Lead is an element of the fourth group of the main subgroup of the corresponding table of elements. Lead in its simplest form is a low-melting, malleable metal, white in color with a silvery tint and a bluish tint.
This type of material has been used for many millennia, as it is easily mined, perfectly processed and distributed in all corners of the world. Although native lead is very rare, it is widely found in a variety of other rocks. About eighty different types of rocks contain lead.
How much does a bucket of lead weigh?
Pivot table
| The name of the product for which you need to find out reference data on the topic: how much the bucket weighs in kilograms. | Bucket capacity in liters. | How much does 1 liter, one liter, one liter jar weigh in kilograms (number of kg). |
| Lead . | 10 l. | 11.3 |
| Dry sand. | 10 l. | 1.4 — 1.7 |
| Currant. | 10 l. | 0.64 |
| Salt. | 10 l. | 1 |
Lead Density:
Density is a scalar physical quantity, defined as the ratio of the mass of a body to the volume occupied by this body.
The Greek letter ρ is commonly used to denote density.
ρ = m / V, where m is the mass of the body, V is its volume.
The density of lead (ρ) is 11.3415 g/cm3 or 11341.5 kg/m3.
The density of lead is given under normal conditions (according to IUPAC), i.e. at 0 °C and pressure 10 5 (100,000) Pa.
For information: 101,325 Pa = 1 atm = 760 mm Hg. Art.
It must be borne in mind that the density of metals can change depending on environmental conditions (temperature and pressure). The exact value of the density of metals depending on environmental conditions (temperature and pressure) must be looked at in reference books.
Note: © Photo https://www.pexels.com, https://pixabay.com
Polls
Does our country need industrialization?
- Yes, we need it (90%, 2,486 votes)
Total votes: 2 758
Search for technologies
Technologies found 1
Might be interesting:
Dispersants for protecting pipelines from corrosion
Heterostructures
UAV for agriculture
Robot truck
Super strong wood
Extrusion plant for the production of consumables for 3D printers
Ultraconcrete – production technology using the gravitational compaction method
Hypersonic aircraft
What is this site about?
This site is dedicated to the Second Industrialization of Russia.
It includes: - the economy of the Second Industrialization of Russia, - the theory, methodology and tools of innovative development - the implementation of the Second Industrialization of Russia, - the organizational mechanism for the implementation of the Second Industrialization of Russia, - a directory of breakthrough technologies.
We do not sell products, technologies, etc. of manufacturers and inventors! You need to contact them directly!
We negotiate with manufacturers and inventors of domestic breakthrough technologies and provide recommendations on their use.
The implementation of the Second Industrialization of Russia is based on a qualitatively new scientific basis (theory, methodology and tools) developed by the authors of the site.
The end result of the Second Industrialization of Russia is an increase in the well-being of every member of society: the ordinary person, the enterprise and the state.
The second industrialization of Russia is a set of scientific, technical and other innovative ideas, projects and developments that have the ability to be widely implemented in economic practice in a short time (3-5 years), which will ensure a qualitatively new progressive development of society in the next 50-75 years.
The country that will be the first to make this comprehensive breakthrough, Russia, will become a leader in the world community and will remain inaccessible to other countries for centuries.
Lead is a soft, heavy metal of a silver-gray color, shiny, but quickly losing its shine. Along with tin and copper, it is one of the elements known to mankind since ancient times. Lead was used very widely, and even now its use is extremely diverse. So, today we will find out whether lead is a metal or a non-metal, as well as a non-ferrous or ferrous metal, we will learn about its types, properties, application and extraction.
How much does a bucket of concrete weigh?
Weight of wall materials and concrete
| Name of building material | How much does a bucket weigh , kg ( weight of building material placed in one 10-liter bucket |
| Asbestos concrete | 21 |
Lightweight concrete | 11-12 |
Lightweight concrete | 5-18 |
Lightweight coke-based concrete | 12 |
What is lead
Lead is an element of group 14 of D.I. Mendeleev’s table, located in the same group with carbon, silicon and tin. Lead is a typical metal, but it is inert: it reacts extremely reluctantly even with strong acids.
Molecular weight is 82. This not only indicates the so-called magic number of protons in the nucleus, but also the large weight of the substance. The most interesting qualities of the metal are associated precisely with its great weight.
Read also: Tool for sanding wood at home
The concept and features of lead metal are discussed in this video:
Concept and features
Lead is a metal that is quite soft at normal temperatures and is easy to scratch or flatten. This plasticity makes it possible to obtain metal sheets and rods of very small thickness and any shape. Malleability was one of the reasons why lead began to be used since ancient times.
