Connecting steel pipes by welding is practical and inexpensive. But if a section of the pipeline must be dismountable, or a valve or other element needs to be inserted into it, then a flange connection is used. The purpose of the flanges is to simultaneously ensure the tightness of the joint and the possibility of its disassembly without damaging the pipeline.
Flange connection
So what is the flange for? And its purpose is to organize a flange connection. Suppose there are two sections of pipe and they can, of course, be welded together, but then it will be a rigid one-piece connection, and in order to organize a quick-release flange connection, flanges are used, which are welded onto the ends of the pipes and tightened with bolts with nuts or studs with nuts, as in photo below.
The flange itself is a flat ring or sometimes made in the form of a square or rectangle with a hole in the middle for inserting the end of the pipe and several evenly spaced holes closer to the outer diameter into which bolts or studs are inserted, nuts are screwed onto them and the two flanges are tightened together. To seal the connection between the flanges, a gasket made of special rubber or other material for this purpose, such as fluoroplastic, is placed. By the way, depending on the type of gaskets, there are different designs; it would be more correct, of course, to use different types of gaskets.
The pipes themselves are often connected to each other, but more often it is necessary to connect some apparatus or devices, for example, heat exchangers with a section of the pipeline through which some kind of medium is supplied. For example, look at the photo below there is an oil cooler MB 25-37 and at the ends two flanges number 1 are clearly visible, which are welded to the pipes and on them there are additionally counter flanges number 2 screwed with bolts and nuts, this is the delivery kit for the manufacture of the heat exchanger. The customer needs counter flanges to organize the connection of the device with the pipeline section.
Let’s say a customer ordered the production of a heat exchanger, brought it to the site, installed it, and needs to connect it. To do this, pipelines are connected to the device, flat steel mating flanges supplied in the kit are welded onto the ends of the pipes and the flange on the cooler and at the end of the pipe are connected with bolts or studs, not forgetting, of course, to put a gasket between them for tightness. Comfortable! Because Periodically, for example, for repairs or preventive maintenance, the need to stop the operation of the device and disassemble it arises. This oil cooler has four flat steel flanges. Two for inlet and outlet of cooling water and two for inlet and outlet of cooled oil.
In the same way, sections of pipelines are connected to various technological tanks. Flanges 1 and 2 refer to the type of flanges of fittings, connecting parts and pipelines.
Thus, we can say that flanges are needed to organize the connection or connection of a pipeline section
to various technological devices and devices: heat exchangers, containers, etc., for supplying and discharging media, as well as for connecting pipe sections to each other.
Go ahead. The number 3 in the figure indicates the same flange, but this one is of the type for vessels and apparatus. This is where the differences begin to appear.
Operating pressure
This is the pressure with which liquid (gas, steam, etc.) is transported through the system. Consequently, the higher the operating pressure in the system, the higher the strength characteristics it is necessary to select fasteners. In turn, the necessary strength characteristics of fasteners are ensured by the correct choice of material, heat treatment modes, etc. Thus, in the temperature range from -40 to + 400 ° C, and at pressures up to 100 kgf/cm2, it is recommended to use fasteners made from steel 35, while increasing pressure to 200 kgf/cm2 requires the use of fasteners made of steel 20X13.
Differences, types and types of flanges
What type, where to use, what material it is made of, under what conditions this or that flange should work is regulated by state standards or simply GOSTs. Two significant types of flanges can be identified: for fittings and for vessels and apparatus
.
Flange types
- for fittings, connecting parts and pipelines. Ru from 0.1 to 20 MPa (from 1 to 200 kgf/cm2). GOST 12815-80 download -, .
- for vessels and apparatus. GOST 28759.1(2,3,4)-90. Download GOST 28759.1, 2, 3, 4.
Those. the former are used to connect parts of pipelines with branch pipes, as in the example above with MB 25-37, simply for connecting pipes, and the latter for the manufacture and joining of parts of apparatus. For example, in photo mb 25-37 you can see flanges 3 that connect the water chamber of the oil cooler to the body. An oil cooler specifically refers to heat exchangers and pressure vessels.
Go ahead. We found out that the first difference between flanges is what they are intended for by considering the two above-mentioned standards. And then within each GOST there are different types of flanges depending on many factors of their application, purpose, and manufacture. Let's see.
