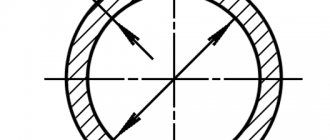
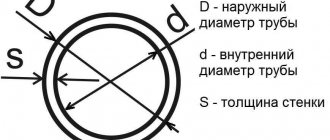
The main types of diameters of galvanized pipes are: external electric welded according to GOST 10704 and internal water and gas pipes according to GOST 3262. The main dimensions of the diameter of a galvanized pipe are the nominal diameter (DN) in inches and millimeters and the external diameter in millimeters. The diameters of galvanized steel pipes are presented in the table below:
| internal diameter of galvanized pipe, mm | internal diameter of galvanized pipe in inches | external, outer diameter of galvanized pipes, mm | wall thickness | weight of a meter, kg per 1 mp |
| DN Ø 6 | ¼″ | Ø 10.2 mm | 1.8, 2.0, 2.5 | 0,37, 0,40, 0.47 |
| DN Ø 8 | ⅓″ | Ø 13.5 mm | 2.0, 2.2, 2.8 | 0,57, 0.61, 0.74 |
| DN Ø 10 | 2/5″ | Ø 17 mm | 2.0, 2.8 | 0.74, 0.98 |
| DN Ø 15 | ½″ | Ø 21.3 mm | 2.5, 2.8, 3.2 | 1.16, 1.28, 1.43 |
| DN Ø 20 | ¾″ | Ø 26.8 mm | 2.5, 2.8, 3.2 | 1.50, 1,66, 1.86 |
| DN Ø 25 | 1″ | Ø 33.5 mm | 2.8, 3.2, 4.0 | 2.12, 2.39, 2.91 |
| DN Ø 32 | 1 ¼″ | Ø 42.3 mm | 2.8, 3.2, 4.0 | 2,73, 3,09, 3.78 |
| DN Ø 40 | 1 ½″ | Ø 48 mm | 3.0, 3.5 | 3,33, 3,84 |
| DN Ø 50 | 2″ | Ø 60 mm | 3.0, 3.5, 4.5 | 4.22, 4,88, 6.16 |
| DN Ø 65 | 2 ½″ | Ø 75.5 mm | 3.2, 4.0, 4.5 | 5.71, 7,05, 7.88 |
| DN Ø 80 | 3″ | Ø 88.5 mm | 3.5, 4.0, 4.5 | 7.34, 8,34, 9.32 |
| DN Ø 90 | 3 ½″ | Ø 101.3 mm | 3.5, 4.0, 4.5 | 8.44, 9.6, 10.74 |
| DN Ø 100 | 4″ | Ø 114 mm | 4.0, 4.5, 5.0 | 10.85, 12,15, 13.44 |
| DN Ø 125 | 5″ | Ø 140 mm | 4.0, 4.5, 5.5 | 13.42, 15.04, 18.24 |
| DN Ø 150 | 6″ | Ø 165 mm | 4.0, 4.5,5.5 | 15.88, 17.81, 21.63 |
Diameters of galvanized steel pipes
Galvanized pipes are produced in accordance with GOST 3262-75 and GOST 10704-91.
Length from 6 to 12 meters. According to GOST 3262, pipes are called galvanized water and gas pipes. Measured by internal diameter in inches and millimeters. Example of designation: VGP galvanized pipe 50x3.5 st3sp dl6m GOST 3262-75.
According to GOST 10704, pipes are called galvanized round electric-welded longitudinal pipes. Measured by outer diameter in millimeters. Designation example: Galvanized pipe 89x4 st3sp dl12m GOST 10704-91.
Our table shows the main diameters of electric-welded galvanized steel pipes.
Galvanized pipe
Galvanized steel water and gas pipes (WGP) are widely used in construction. Due to the galvanized coating, a galvanized water and gas pipe (WGP) acquires anti-corrosion properties. Galvanized water pipes are used for water supply in construction, which is why they are called galvanized water pipes. The dimensions of galvanized steel VGP pipe are the same as those of ordinary black VGP pipe. The indicator is the nominal diameter (DN), but although the wall thickness may be different, only the outer diameter of the galvanized steel water and gas pipe remains unchanged. Due to the great popularity and widespread use of galvanized VGP pipes, manufacturing plants began to produce VGP pipes with zinc coating in accordance with GOST 3262-75.
