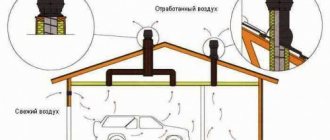
Features of air exchange in various industries
Ventilation of hot shops must cope with high thermal loads and significant emissions of harmful substances, consisting of:
- powerful general active exhaust air exchange from the upper area of the workshop;
- organization of a general supply of filtered air;
- supply airing to create a comfortable environment in the workplace;
- local hoods over sources of intense pollution.
Ventilation of foundries
Highly efficient ventilation of a (hot) workshop must take into account the specifics of production. For foundries, it is of particular importance to accurately calculate the heat balance, maintain a comfortable temperature in the workplace, and quickly remove the resulting compounds - carbon monoxide, ammonia, sulfur dioxide. In food production, the need to use oil and fat filters should be taken into account, protecting air ducts and equipment from fat deposits. The air ducts of such systems are made of heat-resistant metal and are often protected with thermal insulation that prevents heat radiation.
Ventilation of welding production
Welding production is characterized by large quantities of extremely harmful emissions, including nitrogen oxides, fluoride, and metal compounds. Designed, reliable ventilation of welding shops should provide exhaust at the level of:
- 1500…4500 cubic meters per hour per kilogram of consumed welding electrodes;
- 2500…5400 cubic meters per hour per kilogram of flux-cored wire used;
- 1700…20000 cubic meters per hour per kilogram of wire for semi-automatic welding in carbon dioxide.
Ventilation in a paint shop
A paint shop equipped in accordance with standards, the ventilation of which effectively removes solvent vapors and paint fumes, protects surfaces from dust, is equipped according to the following rules:
- Stands, painting baths, drying chambers, degreasing installations, and painting booths are equipped with local hoods;
- exhaust hoods are installed at a level of more than two meters above the roofs;
- two thirds of the total hood falls on the upper area of the room;
- when using the method of dipping products into a paint bath, the air exchange rate should reach five or six room volumes per hour, and when using spray guns it should be at the level of 20...200;
- The equipment uses dust- and spark-proof fans, explosion-proof check valves on air ducts.
For air exchange in woodworking industries, local exhaust hoods are used with mandatory air purification in cyclones, organizing inflow into the upper zone through perforated ducts.
Ventilation in electroplating industries
Special air exchange conditions apply in galvanic production:
- mandatory installation of filters at the air intake;
- threefold air exchange should be ensured in the solution preparation departments;
- air ducts with anti-corrosion coating are used;
- onboard bath hoods;
- hoods over baths with acids and cyanide solutions;
- corrosion-resistant, explosion-proof fans.
Calculation of exhaust ventilation
Calculation of exhaust ventilation for large production workshops and enterprises begins with identifying areas of distribution of unsafe substances and emissions. At the next stage, specialists determine the volumes of air masses for removal and supply in order to ensure sanitary standards.
If there are no active sources of unwanted substances in the space, it is advisable to use a simple formula:
O = m*n
- O – the volume of pure oxygen provided for by sanitary standards and regulations;
- m – average value of oxygen consumption for 1 hour of active work;
- n is the constant number of workers working in the premises every day.
As for the value of m, it has specific definitions documented by SNiPs:
- m = 30 m3 – for ventilated rooms;
- m = 60 m3 – for objects without access to clean air.
Description of certification of industrial premises ventilation systems
The peculiarity of harmful substances is that they tend to spread throughout the entire volume of the workspace, pavilion or production workshop. In this case, the main task is to reduce the level of their concentration to values at which a person can stay and work in the room.
Specific threshold values are provided for each harmful substance. Taking this into account, the volume of fresh air inflow is calculated using the formula:
O = Mb/(Ko-Kп);
- Mb is the average weight of an unwanted or potentially hazardous substance entering the workspace per unit of time (1 hour);
- Ko is the value of the remote concentration of a potentially hazardous substance in the surrounding space;
- Kp – concentration of undesirable substances at the inlet of the air handling unit.
Types of ventilation systems and arrangement rules
An exhaust hood for a welding station, installed according to the rules, can significantly reduce the concentration of hazardous substances in the atmosphere and minimize harm to the environment. The type and power of fans, as well as the routing of air ducts, are selected taking into account the number and location of places for welders. Exhaust structures can be placed on the roofs of workshops or near them; the air intake should not be located in the area for the emission of polluted air.
Local
A welding shop or workshop has local and general hoods.
When creating a local type hood, the ventilation of the posts is selected taking into account the size of the elements being welded and the intensity of the work. The amount and composition of the gases formed depends on these nuances. Thanks to the simple design and design, the productivity of such a system reaches 5.5 thousand m3/hour. During welding and surfacing of large products on tables not equipped with devices, welding aerosols are removed using suction from mobile units with filtration ventilation. For some types of work, it is advisable to use lift-and-swivel hoods. Their design includes a flexible hose with a diameter of up to 200 mm, mounted on a console and directed to the desired area. The receiving pipe is placed at a distance of 7-8 meters from the worker.
The exhaust hood required for welding is not installed directly above the work stations. In such systems, it is better to install tables with air suction through the grate.
General exchange
Exhaust fans at welding stations
The general-exchange type system includes a supply and exhaust fans, as well as air ducts equipped with filters and adjustable supply structures. Such ventilation is designed to provide fresh air to all areas of the workshop and reduce the content of harmful impurities in the atmosphere. It is worth choosing if more than 200 g/hour of electrodes per 1 m3 of the total volume of the room is used during the work. Otherwise, the influx of air masses will be provided naturally.