Types of flanges depending on GOST
GOST 12815-80 contains types of flanges
:
- cast from gray cast iron according to GOST 12817-80 - flanges of cast fittings, connecting parts, machines, instruments, pipes of devices and tanks made of gray cast iron for a nominal pressure Ru from 0.1 to 1.6 MPa and a medium temperature from minus 15 to plus 300 °C.
- cast from ductile cast iron according to GOST 12818-80 - flanges of cast fittings, connecting parts, machines, instruments, pipes of devices and tanks made of ductile cast iron for a nominal pressure Ru from 1.6 to 4.0 MPa and a medium temperature from minus 30 to plus 400 °C.
- cast steel according to GOST 12819-80 - cast steel fittings, connecting parts, machines, instruments, pipes, apparatus and tanks for a nominal pressure Ru from 1.6 to 20.0 MPa and a medium temperature from minus 253 to plus 600 ° C. GOST 12819-80 free download - , .
- steel flat welded according to GOST 12820-80 - standard for steel flat welded flanges of pipelines and connecting parts, as well as for connecting flanges of fittings, connecting parts of machines, instruments, pipes of devices and tanks for a nominal pressure Ru from 0.1 to 2.5 MPa (from 1 to 25 kgf/cm2) and medium temperature from 203 to 573 K (from minus 70 to plus 300 °C). GOST 12820-80 free download - , . The price of flanges according to this GOST 12820-80 can be found in the price list for pipeline fittings. Additionally, I will say that blind steel flanges are manufactured according to the same standard. You can see what it looks like in the photo above in the upper left corner or just below. Essentially it is a flange plug.
- steel butt-welded - collar according to GOST 12821-80 - steel welded flanges of pipelines and connecting parts, as well as for connecting flanges of fittings, connecting parts of machines, instruments, pipes, apparatus and tanks for a nominal pressure Ru from 0.1 to 20.0 MPa (from 1 to 200 kgf/cm2) and medium temperature from 20 to 873 K (from minus 253 to plus 600 °C). GOST 12821-80 can be downloaded in the following format: or . There you can also see drawings and all flange sizes. If you need to see the price and buy flanges according to GOST 12821-80
or contact our sales department. Here I note that, unlike the above, it is possible to use a flange connection at a higher pressure and at lower and higher temperatures. These are their main differences in application. - steel loose on a welded ring according to GOST 12822-80 - steel flanges loose on a welded ring of pipelines and connecting parts of machines, instruments, pipes of devices and tanks for Ru from 0.1 to 2.5 MPa (from 1 to 25 kgf/cm2) and medium temperature from 243 to 573 K (from minus 30 to plus 300 °C).
If necessary, you can download GOST 12822-80 in word or pdf format. The price of flanges is in the price list.
For more detailed information, you must, of course, go to the appropriate guest house.
GOST 28759.1-90 - flanges of vessels and apparatus:
- steel flat welded according to GOST 28759.2-90 - for vessels and apparatus with a diameter from 400 to 4000 mm with a nominal pressure from 0.3 to 1.6 MPa at a working environment temperature from minus 70°C to plus 300°C, intended for operation in chemical, petrochemical, oil refining and other industries.
- steel butt welded - collar according to GOST 28759.3-90 - flanges for vessels and apparatus with an internal diameter from 400 to 4000 mm and an external basic size (bottoms, pipes) from 426 to 720 mm with a nominal pressure from 0.6 to 6.3 MPa , at a working environment temperature from minus 70°C to plus 540°C, intended for work in chemical, petrochemical, oil refining and other industries.
- steel butt welded for octagonal section gasket in accordance with GOST 28759.4-90 - flanges of vessels and apparatus with a diameter from 400 to 1600 mm with a nominal pressure from 6.3 to 16.0 MPa at a working medium temperature from minus 70°C to plus 540°C, designed for use in chemical, petrochemical, oil refining and other industries.
Now it becomes clear what types of flanges there are and what types they are divided into depending on their purpose. All technical characteristics, drawings, designs and dimensions of flanges can be viewed by following the links at the top or selecting the corresponding GOST at the bottom of the article. Let's go find out further.
Production technology
Several methods are used to produce flanges:
- Centrifugal casting
- Stamping or forging
- Cutting from rolled steel sheet using a laser tool.