Galvanized pipes
Steel pipes are durable and reliable, but they have a significant drawback - a high corrosion rate under the influence of water (up to 0.18-1.0 mm per year).
Galvanized pipes - metal products of round cross-section with surfaces coated with a zinc compound - do not have this drawback. Despite the fact that the coating thickness usually does not exceed 30 microns, it significantly reduces the corrosion rate (up to 0.015-0.020 mm per year) and increases the overall service life of the entire pipeline (up to 25 years).
The quality of galvanized pipes is determined by the nature of the surfaces (traces of technical processing and minor dents are acceptable, while scratches, cracks and swelling indicate a violation of the technology) and the degree of processing of the cuts (threads may be absent, but if there are any, they must be smooth, accurate, without burrs).
VGP pipes
Water and gas pipes are a complex category, including metal pipes made of carbon steel (St1, St2, St3), as well as steel grades 08, 10, 20. In this case, the selection of material and production of VGP pipes is carried out in accordance with regulatory documents (GOST 3265-75 , GOST 380, GOST 1050, GOST 3262-75).
Galvanizing is one of the modern and advanced types of anti-corrosion coating, which greatly increases the service life of the metal: galvanized pipes. Galvanized pipes are widely used in road construction: guides and pillars, water outlet and drainage pipes, lighting masts, supports for road signs. Galvanized pipes are also widely used in urban infrastructure: flagpoles, elements of advertising structures, bus stops, sports and playgrounds. Plumbing work, the production of metal structures, laying channels for cables and wires are also areas where galvanized pipe is used.
Installation methods
According to the standards, high requirements are imposed on the sealing of structures involved in the transportation of trains.
Recommended methods for installing galvanized steel pipes are:
- coupling;
- Threads;
- Welding unit.
Combining parts using couplings does not require special equipment, such as welding or a soldering iron. The method is based on bringing the elements together into a lock; the inner part of the coupling is fixed on the pipe.
For strength, the coupling is combined with a threaded connection. The method makes it possible to carry out urgent repairs and reconstruction. Disassembly is done using a nut wrench.
In fire-fighting pipelines operating under high pressure, only coupling connections are used. The thread is made on the outer plane of the pipeline using a die or machine processing. A coupling with a thread of 2-3 turns is secured on top of the pipe. Threaded connections are difficult to manufacture and have a high cost.
Which is better: stainless steel or galvanized?
The formulation “Which is better?” - fundamentally not true. First of all, stainless (alloy) and galvanized steel are produced using completely different technologies, which ultimately determine their physical characteristics, scope and cost.
- The corrosion resistance coefficient of both materials is quite high and largely depends on the characteristics of production and the quality of the raw materials.
- Stainless steel is in many ways more resistant to extremely high temperatures than galvanized steel, which should be taken into account when installing, for example, chimneys.
- The price of galvanizing is usually 20-25% lower.
Features and Specifications
Steel water pipelines have the following characteristics. Some positive aspects have already been partially discussed above, but not everything is so rosy with this pipe rolling range.
It also has negative characteristics:
- Corrosive formations. Unfortunately, steel is susceptible to this effect. And the water supply system feels this with particular acuteness. In it, moisture is constantly combined with atmospheric oxygen. Such a combination is simply destructive for steel.
- Decrease in lumen over time. Such a highway tends to become overgrown over time. Her clearance can catastrophically decrease in just a couple of years.
- Labor-intensive installation and dismantling. Speaking about a steel pipeline, we must immediately make a reservation that assembling it is more difficult than tightening several nuts on fittings of a metal-plastic structure, or welding polypropylene pieces with a small welder. Connecting a steel water pipe will require the participation of a professional welder.
- Impressive weight. This characteristic feature of steel water supply pipe materials greatly complicates transportation and installation.
IMPORTANT! Steel networks can be protected from such a significant drawback as corrosion by priming and painting.
Advantages and disadvantages of galvanized steel pipes
Compared to polymer pipes, galvanized pipes have a number of advantages:
- High index of strength and resistance to intra-circuit pressure and mechanical damage.
- Dimensional stability over a wide range of operating temperatures: no cracking in frost and no expansion under high temperatures.
- High level of heat and energy conductivity.