The lead water pipes of Ancient Rome are well known. Since then, this type of water supply system has been installed more than once and in more than one place, but it did not operate for so long. Which, without a doubt, saved a considerable number of human lives, since lead, alas, with prolonged contact with water, eventually forms soluble compounds that are toxic.
Toxicity is the very property of a metal due to which they try to limit its use. Metal vapors and many of its organic and inorganic salts are very dangerous for both the environment and people. Basically, of course, the workers of such enterprises and residents of the area around the industrial facility are in danger. 57% is emitted with large volumes of dusty gas, and 37% with converter gases. There is only one problem with this - the imperfection of purification plants.
However, in other cases people become victims of lead contamination. Until recently, the most effective and popular gasoline stabilizer was tetraethyl lead. When fuel burned, it was released into the atmosphere and polluted it.
But lead has another, extremely useful and necessary quality - the ability to absorb radioactive radiation. Moreover, the metal absorbs the hard component even better than the soft one. A 20 cm thick lead layer can protect against all types of radiation known on Earth and in nearby space.
Advantages and disadvantages
Lead combines extremely useful properties, turning it into an irreplaceable element, and downright dangerous ones, which make its use a very difficult task.
The advantages from the point of view of the national economy include:
- fusibility and malleability - this allows you to form metal products of any degree of complexity and any subtlety. Thus, for the production of sound-absorbing membranes, lead plates with a thickness of 0.3–0.4 mm are used;
- lead is able to form an alloy with other metals (including tin, copper, zinc, etc.) that under normal conditions do not alloy with each other; its use as solder is based on this quality;
- metal absorbs radiation. Today, all elements of radiation protection - from clothing to the decoration of X-ray rooms and rooms at testing sites - are made from lead;
- The metal is resistant to acids, second only to noble gold and silver. So it is actively used for lining acid-resistant equipment. For the same reasons, it is used to produce pipes for the transfer of acid and for wastewater in hazardous chemical plants;
- The lead-acid battery has not yet lost its importance in electrical engineering, as it allows one to obtain a high voltage current;
- low cost - lead is 1.5 times cheaper than zinc, 3 times cheaper than copper, and almost 10 times cheaper than tin. This explains the very great benefit of using lead rather than other metals.
- toxicity - the use of metal in any type of production poses a danger to personnel, and in case of accidents - an extreme danger to the environment and the population. Lead belongs to substances of hazard class 1;
- Lead products should not be disposed of as regular waste. They require disposal and sometimes it is very expensive. Therefore, the issue of metal recycling is always relevant;
- Lead is a soft metal, so it cannot be used as a structural material. Considering all his other qualities, this should rather be considered a plus.
Read also: DIY beetle sprayer repair
Next, the melting point and density of lead, specific heat capacity and mass, as well as other properties and characteristics of such a metal will be considered.
Properties and characteristics
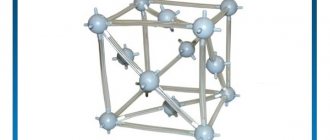
Lead is a soft, malleable, but also heavy and dense metal. The molecular lattice is cubic, face-centered. Its strength is low, but its ductility is excellent. The physical characteristics of the metal are as follows:
- density at normal temperature 11.34 g/cm3;
- melting point – 327.46 C;
- boiling point – 1749 C;
- resistance to tensile load – 12–3 MPa;
- resistance to compressive load – 50 MPa;
- Brinell hardness – 3.2–3.8 HB;
- thermal conductivity – 33.5 W/(m K);
- The resistivity is 0.22 ohm-sq. Mmm.
Like any metal, it conducts electric current, although, it should be noted, it is much worse than copper - almost 11 times. However, the metal has other interesting properties: at a temperature of 7.26 K it becomes a superconductor and conducts electricity without any resistance. Lead was the first element to exhibit this property.
Paints containing lead compounds are almost as resistant to corrosion. Due to toxicity, they are not used indoors, but are successfully used when painting bridges, for example, frame structures and so on.
