How to remove silver from contacts: various ways to obtain the precious metal
Over the past decades, the rapid development of the electronics industry has led to a decrease in the use of precious metals in the production of components and semiconductors.
However, during the existence of the USSR, precious metals were one of the main and extremely important components of manufactured radio electronics.
There is a specialized reference book for the content of precious metals, from which you can find out the list of precious elements that make up a particular electronics component.
The most common noble metal in radio components is technical silver. It is pure metal with minor impurities or no impurities at all.
Thus, technical silver is almost always a high-grade metal of 999 purity. In this article we will tell you where it is found and how to remove this metal from the contacts and separate it from the copper at home.
Chemical composition and main characteristics
An alloy of copper and zinc, which is well known to everyone under the name “brass,” has been used by people since ancient times, making weapons, tools, dishes and many other products from it. Initially, instead of zinc, which was discovered by scientists only 5 centuries ago, zinc-containing ore – galmey – was used to produce such an alloy. The tombak itself was invented in the 17th century. It is believed that the author of the chemical composition of this alloy was the Englishman Christopher Pinchbecker.
Thanks to its characteristics (first of all, its very beautiful color), tombac became known throughout the world in just a few decades. By the way, this alloy gained enormous popularity among scammers who passed off products made from it as gold, deceiving gullible citizens and earning a lot of money from it. Both before and now in everyday life and among specialists you can hear different names for tombak:
- princetal;
- chrysochalk;
- similor;
- oreid;
- Chrysorin.
Cold-rolled brass strip L90 - the material from which tombak products are subsequently made
Tompak, as is already clear from all of the above, is an alloy of copper and zinc, with the first element contained in tombak 88–97%, and the second (zinc) – no more than 10%. There is also such a material as semi-tompak. This is an alloy whose chemical composition is 10–20% zinc.
The amount of zinc in the composition of any brass, including tombac, affects not only the characteristics of the alloy, but also its color. Thus, with an increase in the content of this element in the composition of brass, the color of its surface changes from red to light yellow. Increasing the quantitative content of zinc in the chemical composition of tombac makes it possible to achieve:
- obtaining a noble golden color;
- improving anti-friction characteristics;
- good mechanical and technological characteristics;
- significant reduction in cost (when compared with the price of pure copper).
Chemical composition of copper alloys used to imitate gold
Tompak has a whole list of advantages, which include:
- exceptionally high corrosion resistance;
- increased wear resistance;
- good weldability with various materials (steel, non-ferrous and precious metals);
- high ductility (which makes it possible to use plastic deformation methods for processing tombak and engraving on the surface of products made from it);
- subject to enameling and gilding;
- non-magnetic.
Conditional classification of simple (double) brasses
Tompak also has the following characteristics:
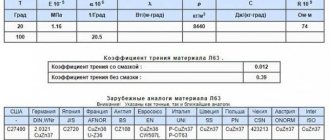
- hardness – up to 145 MPa;
- the temperature at which the alloy begins to melt is 10450 Celsius;
- friction coefficient: without the use of lubricant – 0.44; when using special type lubricants – 0.074;
- tensile strength - 440–520 MPa;
- the relative elongation that the material receives after breaking is 3%;
- material density – 8780 kg/m3.
The characteristics of L90 brass, which is called “tompak,” can be improved if various components are added to its chemical composition in small quantities. This minor modification allows us to obtain a material that optimally combines characteristics such as ductility, strength, good workability, attractive appearance and affordable price.
Modern manufacturers produce tombak in the form of rolled sheets or bars, which determines the options for further use of such material. You can find out exactly what elements and in what quantities are included in the chemical composition of the alloy by its marking. Thus, the letter “L”, which is necessarily present in the designation of tombak, means that this is brass. The numbers after this letter indicate how much base metal – copper – is contained in the alloy. In such brass, in addition to copper and zinc, there are necessarily impurities, the exact amount of which can be found out from special tables. It should be borne in mind that alloys in which copper is less than 90% (L85, L80, etc.) belong to the semi-tombac category.
Foreign analogues of tombak (brass grade L90)
Where is this precious metal found?