In winter, outside air is supplied to the workshop at a temperature not lower than +18 degrees. General ventilation for the welding station must be supplemented with filtration elements that purify the air before being released into the space. The performance of the devices is selected to ensure a 10-fold air exchange. The vertical speed of movement of air masses is maintained at no lower than 0.1 m/s. This value is sufficient for mixing media and eliminating welding aerosols from areas outside the posts.
Inside closed and semi-enclosed spaces
To organize a ventilation system inside a closed or semi-enclosed space, there are several available schemes. In the workshop, you can create an organized air exchange in one container, where clean air will be supplied from outside. Next, the air masses are removed mechanically due to the combined action of inflow and exhaust. The second method involves removing contaminated masses near electric welding arcs; there is also a third option, which involves ventilating only the worker’s breathing zone by supplying clean air under the shield.
The most common type of system is a tank ventilation scheme using a supply jet, which involves the installation of flexible hoses and high-pressure fans. The main advantage of this method is the supply of clean and heated air from the street during the cold season. Tanks in this arrangement are located in specially designated areas. To determine the volume of supplied air, its speed in the work area should not exceed 0.7-2.0 m/s for manual welding. You can avoid the entry of polluted air into the workshop by installing the mass supply from the opposite side.
The supplied stream of purified air must go in the direction from the welder to the arc so that harmful substances do not enter the breathing zone. The volume of air supplied must dissolve the gases and solid aerosol phase that are formed during the work of the first worker in the direction of movement.
Ventilation of welding stations with heat recovery
For such an energy-intensive production as a welding shop, the issue of energy costs is extremely acute. Ventilation supply systems used in welding to heat or purify air also consume a considerable amount of energy. In this case, the air entering the welding room can leave the building due to the exhaust, without having time to transfer heat into the room. Such a supply and exhaust system during welding consumes a lot of electricity, showing dubious efficiency.
For energy-intensive welding, heat recovery systems are used. With it, the exhaust air duct, which removes air from the welding room, has a heat exchange zone with the supply air duct, which carries air into the room and to the areas.
Thus, the ventilation system during welding allows heating the incoming air not only due to the operation of fans, but also due to the outgoing air. Systems with heat recovery during welding help save up to 30% of the electricity used to operate the supply fans.
Welding station ventilation system from professionals.
To order ventilation for the welding area, call us by phone or request a call back on our website. Our specialists will calculate the ventilation of the welding shop, create a project and carry out the installation of an air exchange system for turnkey welding: from the initial calculation of the exhaust system to commissioning activities and drawing up reports on the work performed in the welding room.
We have more than five years of experience in designing and installing air exchange systems for welding stations and other production areas.
We also provide maintenance services for the ventilation system of the welding area and other production posts and workshops.
Purpose of ventilation at the welding station
During plasma and arc welding, toxic compounds are released into the air:
- coating that burns out on the electrodes;
- metal evaporation;
- gas used in welding.
Because of all these emissions, the welder is always equipped with respiratory protection. But you need to prevent these gases from accumulating in the room, so you need an exhaust hood that allows you to:
- remove oxides, compounds and other substances from the air using special suction and exhaust hoods;
- remove gases and fine particles to ventilation;
- supply clean air.
All this can be done by properly organizing the ventilation of the welding station.
The principle of operation of ventilation during welding
Release of pollutants from metal welding
| Table 1. Emission of pollutants during metal welding | ||||||||
| method and brand of welding material | Pollutant release, g/kg welding material | Other pollutants | ||||||
| welding aerosol | manganese compounds | chromium oxides | hydrogen fluoride | nitrogen oxides | carbon monoxide | name | quantity | |
| Manual arc welding of steels with electrodes | ||||||||
| UONI-13/55 | 18,6 | 0,97 | — | 0,93 | — | — | fluorides | 2,6 |
| UONI-13/65 | 7,5 | 1,41 | — | 1,17 | — | — | fluorides | 0,8 |