- Hot forging from blanks in the form of rolling rings.
- Semi-manual method using CNC machines or semi-automatic turning and milling.
The most productive method, often used to produce a serial batch, is stamping, carried out in closed forms - stamps. The least expensive method is to cut parts from sheet steel. The method requires additional ultrasonic testing for the absence of cavities.
During the manufacturing process of parts, regular quality control is carried out. The performance of the lines depends on the quality of the flange; in the event of a failure or accident, the user will incur significant losses. One of the main tests is to check for mechanical integrity and surface evenness.
Currently, a large number of imported equipment adapted to international standards are being purchased. The enterprises have launched the production of “transitional type” flanges, combining the parameters of different standardization systems.
To protect flange connections from exposure to aggressive environments, the flanges are coated with special materials that increase their service life. The surface layer of steel is treated with nickel, chromium, zinc and other materials that prevent premature destruction. The type of coating is determined by the customer.
Flange versions
Flange version
this is essentially the design or type of the end surface of the flanges between which a flange connection is created. And here, too, the geometry of surfaces is regulated by GOST. Let's look at an example.
GOST 12815-80 contains 9 versions:
- version 1 - there is a connecting protrusion at an angle of 45 0 as a chamfer, by the way the most common.
- version 2 - also with a projection but at an angle of 90 0.
- version 3 - with a projection at 45 0 plus a depression, sampling from the inside.
- version 4 - flange with a spike, the same as the previous one, only a projection of 90 0.
- version 5 - with groove. It looks like a ring sample.
- version 6 - for lens spacer. Has an internal chamfer.
- version 7 - for an oval gasket. Oval groove on the end surface.
- performance 8 and 9 - performance 8 is the same as the 4th, and the ninth is the same as the 5th. How they differ I don’t understand the difference. I would be glad if anyone writes in the comments to this article.
GOST 28759.2-90 contains 15 versions, and 28759.3-90 - twelve. There is no point in listing them, so I ask you to follow the links to these GOSTs and see everything in detail, what they look like, etc.
Where are flanges used?
*
This type is used for pipeline assembly; installation of any flange occurs only if there is a pipe of the appropriate diameter. There are several areas of application for the part:
- assembly of civil central pipelines;
- gas pipeline assembly;
- installation of domestic water supply systems;
- installation of heating mains;
- assembly of industrial systems and communications.
Flange connection
These parts can be pipe, shaft, fitting or body parts. This is a universal product that, when connected to another part, can provide a tight seal. The element can withstand high temperatures and pressure, so this type of fastening can be used in gas and water pipelines. The parameters by which they are selected are the dimensions, shape of the sealing surface, as well as the method of fastening.
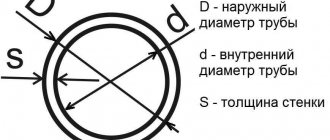
Geometric dimensions and weight of flanges
Very important parameters, both at the stage of designing devices, containers, etc., and at the stage of operation and repair, including procurement, because you need to know which part to buy. Therefore, it is very important to know what connection and overall dimensions
available on certain flanges. There are a lot of sizes, but the main one is a nominal bore. The choice of flange when purchasing and during design is based on it. Let's go into a little more detail.
Nominal size of flanges
Let's say there are two pipes that are connected to each other or a pipe on a heat exchanger or some container. The pipes and the nozzle have an outer diameter and it is sometimes believed that it should correspond in the designation to the inner diameter of the flange, but this is not the case. For example, DN100 corresponds to an outer diameter of the pipe of 108 mm or 114 mm, by the way, according to Yandex statistics, the flange most often searched for is DN 100, and for DN 125 the pipe diameter is 133 or 140 mm, for DN 150 they choose a pipe with a diameter of 152, 159 or 168 mm, depending on execution and from the letter A, B, B indicated in the GOST table. When an order is placed, a letter must be indicated next to the flange designation; if it is not there, then it is considered that the letter A is selected.
This dependence exists for flat flanges and flanges with a welded ring, but for collar flanges - butt joints do not have this. If you go to GOST, you will see everything in detail.
The nominal diameter of the flanges is a fundamental parameter on which all basic geometric dimensions depend. Those. knowing the nominal diameter of the flanges
all the rest are assigned automatically, except for one nuance called a row.
