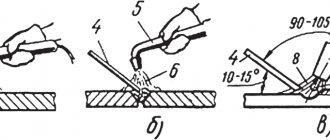
The world of pipeline fittings is huge and diverse, and at first acquaintance it may seem chaotic and obscure.
But if you understand the principles of its classification proposed in regulatory documents, it will become well structured and orderly. Classification is a very convenient and useful tool that assigns each product its place and positions it relative to other products, the tasks that it must solve, the fundamental design, design features, materials used in it, etc.
In relation to pipeline fittings, we can talk about two basic principles of classification ─ types and types of pipeline fittings.
Main types of pipeline fittings
- Valves.
Valves are used as shut-off and control valves. As shut-off valves, they are installed on pipelines with a cross-section of no more than 30 cm. They are used when carrying out repairs in dead-end sections of the system. The valve has a locking element that rotates along an axis located at an arbitrary angle relative to the pipe central.
- Valves.
In pipelines with low hydraulic resistance, small-sized shut-off elements - valves - are used.
Depending on the design they are divided into:
- wedge (with solid, elastic and composite wedge);
- parallel (gate).
In low-pressure systems, a type of pipeline fitting such as parallel-type valves is installed.
They act as a locking mechanism and operate only in the “closed” or “open” position. Valves are rarely used as regulators.
They are widely used in full-bore systems, such as main pipelines, when the pipes are of the same cross-section and it is possible to move the working medium in a continuous flow and at high speed.
A special feature of the valves is the presence of a spindle - based on the design features, it can extend or not.
Conditions for using valves:
- temperature – up to +450 °C;
- pressure – up to 25 MPa;
- range of pipe diameters - from 5 cm to 1.2 m.
These fittings are suitable for systems where alkalis, oil, acids, water, steam, etc. are used.
For pulp and paper production, fecal wastewater, or where there are foreign objects in the working environment, gate valves (parallel) are used, since their design has a metal wedge that cuts through foreign objects when moving.
Wedge valves are installed during scheduled system repairs. The body of this fitting is cast iron, inside there is a rotating spindle connected to a wedge. The body and cover of such products are welded from parts that are cut from sheet carbon or corrosion-resistant steel. They are used in gas and liquid transportation systems that do not react with the pipeline material.
As a rule, valves with large diameters are equipped with an actuator for ease of adjustment. Actuators can be pneumatic, electric or hydraulic. You can also adjust it manually, but you need a gearbox to make this process easier.
- Valves.
Another type of pipeline fittings are valves. They are designed to close or open to achieve a certain pressure in the system, as well as when changing the direction of the working medium.
There are several types of valves: single-seat and double-seat. A more convenient valve in production is a double-seat valve due to the ability to perform two functions at once - control and distribution.
Also, depending on the flow of the working medium, valves are: straight-through or through (if the direction of the medium flow is unchanged) and angular (if the working medium changes direction directly perpendicular).
To ensure tightness and better reliability, shut-off valves are used that completely block the flow inside the pipe.
Check valves are used to prevent a sudden change in the direction of movement of the working medium. This can happen if the pump fails or there is a loss of flow.
Because control valves can change the size of the flow area, they are used to control the amount of gas or liquid supplied to the system.
Shut-off and control valves perform both functions at once: shut-off and control.
A huge advantage of using such valves is that they can operate both in corrosive environments, vacuums, and at high temperatures and pressure. Maintenance and repair are not labor-intensive.
- Cranes.
A distinctive feature and a huge advantage among other types of pipeline fittings is that taps are used as distribution, control and shut-off devices for liquids of various viscosities, as well as for gases.
The design of the taps: body and shutter (plug) with a hole in the center. The valve can have different shapes: spherical, cylindrical or cone-shaped. The material from which the taps are made: steel, cast iron, bronze, brass, porcelain and special plastic (for aggressive environments) are also found.
Depending on the direction of flow, as well as on the number of pipes, taps are divided into groups:
- corner;
- checkpoints;
- three-way;
- multi-pass.
According to the principle of shutter movement, taps are available with spin, with rotation, with or without lifting the shutter.
According to the control method, cranes are divided into:
- manual;
- with electric drive;
- with pneumatic drive;
- with hydraulic drive.
