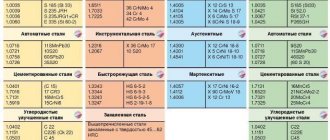
Main indicators of pipe steel strength groups
Pump pipes
Strength characteristics of rods and conditions of their use
| Steel | Heat treatment | Working conditions in the well |
| Normalization | For light operating conditions: small suspensions, absence of corrosive environment with permissible reduced stress σ < 70 MPa | |
| 20NM | » | For average operating conditions: with pump hangers of all diameters at 70 < σ < 90 MPa When pumping corrosive liquid σ < 60 MPa |
| Normalization + HDTV | For severe operating conditions: (large suspensions and forced pumping) For pumps 28, 32, 38, 43 mm o ^120 MPa For pumps 56, 70, 95 mm o < 100 MPa | |
| 20NM | Normalization + HDTV | For particularly severe operating conditions: (deviated wells, the presence of a corrosive environment, more suspension) For pumps 28, 32, 38, 43 mm σ < 130 MPa For pumps 56, 70, 95 mm σ < 110 MPa |
Frequent lowering and lifting of rods leads to an increase in the frequency of rod breaks. Relevant instructions regulate the rules for storing, transporting and assembling rods and rod columns.
Tubing pipes (tubing) come with smooth and upset (equal strength) ends. Pipes with smooth ends have a constant diameter along their length and therefore are somewhat weakened in the places where they are cut for coupling joints. Pipes with exposed ends have thicker ends where they are cut for coupling joints and therefore have increased strength of the cut part of the pipe.
According to the length of the tubing, they are divided into three groups: 1 - from 5.5 to 8 m; II - 8 - 8.5 m; III - 8.5 - 10 m.
Pipes are made from steels of five strength groups: D, K, E, L, M. Smooth pipes and couplings for them of strength groups K, E, L, M, as well as all pipes with upset ends are subject to heat treatment (Table 10.3).
Table 10.3
| Indicators | D | TO | E | L | M |
| Tensile strength σв, MPa | |||||
| Yield strength σт, MPa |
The main characteristics of tubing used in oil production are given in Table. 10.4. The nominal diameter of the pipe coincides with the outer diameter of the pipe body to within a few tenths of a millimeter.
Tubing in wells, especially with SSNU, carry a heavy load. In addition to stretching due to their own weight, they are subject to load from the weight of the liquid column filling the tubing, and sometimes from the weight of the rod string when they break at the top or when the plunger is seated on the suction valve rod. In curved wells they are subject to friction by rod couplings. At high back pressures at the wellhead, a force is added equal to the product of the wellhead pressure and the pipe area (in the open). Typically, the safety factor is taken to be 1.3 - 1.5, based on the load corresponding to the yield stress σt.
Pipes are marked at the coupling end. The stamp indicates the nominal diameter, wall thickness (mm), plant trademark, strength group (letter), month and year of manufacture. Wall thickness is indicated only for pipes 73 and 89 mm, of which there can be two (see Table 10.4).
Table 10.4
Pump pipes
Strength characteristics of rods and conditions of their use
| Steel | Heat treatment | Working conditions in the well |
| Normalization | For light operating conditions: small suspensions, absence of corrosive environment with permissible reduced stress σ < 70 MPa | |
| 20NM | » | For average operating conditions: with pump hangers of all diameters at 70 < σ < 90 MPa When pumping corrosive liquid σ < 60 MPa |
| Normalization + HDTV | For severe operating conditions: (large suspensions and forced pumping) For pumps 28, 32, 38, 43 mm o ^120 MPa For pumps 56, 70, 95 mm o < 100 MPa | |
| 20NM | Normalization + HDTV | For particularly severe operating conditions: (deviated wells, the presence of a corrosive environment, more suspension) For pumps 28, 32, 38, 43 mm σ < 130 MPa For pumps 56, 70, 95 mm σ < 110 MPa |
Frequent lowering and lifting of rods leads to an increase in the frequency of rod breaks. Relevant instructions regulate the rules for storing, transporting and assembling rods and rod columns.
Tubing pipes (tubing) come with smooth and upset (equal strength) ends. Pipes with smooth ends have a constant diameter along their length and therefore are somewhat weakened in the places where they are cut for coupling joints. Pipes with exposed ends have thicker ends where they are cut for coupling joints and therefore have increased strength of the cut part of the pipe.
According to the length of the tubing, they are divided into three groups: 1 - from 5.5 to 8 m; II - 8 - 8.5 m; III - 8.5 - 10 m.
Pipes are made from steels of five strength groups: D, K, E, L, M. Smooth pipes and couplings for them of strength groups K, E, L, M, as well as all pipes with upset ends are subject to heat treatment (Table 10.3).
Table 10.3
| Indicators | D | TO | E | L | M |
| Tensile strength σв, MPa | |||||
| Yield strength σт, MPa |
The main characteristics of tubing used in oil production are given in Table. 10.4. The nominal diameter of the pipe coincides with the outer diameter of the pipe body to within a few tenths of a millimeter.