For precious elements in electronics, properties such as thermal and electrical conductivity, as well as light reflection, play an important role.
Thus, noble metals are used in the following radio components:
- Microcircuits . The most promising options for metal mining are Soviet-made microcircuits. It is preferable to disassemble microcircuits of the 564, 530, 133, 134, 142, 155 and 1533 series.
- Capacitors . In addition to silver, palladium, platinum and gold can also be found here. The volume of certain metals depends on the type of case (ceramic, yellow, silver and tantalum), as well as on the year of manufacture of the devices. These components were used in various computers, electronic devices and automatic telephone exchanges, as well as in tube televisions and tape recorders.
- Resistors . The basis of these radio-electronic elements is silver. The most cost-effective components are resistors of the PTP, PPBL, PPML and 5K series. It is recommended to collect Soviet resistors produced before 1982. The key difference between this component is the diamond-shaped marking.
- Connectors . These devices, both Soviet and foreign made, are suitable for extracting silver, technical gold and other precious metals. However, the content of precious metals in foreign-made components will be approximately five times lower.
- Transistors . Another electronics component containing a relatively large number of noble elements. The most preferred for silver mining are transistors with the index 2T935A, 2T944A, 2T945A and 2T998A.
In addition to the above radio-electronic components, technical silver may be contained in:
- generator lamps;
- LEDs;
- switches;
- buttons.
What is brass
The main components of brass alloy are copper and zinc. The proportional components of these metals may be different. The amount of zinc varies. Its minimum value is 20%. The maximum reaches 50%. At the same time, the alloy changes its color: it can be golden, yellow or green.
The percentage of zinc is so important that it can change the characteristics of the material. This refers to its ductility and hardness.
Properties and composition of pseudo-precious brass
Brass has been known for a very long time, since the times of the ancient Romans, and this despite the fact that zinc was discovered only 5 centuries ago. In those distant times of antiquity, galmei (zinc ore) was added to the mentioned alloy instead of pure Zn. But the tombac that we know today was invented by Christopher Pinchbecker in the 17th century. The alloy became widespread not only in England; within a few decades people learned about it all over the world. And by the way, many scammers got rich by passing off coins, various jewelry and products made from this type of brass as gold. Today in everyday life you can find other names for this alloy - similor, princetal, chrysochalk, oreid and chrysorin.
As you may have guessed, it is an alloy of copper and zinc. The content of the first element ranges from 88 to 97%, and the second - no more than 10%. If you increase the share of Zn to 10–20%, then you get a semi-tompak. The content of the last element affects the properties of brass and its color. As it increases, the color changes from red to yellow. Sometimes tombac bars can be confused with precious gold in the photo. Such a change leads to improved antifriction, technological and mechanical properties, and the cost, on the contrary, decreases. This is due to the relative cheapness of zinc compared to copper.
The material has excellent anti-corrosion properties and wear resistance. It welds perfectly with various steels and precious metals. It is distinguished by increased plasticity. Easily amenable to enameling and gilding, forging, drawing and engraving.
Another feature is the complete absence of magnetic properties.
Product made from tombak
The hardness of the material reaches 145 MPa. The temperature at which the melting process begins is 1045 °C. Without the use of lubricant, the friction coefficient is 0.44. If you use special lubricants, this figure can be reduced to 0.074. Tensile strength ranges from 440 to 520 MPa, and elongation after break is about 3%. Brass L90 has a density of 8780 kg/m3. To obtain the specified characteristics, additional elements are introduced into the composition of the tombac alloy. Their content is only a few tenths of a percent. The result is a material with an ideal ratio of ductility and strength, excellent appearance and reasonable price.
The alloy, depending on the further fate, can be sheet or in bars. The marking indicates the letter “L” first, followed by the percentage of copper. For example, L96 consists of 95–97% Cu, no more than 0.2% impurities and the rest is Zn. But if you see the designation L90 on a product, it means that the main element is contained within 88–91%, impurities are less than 0.2%. Brands L85 and L80 belong to semi-tompak. The share of additional components in them can reach 0.3%.
Characteristics
The main quality in the characteristics of brass is its corrosion resistance. But it also has other properties:
- The ability of the alloy to withstand aggressive environments, especially after coating the surface with varnish.