| ANO-4 | 6,0 | 0,69 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| ANO-6 | 16,3 | 1,95 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| ANO-11 | 22,4 | 0,87 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| EA-606/11 | 11,0 | 0,68 | 0,6 | 0,4 | 1,3 | 1,4 | — | — |
| M33-III | 40 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| TsT-15 | 7,9 | 0,55 | 0,35 | 1,61 | — | — | Nickel oxides | 0,39 |
| Manual arc welding of cast iron | ||||||||
| TsCh-4 | 13,8 | 0,43 | — | 1,87 | — | vanadium | 0,54 | |
| Manual arc welding of copper | ||||||||
| ShchZCh-1 | 14,7 | 0,47 | — | 1,65 | — | copper | 4,42 | |
| Tungsten under helium | 20 | — | — | — | — | — | tungsten | 0,08 |
| copper | 2,1 | |||||||
| SRM-0.75 (wire) Manual welding of aluminum | 17,1 | 0,44 | — | — | — | copper | 15,4 | |
| OZA-1 | 38,1 | — | — | — | — | — | oxide aerosol | 20 |
| aluminum | ||||||||
| Wire | ||||||||
| EP-245 | 12,4 | 0,54 | — | 0,36 | — | iron oxides | 11,5 | |
| PP-106, PP-108 | 12 | 0,7 | — | — | 0,8 | — | iron oxides | 0,7 |
| Wire | ||||||||
| SV-08G2S | 9,7 | 0,5 | 0,02 | — | 14 | iron oxides | 7,48 | |
| SV-H19N9F2SZ | 7 | 0,42 | 0,03 | — | — | 14 | iron oxides | 0,04 |
| SV-10Х20Н7СТ | 8 | 0,45 | 0,03 | — | — | — | — | — |
| SV-16Х16Н25М6 | 15 | 2 | 1 | — | — | Nickel oxides | — | |
| EP-245 | 12,4 | 0,61 | — | — | — | 3,2 | — | — |
| SV-O8KhGN2MT | 6,5 | — | 0,03 | — | 0,8 | 11 | titanium oxides | 0,4 |
| copper | 11 | |||||||
| Wire | ||||||||
| MNZH-KG5-1-02-0.2 | 18 | 0,3 | — | — | — | — | Nickel oxides | 0,8 |
| KMC | 8,8 | 0,6 | — | — | — | — | copper | 6 |
| Wire | ||||||||
| D-20 | 10,9 | 0,09 | — | — | — | — | aluminum oxides | 7,6 |
| AMC | 22,1 | 0,62 | — | — | 2,45 | — | — | 20 |
| AMG-6T | 50 | 0,25 | — | 0,33 | — | — | 8,5 | |
| Aluminum | 10 | — | — | — | 0,9 | — | — | — |
| Titanium | 14,7 | — | — | — | — | — | titanium oxides | 5 |
| Non-consumable electrodes | 61 | — | — | — | — | — | aluminum oxides | 28 |
| OZA-2/ak, OZA-1 | 38,5 | — | — | — | — | — | — | 20 |
| Welding steel with fluxes | ||||||||
| OSP-45 | 0,09 | 0,03 | — | 0,2 | 0,006 | — | other fluorides | 0,36 |
| FC-2, FC-6, FC-7 | 0,09 | 0,01 | — | 0,05 | 0,005 | — | silicon compounds | 0,03 |
| FC-11, FC-12 | 0,09 | 0,05 | — | 0,02 | — | — | — | 0,05 |
| AN-22 | 0,12 | 0,01 | — | 0,02 | — | — | — | — |
| AN-26, AN-30, AN-42 | 0,08 | 0,05 | — | 0,03 | — | — | — | — |
| AN-60, AN-64 | 0,09 | 0,02 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| AN-348A | 0,1 | 0,03 | — | 0,2 | 0,006 | — | other fluorides | 0,16 |
| ANK-30 | 0,26 | 0,12 | — | 0,018 | — | — | silicon compounds | 0,05 |
| ZhS-450 | 5,8 | 0,142 | — | 0,18 | — | 22,4 | — | — |
| K-1 | 0,06 | 0,023 | — | 0,15 | — | 0,5 | — | — |
| K-8 | 4,9 | 0,13 | — | 17,8 | — | — | ||
| K-11 | 1,3 | 0,089 | — | 0,14 | 0,6 | — | — | — |
| Table 2. Maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances in the air of the working area of welding shops | ||||
| Name of substance | MPC, mg/m3 | Hazard Class | Physical state (a - aerosol, p - vapor) | Note |
| manganese content in welding aerosols, wt.% | ||||
| up to 20 | 0,20 | 2 | A | |
| until 20-30 | 0,10 | 2 | A | |
| chromates, bichromates | 0,01 | 1 | A | in terms of CrO3 |
| chromium oxide (Cr2O3) | 1,00 | 2 | A | |
| nickel and its oxides | 0,05 | 1 | A | in terms of Ni |
| zinc oxide | 0,50 | 2 | A | |
| titanium and its dioxide | 10,00 | 4 | A | |
| aluminum and its alloys | 2,00 | 2 | A | by Al |
| copper metal | 1,00 | 2 | A | |
| tungsten | 6,00 | 3 | A | |
| amorphous silicon dioxide in the form of a condensation aerosol at a content of 10 to 60% | 2,00 | 4 | a | |
| nitrogen dioxide | 2,00 | 2 | P | |
| ozone | 0,10 | 1 | P | |
| carbon monoxide | 20,00 | 4 | P | |
| hydrogen fluoride | 0,05 | 1 | P | |
| hydrofluoric acid salts: | ||||
| highly soluble (NaF, KF) | 0,20 | 2 | A | by HF |
| poorly soluble (AIF2, NaAIFd) | 0,50 | 2 | A | by HF |
| Table 3. Pollutant emissions during gas and plasma cutting of metals | |||||||||||||
| Cutting method, type and thickness of metal | Release per cut m, g/m for 1 hour of work, g/h, including oxides | ||||||||||||
| Aerosol, total | Mg | Cr | Ni | Al | CO | NOx | |||||||
| g/m | g/h | g/m | g/h | g/m | g/h | g/m | g/h | g/m | g/h | g/m | g/h | g/m | g/h |
| Gas cutting carbon steel thickness | |||||||||||||
| 5 mm | 2,25 | 74 | 0,07 | 2,3 | 1,5 | 50 | 1,2 | 40 | |||||
| 10 mm | 4,5 | 130 | 0,13 | 3,8 | 2,2 | 6,3 | 2,2 | 65 | |||||
| 20 mm | 9 | 200 | 0,27 | 6 | 2,3 | 65 | 2,4 | — | |||||
| Cutting gas steel with de-alloyed thickness | |||||||||||||
| 5 mm | 2,5 | 80 | 0,12 | 4 | 1,3 | 43 | 1 | 35 | |||||
| 10 mm | 5 | 150 | 0,23 | 6,7 | 1,9 | 55 | 1,5 | 43 | |||||
| 20 mm | 10 | 225 | 0,47 | 10,5 | 2,6 | 57 | 2 | 45 | |||||
| Gas cutting of manganese steel thickness | |||||||||||||
| 5 mm | 2,5 | 80 | 0,6 | 20 | 1,4 | 46 | 1,1 | 36 | |||||
| 10 mm | 5 | 140 | 1,6 | 35 | 2 | 58 | 1,6 | 47 | |||||
| 20 mm | 10 | 220 | 2,4 | 55 | 2,7 | 60 | 2,2 | 50 | |||||
| Gas cutting of thick titanium alloys | |||||||||||||
| 4 mm | 5 | 140 | 4,7 | 130 | 0,6 | 17 | 0,2 | 6 | |||||
| 12 mm | 15 | 315 | 14 | 280 | 1,5 | 32 | 0,6 | 13 | |||||
| 20 mm | 25 | 390 | 22 | 345 | 2,5 | 38 | 1 | 16 | |||||