Non-galvanized steel analogues are inferior to galvanized ones in a number of characteristics:
Resistance of the external and internal circuit to corrosive processes.
- The smooth inner surface of the pipes is not prone to the formation of internal build-up, which narrows the passage opening. In addition, this feature allows the use of galvanized pipelines for organizing drinking water supply.
- The antiseptic properties of zinc disinfect water transported through pipes.
Among the disadvantages it should be noted:
- Unpresentable appearance.
- Reduced anti-corrosion resistance when the galvanized layer is damaged.
- Higher cost compared to plastic and conventional metal pipes.
Welding method
A frequently used method for installing galvanized products is through electric welding. The work process is carried out in ventilated rooms. The welding areas must be degreased.
- Under the influence of the high temperature of the arc, the zinc goes into a gas state, guaranteeing a tight fit of the parts.
- After welding, the space around the seam is cleared of zinc to prevent cracks from appearing during cooling.
- When thin-walled products up to 5 mm are welded, copper overlay rings are used.
After completion of the work, the linings are removed, preserving the integrity of the zinc ball.
Galvanizing process
Galvanizing technology involves coating steel pipes with a thin layer of zinc, both inside and outside. The resulting zinc coating has a characteristic light shade, for which it is called “white rust.” The service life of the pipeline depends on its thickness and quality of application.
There are 5 technologies for galvanizing pipes, of which the first 3 are the main ones:
- Electrogalvanic.
- Thermal diffuse.
- Hot.
- Cold.
- Gas thermal.
Electrogalvanics (galvanostegy)
Electrogalvanics, or more precisely, its subsection - electroplating - is the most common method of galvanizing metal pipes. Through electrolysis (exposure to electric current passing through cyanide, non-cyanide or acidic electrolytes), zinc electrodes are dissolved, followed by the deposition of zinc on the pipes. Production processes are regulated by GOST 9.301-86.
The thickness of the zinc coating applied by electroplating varies in the range of 10-30 microns and depends on the technical parameters of production: current strength, heating temperature, etc.
Advantages of electrogalvanic galvanizing:
- Integrity, uniformity and high density of the zinc layer.
- Attractive glossy appearance, thanks to which these products are widely used as stair railings, in the manufacture of furniture and stand equipment.
- Low price category.
Requirements for their production are standardized by several GOSTs
A galvanized pipe is the same as a steel pipe, but with a layer of zinc applied to its surface. Depending on the conditions in which it will be used, this layer can be applied inside or outside. For products of different sizes, different galvanizing technologies are used, but the result is always the same: a layer is formed that protects the steel from corrosion. And if the pipe is galvanized, then its marking will contain the designation (C).
Types of galvanized pipes (range) and their technical characteristics (dimensions and weight)
Based on wall thickness, pipes are divided into:
- Lungs (wall thickness - from 1.8 to 4 mm).
- Standard or ordinary (2 - 4.5 mm).
- Reinforced (2.5 - 5.5 mm).
Galvanized pipes are produced in a wide range of diameters in lengths of 4-12 meters. The outer diameter of the most popular models ranges from 10.2 to 165 mm, conventional - from 6 to 150 mm.
Gas and water
The main purpose is the arrangement of internal water supply and gas communications. The requirements of GOST 3262-75 require the use of only high-quality steel with a density of 7.85 g/cm³ and a zinc coating thickness of up to 0.03 mm for the manufacture of water and gas shut-off pipes (VGP pipes).
The mass of VGP pipes is usually taken from the corresponding tables:
Electric welded
They are used primarily in construction, the agricultural sector and mechanical engineering. Their production is regulated by GOSTs 10704-91 and 10705-80. They are produced mainly in round sections.
Round (seamless)
They are considered universal, because the scope of their use is not limited in any way. Manufactured from high-quality alloy or carbon steel, they are characterized by a long service life and ease of installation. Depending on the forming method, manufacturing technologies are regulated by GOSTs 8734-75 and 8732-78.
Profile
Profile are pipes that have a cross-section different from round - square, rectangular, triangular, etc. The main GOST is 13663-86; separate GOSTs have been developed for each type of configuration: 8639-62 (square), 8645-68 (rectangular), etc.
Sandwich pipes
Sandwich pipes are a double-circuit structure of pipes of different diameters inserted into one another, usually with a layer of thermal insulation material.