Rows of flanges
There are only two of them, 1st and 2nd, but they affect the overall dimensions. Depending on which row of flanges 1 or two
Dimensions depend on:
- diameters D3, D4, D5, D6.
- d - diameter of holes for studs or bolts.
- n is the number of these mounting holes.
- h1 is the height of the protrusion and the depth of the tenon.
- h2 is the depth of the groove.
- h3 is the depth of the oval groove.
- nominal diameters of bolts or studs.
Rows of flanges
All other connection or overall dimensions depend only on the nominal diameter. In accordance with GOST, flanges must be manufactured according to the preferred row 2 if 1 is not specified.
All dimensions in the drawings and tables, depending on the nominal diameter and row, can be viewed in GOST.
Weight or mass of flanges
Another important quantity is the mass of the flanges
, rather from a practical point of view, for example, to determine the weight of the entire batch, if there are other options, please put your comments at the end of this material, I will be very grateful. This value can also be found in the tables of the required GOST.
So we got acquainted with the basic, from my point of view, geometric and conventional dimensions and sizes of flanges. And all the rest can be found and viewed on site, they have already been determined by various strength calculations of strength materials. The dimensions are clear, but since the flange is steel and made from some kind of metal, of which there are a lot of brands, the question will accordingly arise: “What metal or grade of steel are the flanges made of and how to choose the right one if necessary, or how to choose the grade of steel, cast iron and alloy flanges"?
Technological.
These characteristics are related to the characteristics of production (from what blanks and by what technologies the flange is made).
Round and square flanges. Currently, a small number of gate valves, valves, etc. are produced for pipeline fittings that have a square flange as a connecting unit. Therefore, in accordance with GOST 12815-80, up to a nominal pressure of 4 MPa (40 kgf/cm2), both round and square flanges are provided by design. When ordering square flanges, it is necessary to remember that there is a direct dependence of the flange diameter on the nominal pressure: the higher the pressure, the smaller the diameter of the flange can be produced (Table 2).
| Ru, kg/cm2 | 1,0; 2,5; 6,0 | 10,0; 16,0 | 25,0; 40,0 |
| Du, mm | 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80, 100 | 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 65, 80 | 10, 15, 20, 25, 32, 40, 50 |
Materials or grades of steel, cast iron or alloys of flanges
In order to select the material from which the flanges are made
There is GOST 12816-80 and it has one wonderful table, once you see it, everything becomes clear. Let's say we are interested in a collar flange or, in other words, a steel butt weld in accordance with GOST 12821-80. The first thing we pay attention to is the conditional pressure at which it operates. Let's say it is 150 kgf/cm2 or Ru 15MPa. We look where it is located, we find that in the second column and the second part it is in the range from 0.1 to 20 MPa, because the first part does not suit us 0.1 to 10 MPa.
Next, we look at the operating temperature conditions, for example, from -40 0C to +450 0C and find that a stainless steel flange 12x18n9t is suitable for us, although 12x18n10t is currently used as the most common grade of stainless steel, and studs, bolts and nuts and steel grade 20x13 are corrosion-resistant heat-resistant, used in power engineering. That's all science is.
There are many different grades of steels and alloys, but the most popular are st20, st3, 09g2s, 12x18n10t and 15xm, as they are most often used for the manufacture of flanges because There are many more such working conditions. There are, of course, specific brands, but there are very few conditions under which they should work. It is worth noting that there are many fittings made of cast iron or ductile iron, therefore flanges are used from the corresponding grades of cast iron SCh 15 and KCh 30. All other materials, if necessary, look at GOST 12816-80. You can also download it.
Flange - definition of the concept
According to the terminology reference book, a flange is a flat piece with holes that acts as a connecting part of pipes. Studs, bolts and other fasteners are attached to the holes in the part to help secure it to the pipeline. The dimensions of the flanges correspond to the diameter of a certain pipe, so the manufacturer often equips the pipe with such an element in advance.
Type of flange
The main requirement for connecting pipes is tightness: this criterion is precisely ensured by the flange. It reliably tightens the parts, gives the connection reliability, strength, and the ability to use in a wide temperature range. If timely maintenance is carried out, the flange connection will last for many years. This type of part is manufactured in accordance with GOST, so it has special requirements.
