CJSC "Zavod Trud" offers galvanic coating services in its own galvanic shop.
The plant has the most modern equipment:
- galvanic lines made in France
- automatic conveyor line for powder coating
- towing installations for dry and wet polishing of products
- chamber electric furnaces for heat treatment
Why should you order galvanic coating services from Trud Plant CJSC:
- Orders are fulfilled by highly qualified employees with more than 10 years of experience in the plant’s galvanic shop.
- All coated products undergo multi-stage quality control control.
- All technical processes are regulated according to the quality management system and confirmed by the GOST ISO 9001-2011 (ISO 9001:2008) certificate.
- Huge production capacity is a guarantee of fast and high-quality execution of your order.
- CJSC "Zavod Trud" has been operating for more than 120 years, since 1893 it has been a stable developing enterprise, ready to become a reliable partner for your organization.
Galvanizing with rainbow chromate
Protection of steel from corrosion under various operating conditions. Designation: Ts [thickness] hr. Applicable to all types of steel, cast iron, TsAM. Microhardness: 500-1200 MPa. Specific resistance (18°C): 5.75*10 Ohm*m. Operating temperature: up to +300°C.
Advantages of coverage:
- Protects steel from corrosion in both light and severe operating conditions, even in the presence of scratches or chips of the coating (anodic protection);
- Restores protective properties over time in case of minor mechanical damage (the “self-healing” property of the chromate film);
- Ensures easy screwing of threaded parts;
- Average ductility, in some cases withstands bending, flaring, etc.
Disadvantages of coverage:
- Low abrasion resistance of chromate film;
- protective properties decrease at temperatures above +70°C;
- Increased fragility at temperatures above +250° and below -70°C;
- Low chemical resistance to the effects of products released during the aging of organic materials and in salt environments.
Galvanizing services
Galvanic galvanizing is the application of zinc to iron using an electrochemical process.
The treated surface becomes able to resist corrosive processes. Possible types of chromatization:
- colorless chromate
- rainbow chroming
- black chromate
- olive chromate
The thickness of the coating depends on the operating conditions of the products:
- 6 microns - light operating conditions.
- 12–15 µm - average operating conditions.
- 30 microns - severe operating conditions.
The thickness of the protective layer can be increased to 500 micrometers.
Advantages of galvanic galvanizing:
- Improved performance
- Low cost
- Optimal level of metal protection
- Uniform coverage (no drops, smudges)
- The application of zinc coating to a product does not depend on the structural complexity of the product.
- Decorative coatings (smoothness and shine), parts do not need additional processing.
| Individual approach | Speed | Quality |
| We produce any parts according to existing samples or according to your drawings and sketches | Our production facilities allow us to fulfill orders of any volume in the shortest possible time | Constant quality control at all stages of production. The plant is certified according to the ISO quality system |
Galvanizing with colorless chromium plating
Protection of steel from corrosion in light conditions, decorative finishing. Designation: C [thickness] chrome.btsv. Applicable to all types of steel, cast iron, TsAM. Microhardness: from 500 to 1200 MPa. Specific resistance (18°C): 5.75*10 Ohm*m. Operating temperature: up to +300°C.
Advantages of coverage:
- Improves the appearance of parts. Has a uniform silver color;
- Protects steel from corrosion even if the coating is scratched or chipped (anodic protection);
- Ensures easy screwing of threaded parts;
- Average ductility, in some cases withstands bending, flaring, etc.;
- Meets European environmental requirements (does not contain hexavalent chromium).
Disadvantages of coverage:
- Low abrasion resistance of chromite film;
- Chromite film does not have the property of “self-healing”;
- Increased fragility at temperatures above +250° and below -70°C;
- Low chemical resistance to the effects of products released during the aging of organic materials and in a saline environment.
Galvanizing with olive chromate
Excellent protection of steel against corrosion under harsh operating conditions. Designation: C [thickness] khaki. Applicable to all types of steel, cast iron, TsAM. Microhardness: from 500 to 1200 MPa. Specific resistance (18°C): 5.75*10 Ohm*m. Operating temperature: up to +300°C.