What kind of pipe is this
The abbreviation VGP stands for “water and gas pipeline”. Naturally, a pipe under this name is produced for use in gas and water pipelines.
It finds application in situations in which polymer pipes cannot be used due to their properties. For example, highways in the open air, pipes in stove heating and other options for using VGP bends show how indispensable such pipe products are in certain areas of economic life.
Approximate prices
The cost of galvanized pipelines depends on a number of factors (steel grade, galvanizing method, standard size). The price is usually indicated per linear meter or ton (relevant for large-diameter pipes).
| Pipe type | Diameter, mm | steel grade | Length | Price |
| Electric welded VGP | 15 | st3ps-5 | 6 m.; 12 m. | 88 rub./l.m. |
| Electric welded (ESW) | 25 | st3ps-5 | 6 m.; 12 m. | 160 rub./l.m. |
| Electric welded VGP | 159 | st3ps-5 | 6 m.; 12 m. | 890 rub./l.m. |
| Electric welded (ESW) | 820 | 12Х18Н10Т | 6 m. | 27,000 rub./t. |
| Electric welded VGP | 15 | Art.1-3 | 7.8 m. | 56,000 rub./t. |
| Electric welded (ESW) | 133 | Art.1-3 | 7.8 m. | 54,500 rub./t. |
Where are galvanized pipes used?
In addition to the above-mentioned water and gas supply systems, steel pipes coated with a layer of galvanization are actively used in a variety of industries, agriculture, utilities, and construction:
- Arrangement of heating circuits, sewerage systems and chimneys.
- Laying a protective circuit for electrical cables and other wires.
- Construction of building frames, fences, gazebos, benches.
- Arrangement of playgrounds, public transport stops, road signs.
- Creation of advertising and lighting structures.
On a note! The opinion that the use of galvanization for drinking water supply is dangerous to human health is a prejudice. Provided that uninterrupted supply is ensured, the zinc content in water (5 mg/l) does not exceed standard values (10-15 mg).
Is it possible to use galvanized chimney?
Galvanized steel is successfully used for arranging chimney circuits. However, some properties of galvanizing, namely toxicity when heated and instability to extremely high temperatures, somewhat limit the scope of its use as a chimney.
It is important to remember that when heated above 419.5⁰C, zinc begins to release metal oxide fumes that are toxic to humans. The greatest danger is posed by the so-called technical zinc, during the production of which even more harmful lead, arsenic and antimony are added to the composition.
Therefore, galvanized chimneys are prohibited from being installed in systems with a heating temperature of more than 350⁰C, which means they are not suitable for heat generators running on coal or wood. But in symbiosis with a heating unit running on gas or diesel fuel, galvanized chimneys are quite safe.
Life time
The “life” period of a galvanized chimney depends on a number of factors:
Wall thickness, which must be at least 1 mm. At lower rates, the pipe burns out already in the first or second heating season.
Buildings. Single-walled ones, as a rule, require replacement after a couple of years, while double-walled (double-circuit) ones can last about 45 years.
The presence of a thermal insulation circuit. Without insulation, harmful condensation forms in the pipe and soot begins to accumulate, which increases the risk of a chimney fire and reduces its service life by at least 3 times.
Types of chimney pipes
Galvanized chimneys and components for them are classified into:
- Single-walled (single-circuit).
- Insulated sandwich chimneys (double-circuit), which in turn are also divided into:
- Mono-structures in which both metal contours are made of galvanized steel;
- Combo designs in which the outer contour is galvanized and the inner contour is made of stainless steel.
Combined chimneys have the best technical characteristics, because... Stainless steel is more resistant to burnout and the influence of an acidic environment, and its lower cost compared to chimney pipes made entirely of stainless steel allows you to significantly save your budget.
Galvanized mono-structures minimize the production of condensate, but cannot withstand heating above 450⁰C. Most often used for lining brick chimneys.
Standard service life
Departmental building codes (VSN-88) establish the timing of the functioning of various communications in residential buildings.
With regard to galvanized pipes, they last much longer than with ordinary pipes made of black steel.
Thus, for taps in a cold water supply system, the service life is set at 30 and 15 years, respectively, for DHW taps - 20 and 10 years.
Destructive factors and actual service life
In practice, the time required for effective operation of water pipelines is shorter. Let's consider the reasons for this phenomenon.