Based on valve geometry, valves are divided into:
- cylindrical;
- conical;
- ball;
- needle-shaped
Based on the method of ensuring tightness, valves are divided into tension and gland valves.
The valve functions as a shut-off device when it is necessary to stop the full flow. The tap can also be used to regulate the flow of liquid or gas and change the position of the valve.
- Shutters.
The main part in the design of shut-off valves is the valves. The performance of the entire system depends on this type of pipeline fittings - complete or partial blocking of the flow of gas or liquid. In the event of the slightest malfunction, serious consequences can occur, including an explosion of hazardous gases and an environmental disaster. In order to prevent such situations, it is very important to pay attention to the material from which the valve is made, as well as to the operating conditions.
There are different types of shutters:
- Disk
(most frequently used). Used for heating systems, steam supply, water supply, non-aggressive working environments or petroleum products.
- Flanged
(the name comes from the installation method - using flanges).
Materials from which valves are made: steel (carbon, stainless and alloy) and cast iron. Gates made of steel can be used in the temperature range from -60 °C to +700 °C at an excess pressure of up to 10 MPa. They have found widespread use in aggressive work environments. Gates made of steel are used more often than cast iron.
Shutter advantages:
- easy to install and repair;
- compact in size and weight, easily mounted in small areas;
- easily replaced when the expiration date comes to an end;
- do not jam during use;
- pretty cheap.
Various types of liquid and gaseous substances, including toxic ones, flow through the pipeline, and to stop the leak or block their flow in the right place without disrupting the operation of the entire system, gates are used. Therefore, the reliability of the entire system, as well as the safety of operating personnel, depends primarily on their serviceability. Despite its ease of use and low price, this fitting is the most important element in the entire pipeline system.
This is interesting: Aluminum wire for welding and features of its use
General rules for installing plumbing fixtures
If you strictly follow the simple requirements below for the installation of plumbing fixtures, you will ensure yourself comfort during its operation and the absence of problems in the operation of your plumbing fixtures for many years.
It is best to use valve type shut-off valves. Valves are installed on pipes with a diameter of 50 mm or more.
Water meters are installed at a distance of 0.3-1.0 m from the floor. Toilet taps, as well as mixers, should be installed above the sides of washbasins at a height of 0.2 m. Water taps and mixers are installed 0.25 mm above the sides of sinks and 0.2 m above the sides of sinks. Toilet flush taps are installed at a height of 0.8 m from the floor to the axis of the tap. Shower nets are installed at a distance of 2.1-2.25 m from the bottom of the net to the floor, mixing fittings for showers - at a height of 1.2 m from the floor. Water taps for baths are installed at a short distance - 0.8 m from the floor. Common mixers for bathtubs and washbasins are installed at a height of 1.1 m, and mixers for bathtubs and shower trays - at a height of 0.8 m from the floor to the horizontal axis of the mixers.
Read material on the topic: How to choose a bath faucet: 12 tips
Fire hydrants are installed at a height of 1.35 m from the floor, if necessary, one above the other, in cases where the hydrants are paired by design, it is important to ensure a small distance of 0.15 m or more from the horizontal axis of the fire hydrant to the bottom shelf cabinet and from the vertical axis to the cabinet wall.
In valve-type fittings, for greater density and reliability, it is necessary to use gaskets made of rubber, plastic, hard rubber, the material of which must be selected depending on the characteristics of the working environment.
For reliable and long-term operation of plumbing fixtures, it is important to follow the above requirements during installation; the deviation during installation work can be no more than 20 mm.
If prefabricated equipment is used, then it is better to assemble it directly at the installation site; if otherwise provided, then it is assembled in a specially designated place.
If galvanized pipes are installed in the water supply system, then galvanized steel connecting parts or non-galvanized ones made of ductile cast iron should be used.
Now a few words about what materials need to be used to seal the fastening points: at temperatures up to 105 degrees - tape made of fluoroplastic sealing material or flax strands impregnated with red lead or white mixed with natural drying oil; at temperatures above 105 degrees - FUM tape or asbestos strands together with flax strands, impregnated with graphite mixed with natural drying oil.
The distance from the main line to the shut-off valves on the branches should be within 120 mm.
Pipelines whose axis is vertical cannot deviate from the vertical by more than 2 mm per m of pipeline length.