Advantages of coverage:
- Maximum protects steel from corrosion (compared to other types of galvanizing) under severe operating conditions, even in the presence of scratches or chips of the coating (anodic protection);
- Restores protective properties over time in case of minor mechanical damage (the “self-healing” property of the chromate film);
- Ensures easy screwing of threaded parts;
- Average ductility, in some cases withstands bending, flaring, etc.;
- It is used in processing parts of military equipment and has a characteristic khaki color.
Disadvantages of coverage:
- Low abrasion resistance of chromate film;
- Increased fragility at temperatures above +250° and below -70°C;
- Low chemical resistance to products released during aging of organic materials.
Questions - Answers
Since the main focus of this site is informational and educational
, The Site Council decided not to create a “Forum” section, which, as is well known, often turns into an unprofessional and, often, illiterate discussion club.
To receive qualified
answers to questions and for consultations, a section
“QUESTIONS - ANSWERS”
, to which you can send letters by
All questions will be forwarded to leading Russian specialists in the field of electroplating and surface treatment
and then questions and answers will be placed in the same section.
Tip: By clicking the "forward" link, you can view the questions in chronological order. Using the “back” link, you can scroll through the questions in reverse chronological order, starting with the newest ones.
Popular about electroplating and electroplating
- Chrome plating at home
- How to organize electroplating of parts in an auto service station
- Are batteries harmful and what are the consequences of electrolyte evaporation?
- Service life of galvanic coatings
- Electroplating at home (in the garage)
- Is it dangerous to live in a house built on the site of a galvanizing shop?
Economic and legal issues
- Certification of electroplating production according to ISO
- Is certification of galvanic equipment required?
- Pricing in electroplating
- How to reduce fines for exceeding maximum permissible concentrations
- The question of the mandatory nature of REACH and other European regulations in Russia
- Occupational safety and health Interindustry rules on labor protection when applying metal coatings
- Manual loading and unloading of large and heavy products into baths
Processes of electrodeposition of metals and alloys
- Galvanizing newProblems with additives (emulsifier or brightener) in the weakly acidic ammonium-free galvanizing electrolyte
- newWhite coating on zinc coating
- Hydrogenation of thin-walled parts in zincate electrolyte
- Dark spots on the zinc coating of complex profile products
- Cracking and peeling of zinc coating with paintwork from steel on parts with a screw connection
- Differences in the properties of zinc coatings made from electrolytes with additives from different manufacturers
- Treatment of zinc coating before painting
- Porosity during galvanizing of TsAM
- Why is a zinc generator better than anodes or baskets in a galvanizing bath?
- Galvanizing of hardened nitro-carburized steels in zincate electrolyte
- Increasing the rate of dissolution of zinc anodes
- Question about the composition of ammonia electrolyte for galvanizing and passivation bath
- Anodic film, does it interfere with the alkaline galvanizing process?
- Zinc coatings on steel at high temperatures
- Permissible volumetric current density for zincate electrolyte
- Peeling of zinc coating during rolling process
- Problems of bright galvanizing with Colzinc
- Black dots on zincate electrolyte coating
- Selection of brightening agent and type of passivation for bright galvanizing
- Do matte and shiny zinc coatings differ in corrosion properties?
- Overheating of the galvanizing bath
- Comparison of zinc coatings
- Selecting an electrolyte for galvanizing window fittings
- Application of ammonia-free galvanizing electrolyte without brighteners
- Thermal diffusion galvanizing of springs
- Prevent heating of alkaline galvanizing electrolyte
- Galvanizing of parts that have previously undergone nitrocarburization
- Drum galvanizing at high current density
- Potassium chloride galvanizing
- Dark spots during potassium-chlorine galvanizing of bolts on hangers
- Galvanizing of contaminated threaded products
- Problem with galvanizing in ammonia electrolyte
- Problems with galvanizing in a drum
- Questions about galvanizing in cyanide-free alkaline electrolytes
- Dewatering of thin steel discs
- newAbout the causes of turbidity in nickel coating
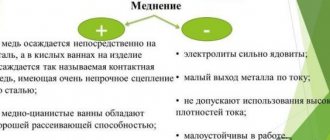
- How to preserve the color of copper?
