positions.
Flux Welding Wire
Such wire has a high degree of melting, making it possible to work with the most refractory metals. When welding, metal particles do not splash and the crust formed during work reliably protects the arc and the metal itself from external influences. Because of this, the seam is dense, durable and uniform.
It is precisely due to high productivity and the absence of metal splashes that wire is so popular. It is safe for health and can be purchased at almost any hardware store at a low price.
Welding wire for stainless steel
This material is used when welding stainless steel parts. This wire protects the seam from corrosion due to the content of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, nitrogen and chromium.
Wire is made by drawing steel. Based on the nature of processing, it is divided into:
- hard;
- soft;
- thermal.
To obtain the highest seam strength, experts advise using products with the same characteristics as the parts being joined. The price of such wire is now quite significant - about $15 per kilogram.
Fine-tuning parameters such as voltage and pulse feed will help save material during work. Stainless steel products are especially widely used in the production of automobiles, food production and for the manufacture of medical instruments.
Aluminum Welding Wire
This type of wire is used to work with aluminum and its alloys. It is durable, resistant to corrosion and quite flexible. Made from aluminum and contains manganese, silicon and magnesium.
Work with such wire is carried out in a protective gas environment using an argon-arc apparatus. Aluminum wire oxidizes quickly, so it must be used immediately after unpacking. Otherwise, the welding quality may suffer.
In areas where there is high humidity, work should be especially careful. Aluminum wire is especially often used in light industry, oil production and shipbuilding.
What to choose – welding electrodes or wire?
Both materials solve one problem - they allow you to obtain a high-strength, high-quality weld. In the end, the wire itself plays the role of a welding electrode during the work process. However, the methods for solving such problems are technologically different.
- Electrode rods are coated and provide alloying of the weld metal not only due to the metal of the rod, but also the composition of the coating. Alloying in the case of wire is provided only by its metal.
- Wire welding is always a mechanized process, semi-automated or fully automatic.
- When welding with electrodes, a protective gas environment is not required. In addition, it can be created in hard-to-reach places - directly on the construction site, which is impossible or difficult in the case of stationary machines.
However, in some cases, welding wire is preferred. In particular, it is recommended when working with stainless steel, which is quite difficult to cook. It is this that allows you to obtain a perfectly precise connection when working with critical structures - in the case of MMA, only an experienced professional welder can give the same result.
In addition, electrodes often require preliminary calcination - and this is an additional working step that requires appropriate equipment and time (from half an hour to two hours). Finally, the issue of price also plays an important role: wire is much cheaper than coated electrode rods.
Samples of these products are presented in the catalog. Here you will find welding wire in coils, barrels and cassettes (coils), as well as in rods. The high quality of products from leading manufacturers is confirmed by certificates.
Steel
Welding wire is made by cold drawing steel blanks with a low carbon content, a moderate amount of alloying additives and from high-alloy raw materials.
GOST 2246 70 standardizes the characteristics of welding wire made of all types of steel. The standard stipulates the division of products into two groups. The first is wire for surfacing, the second is for making electrodes. Belonging to the second group is marked with the letter E.
A product with a low carbon content and a moderate amount of alloying additives is available with or without copper plating. Copper-plated welding products are marked with the letter O.
The specific concentration of copper in the coating is specified in the technical specifications (TS) approved for each type of wire product. The standard specifies the thickness (diameter) of all products with maximum permissible deviations.
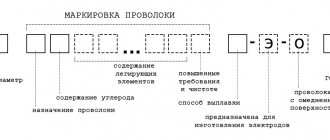
The marking includes a set of letter designations and numbers that you need to navigate to correctly select wire products.
The designation St informs that this type of welding product is intended for welding. The next number displays the mass fraction of carbon expressed as a percentage. The following are letters indicating the presence of additives.
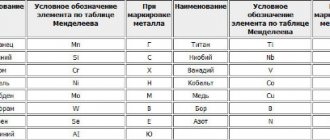
Nitrogen is contained only in wire products with a high degree of alloying of steel raw materials. In such cases, indicate the letter A. The presence of niobium is indicated by the letter B, tungsten - B, manganese - G, copper - D, molybdenum - M, nickel - N, silicon - C.
The presence of titanium is indicated by the letter T, vanadium - F, chromium - X, zirconium - C, aluminum - Y. You should pay attention to the information presented also because the letter does not always correspond to the name of the chemical element.
Each letter symbol is followed by a number indicating the average mass fraction of the element in the steel alloy. If the number is not indicated, it means that the additive is contained in a trace concentration.
The letter A present at the end indicates a high degree of purification of the material from sulfur and phosphorus. If there are two letters A at the end, then the concentration of sulfur and phosphorus is negligible.
Manufacturers and suppliers are required to guarantee proper storage and subsequent transportation of wire products. This requirement is also specified in the standard.
Quality requirements and acceptance rules
BP 2 wire must meet all the requirements of GOST 7348 81. In this case, the presence of cracks, chips, delaminations and cavities on the surface is not allowed. The presence of rust spots and dents is allowed in a minimum amount. Packed skeins should not have tangled or bent ends, mixed up rows or breaks. The weight of each skein is no more than 100 kg.
The straightness of the rods is standardized. The bend of a straight section 1 m long should not exceed 40 mm.
Before you buy GOST 7348 81 wire, you must take into account the following acceptance rules:
- The supplied batch must have one accuracy group and one diameter.
- All rental characteristics and release date are reflected in the attached passport.
- Upon receipt of the goods, the diameter of each coil or rod in the bundle is checked.
- To check the strength characteristics of the entire batch, 10% of the coils or rods are selected.
Large batches of skeins are combined into coils weighing up to 1.5 tons. The rods are collected in bundles tied in two places. Rolled products packaged in this way are supplied without lubricant. At the customer's request, the skeins can be supplied in special packaging that protects the product from precipitation.