The distance from the cladding surface to pipelines that do not have external insulation should be 35 mm for pipe diameters up to 32 mm, and if their diameter is larger - from 40 to 50 mm, then the distance should be 50 mm, an error within 5 mm is possible in that or the other side. This is applicable both in heating and water supply systems for different temperatures when they are laid open.
Pipelines installed in specially equipped tracks - shafts should not come into contact with the surrounding parts of buildings and structures. At the same time, they must be reliably strengthened; it is forbidden to use wooden fasteners, since they do not provide the necessary reliability and crumble over time. Supporting structures must allow the working environment of the pipe to function freely at any temperature.
If you need to bend a galvanized pipe, it is best to do this when the pipe is still cold. In this case, it is necessary to observe the value of the ratio of the difference between the largest and smallest outer diameters to the largest outer diameter of the pipe; it should be no more than 10%. Pipes are turned using special angles; this applies to heating and water supply systems with different temperatures of working media.
Heating, hot water supply, and condensate pipelines made of steel are enclosed in special sleeves in those places where they come into contact with other structures; this also allows the pipes to freely move the medium at different temperatures in the range from 40 to 105 degrees Celsius. The sleeves are installed in a special way within 30 mm from the floor covering mark.
When the temperature of the working environment is more than 105 degrees, the sleeves must be made of non-combustible materials, this will be reliable protection even for structures that can ignite, the distance from the sleeve to the pipe along the entire circumference must be left from 15 mm when filling it with asbestos and at least 100 mm, if there is no such isolation.
Those places where pipes intersect with firewalls are filled with asbestos for additional safety. In cases where working pipes with a cold working medium are directly mounted into wooden building structures, they must be additionally wrapped with roofing felt.
In non-industrial premises, such as apartments and public places, fastenings for steel pipe risers are not installed if the floor height is within 3 m; if the floor is higher than 3 m, then fastenings for them are installed at half the height of the floor.
Checking the serviceability of plumbing fixtures, all its tests must be carried out as long as its hidden parts are still accessible for visual inspection, that is, it is still possible to correct errors, and while the visible areas are not isolated.
Systems that use water as a working medium must be thoroughly flushed with a stream of water before putting the plumbing into operation. In the case of installation of pipes in the cold season, the connection of the internal and external parts of pipelines, in which a high temperature of the working environment is provided, the connection must be made immediately before starting the system.
Functional purpose
Depending on the function performed, the product can be of the following types:
- Constipated . When a tap, valve or valve is closed, the movement of the working medium completely stops. Shut-off valves allow the substance to move without restriction when the corresponding mechanisms are opened. The need to open or close the flow through a pipeline most often arises for technical reasons. The classification of types of shut-off valves for pipelines also includes elements designed to drain a substance from a container or enter it into control and measuring instruments (for more details: “What shut-off valves for pipelines are on the market and which one is better to use”).
- Regulating . Using various valves, condensate drains and valves, you can regulate the temperature, pressure, pressure or level of the working medium. Regulatory mechanisms allow you to control the consumption of the transported substance. Safety. If the pressure of the transported substances increases significantly, safety valves or diaphragm fuses are automatically activated. As a result, excess working medium is discharged.
- Protective . In the event of an unexpected change in the parameters of the transported substances, the equipment or section of the pipeline is switched off, and the reverse flow of the working medium is blocked. As a result, the main line and mechanisms remain protected. Pneumatic gate valves, check valves and shut-off valves are used as protective fittings.
- Phase separation . Such reinforcement separates substances that have different phase states. For example, separation of condensate, oils, gases or air.
- Distribution and mixing . Using special taps or valves, the flow of the working medium is given a certain direction. And with the help of mixers, several streams are combined into one.
- Control . These include level sensors and plug valves that monitor the level of the transported substance and its movement.
Control valves of the water supply network
This type of fittings regulates the water parameters in the water supply system by changing the flow rate or changing the flow area of the water supply system.
Control valves include:
- Control valve (option of combined fittings);
- Regulators:
- Pressure;
- Regulators of direct and indirect action;
- Pressure from yourself;
- Pressure regulators after themselves;
- Apartment pressure regulators
This is a variant of the pressure regulator “after itself”. Designed for installation in apartment water supply systems. Limit and stabilize water pressure in the system. Shut off the pipeline when the water is turned off.