- newOperation of tin-nickel electrolyte
- Applying gold with a nickel sublayer to parts made of MD40 alloy
- Cyanide brass plating of TsAM alloys: coating color
- newPitting in cobalt hydrometallurgy
- About the corrosion resistance of copper-nickel-chrome coating and options for its replacement
Chemical coatings
- newColor of chemically deposited nickel coating after heat treatment
- newFiltration of electroless nickel plating solution
- Replacing chemical nickel with electrolytic nickel for soldering
- Conductive coating, resistant to marine environments
- Heating an electroless nickel plating solution using a steam jacket
- About the solderability of chemically deposited nickel
- Heating the electroless nickel plating solution
- Hard nickel plating
- Is it possible to coat part of an aluminum part with chemical nickel?
- About replacing enameled buckets in the electroless nickel plating process
- “Boiling” of the electroless nickel plating solution
- The role of lead sulfide in the electroless nickel plating process
- Deterioration of solderability of parts with chemical nickel-phosphorus coating
- Local overheating of the electroless nickel plating solution
- Anodic protection of titanium nickel plating baths
- Chemical metallization - a question from the Society of Novice Electroplaters
Surface treatment
- Pre-treatment Degreasing AMG
- Titanium etching
- Grinding copper parts with electrocorundum
- Degreasing of parts made of different materials in one solution
- Electrical steel pickling
- Preparation of brass parts before nickel plating
- Steel wire pickling
- Iron precipitate and its permissible concentration in the clarification bath
- Descaling
- About the time between galvanizing and chromating zinc parts
- Colorless passivation after galvanizing
- Temperature of surface preparation with phosphating solution with KFA-8
- Cold oxidation of steel
- newChoice between An.Ox.black. and Chem.Ox.black.
Anodes and anodic processes
- Anode for nickel plating of the inner surface of the cylinder
- Depolarized Nickel Anodes
- Cathode material when anodizing aluminum
- Anodic film, does it interfere with the alkaline galvanizing process?
- Passivation of anodes during nickel plating
- Location of anodes during galvanizing in drums
- Anodic area during galvanizing using titanium baskets
- Anodes for galvanizing in cyanide-free alkaline electrolytes
- Selection of nickel anodes for nickel plating from sulfamate electrolyte
- The influence of temperature and quenching time on the service life of titanium anodes ORTA and ORTA-I (iridium)
- Features of the anodic process in various galvanizing electrolytes
Corrosion protection
- On the possibility of replacing cadmium coatings with zinc-lamella or zinc-nickel alloy
- Corrosion of nickel-plated steel parts during storage
- How to Remove Greenery from a Gilded Bronze Chandelier
- Protecting silver items from tarnishing
- Color change of "colorless" passive film upon drying
- Is Dacromet suitable for protecting fasteners before embedding in concrete?
- Corrosion protection of the diesel locomotive water system pipeline
- Protection of the walls of the internal channels of the cooling system from corrosion
- Question about the universal protective coating “METAS-anticorrosive”
- Adhesion of Dacromet 500 LC coating and compatibility with epoxy paints
- Corrosion resistance of parts in climatic conditions UHL 5
- Corrosion resistance and wear resistance of zinc coatings compared to nickel
- Methodology for determining the corrosion resistance of zinc coating after passivation
- Service life of galvanic zinc coating in alkaline environment
- On the durability of nickel coatings on copper when working in transformer oil
- Dacromet coating, its corrosion properties and the possibility of use in the tropics
- Measuring the degree of corrosion of phosphated and painted surfaces
- Protection of steel products in various climatic conditions
- Protection against atmospheric corrosion. Comparison of galvanizing, anodizing and chrome plating
Electrotype
- Electroplating technology of silver and silver alloys
- What is needed to organize an artistic electroplating workshop?