- Strength of brass.
- Plasticity of the alloy.
- The ability of the material to be processed by pressure. The process is carried out both hot at high temperatures and cold.
- The alloy can be subjected to resistance welding and soldering.
- Thermal conductivity, which increases with increasing percentage of copper.
- Melting point, which is 880–950 degrees. With less zinc added, the melting point decreases.
- The material has non-magnetic properties.
The main factor in the hardness and ductility of the joint is zinc. An increase in its quantitative content is directly related to an increase in strength characteristics. Plasticity increases only up to a quantitative zinc content of 36%. With a subsequent increase to 45%, this indicator decreases.
In order to increase the hardness of the alloy, a heat treatment called cold hardening is carried out. It helps not only to increase the strength index, but also relieves internal, structural stresses.
Alloying additives affect the performance characteristics. Their influence is indicated in the table:
| Name of alloying element | Effect on brass characteristics |
| Silicon | Its high presence leads to a decrease in the hardness of brass. |
| Lead | Improves anti-friction properties. |
| Manganese, aluminum and tin | Increases resistance to tearing. Corrosion resistance is increasing. |
| Nickel | Reduces the risk of material cracking. The alloy acquires a peculiar color. This connection is called “white brass”. |
| Arsenic | The material has the ability to work in liquid, fresh media. |
Marking
There are 2 types of alloys:
- Two-component. The main components are copper and zinc. They are marked with the letter L. Next are numbers indicating the amount of copper in percent. L60: contains 60% copper, and the remaining 40% zinc.
- Multicomponent. In addition to the main components, alloying elements are added. Also in front is the letter L. Then follows a list of additives. At the end, numbers are written through a dash indicating the percentage of each component. The amount of zinc is not indicated, but calculated. For example: Brand LAZhMts66-6-3-2 has 66% Cu, 6% Al, 3% Fe and 2% Mn. By calculation, the amount of zinc is determined to be 23%.
How to distinguish gold from brass
Even though gold and brass look similar, there are ways to tell one from the other. This is checked as follows:
- Gold has a more saturated color. In addition, over time, brass darkens because it oxidizes in air, but gold does not.
- If you put a magnet near it, brass will be attracted, but gold will not.
- Brass has a higher density, which means it is heavier. This is noticeable when throwing pieces of metal in your palms.
- Availability of sample.
- If you test with acid, the gold will not react and the brass will discolor.
This is interesting: Heat-resistant steel - grades, types and composition of heat-resistant steels and alloys
Advantages and disadvantages
Brass alloy has characteristics that are positive in one case and negative in another. They consist of the following:
- Light weight. This quality, together with high strength, is used in certain industries.
- The alloy has good ductility.
- Low cost.
- Corrosion resistance decreases with increasing amount of copper.
- Thermal conductivity indicators are lower than those of pure copper and bronze.
How to obtain silver from radio components at home?
Silver is a highly inert metal, which means that this element has weak reaction-chemical properties. In other words, it is not easily dissolved.
Under normal conditions, silver does not dissolve in hydrochloric and sulfuric acids, as well as in aqua regia , like gold.
However, this metal has good solubility in oxygen-containing nitric acid.
The answers to the questions of how to isolate, smelt or otherwise extract technical silver from radio components come down to three main methods :
- Mechanical processing is the simplest method, suitable for some types of contacts that can be easily separated using pliers and wire cutters.
- Heat treatment - in cases where it is not possible to extract silver mechanically, there is an option to resort to using a gas blowtorch. When the heat is high, the silver elements can be easily separated from the holder using available means.
- Treatment with nitric acid - this method is used to extract precious metals from massive parts of radio-electronic parts. The method requires high care and accuracy at each stage of processing.
Where is Tompak used?
Tombak is used for cladding steel, i.e. coating the surface of steel products with a thin layer of an alloy, which is used in the manufacture of charges and bullets for firearms and producing a steel-brass bimetal. The use of such bimetallic sheets saves stainless steel and non-ferrous metals, protecting the steel core from corrosion and destruction and giving the surface the desired properties. This technology can dramatically reduce the cost of the product. Bimetal is used for various elements of chemical equipment, where other coatings cannot cope with corrosion. Bimetallic wire is used for communication lines. Tombak is used for the manufacture of high-precision measuring and other equipment.