- Regulators for differential pressure, flow, temperature, level;
- Various combination regulators.
Read: What is a water distribution comb
Control methods
Based on the type of control, two types of valves are determined:
- Automatic . Such mechanisms are activated autonomously without the participation of the human factor.
- Manual . To activate such a mechanism, it is necessary to perform some manipulations by hand or using a drive. Most types of fittings for pipes with a diameter of less than 40 cm are controlled using a manual drive. Such actions proceed very slowly and require enormous physical effort.
The water supply network fittings are
The basic equipment of a water supply network is water pipes. It is through them that water is transported to a given place.
However, the pipeline will be useless without plumbing fixtures. With its help, we can shut off or open a water supply system, protect it from increased pressure, distribute water to consumers and solve a lot of other necessary problems.
Pipeline connection methods
The connection of fittings and pipeline can be done in several ways:
- Coupling connection . For this method, couplings with internal threads are used. The method can be used on products made of metal-plastic, polyethylene and polypropylene. The diameter of the pipe for the coupling connection should not exceed 8 cm, and the pressure of the working medium should not exceed 10 atmospheres.
- Flange connection . For such a connection, a bolt tie is used. This makes it possible to repeatedly assemble and disassemble the connection for cleaning the fittings or for repair work. Bolt fastenings require periodic inspection, as they tend to weaken during operation.
- Welding connection . Joining parts using socket or butt welding is considered the most reliable and airtight, therefore it is used on pipelines transporting hazardous substances.
- Pin connection . Small parts operating under high pressure conditions are connected using male threaded pipes.
- Union connection . Pipelines whose elements have a diameter of less than 15 mm are connected using a fitting.
Classification by mounting method
A modern customer can choose from a coupling, flange, fitting, clamping, pin-type system or a welding model.
- Coupled pipeline fittings are, as a rule, cast iron valves, ball valves with a DN value of up to 50–80 mm (elements that can be purchased at a low price). They are fastened with couplings - threaded, cylindrical, pipe or conical (internal).
- Flange products are one of the most common options (described in detail in GOST 12815–80). Mounted with flanges, they are represented by cast iron and steel valves.
- Union pipeline fittings are connected to the pipeline using threaded pipes. The second fastening block is a fitting with internal thread.
- The clamping device is connected using studs and a flange connection on the pipeline. The products do not have their own flanges. This mounting method is often used with check valves, control products, butterfly valves, and gate valves.
- The welded fastening method is reliable and affordable. Installation is carried out using pipes made for welding.
- The pin-type model uses a fastener with an external thread and a collar for the seal for installation.
Sealing method
Sealing of mechanisms is carried out in several ways:
- The gland seal is achieved using a gland packing, which is asbestos fibers or hemp impregnated with a sealant.
- Membrane sealing is achieved by a membrane placed between the cover and the valve body.
- Bellows sealing involves the use of a bellows assembly to seal moving elements.
- Hose sealing requires the design of an elastic hose that, when clamped, reliably cuts off the flow.
This is interesting: Is stainless steel magnetic: magnetic properties of stainless steel
Return valve for water supply network
This type of fitting prevents the reverse flow of water automatically. In apartments it is well known by the check valve installed when installing the water meter.
There are:
- Check valve (OK) and shutter (slam);
- The foot valve is a check valve mounted in front of the pump;
- Lifting OK;
- Axisymmetric OK;
- Non-return-locking gate;
- Non-return-controlled shutter;
- Non-return shut-off valve;
- Non-return controlled valve;
- Shut-off, high-speed valve;
- Reverse double-leaf valve.
Method of moving the working mechanism
Depending on the method of movement of the working mechanism, the following types of pipeline fittings are distinguished:
- Cranes are locking elements with a body of rotation, the movement of which is carried out by movement around its axis. Can be positioned arbitrarily in relation to the direction of flow.
- Valves are elements that regulate or block the direction of flow by moving across the main flow.
- Gates or dampers are elements made in the form of a disk that can rotate around its axis perpendicularly or at an angle to the flow.
- Valves are parts in which locking and regulating elements are mounted on a spindle. When they move back and forth parallel to the flow, the cross section in the horizontal plane is blocked. The working medium for such fittings can be liquid or gaseous. Valves come in valve and ball types.