Removal of electroplating
- Electrochemical removal of chrome plating
- Permissible density of sulfuric acid in solution for removing nickel coating
- Sandblasting removal of galvanic coating
- Removing nickel coating from copper-steel assemblies
- Isolation of a porous surface during chemical removal of nickel plating
- Dewatering tempering of steel after removing the chrome coating
- Removing nickel from a multilayer copper-nickel coating from TsAM zinc alloy parts
- Mechanical and chemical ways to remove chromium
Ecology of galvanic production
- Water consumption issues Calculation of water consumption for washing by spraying parts above the bath
- Washing scheme after chrome plating
- Calculation of water consumption for flushing using a two-stage scheme
- How to prepare water for an evaporator to avoid scale
- The question of drainless technology of galvanic processes with a closed cycle of use of wash waters
- Vacuum wastewater evaporation method
- Removal of excess carbonates from cyanide electrolytes prepared on the basis of potassium salts
- Disposal of hydrochloric acid after removing zinc coating with it
- How ferritization of galvanic sludge affects the hazard class of waste
Electroplating equipment
- newSelection of material for the heat exchanger
- newCombination of ventilation from the oil bath and galvanic bath
- Insulation of suspension devices with galvanic tape or plastisol
- Zirconium heating elements for heating electrolytes of nickel sulfate plating
- Possibility of using aluminum cathode rods for chrome plating
- Selecting a heater and material for an electroless nickel plating bath
- Thermal insulating floats made of polypropylene
- How to properly design an aluminum hard anodizing bath
- Voltage of heating elements in galvanic baths
- What temperature can PVC and polypropylene equipment withstand?
- Drums with partial immersion in electrolyte
- Criteria for choosing suspension design
- Materials for lining chrome plating baths
- AC Rectifiers Which rectifier is needed for the aluminum anodizing process
- Special requirements for current sources used for chrome plating
Quality control
- Methods for determining antimony in silver electrolyte
- Quantitative determination of copper impurity in bright nickel plating electrolyte
- Determination of chloride ions in chromic acid anodizing electrolyte
- Purification of cadmium sulfate electrolyte
- Measuring the concentration of gold and nickel with the Corian-3 analyzer
- Analysis of electrolyte for chemical oxidation of aluminum for chromium and fluoride content
- Express methods for determining phosphorus compounds in electrolyte for chemical nickel plating
- Methods for analyzing gold plating electrolyte
- Analysis of nickel plating electrolyte for iron content
- Determination of the presence of hexavalent chromium compounds in conversion films on zinc
- Method for determining the current efficiency of zinc
- Express methods for determining hexa- and trivalent chromium in chromic acid electrolytes for chrome plating
General engineering issues
- Terminology Is anodic film an electroplating?
- Difference between Chemical Ox.fluorine and Chemical Ox.e coatings
- Coating Chemical Ox.e
- English terms for electroplating
- What is the difference between a metal coating shop and a site?
- Digital designation of types of electroplating
- newChoice between An.Ox.black. and Chem.Ox.black.
- newPowder Coating Remover
Information and its sources
- newGOST for nickel-phosphorus coating
- Methods for determining potassium silicofluoride
- Copper plating modes on reverse current
- Error in analyzes of electrolytes for gilding, silvering, and palladizing
- Question about advanced training courses in galvanizing
- Mechanical and corrosion properties of zinc coatings according to M.A. Schluger and in the reference book of Yu.D. Hamburg
- Search for Zinclamel Coating Services
- Erroneous data in report abstracts
- About the article on “trivalent chromium plating” in the magazine “World of Electroplating”
- About the book “Physico-chemical foundations of electrochemistry” by Lukomsky and Hamburg
- Hard Anodizing Processes
- Search for companies using galvanic production
- At which enterprises over the past 5-10 years have they created new galvanic workshops or carried out reconstruction?
- Electrolysis at very high current densities in stationary and pulsed modes
Galvanizing with black chromating
Decorative blackening of steel with high anti-corrosion properties. Designation: Ts [thickness] hr.ch. Applicable to all types of steel (including stainless steel), cast iron, TsAM. Microhardness: from 500 to 1200 MPa. Specific resistance (18°C): 5.75*10 Ohm*m.
Advantages of coverage:
- Deep black color;
- Protects steel from corrosion even in the presence of scratches or chips of the coating (anodic protection), in contrast to chemical oxidation;
- It perfectly replaces chemical oxidation of steel in cases where increased requirements for corrosion resistance are imposed on products.
Disadvantages of coverage:
- Obligatory oiling is necessary;
- Low abrasion resistance of black chromate film;
- Increased fragility at temperatures above +250° and below -70°C;
- When bending or flaring, black chromate film can be damaged.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Zinc - metallurgy and its grades
- High temperature galvanizing
- Lead and its electrolytes
- Reasons for the appearance of defective products on a hot-dip galvanizing unit
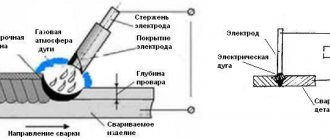
- Electric arc metallization
comments powered by HyperComments