Features of connecting pipes or pipes with a flange
Here I will talk about the features of connecting the pipeline or pipes of devices or containers directly to the flange itself. Because the most common are steel welded flat, steel butt welded or collar and steel free on a welded ring, then we will focus on them.
Connection of steel flat welded flanges to a pipe or pipe
During installation, the pipe is inserted into the flange and welded with two seams, one inside and the other outside along the end surface. The most labor-intensive connection, because you need to make two welds and to align the holes you will have to twist the pipe.
Connection of steel butt welded flanges - collar
For installation, the end of the pipe is leaned against the end of the flange or the so-called collar, which is why they are called collar collars, the one that is cone-shaped and is welded with just one weld. Much faster and easier.
Connection of steel loose flanges on a welded ring
Here a pipe is taken, the flange itself is put on it, then the pipe is inserted into the ring and scalded. The other part of the connection is exactly the same. It turns out that only the rings are welded to the pipes, and the flanges rotate freely on the pipes or pipes. Next, the ends are brought to each other, rotating the flanges until the holes match along the contour and studs or bolts are inserted and everything is tightened with nuts. Extremely convenient, because... there is no need to rotate the pipe or ensure exact alignment of the holes before welding, which is not always possible. Very practical in hard-to-reach places or where frequent inspection of flange connections is required, for example in the chemical industry. It may be cheaper because... It is allowed to use only a stainless steel ring, and the flange itself is made of ordinary carbon steel 3 or steel 20.
So we looked at how the most common types of flanges are joined and now I would like to show how to correctly designate them.
Working temperature
- One of the most important parameters is the operating temperature. Based on the temperature of the medium that will be transported through the pipeline, as well as taking into account the external environment, the grade of steel from which the fasteners will be made depends. Each grade of steel has a certain range of operating temperatures at which the fastener can provide strength and reliability of the connection.
- For example, at the same nominal pressure at a temperature not lower than -30 °C, it is recommended to use studs made of steel 35, while at an expected operating temperature of up to -70 °C, fasteners made from cold-resistant steel grades, for example, 09G2S, should be used or 10G2.
Flange designation
Designation of flat weld flanges
Flange 1-450-10 st. 20 GOST 12820-80 - this is the designation for a conventional flat flange of version 1 (with a connecting projection) with a nominal bore of 450 mm, designed for a nominal pressure of 10 kgf/cm2 or 1 MPa, made of steel 20.
And if the flange is square, with DN 1200 made of steel 3, then: Square flange 1-1200-10 st. 3 GOST 12820-80.
When ordering flanges with a nominal diameter of DN 100, 125 and 150 m, the letter of the corresponding pipe diameter is indicated.
When ordering tongue-and-groove flanges for fluoroplastic gaskets, the letter F is placed after the nominal pressure numbers.
Designation of collar flanges - butt welded
Flange 1-1000-100 st. 12x18n10t GOST 12821-80 - collar flange version 1, nominal diameter DC 1000 mm, PN 10 MPa or 100 kgf/cm2, made of stainless steel.
Square flange 1-800-10 st. 12x18n10t GOST 12821-80 - if square. And here Du is 800, and Ru is 1 MPa.
And if the design is tongue-and-groove, then the letter F is added.
Designation of loose flanges
Flange 125-6 st. 3sp GOST 12822-80 - DN 125, Ru 0.6 MPa, steel 3 sp.
Square flange 400-6 st. 15khn GOST 12822-80. Here the nominal diameter is 400 mm and the steel is 15ХМ.
Because When a welded ring is used in a pair, it is designated as follows:
Ring 1-400-6 st. 15ХМ GOST 12822-80 - version 1, DN 400 mm.
When ordering diameters 100, 125, 150, you need to add the letter you need. And when ordering a flange for tongue-and-groove fluoroplastic gaskets, the letter F is added.
So we looked at how the main types of flanges are designated
and we can move on to the next question, which I think is very important. And he’s talking about how to buy flanges, where to look at the price, and maybe look at the price list with the range, availability and prices.
Rows
- If the design details of the connecting dimensions (row 1 or 2) are not specified when ordering, then the flange is manufactured by default in accordance with row 2. The structural difference between the flanges of row 1 and the flanges of row 2 is the different number of holes in it for mounting bolts (studs) and their diameters.