How is the production of sanitary fittings carried out?
Today, the market for plumbing fittings is extremely wide and is represented mainly by products made mainly from modern plastic and plastic materials, this is due to their availability, lightness, lack of corrosion and other positive qualities. In connections of pipes and other parts, gaskets with special plastic rings are used, which ensures reliable fastenings and tightness of the working system during operation of the equipment. The fasteners are also made with layers of rubber, which is durable and does not corrode. This equipment collection system is convenient and makes it easy to assemble and dismantle plumbing fixtures.
Conditional pressure of the working medium
According to the nominal pressure, fittings are divided into several types:
- Vacuum - necessary to isolate the vacuum chamber or part of it from the pumping system.
- Absolute pressure fittings are used on equipment to measure pressure up to 0.1 MPa.
- Low pressure parts, less than 1.6 MPa, are used on metal-plastic, polyethylene and polypropylene water supply systems for domestic use.
- Medium pressure fittings, less than 10 MPa.
- High pressure products, less than 100 MPa.
- Ultra-high pressure mechanism, over 100 MPa.
History of origin
People began to use pipeline fittings a long time ago. According to historians, in 5000 BC, people built simple piping systems that included valves and taps.
But the existence of reinforcement was proven in ancient times by the Roman Empire. Archaeologists studying this culture found a plug tap during excavations. The Romans used this device to open and close water. The tap is cast from bronze.
The history of the creation of industrial pipeline fittings began in the 19th century. This is the time of the first development of steam engines, the designs of which required a device that could block the flow of hot steam through the pipes.
Fig 1. History
The first notable steps in industrial valve engineering belonged to Timothy Hackworth and Joseph Hopkinson, who developed the world's first wedge gate valve.
For Russia, industrial valve manufacturing became possible thanks to the work of a foreign industrialist named Grosh. He founded a foundry (1878) in St. Petersburg, which was engaged in the serial production of fittings. And 10 years later the company was bought by a German. The company was named JSC Langensiepen and Co. In the future, several more factories will open under this name throughout Russia and begin mass production:
- fittings for boiler houses and fire departments;
- fire hydrants;
- pumps;
- pressure gauges;
- copper pipes.
After nationalization, in 1922 the Lagensiepen plant was renamed Petrograd Reinforcement Plant. It was from this moment that the history of Soviet valve manufacturing began.
Working temperature
Depending on the temperature of the transported substance, the fittings are divided into the following types:
- Cryogenic – for operation at temperatures below -150
0WITH.
- Refrigeration fittings – for temperatures from -60 to -150
0WITH.
- Low temperature – from -20 to -60
0WITH.
- Average temperature – no more than 400
0WITH.
- High temperature – within 600
0WITH.
- Heat-resistant fittings can operate in environments with temperatures above 600
0WITH.
Types of shut-off valves
The following types of shut-off pipeline valves are distinguished:
- taps;
- gates (valves);
- valves;
- flaps.
Crane classification
Shut-off valves are primarily designed for low-pressure domestic pipelines.
The shut-off valve design is as follows:
- frame;
- locking element;
- handle;
- set of sealing gaskets.
Elements included in the stopcock
Devices can be classified according to several criteria:
- type of locking element;
- installation method.
An element that blocks the flow of a passing medium can be:
- ball. In accordance with this, the valve is called a ball valve (figure above);
- cone in the form of a plug (plug valve).
Plug type stopcock
The taps can be attached to the pipeline:
coupling method. The fixing nuts are screwed onto the thread prepared on the pipe;
Threaded tap
- flange method. The fixing elements are flanges connected to each other with bolts;
- welding method.
Devices mounted on flanges and by welding
Each tap has its own symbol. The markings on the device body must include:
- nominal diameter (DN);
- conditional pressure for which the device is designed (PN);
- material used to make the tap;
- manufacturer;
- additional reference materials (date of manufacture, batch number, etc.).
Symbols of the main parameters of the crane
If you know the markings, you can always choose a locking device yourself.
Using Gates
A shut-off valve (valve) consists of a body with two ends for attaching the device and a seat that is closed by a shutter.
Pipe shut-off valve
The main distinguishing feature of a valve from a faucet is its high tightness class, which allows the device to be used on gas pipelines.