Rust should not appear in galvanized pipes. Sediments and other debris do not linger on their smooth walls. However, if the pipeline taps are not opened completely, then the flow does not have time to wash away the waste coming from the central network into the home system. Gradually, the accumulation of contaminants is cemented with lime and iron oxide and a plug appears. One solution to this problem is to install a coarse filter.
Another cause of an emergency is the use of welding during the installation of the pipeline. In places where welded joints are made, the galvanization burns out and a black metal spot forms, which becomes a source of corrosion.
In cold water supply systems, taps with black spots will rust faster than in hot water supply systems. In the heat, condensation forms on their surface, which contributes to the rapid spread of rust and overgrowing of the outlets.
With proper installation and proper operation, galvanized channels can last over 50 years. However, in this regard, they are inferior to corrugated stainless steel pipes and their polypropylene counterparts, the service life of which is claimed to be even longer.
Normative documents
Galvanized water pipes are produced mainly in accordance with GOST 3262 75.
In addition, there are two more GOSTs: 10704 91 and 10705-80. They regulate the production of electric-welded galvanized elbows, also suitable for water supply.
The differences between the standards lie in some standard sizes and operating pressure indicators that standardize the documents. Thus, products with a diameter of up to 102 mm, manufactured according to the latest two standards, must withstand 6 MPa and 3 MPa hydraulic pressure.
Seamless pipes are produced in accordance with GOSTs 8732-78 and 8734-75. They are rarely used in simple home plumbing because... they are more expensive than their suture counterparts.
Installation of water supply networks is carried out in accordance with the rules of SNiPs 3.05.01-85 “Internal sanitary systems” and 2.04.01 “Internal water supply and sewerage of buildings”.
Is it possible to paint galvanized steel?
Not only is it possible, but it is necessary! Painting gives products a presentable appearance and extends their service life by an average of 10-30 years. However, there are several nuances in the matter of painting galvanized steel:
- The zinc coating must age. Those. Before painting, galvanizing is aged for about 1-2 years under natural conditions. During this time, oxidation products disappear, a durable zinc patina (“white rust”) and some roughness are formed, due to which the adhesion to the paint will be stronger.
- For painting galvanized steel, only special paint compositions that are characterized by a high level of adhesion, hardness and elasticity are suitable. These include:
- Polymer powder paints based on resins and hardeners. When heated, the composition polymerizes, thereby providing strong adhesion to the zinc coating.
- Alkyd, plastisol, polyester and aluminum enamels, characterized by resistance to ultraviolet radiation, moisture, temperature changes and seasonal changes.
On a note! Oil paints are not suitable for painting galvanized steel because... Over time, they oxidize, reacting with zinc, which reduces their adhesive properties.
High-quality coloring is difficult to do on your own without the appropriate skills. Therefore, painting of galvanized steel is most often done in factories or specialized workshops.
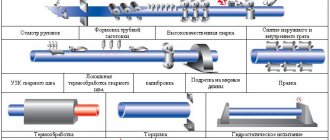
How water and gas pipes are made
VGP pipes are welded structures. They are made by folding a metal sheet and then welding its side edges together. Most often, VGP electric-welded steel pipes are manufactured in a straight-seam design. For their production, furnace welding, electric welding and inert gas welding are used.
Manufacturing technology and standards
Furnace welding is carried out in a special tunnel furnace.
Metal strips cut to size—strips—are placed in an oven with a temperature of 1300 °C. There they are heated and cleaned of scale with hot air.
The sheets are then passed through a forming-welding device, where they are welded with a straight seam.
Next, the finished workpiece is pulled through a sizing mill, which compacts and makes the seam stronger.
The quality of the seam is subjected to comprehensive testing using radiographic and mechanical methods.
Galvanization is carried out on finished VGP products.
The essence of the process is to apply a protective layer of zinc to both sides of the surface of the VGP pipe. This is done in one of three ways:
- Electrochemical - immersion in a bath with a zinc electrolyte solution.
- Hot-dip galvanizing - soaking in molten zinc.
- Diffuse galvanizing - treatment with zinc vapor at high temperature in a closed container.
Based on the results of the operations, the thickness of the zinc coating of the VGP outlet should be at least 30 microns.
When the VGP pipe is already galvanized, a thread is applied to it, if necessary, and verification tests are carried out.