| 30 mm | 35 | 350 | 33 | 335 | 2,7 | — | 1,5 | — | |||||
| Plasma cutting of thick carbon steel | |||||||||||||
| 10 mm | 40 | 810 | 0,12 | 24 | 1,4 | 7 | |||||||
| Plasma cutting of low-alloy steel thickness | |||||||||||||
| 14 mm | 6 | 790 | 0,18 | 24 | 2 | 265 | 10 | 130 | |||||
| 20 mm | 10 | 960 | 0,3 | 29 | 2,5 | — | 14 | — | |||||
| Plasma cutting of alloy steel thickness | |||||||||||||
| 5 mm | 3 | 990 | 0,14 | 46 | 1.5 | — | 6 | 200 | |||||
| 10 mm | 5 | 1370 | 0,24 | 66 | 1.9 | 470 | 10 | — | |||||
| 20 mm | 12 | 1600 | 0,58 | 77 | 2.1 | — | 13 | — | |||||
| Plasma cutting of thick manganese steel | |||||||||||||
| 5 mm | 4 | 790 | 0,72 | 140 | 1,4 | — | 7 | 128 | |||||
| 10 mm | 6 | 765 | 1,16 | 1,50 | 2 | 265 | 10 | — | |||||
| 20 mm | 10 | 920 | 1,73 | 170 | 2,5 | — | 13 | — | |||||
| Cutting thick aluminum alloys | |||||||||||||
| 8 mm | 3 | — | 2,5 | — | 0,5 | — | 2 | 612 | |||||
| 20 mm | 4 | 480 | 3,5 | 440 | 0,6 | 75 | 3 | — | |||||
| 80 mm | 6,5 | — | 8 | — | 1 | — | 9 | — | |||||
| Plasma cutting of thick titanium alloys | |||||||||||||
| 10 mm | 3 | 455 | 2,7 | 425 | 0,4 | — | 11 | 160 | |||||
| 20 mm | 7 | 645 | 6,4 | 515 | 0,5 | 40 | 15 | — | |||||
| 30 mm | 12,5 | 680 | 12 | 640 | 0,6 | — | 19 | — |
Read with this
Types and rules of arrangement
There are two ways to arrange a ventilation system in a welding shop: general and local. They are used together, in addition to each other.
The local scheme is capable of eliminating up to 75% of all harmful substances released during work. To eliminate the remaining 25% of harmful substances, a general metabolic system is used.
- Dead spots (from which air cannot be removed in any way) should not be allowed to form in the workshop, especially in the corners. Air containing a large amount of harmful substances stagnates in them.
- Supply ducts with fans should be installed at a height of up to 4 meters. Exhaust ducts should be mounted on the opposite wall, and the height of both ducts should be the same.
- The distance from the wall with inflow to the wall with exhaust cannot be more than 100 meters - this is prohibited. At a greater distance, exhaust air will accumulate in the central zone of the room.
- If necessary, a mobile suction unit can be installed in the local exhaust system, which will allow, if necessary, to move the exhaust hood along with the welding equipment.
- The workshop ventilation system must be equipped starting with the installation of a general supply and exhaust system. When its installation is completed, they move on to installing a local ventilation system.
Now let's take a closer look at the design features of these circuits.
Local scheme
The main purpose of the local scheme is to purify the air locally, that is, right at the work site. It is at the site where welding work is carried out that the most harmful substances accumulate. But already 3-4 meters from the workplace the air can be absolutely clean and meet sanitary standards.
Ventilation for welding station
There are two ways to install local ventilation: through local suction or through lift-and-turn exhaust devices.
In the first case, the suction units are mounted at a height of one and a half meters from the welding station. Sometimes they are mounted directly into welding tables, which is also a good option. Ultimately, local suction is connected to the general ventilation of the workshop using special sealed hoses.
The second option is an air intake, which is attached using hinges and a hose (its diameter can reach 200 mm) in any position. The hose connects the air inlet and the centralized air exhaust system.
Typically, due to this design, it is possible to remove up to 85% of various harmful components from the room. Its advantage is the possibility of installation next to welding equipment. In general, a lift-and-swivel hood allows you to effectively purify the air at a distance of up to 8 meters from the welding station.
General exchange scheme
The general exchange circuit consists of a system of air ducts to which exhaust fans are connected.
The mechanism of operation of the method is as follows: the air flow, passing through the grille, is dissected, after which it rises vertically upward and is distributed throughout the workshop. The speed of passage of air masses in the workshop is 0.1 m/s, which is sufficient in most cases.
Air exchange is ensured by installing fans under the floor. The removal of exhaust air is ensured by installing fans on the roof with a capacity greater than that of the supply fans.
20 minutes of continuous operation of such a system is enough to remove most harmful substances.
Several rules for arranging a general exchange scheme:
- in the case when less than 0.2 g/hour of electrodes is consumed per 1 m³ of workshop, installation of a general ventilation system may not be necessary;
- the supply speed of fresh air masses should not exceed 0.9 m/s;
- If a local circuit is not additionally installed, then mechanical ventilation should ensure that 2/3 of the air is removed from below and 1/3 from above.