The video below will show you how to make pure lead:
Historical information
Lead has been used for thousands of years because it is widespread and easy to mine and process. It is very malleable and melts easily. Lead smelting was the first metallurgical process known to man. Lead beads dating back to 6400 BC. BC, were found in the Çatalhöyük culture. The oldest object made of lead is often considered to be a figurine of a standing woman in a long skirt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, dating back to 3100-2900. BC BC, stored in the British Museum (stock number EA 32138). It was found in the Temple of Osiris at Abydos and brought from Egypt in 1899. In Ancient Egypt, lead medallions were used. In the Early Bronze Age, lead was used along with antimony and arsenic. Lead is referred to as a specific metal in the Old Testament.
Lead pipes of an ancient Roman water supply with inscriptions
The largest producer of lead in the pre-industrial era was Ancient Rome, with an annual production of 80,000 tons. Roman mining of lead took place in Central Europe, Roman Britain, the Balkans, Greece, Asia Minor and Spain. The Romans widely used lead in the production of pipes for water supply systems, and lead pipes often bore the inscriptions of Roman emperors. True, even Pliny and Vitruvius believed that this was not good for public health.
Papal bull of 1637 with lead seal
After the fall of the Roman Empire in the 5th century. n. e. Lead use in Europe fell and remained low for about 600 years. Then lead began to be mined in eastern Germany. Lead sugar has been added to wine since Roman times to improve its taste; this became widespread and continued even after the ban by a papal bull in 1498. This use of lead in the Middle Ages led to epidemics of lead colic. In Ancient Rus', lead was used to cover the roofs of churches, and was also widely used as a material for hanging seals on letters. Later, in 1633, a water supply system with lead pipes was built in the Kremlin, through which water came from the Vodovzvodnaya Tower; it existed until 1737.
In alchemy, lead was associated with the planet Saturn and was represented by its symbol ♄. In ancient times, tin, lead and antimony were often not distinguished from each other, considering them to be different types of the same metal, although Pliny the Elder distinguished between tin and lead, calling tin “plumbum album” and lead “plumbum nigrum”.
The Industrial Revolution led to a new increase in the demand for lead. By the beginning of the 1840s. annual production of refined lead exceeded 100,000 tons for the first time and grew to over 250,000 tons over the next 20 years. Until the last decades of the 19th century, lead mining was primarily carried out by three countries: Britain, Germany and Spain. By the beginning of the 20th century, lead mining in Europe had become less than in the rest of the world, thanks to increased production in the United States, Canada, Mexico and Australia. Until 1990, large quantities of lead were used (together with antimony and tin) to cast typographical fonts, and also in the form of tetraethyl lead to increase the octane number of motor fuels.
Application area
The first use of lead - in the manufacture of water pipes and household items, fortunately, dates back to quite a long time ago. Today, metal enters a home only with a protective layer and in the absence of contact with food, water and humans.
- But the use of lead for alloys and as solder began at the dawn of civilization and continues to this day.
- Lead is a metal of strategic importance, especially since bullets began to be cast from it. Ammunition for small arms and sporting weapons is still made only from lead. And its compounds are used as explosives.
- 75% of the world's metal production is used to produce lead-acid batteries. The substance continues to be one of the main elements of chemical current sources.
- The corrosion resistance of the metal is exploited in the manufacture of acid-resistant equipment, pipelines, and protective sheaths for power cables.
- And, of course, lead is used in the equipment of X-ray rooms: cladding of walls, ceilings, floors, protective partitions, protective suits - everything is made with the participation of lead. At testing sites, including nuclear ones, metal is indispensable.
Read also: What color is the phase and neutral wire?
The cost of metals is determined on several world-wide exchanges. The most famous is the London Metal Exchange. The cost of lead in October 2016 is $2087.25 per ton.
Lead is a metal that is in great demand in modern industry. Some of its qualities—corrosion resistance, the ability to absorb hard radiation—are completely unique and make the metal irreplaceable despite its high toxicity.
This video will tell you what happens if you pour lead into water:
The main characteristic affecting the weight of a metal is its density.
What does metal density mean?
The density of a metal refers to its weight per unit of occupied volume. Volume is often measured in cubic meters and cubic centimeters. What is the reason for such large, by earthly standards, weight and density? The density of a metal and its weight depend on how small the radius of the atom is and how large its weight is.