A valve, like a faucet, can be connected to a pipeline using couplings, flanges or welding.
Valves are produced that are actuated by:
- flywheel (manual control);
- electric drive (electronic control), including using a remote control.
The marking of shut-off valves also contains:
- symbol of the device model;
- passage;
- designation of the type of connection to the pipeline;
- pressure;
- execution material;
- Climatic performance;
- document on the basis of which the valve is manufactured.
Designation of valve parameters
Purpose and types of valves
The most commonly used element of any pipeline is the valve. The device consists of a body and a cover, between which the shutter is located.
The simplest type of shut-off valves
The purpose of shut-off valves - valves - is any pipelines whose diameter varies from 15 mm to 2000 mm.
The advantages of the device, compared to other types of shut-off valves, are:
- ease of maintenance and design;
- small sizes;
- low resistance.
Gate valves can be made from the following materials:
- become;
- cast iron;
- non-ferrous metals and alloys made from them.
The valves are controlled:
- manually (rotating the handle);
- electric drive;
- hydraulic drive.
Valves with electric or hydraulic drive are mainly installed on industrial pipelines.
The designation of shut-off valves (valve) determines:
- type and name of the device;
- nominal working diameter;
- maximum pressure in the system;
- type of drive;
- position of the device in working condition;
- accommodation category;
- Climatic performance;
- type of connection of the device to the pipeline.
Designation of valve parameters
Purpose of dampers
The closing element in the damper is a disk that rotates around an axis.
Type of shut-off valves for pipelines
Valves are mainly used on pipelines that have a large diameter and are under low pressure, since the tightness class of the device is quite low.
The damper can be controlled:
- a flywheel that drives the axis of rotation (manual control);
- hydraulic drive;
- electric drive.
In most cases, the body of the locking device is made of cast iron, and the rotary disk is made of steel.
Dampers are installed:
- welding method;
- flange fasteners.
The valves can be used in chemical pipelines and sewer systems. They are practically not used for water supply or heating.
The brand of shut-off valves - valves, as well as the batch number, diameter, pressure and area of definition are indicated on the device body similarly to the previously given diagrams.
Classification, labeling and standard requirements
Pipeline fittings, due to their ability to change the internal cross-section of the pipeline, make it possible to effectively control the flow of various types of media. Thus, its use makes it possible to perform the following operations:
- distribute the phases of movement of working media;
- reset the flow;
- turn off the supply;
- provide mixing of several streams;
- adjust flow parameters;
- distribute the work environment.
The classification of fittings is based on its functionality. So, depending on this parameter, pipeline fittings can be of the following types.
Regulating type
With the help of such pipeline fittings, the flow parameters of the working medium and, accordingly, its main characteristics are changed. In this category, throttle and shut-off and control types are distinguished. With the help of the first type of fittings, which are often called pressure-reducing fittings, it is possible to reduce the working load in the pipeline, which is done by increasing the hydraulic resistance in its flow zone. Shut-off and control pipeline valves are a set of devices that help regulate the parameters of the working flow and shut it off.
Shut-off valves for different pipe diameters
Locking type
Such pipeline fittings are used to hermetically shut off the flow of the working medium. If it is used to control the flow of the working medium into control and measuring units, then it is called control. There are also drainage shut-off valves, due to which the working medium is discharged from pipelines or containers.
Mixing and distribution type
Such pipeline fittings ensure mixing of working fluid flows, as well as their distribution along the required directions of movement.
Protective
This pipeline fittings are used to protect system elements from the consequences caused by changes in the flow parameters of the working medium. Such changes can most often be the consequences of emergency situations in the system. Fittings of this type can also provide protection against changes in the direction of movement of the working flow.
Phase separation
This is a pipeline fitting that divides the working environment into different phase states. For example, it can separate superheated steam and the working environment, retain condensate (condensate trap), and also solve a number of other problems.
Safety
This type of pipeline fittings protects the system from a critical increase in pressure in the working environment.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
Pipeline fittings, according to the requirements of State Standard R52720-2007, are characterized by two main parameters:
- conditional pressure;
- conditional pass.
Conditional pressure, designated Ru or PN, characterizes the value of this parameter at which tanks or pipelines can be operated for a certain period of time, provided that the temperature of the working environment is +20 degrees Celsius. The classification of pipeline fittings and the nominal values of this parameter are stipulated by State Standard 26349-84.