If welding work is carried out inside a container, then the air mass flow rate must exceed 0.7 meters/second, at a temperature of at least 20 degrees inside.
Click “Like” and receive only the best posts on Facebook ↓
Types of ventilation system
Knowing the requirements for welding hoods and the features of the workspace where it will be installed, you can move on to studying the types of ventilation and choosing the appropriate one.
To begin with, they can be local and general exchange. Local assumes that the welder will be working in a small space, such as a fume hood, and therefore ventilation will only be in that area. The general exchange welding hood covers the entire workshop space. These types of ventilation can be used together.
General ventilation can be vertical or horizontal. This indicates different flow directions:
- Horizontal ventilation has equipment of equal power for supplying air and pumping it out. The distance between the walls is important here.
- Vertical ventilation allows you to reduce the power of supply fans, since air pumping devices are placed at a height of up to 6 m. If installed higher, the circulation will worsen.
In more detail, when organizing a horizontal welding hood, you need to use equipment that evenly distributes clean air flow throughout the room, without stagnation. It is advisable to have electric fans and a deflector system. For a typical workshop of 30x20 m, horizontal ventilation will be quite sufficient.
A vertical welding hood system involves forcing air flow through shafts, so fans are sometimes installed in basements or, conversely, on roofs. The channels are located along the floors and are closed with metal gratings, with cells of at least 5x5 cm.
The ventilation speed at the inlet here should be no lower than 0.1 m/sec. The performance of exhaust fans on the roof is 2 times higher than that of the supply fans, so this way you can organize accelerated ventilation in the welding shop.
Varieties
There are two types of welding stations: stationary and mobile. Stationary stations are located in the workshop and are designed to work with small parts, since the working surface of welding tables is often limited. Mobile posts can be located both inside the workshop and outside. These can be small frames on wheels into which the equipment is built, or a special cart.
Let's take a closer look at each post type.
Stationary post
Below is a diagram of a stationary type welding station. In most cases, the stationary post is located in a separate cabin without a roof, but with closing screens. The area of such a cabin must be at least 3 m2.
A stationary welding station must be made of non-flammable materials, so the screens are made of polymers, and the frames are made of metal. The height of the cabin itself must be at least 2 meters. The interior walls of the cabin are coated with a fire-resistant compound that does not support combustion.
Each stationary post has not only equipment, but also a welding table. Its size is determined by the nature of the work. If welding is done in a sitting position, then the height of the table should be about 60-70 cm. If in a standing position, it should be from 85 and above. The size of the working surface must be at least 100x100 cm.
A separate requirement is good ventilation for the welding station. Local ventilation during welding can be either natural or forced. Forced ventilation is preferable. Local suction from the welding station is also necessary to quickly remove metal shavings, dust from grinding, etc.
Mobile post
The welding station for manual arc welding can be mobile or portable. Often, a mobile welding station can be set up with less effort, since it does not require compliance with many rules. There is no need to organize ventilation, observe the size of the working area, etc.
But what is worth doing is a canopy over the mobile station so that the welder can work in bad weather or under the sun. Also, the mobile post should have comfortable wheels so that even heavy equipment can be transported without much difficulty.
The mobile post must have compartments and niches for storing components. If this is a mobile gas welding station, then there must be space for a gas cylinder. Ventilation of the welding station can be natural, since work in most cases takes place outside.
Requirements for hoods
Safe welding in confined spaces can only be ensured by a high-quality hood, so before creating it, you need to know the technical requirements.
The welding hood must be autonomous and not use the same air masses. If it is not possible to make an autonomous hood, then lifting and ventilation panels will be required.
Since clean air for exchange will be taken from the street, it must be heated or cooled before supply.
There is no significant release of heat sufficient for circulation during welding, so it is necessary that the ventilation of the welding station itself drives the flows at the required speed.
Exhaust hoods are installed near each workplace, but to the side of the welder, and not directly above his head, so that the draft of air does not force him to inhale harmful particles and these do not create a load on the protection. Umbrellas will remove up to 75% of harmful particles. For small-sized tasks, a fume hood is installed, which should remove 90% of harmful impurities. The remaining vapors are removed by the general ventilation of the welding shop.
It is important that this welding hood cannot be combined with the ventilation of other rooms so that the poisoned air does not get anywhere except the street.
In order to comply with all sanitary rules for welding hoods, they rely on SNiP II-33–75 and SP 1009-73. Here are the following:
- Permissible concentrations of toxic substances. Within a radius of 4 meters from the work site it should not exceed the maximum.
- Dimensions of equipment, depending on the area of the room, the number of people involved in welding, as well as the tools they use.
- Sections and positions of channels for the removal of harmful substances, etc.
How to make a hood in a 6 by 4 garage?
#2 svarnoi69
that's it)) why the extra expense by email? energy, an umbrella against which you will hit your head, noise from the engine.
Works great without a fan.
bottom box 20x20-25x25.
top along the entire length of the garage150x150-200x200
Post edited by svarnoi69: 10 December 2013 19:30
#4 user_k
Place the motor on the visor, or rather inside it, preferably with a speed controller. Or a kitchen hood would be fine.
The thicker the paint layer, the more beautiful the seam.