Due to its good resonator properties, the bells of brass wind musical instruments are made from the alloy. It is used to make:
- artistic products (paintings made using metal chasing technique);
- radiator tubes and drawn pipes with a diameter of up to 30 mm;
- insignia;
- accessories;
- cigarette cases and cigarette holders;
- some types of medals and coins.
For example, Russian coins in denominations of 10 and 50 kopecks. School Gold medals are made from tombac and then gilded. The bronze medals of the 1980 Summer Olympics in Moscow were made of tombac. In 1942-1943, Canada issued tombac coins in denominations of 5 cents.
Due to its beautiful color and ease of processing, tombak is widely used by jewelers in the manufacture of costume jewelry. The alloy is used to make dishes, figurines, candlesticks, and in interior decoration and furniture. In Eastern countries, elegant thin-walled waterware, jugs, bowls, and trays are made from tombac, which is decorated with unique patterns, thereby creating works of art. The dishes are protected from the destructive effects of water on the alloy by tinning with tin, which allows the artistic beauty of the products to be preserved for a long time.
Sales of the resulting metal raw materials and its average price per gram
For the subsequent sale of precious metal from contacts, you need to know its resulting mass and sample. As mentioned earlier, technical silver used in radio electronics is a pure metal of 999 purity.
Accordingly, metal obtained mechanically or by smelting will be 999 fine. If silver was extracted chemically using nitric acid, the output would be a metal of approximately 980 fineness. This is due to the copper impurities present in silver.
The direct cost will depend on two main factors :
- percentage of pure silver in the resulting alloy;
- places of sale of precious metals.
For 2022, the price for 1 gram of technical silver scrap is as follows :
- sample 999 – from 24 to 35 rubles;
- 980 – from 21 to 27 rubles;
- 960 – from 16 to 22 rubles;
- 925 – from 9 to 11 rubles.
When selling more than 1 kg of precious metal, you can earn 2-4 rubles more for each gram of it.
It is also most likely that on the Internet, using thematic sites and forums, you can find buyers who are ready to offer a higher price for those. silver from contacts than from a pawn shop.
What is a semi-tompak?
Semi-tompak should be included in a separate category. The differences lie in the concentration of zinc, which increases to 10-20%. Due to this, the basic properties of tombak change. The key features are the following:
- The product takes on a more yellow tint.
- The degree of ductility decreases and refractoriness increases.
- The material is often used to make technical parts.
This alloy is found much less frequently in comparison with tombac. This is due to the fact that an increase in the amount of zinc causes a large number of deficiencies to appear.
How to remove gold plating from silver?
Precious metals are used in the production of valuable coins, jewelry and other expensive products. Sometimes owners of products want to transform them by removing the gilding. How to do it yourself at home? It is in this article that everyone will find the answer to this question, making the task as simple as possible.
Of course, the easiest way to complete this procedure is to turn to specialists and take the jewelry to a special workshop. However, there is not always time for this, and it is difficult to find a good professional in his field, so many people want to carry out the procedure themselves.
You can remove gold plating from silver in one of two ways:
Production methods
Today, tombak can be produced using a variety of technologies. The most widely used option is the use of an electric oven, which heats the composition to 1400 degrees Celsius. When exposed to such a temperature, silicate is released, which floats to the surface and is removed.
Among other features, we note the following:
- The result is base metal, which is poured into a special container. There are quite a large number of different devices whose purpose is to release tombak. The base composition must be heated to a temperature of 1400 degrees Celsius. In this case, certain safety rules must be observed.
- The next step is to flush the resulting composition with oxygen. Special equipment is also used for this. The purging procedure leads to the active release of thermal energy and a chemical reaction.
- As a result of a chemical reaction when exposed to oxygen, copper is formed. It is characterized by the fact that it has a large number of various impurities, due to which the properties are significantly reduced.
- Next, the composition is electrically cleaned using special acidified copper sulfate.