Density of metals table
| Metal | g/cm 3 | kg/m 3 | Metal | g/cm 3 | kg/m 3 |
| Lithium | 0,534 | 534 | Samarium | 7,536 | 7536 |
| Potassium | 0,87 | 870 | Iron | 7,87 | 7874 |
| Sodium | 0,968 | 9680 | Gadolinium | 7,895 | 7895 |
| Rubidium | 1,53 | 1530 | Terbium | 8,272 | 8272 |
| Calcium | 1,54 | 1540 | Dysprosium | 8,536 | 8536 |
| Magnesium | 1,74 | 1740 | Niobium | 8,57 | 8570 |
| Beryllium | 1,845 | 1845 | Cadmium | 8,65 | 8650 |
| Cesium | 1,873 | 1873 | Holmium | 8,803 | 8803 |
| Silicon | 2,33 | 2330 | Nickel | 8,9 | 8900 |
| Bor | 2,34 | 2340 | Cobalt | 8,9 | 8900 |
| Strontium | 2,6 | 2600 | Copper | 8,94 | 8940 |
| Aluminum | 2,7 | 2700 | Erbium | 9,051 | 9051 |
| Scandium | 2,99 | 2990 | Thulium | 9,332 | 9332 |
| Barium | 3,5 | 3500 | Bismuth | 9,8 | 9800 |
| Yttrium | 4,472 | 4472 | Lutetium | 9,842 | 9842 |
| Titanium | 4,54 | 4540 | Molybdenum | 10,22 | 10220 |
| Selenium | 4,79 | 4790 | Silver | 10,49 | 10490 |
| Europium | 5,259 | 5259 | Lead | 11,34 | 11340 |
| Germanium | 5,32 | 5320 | Thorium | 11,66 | 11660 |
| Arsenic | 5,727 | 5727 | Thallium | 11,85 | 11850 |
| Gallium | 5,907 | 5907 | Palladium | 12,02 | 12020 |
| Vanadium | 6,11 | 6110 | Ruthenium | 12,4 | 12400 |
| Lanthanum | 6,174 | 6174 | Rhodium | 12.44 | 12440 |
| Tellurium | 6,25 | 6250 | Hafnium | 13,29 | 13290 |
| Zirconium | 6,45 | 6450 | Mercury | 13,55 | 13550 |
| Cerium | 6,66 | 6660 | Tantalum | 16,6 | 16600 |
| Antimony | 6,68 | 6680 | Uranus | 19,07 | 19070 |
| Praseodymium | 6,782 | 6782 | Tungsten | 19,3 | 19300 |
| Ytterbium | 6,977 | 6977 | Gold | 19,32 | 19320 |
| Neodymium | 7,004 | 7004 | Plutonium | 19,84 | 19840 |
| Zinc | 7,13 | 7130 | Rhenium | 21,02 | 21020 |
| Chromium | 7,19 | 7190 | Platinum | 21,40 | 21400 |
| Tin | 7,3 | 7300 | Iridium | 22,42 | 22420 |
| Indium | 7,31 | 7310 | Osmium | 22,5 | 22500 |
| Manganese | 7,44 | 7440 |
The table shows that the specific gravity of a cube of metal varies greatly. The difference in weight between the heaviest and lightest metal is 42 times. Osmium, whose weight is 22500 kg per m 3 and lithium, which has the lowest density, whose weight is 534 kg per m 3. The metal that has the greatest density also has the greatest weight and it is osmium, as we already understood.
The average density among all metals is 11.5 g per cm3.
It is also noteworthy that there are metals whose density is less than water. There are several of them: lithium, potassium, sodium.
For reference, we can add that osmium is not only the heaviest, but also the rarest. It is mined at around 100 kg per year.
Metals similar to gold in specific gravity
Some other metals also have a density similar to gold. In particular, tungsten and uranium. Uranium cannot be passed off as a noble gold metal for the following main reasons:
- high radioactivity;
- inaccessibility.
Counterfeiters have more options when working with tungsten. But this metal differs significantly from gold in color and hardness. Despite this, the counterfeiters found a way out. They cover tungsten ingots with molten gold.
In addition, tungsten is often used in the production of gold-plated jewelry. They are very similar in appearance to real gold jewelry, but their cost and durability set them apart from gold jewelry.
Gold plating is also applied to lead products, the structure of which is much softer. The common belief that specific gravity will distinguish a fake lead from a real gold metal is incorrect. This is a misconception, since gold in its pure form is not used to make jewelry.
You can often find gold jewelry with unusual colors on sale. Often these are ordinary sprayings. If the product is made of alloy, then its price will be much higher. For example, gold comes in blue, pink, black, purple and other shades. They are obtained by including other compounds in the ligature.
Today, unscrupulous jewelers do not hesitate to pass off other metals as precious gold. To avoid purchasing a counterfeit, you should only contact specialized stores that have the appropriate certificates and licenses.