#12 LamoBOT
Argon, like helium, is an inert gas and does not enter into any chemical reactions. reactions, and of course they don’t destroy teeth. There is almost 1% argon in the air, which is where it is extracted. But if the room is hermetically sealed, then argon will accumulate near the floor, because 2 times heavier than air. If, for example, there is a cellar and argon has accumulated there, it is very likely that you will not return from there. Therefore, in a fit of paranoia, I would probably provide a small cross-section and low capacity exhaust pipe from the floor level. There are 6 cubic meters of gas in a 40 liter cylinder. In principle, with such an area it is not dangerous.
Types and differences of air ducts for hoods
The exhaust duct can be divided according to the following characteristics:
- According to the material from which the channel is made: plastic or metal.
- Shape: round or rectangular.
- By rigidity: flexible or rigid.
Features and advantages of metal (corrugated) air ducts
Corrugated metal (or rather, aluminum) pipe is the most popular option for creating an air duct. You can read more about the selection and installation of corrugations for the hood separately. Let's look at this option briefly below.
Corrugated air duct in the kitchen interior
- Diameter 100 mm: about 90 rubles per meter.
- Diameter 120 mm: about 120-130 rubles per meter.
- Diameter 150 mm: about 135 rubles per meter.
The advantages of such an air duct include:
- flexibility (the corrugation can be easily bent to give the air duct the desired shape);
- the ability to stretch and fold (and therefore the ability to adjust the length of the channel);
- ease of connection (for corrugation there is no need to separately purchase and install adapters and connecting elements).
Of the minuses:
- relatively high noise level (however, the noise of the motor of a running hood will still cover the noise from the air passing through the duct);
- faster contamination (than with PVC products);
- unsightly appearance (corrugation spoils any interior, so the metal air duct is almost always covered, which means you need to spend additional time and money on creating a “cover”).
Features and advantages of plastic air ducts
A plastic pipe is a rigid product that does not bend. The cross-sectional shape can be either round, rectangular or square.
Rectangular plastic duct for exhaust hood
The main advantages of plastic (compared to metal):
- noiselessness (a smooth, flat surface does not contribute to noise);
- ease of maintenance (smooth surfaces become dirty much more slowly and are easier to clean);
- aesthetic appearance: in the interior, a plastic pipe looks much neater than corrugated pipe.
The most successful solution is to use a rectangular duct. It is easy to run such a pipe along the wall, saving space. On the other hand, such a channel requires an adapter with which the rectangular pipe will be connected to the round openings of the hood and shaft. You will also need connecting elements to hold together a system of several sections.
Of the minuses:
- more complex installation;
- higher cost than corrugated pipes (both the pipes themselves are more expensive, and in addition you will need to buy additional adapters and elbows);
- inability to bend, stretch or compress the pipe.
More complex installation is the most serious disadvantage of plastic. The corrugated metal sleeve is flexible, it bends, stretches and folds easily. Even if you made a mistake in the calculation, it can be adjusted to the required conditions without any problems. But this will not work with a plastic air duct: it needs to be measured and planned as accurately as possible.
Plastic Air Duct Parts
- Plastic adapter from a rectangular channel 60x120 mm to a round hole with a diameter of 120 mm: about 150 rubles.
- Flat air duct, cross-section 110x55 mm: about 260 rubles per 1 meter.
- Round air duct, diameter 100 mm: about 250-270 rubles per 1 meter.
Which option is better?
The question of which air duct to choose (corrugated or plastic) is not critical. If it is correctly calculated and laid, the hood will work normally.
Minor differences include several points:
- Exterior to interior. Here plastic clearly wins. However, air ducts are often decorated, so the corrugation will still not be noticeable.
- Ease of installation. In this regard, it is clearly easier to take corrugation.
- Air duct price. Corrugation will cost a little less.
S is the opening area of an exhaust-type installation. Features of ventilation in workshops of various types
Mechanical shop ventilation
Hazards: heat emissions from electric motors, personnel, vapors of aerosols and coolants, oils, emulsions, dust - emery and mechanical.
Heating: air, combined with ventilation system
Local suction: above grinding/grinding machines, machines without cooling, emulsion tanks, baths for washing parts.
General exchange: air flow from above; calculation of air based on excess moisture and heat - at least 30 m3 per person.
Ventilation of a woodworking workshop
Hazards: heat from presses, solvent vapors, glue, woodworking waste - dust, shavings, sawdust
Heating: air, combined with ventilation system
Local suction: floor and underground for wood waste, suction from machine tools; Air purification occurs in bag filters, cyclones
General exchange: dispersed air flow into the upper zone, through perforated air ducts (mostly)
Ventilation of a woodworking workshop
Ventilation of galvanizing shop
Hazards: fumes of alkalis, acids, electrolytes, excess heat and moisture, dust, hydrogen cyanide
Heating: air, combined with ventilation system
Local suction: on-board for baths, independent exhaust systems above baths with cyanide and acidic solutions, explosion-proof fans, mandatory equipment of suction for baths with acids of various types with backup fans. Mandatory filtration of extracted air masses
General exchange: air ducts made of anti-corrosion materials or mandatory anti-corrosion coating of all air ducts; supply of 5% of the inflow to all adjacent rooms; 3-fold air exchange in the compartments for preparing solutions and cyanide salts. Mandatory filtration of extracted air masses.
Ventilation of galvanizing shop
Welding shop ventilation
Hazards: fluoride compounds, nitrogen oxides, carbon oxides, ozone
Heating: air, combined with ventilation system
Local suctions: desirable (if possible)
General exchange: exhaust: 2/3 from the lower zone, 1/3 from the upper. Calculation of air for diluting harmful emissions from welding to the maximum permissible level.
The calculation is made based on the weight of welding electrodes, which are consumed in 1 hour: for manual welding - 1500-4500 m3*h per 1 kg. electrodes, 1700-2000 m3*h for semi-automatic carbon dioxide, 2500-5400 m3*h - for welding using flux-cored wire.