- For example, a flange for DN 300 mm and PN 63 kgf/cm2 for row 1 has a mounting hole diameter of 36 mm, and for row 2—39 mm. Similarly, the flange for DN 80 mm and PN 10 kgf/cm2 of row 1 has a mounting hole diameter of 18 mm with a total number of 8 pcs., and row 2, respectively, has 18 mm and 4 pcs. Therefore, this feature must be taken into account when ordering flanges as counter flanges for shut-off valves.
How to buy steel welded flanges, prices and price list
In order to see the price for any flange, flat, collar, loose or mating, you can request a price list from the sales department by phone +7(351)735-95-75 or by email This e-mail address is being protected from spambots, for You must have Javascript enabled to view it. You can also send a request to the specified coordinates and get the best prices
, since the cost changes and the price list is not always updated quickly, issue an invoice and buy. You can arrange for the goods to be shipped. The price of flanges can be viewed by visiting the price list page for pipeline fittings. You can download it in a format convenient for you to your computer and keep it always at hand. There is also the cost of gate valves, valves, bends, taps and other fittings.
Thread diameter
- All threaded fasteners have an internal (nuts) and an external (studs and bolts) thread diameter. Depending on the purpose and the regulatory document according to which the product is manufactured, the thread can be metric or inch. Metric thread pitch is measured in millimeters, and inch thread pitch is measured in inches. Example: M12 - metric thread with a nominal diameter of 12 mm; 3/4" is an inch thread with a nominal diameter of 3/4".
- Example: M12x1.25 bolt - a bolt with a metric thread, a nominal diameter of 12 mm and a fine thread pitch of 1.25 mm.
- Example: for a nut with a nominal thread diameter of 16 mm, a spanner size S of 24 mm is provided.
- Bolt length - the length indicated in the product designation when ordering, in most cases is not a dimensional characteristic. Mostly, the length of the bolt indicated in the product designation is equal to the length of the bolt shank, i.e. the height of the bolt head is not taken into account.
- Example: for a bolt M12x120 - the length of the bolt shaft is 120 mm, while the total overall length is greater by the height of the bolt head by 7.5 mm, i.e. the total overall length is 127.5 mm. In Fig. 3: l - bolt length; l+ k = overall overall length of the bolt.
Stud length
- For most studs, the length l specified when ordering indicates the overall overall length of the stud. However, some regulatory documents do not include the entire length of the stud in the designation of studs.
- Example: GOST 22032-76, which applies to studs with a screw-in end of length dv, provides for the designation of the length of the stud, which does not include the length of the screw-in end. l is the length of the pin, b is the length of the screwed end (Fig. 4).
Version 1
- tolerance field indicates the accuracy of the thread.
- The larger the tolerance field value, the greater the deviation of the thread parameters from the nominal ones.
- For most fasteners, a sufficient thread tolerance zone for external threads is 6d, for internal threads—6H.
- Threaded end length is the length of the part of a bolt or stud designed to screw on a nut.
Quality groups
Depending on the purpose of the fasteners and the operating conditions of the fasteners, five quality groups of finished products have been established (Table 1, GOST 20700-75).
| Quality group number | Type of test | Number of products per batch |
| 1 | Determination of mechanical properties | 100% |
| Hardness Determination | 100% | |
| 2 | Determination of mechanical properties | 2% not but not less than 2 pieces |
| Hardness Determination | 100% | |
| 3 | Hardness Determination | 100% |
| 4 | Hardness Determination | 2% not but not less than 2 pieces |
| 5 | No tests | — |
Fasteners
The role of fasteners in flange connections cannot be underestimated. Bolts or studs have to “bear the blow” of mechanical loads that tend to break the connection. Fasteners (bolts, studs, nuts) are usually made of the same or similar material properties as the flanges themselves. By avoiding significant differences in linear expansion coefficients, it is possible to ensure synchronism in the response of the flange and fasteners to temperature changes, which is important during operation.
Holes for fasteners in the flanges of pipeline fittings must be located symmetrically with respect to both vertical and horizontal main axes. But not on themselves.
To save time spent on selection and reduce the cost of delivering the necessary fasteners, it is convenient to order it complete with flanges from one company. This will also serve as a guarantee of their full compatibility. This opportunity is available to customers who contact ARMATEK. It will also help to equip flanges with wafer gaskets made of various materials. After all, the tightness of the flange connection largely depends on their properties and qualities.