- Zinc is introduced into the resulting straightened copper. This material increases strength and corrosion resistance.
The above information indicates that the process of obtaining such a composition is quite complex and time-consuming. That is why the cost of tombak is quite high, but much less than the cost of the precious metal.
Do not forget that tombac is an alloy of copper and zinc. This composition has very attractive characteristics and is used in the creation of various high-precision measuring and other equipment. In addition, decorative characteristics are highly valued. At a certain ratio of the main components, the alloy resembles gold, but the properties are significantly different.
Chemical method
In this case, the well-known “aqua regia” will help remove gold from jewelry. This procedure must be carried out extremely carefully, because it is necessary not only to remove the gold layer, but also to preserve the jewelry, leaving the silver without damage. If silver is visible on a precious coin, it must be covered with asphalt.
The method itself includes the following procedure:
- Cleaning coins from all types of contaminants.
- Pour aqua regia into a porcelain cup.
- Warm up the coin a little and immerse it in the liquid.
- Heat the container in a sand bath (do not bring to a boil).
- If dark spots (silver chloride) appear on the coin, it must be removed from the liquid and washed under the tap.
- The product is immersed in an ammonia solution to remove silver chloride.
- Remains of gilding are removed with a brush.
Electrochemical method
Here the coin acts as an anode immersed in an electrolytic bath. A copper plate should be used as a cathode, and the electrolyte itself is a 7% solution of potassium cyanide in distilled water. After completing the procedure, the precious coin must be removed, rinsed thoroughly under the tap, removing any remaining gold with a brush.
To carry out the procedure you will need:
- Distilled water.
- Power supply with the ability to change voltage and polarity.
- Electrolyte.
- Teourea.
Removal of gilding using the electrochemical method is carried out as follows:
- Electrolyte preparation.
- Preparing a glass jar and lid for it.
- The cathode is stainless steel or titanium.
- Immerse a coin in the solution and apply a voltage of about 4 Volts.
Important! During the procedure, the jar must be closed with a lid, since hydrogen sulfide is released due to the chemical reaction.
Gold mining by electrolysis
For the procedure you need to prepare:
- Potassium cyanide (50 grams).
- Distilled water (1 liter).
- Porcelain or glass container.
- Silver or iron plates are the cathode.
The procedure itself includes the following steps:
- First of all, you need to clean the gold-plated object from all contaminants.
- Hang it from the anode and lower it into the solution.
- Turn on direct current with voltage up to 15 V.
- Remove gold from cathode.
Important! You can also take sulfuric acid as an electrolyte, lead will be the cathode, and the voltage will be 4 V.
We extract gold with an oxidizing agent
The chemical method is based on the inertness of gold, because it reacts with halogens only when heated. In this case, you need to use the previously described remedy - “royal vodka”. First of all, you need to prepare it by preparing concentrated acids (hydrochloric and nitric) and mixing them in a 3:1 ratio. It is worth noting that its smell is extremely unpleasant, so it is better to act with a respirator. Remember that aqua regia is one of the strongest oxidizing agents.
Important! The solution must be prepared immediately before use. After all, it loses its properties and decomposes, releasing gaseous products.
As for the procedure for extracting gold, the solution simply eats it away from radio components and other objects, as a result of which all metals except gold dissolve. As for the gold, it will float in the liquid like foil that needs to be collected and filtered.
Important! To filter gold you need to use a thick cloth. Medical gauze is not suitable because the holes are too large.
The process itself must be carried out according to plan:
- Procurement of raw materials - you need to rid gold-plated objects as much as possible from others (pull out contacts, bite them, etc.).
- Take a glass, porcelain or stone container.
- Prepare a chemical solution by mixing concentrated acids.
- Pour the liquid into the prepared container and throw the part there.
- Wait until the “chlorine gold” appears.
- Add sodium sulfide to aqua regia to obtain pure gold.
- Collect the gold powder and filter with a thick cloth.
- Wash and dry the gold.
- Melt precious dust into an ingot.
Important! As a result of this method, it is possible to obtain gold, but it will be of low quality and will require additional cleaning, and the loss of the precious metal will be significant.