Welding shop ventilation
Paint shop ventilation
Hazards: solvent/thinner fumes, paint particles
Heating: central or air, which is combined with ventilation
Local suction: at degreasing units, painting booths, jetting installations, drying chambers, tables, stands, dipping baths.
General exchange: inflow to compensate for local exhaust + 1 times, general exchange exhaust ventilation at least 1 times from the upper zone.Ventilation of the paint shop
More details in the article “Ventilation of a paint shop”
Ventilation in foundries
The main task of foundry ventilation is to cope with the enormous amount of heat that is released into the production premises.
Harmful: radiant heat, huge amounts of heat, ammonia, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide
Heating: together with ventilation system
Local suction: for almost all types of hot shop equipment
General exhaust with mechanical drive in the upper zone of the workshop + aeration + showering of workplaces + general supply ventilation.
Foundry ventilation
The creation and design of ventilation in production workshops for any purpose is entrusted exclusively to professionals who will ensure compliance with all necessary standards and perform calculations taking into account the specifics of your production.
You can receive a free draft design and cost of ventilation for your boiler room
Get!
The need for ventilation in a welding room
The welder's workplace is equipped with additional hoods.
Welding work is classified as a hazardous process due to the release of many hazardous substances, including oxides of iron, chromium and manganese, fluorine compounds and silicon dioxide. They are dangerous to human health and harm the environment, so every room where welding is carried out on an ongoing basis is supplemented with hoods.
Ventilation of a welding shop solves several main problems:
- removal of chemical components that pose a threat;
- creating and maintaining an optimal microclimate indoors, taking into account its temperature, humidity and in accordance with GOST and SNiP standards;
- continuous supply of oxygen.
Air exchange in workshops, welding areas and posts must be carried out autonomously. If an industrial welding room is located in the same building as others, they do not have combined ventilation. It is also not recommended to design systems with cyclic and repeated use of air masses. During the work, a natural system is not used, since there is no significant heat generation in this case. Before being supplied inside the space, the air is brought to the required temperature, taking into account the weather conditions outside.
In addition to installing a hood, various means are used to protect welders from radiation, including thermal insulation of heated surfaces and shielding. Thermal insulation work is considered the most effective way to reduce the intensity of rays and prevent possible burns. Special materials and structures, such as concrete, brick, asbestos and felt, are used to equip workplaces in combination with screens or separately from them.
Making a welding station with your own hands
The welder’s workspace with a set of necessary equipment, tools, consumables and the welding machine itself is called a welding station. You can organize it yourself if you carefully study the standards and safety requirements for such offices.
The stationary type of welder’s workplace does not need to be moved, so when organizing it there is no need for supports on wheels, etc.
Regardless of the type of welding station, the work will require non-flammable materials to eliminate the risk of fire: for both permanent and temporary use of welding, it is important to provide the craftsman with safe working conditions
Current tools and materials
When setting up a workplace for welding work, it is important to select a full range of tools and equipment that are relevant for the job. Welding booth layout
Welding booth layout.
The list may change at the discretion of the welder, but there are positions that are extremely difficult to do without:
- welding machine;
- a device for storing filler materials and other types of auxiliary devices;
- constant power supply of electric current;
- comfortable landing place;
- switch for turning the voltage supply on and off;
- high-quality ventilation system, exhaust chamber;
- storage systems for small equipment: portable baskets, drawers, shelves, etc.;
- electric holder
The above elements, with rational planning of the workplace space, will take up relatively little space.
Equipping a welding station yourself must be carried out taking into account all safety requirements. The optimal length of the working space is 2 m, width – 2.5 m, height – 2 m. In no case should you create a closed upper part of the welding station.
To organize the walls, it is worth using thin steel or plywood impregnated with a fire-resistant solution.
To perform assembly and welding operations of metal parts inside the master’s office, it is important to install a comfortable table. The optimal parameters of the welding table are as follows: the height is 50-60 cm when working while sitting and about 90 cm when working while standing, and the area is about 100 cm2
Steel bolts should be welded to the table, onto which the current-carrying wire from the welding current source, as well as the grounding wire of the work table, are attached.
On the side there are nests adapted for storing electrodes and filler materials. Drawers can be used to store small hand tools or technological documentation.
The main type of equipment in welders' offices is considered to be single- or multi-station arc power sources.
Often, in the workspace, welders use single-station power sources, since in the case of power from multi-station sources, the welding current must be distributed throughout the cabins through the use of current-carrying wires or buses. Also, a switch must be installed in the cabin to turn the welding current on and off.
Step-by-step arrangement of a welding station
General view of a typical welding station.
Welding stations can be organized in a spacious garage, service station, construction site, etc.
In any case, all operations for their arrangement can be divided into the following stages:
- choosing a place to organize the master’s workspace, clearing it of foreign objects, cleaning;
- arrangement of the walls of the working area using steel or plywood impregnated with a fire-resistant composition;
- arrangement of a table with a table top and storage systems made of non-flammable material;
- providing access to a source of electricity for the operation of electrical equipment;
- organization of a reliable ventilation system;
- visual inspection of the work result before welding.
Calculation of the ventilation system of the welding station
Having chosen a hood, you will need to make calculations for its proper installation and use.
Thus, the calculation of the performance of a ventilation system includes the determination of:
- Air flow speeds for the hood. Usually it turns out to be at least 1.5 m/sec, but it still needs to be calculated using GOST 12.3.003–86. The same document explains how to set the ventilation to the ideal flow rate.