The values of the nominal diameter of the fittings, which is designated DN or DN, characterize the parameters of the elements that make up the pipelines. The permissible values of this parameter are stipulated by State Standard 28338-89.
» data-lazy-type=»iframe» src=»data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7″>
Purpose and scope of application
The fittings are divided into the following types according to their area of use:
- Industrial (industrial pipeline) - used in various industries without any special requirements from users.
- Special (tailored) - designed for operation in conditions with specific characteristics of the transported and environment.
- For hazardous facilities - used at facilities where reagents that are harmful and dangerous to human health (flammable, explosive, flammable, toxic and other substances) are used, as well as equipment operated under pressure from 0.07 MPa or at temperature parameters working fluid over 115 °C.
- Sanitary (sanitary, plumbing) - shut-off valves for water supply, mounted on sanitary equipment. The average consumer most often encounters ball valves installed under sinks and toilets in front of flexible hoses, when connecting washing machines and dishwashers to the water supply.
- Ship (ship, marine) - placed on pipe communications and equipment of ships.
- Vacuum - operating at pressures below atmospheric.
- Control (monitoring) - regulating the supply of medium to control, measuring equipment and devices.
- Cryogenic - operating in an environment with a temperature from 0 to 120 °K.
- Shut-off (quick-acting) - quick-acting in accordance with the production process.
- The inlet is of the reverse type, mounted at the end of the pipeline before the electric pump.
- Antisurge - responsible for reducing the difference in the flow rate of the working fluid of compressors.
Rice. 5 Plumbing fittings in public utilities
- Pressure-reducing (throttle) - performing the functions of reducing pressure in networks by increasing hydraulic resistance.
- Drain (bleed, blow-off, drain) - performs the functions of discharging large volumes of liquids from tanks and pipeline systems in a short time.
- Sampling and bleed - used when taking samples and determining the presence of a medium, discharging it from various types of tanks and boiler equipment.
- Wellhead, oil-and-gas field - designed for operation in the pipes of oil production wells, their piping and beyond the boundaries of pipelines.
- Oil and gas production or fountain (Christmas tree) - installed at the mouth of well pipes during oil and gas production.
- Fountain (wellhead) tree (christmas tree) is an auxiliary variety when installing wellhead devices, designed to ensure the normal functioning of the latter.
- With heating (with heating, jacketed) - has an electric cable built into the body or is covered with a heat-protective casing on top. A heat carrier, for example, steam or heated air, is supplied into the space between the housing and the casing.
- Energy (energy, power) - refers to special varieties for functioning at energy industry facilities.
Rice. 6 Flanges and weld ends
What materials is it made from?
Various materials are used to produce pipe fittings. GOST R 55509-2013 specifies the requirements for the composition of the metals used. Cast iron used:
- gray SCh15, SCh20;
- malleable KCh30-6;
- with spherical graphite VCh40, VCh45.
The metal alloys used are:
- carbon steel, alloyed, high-alloyed;
- non-ferrous metals and alloys - bronze, brass, titanium alloy, aluminum, nickel.
Plastic products are widely used, these are polyvinyl chloride, polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene. Used to transport aggressive substances.
Tip: Recently, Walraven star Quick plastic clamps with a ratcheting actuator, which speeds up the installation process, have become increasingly common.
Shut-off valves for heating and water supply - manufacturing materials
Shut-off valves for heating and water supply systems are made from a wide range of metal and polymer materials.
The housings of units for industrial and municipal use are mainly made of cast iron and various grades of steel - both low-carbon and alloyed with various additives, which give the metal increased anti-corrosion properties and heat resistance.
The vast majority of shut-off valves for water supply used in households are made of brass without or with chrome plating, and less often of stainless steel. Recently, due to the popularity of polymers, shut-off valves for water supply systems are often produced in housings made of PP polypropylene or HDPE low-density polyethylene.
Gate wedges for large-sized valves are produced from low-carbon steels, with overlays made of corrosion-resistant, hard-alloy, heat-resistant and wear-resistant materials. Sealing rings in seats are also made by fusing metals with high physical and chemical characteristics (bronze, stainless steel).