- The need to install a crevice nozzle on the hood if semi-automatic cooking is planned. Its slot length is 3.5 cm, and it should be located at a distance of at least 5 cm from the working area. If such a nozzle cannot be installed, it can be replaced with several conventional outlets.
Mistakes when installing a kitchen hood
1
Some people, of course, leave a grille for natural air movement, but still manage to block it with the air duct itself.
2
Recommended dimensions for round air ducts are d=125mm. For rectangular ones - 204*60mm.
3
In most cases, this is prohibited by the rules. Specific points will be given below in the text.
You can, of course, lay a separate box along the facade straight to the roof. But is it worth it? Although in restaurants and cafes located on the ground floors of high-rise buildings, this solution is widely used.
By the way, the ban on venting air to the street through a wall does not apply to private houses, but only to high-rise buildings.
4
First of all, this will affect the noise. Although, of course, the turns themselves are not the greatest evil. And sometimes you can’t do without them.
It is the turns that follow one after another, without acceleration sections, that are dangerous.
5
Remember that a productivity of 200-300 m3/h is quite enough to effectively remove all odors, with minimal load on the ventilation of the house.
6
The installation height directly depends on what kind of stove you have - gas or induction hob.
7
Believe me, sometimes this structure has to be disassembled.
8
Why this is a mistake, and when it is still possible to do this, is discussed below.
9
As a result, connecting it haphazardly, through carriers and extension cords. Do not forget that in the end this is not a portable device, such as a fan, heater or mobile air conditioner.
This means that the wiring for it needs to be done stationary and wisely.
10
It must be embedded and installed in compliance with the appropriate angles and inclinations. Otherwise it will work every other time.
In general, installation of a hood can be divided into two main stages. The first is its connection to electricity. The second is the air duct structure and everything connected with it.
Let's look at each of them separately.
DIY hood installation
Homemade exhaust hood for a welding table in a garage made of plastic pipes
According to the rules and requirements for safety standards, in large welding rooms with several stations, the ventilation system must be installed by qualified specialists who can make accurate calculations. In small workshops, you can create an air exchange system yourself according to drawings, following standard instructions. In this case, the work is divided into two stages. First of all, a supply-type hood is installed, using a mixed type of air supply and outlet in horizontal and vertical modes; the second option is more preferable:
- A ventilation chamber is installed near the wall with access to the street, in which a fan is installed, equipped with the functions of filtering, cooling and heating air.
- A hole is made in the wall through which the fan will draw in fresh air.
- A channel is laid from the ventilation chamber to the ceiling to supply air.
- An additional fan equipped with air purifying filters is installed in the attic. A special pipe is installed from it to the roof, removing exhaust air masses.
- Two or three holes are made in the ceiling, which are connected to the attic fan using ventilation ducts.
When the general air exchange system is ready, you can begin installing the local line. Ventilation for a welding station of this type is a suction structure, from which a channel is laid towards the roof. It is selected taking into account the configuration of the production enterprise for a specific workshop.
Local exhaust hood is able to remove most of the contaminants autonomously, preventing their spread throughout the room. If necessary, install a mobile suction unit that moves the hood together with the welding machine.
Selecting a ventilation scheme for a production welding room
During the selection of the optimal general ventilation scheme for the workshop for performing connecting work, all important points are taken into account, including the exit of convective flows to the top of the room. These flows can be enhanced by directed supply air jets
It is also possible to direct convective currents in jets to the air intake panels.
It is necessary to pay attention to the fact that unstable convective flows are often disrupted due to the movement of masses of aeration air, or not without the participation of a cooled influx returning downward along with harmful substances. All these and many other processes can most likely cause certain difficulties in dealing with them
If the air inside the workshop is artificially mixed by directed jets, a concentrated influx, the concentration of harmful substances inside the room is practically equalized. As a rule, work on joining metals is carried out with a large emission of dust, and therefore the general exchange system must be made of a mechanical supply and exhaust system, and the air must be heated in winter.
According to the instructions of SNiP, during the welding process the influent must be supplied directly to the work area. It is allowed to supply air from air distributors, which are located at a level of 6 meters from the floor surface of the room, with air jets directed down vertically, with horizontal, as well as inclined air jets at a level of 4 meters and above, as an air supply to the welding area.
Exhaust devices for welding
Industrial cantilever hood Afalina
Hoods for welding in production are divided into several available varieties. The most popular are devices with a lift-and-swivel design. They consist of an air receiver, which can be fixed in any position using hinges, as well as a hose connecting the air receiver and the central exhaust system. This design makes it possible to eliminate 85% of substances hazardous to health, since it can be placed close to any welding machine. Hoods help to completely purify the air at a distance of up to 8 meters from the installation site. Users note such models as “Fallow deer” and “Octopus”.
In second place in demand are local suction units, which must be installed at a height of up to 1.5 meters from the welder’s position.
The hood above the working welding table can be external or internal; in the second case, it is connected to the general ventilation system using special hoses. To ensure proper air circulation, it is better to give preference to supply exhaust ventilation, providing an influx of air masses at a speed of over 40 m3/hour.
Ventilation of fish production
The production process is characterized by the presence of a sharp, specific odor that accumulates at the bottom of the premises. The ventilation system device provides:
- acceptable working conditions for personnel, removing the air flow filled with a specific odor;
- quality of fish products. The preparation of fish products is accompanied by culinary and heat treatment. In this case, particles of fat, burning, and associated odors enter the working air environment. To remove them, local exhaust is used;
- required storage period. Removing excess water vapor, odor, and along with them various microorganisms allows you to adhere to standards for shelf life of products.