The spheres of ball valves used in everyday life are made of brass or bronze with a chrome coating, as well as stainless steel.
Handwheels, consoles and handles are made of steel, cast iron; in small-sized appliances for household use, they are made of plastic, aluminum, and steel.
In addition to gland seals, shut-off control valves for heating systems for industrial, municipal and domestic use are equipped with sealing materials made of rubber, graphite, Teflon (PTFE), ethylene propylene diene (EPDM) and acrylonitrile butadiene (NBR), synthetic and fluorinated (SFC, Viton) rubbers.
Rice. 20 Brass small-sized shut-off valves in section
Basic classification
The classification divides reinforcing products according to material characteristics, design, price categories, sizes, and brands. The most common classification feature is by purpose. There are 4 classes here.
- The largest group is shut-off valves . It is used to shut off the flow and provides an excellent degree of tightness of the closed network (shut-off function). Considering that such devices are required to cut off the supply of the working medium as completely as possible, it is obvious that the qualitative characteristics of the shut-off series are the degree of tightness and the service life of ensuring shut-off.
- Control valves allow you to set pipeline operating parameters - pressure level, temperature, flow volume and other conditions. Thanks to products of this class, it is possible to fine-tune technical processes as precisely as possible to obtain a cost-optimized result. The flow rate of the working medium is also largely determined by the control valves. And the regulating series is represented by valves and valves, throttling devices. The latter are indispensable in pipelines with high pressure levels and constant pressure changes.
- Protective fittings. From its name it is clear that it is used to protect equipment and devices connected to them from dangerous fluctuations in operating parameters. The key task of the protective device is to completely shut off a separate area when an “alarm” signal (reaches a critical level of specified indicators). This allows you to close the area from negative influences and flows of the working environment in the event of an accident. The most popular options for protective fittings are safety valves, dampers, gate valves and taps.
- Safety view of pipeline fittings . It works on a similar principle to the protective principle. Only, unlike the latter, it reacts not to an already realized threat, but to potential risk factors. Safety elements do not turn off the entrusted areas in order to “close” them, but work to prevent an accident - they bleed/dump excess working medium or pressure. Mostly these are safety and bypass valves, membrane bursting devices, and pulse devices.
Classification by field of operation
Depending on the scope of use, there are 5 types of pipeline fittings .
- Universal products. These are mass-produced products that are used in a variety of pipelines without reference to the profile of the enterprise that uses them.
- Special-purpose devices are made to specific parameters, taking into account the specifics of the network and the characteristics of its operation.
- Products for special conditions of use. They are equipped with pipelines, the requirements for safety, reliability, and controllability of which are significantly increased due to the responsibility of the user for their operation. As a rule, we are talking about highways for transporting toxic, explosive and other aggressive working media.
- Narrow profile products. The purpose of pipeline fittings of this type is the arrangement of pipelines of transport enterprises and shipyards.
- Sanitary products for the installation of household networks. Like universal products, it is produced on a conveyor belt, but unlike the former, its types are subject to serious requirements in terms of design and ease of connection, use, and replacement.
Fittings for pipelines at nuclear power plants
Nuclear power plants are considered high-risk industries. Therefore, equipment at sites must function with extreme precision.
There are special requirements for the installation of mechanisms at nuclear power plants:
- The parts are installed so that the direction of the working medium coincides with the indicating arrow on the body.
- The fittings are used in strict accordance with their intended purpose.
- Any system node must have a free access zone.
- High-temperature fittings must be covered with a heat-insulating structure of a removable and collapsible type.
What industries is it used for?
Substance flow control devices are used in:
- water supply, heat supply and sewerage systems (utilities);
- gas supply and transportation of natural gas;
- oil industry;
- energy enterprises, nuclear and nuclear power plants, hydroelectric power plants;
- chemical production;
- shipbuilding.
Overall dimensions, weight, and materials used to manufacture fittings vary for each industry. This is characterized by the peculiarities of the operation of pipeline networks in each specific area. For example, for ship construction, fittings are produced that are compact and lightweight. But for chemical production it is resistant to highly aggressive working environments and high pressures.
The fittings are divided into two groups:
- general purpose industrial pipeline fittings;
- operated under special conditions.
The first is mass-produced in large quantities and is industry-wide. The second one is made according to special orders.