Tubing in wells, especially with SSNU, carry a heavy load. In addition to stretching due to their own weight, they are subject to load from the weight of the liquid column filling the tubing, and sometimes from the weight of the rod string when they break at the top or when the plunger is seated on the suction valve rod. In curved wells they are subject to friction by rod couplings. At high back pressures at the wellhead, a force is added equal to the product of the wellhead pressure and the pipe area (in the open). Typically, the safety factor is taken to be 1.3 - 1.5, based on the load corresponding to the yield stress σt.
Pipes are marked at the coupling end. The stamp indicates the nominal diameter, wall thickness (mm), plant trademark, strength group (letter), month and year of manufacture. Wall thickness is indicated only for pipes 73 and 89 mm, of which there can be two (see Table 10.4).
Table 10.4
GOST 16523-89
| GOST 16523-89: Rolled thin-sheet carbon steel of high quality and ordinary quality for general purposes |
Technical Requirements
For thin sheet hot-rolled and cold-rolled carbon steel of high-quality and ordinary quality for general purpose, manufactured with a width of 500 mm or more, a thickness of up to 3.9 mm inclusive.
Rentals are divided into:
- by production method:
- hot rolled,
- cold rolled;
- sheets,
- rolls;
- cold rolled: especially high finishing - I,
- high finish - II,
- advanced finishing - III (IIIa, IIIb);
- hot rolled: high finish - III,
- regular finishing - IV;
- deep - G,
- normal - N.
- by type of product:
- according to the minimum value of tensile strength (B) for strength groups: K260V, K270V, K300V, K310V, K330V, K350, OK360V, OK370V, K390V, OK400V, K490V;
- according to standardized characteristics into categories: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6;
- by quality of surface finishing into groups:
- by drawing ability (cold-rolled steel up to 2 mm thick, strength groups K260V, K270V, K310V, K330V, K350V):
In terms of product range, rolled products must comply with the requirements of GOST 19903 hot-rolled, GOST 19904 cold-rolled. Rolled products are produced:
- made of carbon steel of ordinary quality of strength groups OK300V, OK360V, OK370V, OK400V;
- made of high-quality carbon steel of strength groups K260V, K270V, K310V, K330V, K350V, K390V, K490V. Steel grades and chemical composition requirements for each strength group are given in Table 1.
Table 1
Steel grades used and chemical composition requirements
| Strength group | Steel grades | Mass fraction of elements and maximum deviations, % |
| K260V | 08kp | According to GOST 1050 For rolled steel grades 08kp and 08ps, the lower limit of the mass fraction of carbon and silicon is not limited |
| K270V | 08ps, 08, 10kp, 10ps, 10 | |
| K310V | 15kp, 15ps | |
| K330V | 15, 20kp | |
| K350V | 20ps, 20 | |
| K390V | 25, 30 | |
| K490V | 35, 40, 45, 50 | |
| OK300V | St1, St2 (for all degrees of deoxidation) | According to GOST 380 The mass fraction of chromium, nickel and copper is formed at the request of the consumer. The lower limit of the carbon mass fraction is not limited. For rolled steel with grade numbers 3, 4, 5 (all degrees of deoxidation), the mass fraction of manganese can be reduced by 0.10%. When deoxidizing semi-quiet steel with aluminum, titanium or other deoxidizing agents that do not contain silicon, as well as several deoxidizing agents (ferrosilicon and aluminum, ferrosilicon and titanium, etc.), the mass fraction of silicon in the steel is allowed less than 0.05%. In this case, the mass fraction of aluminum is allowed up to 0.07%. Deoxidation with titanium, aluminum and other deoxidizing agents that do not contain silicon is indicated in the quality document. |
| OK360V | St3 (all degrees of deoxidation) | |
| OK370V | St3ps, St3sp | |
| OK400V | St4 (all degrees of deoxidation St5ps, St5sp) |
The weldability of rolled steel of strength groups OK300V and OK360V, OK370V categories 4 and 5 is ensured by the manufacturing technology and chemical composition of the steel. Categories of rental depending on the standardized characteristics are given in Table 2.
table 2
| Category | Standardized characteristics | Mode of production | Strength group | |||
| K260V, K270V, K330V, K350V, K310V | K390V | K490V, OK400V | OK370V | |||
| 1 | Bend test | Hot rolled Cold rolled | — | — | — | + |
| 2 | Spherical Well Draw Test | Cold rolled | + | — | — | — |
| 3 | Spherical dimple bending and stretching test | Cold rolled | + | — | — | — |
| 4 | Mechanical properties test | Hot rolled Cold rolled | + | + | + | + |
| 5 | Mechanical and bending testing | Hot rolled Cold rolled | + | + | — | + |
| 6 | Testing of mechanical properties, spherical dimple stretching and bending | Cold rolled Hot rolled (according to customer's request) | + | — | — | — |
The mechanical properties of rolled products and the diameter of the mandrel when tested for 180-degree bending in a cold state must comply with the requirements of Table 3.
Table 3
| Strength group | Tensile strength N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) | Relative elongation in %, not less | Bending until the sides are parallel (a is the thickness of the sample, d is the diameter of the mandrel) | ||||
| hot rolled steel | cold rolled steel | ||||||
| up to 2 mm will turn on. | over 2 mm | up to 2 mm will turn on. | over 2 mm | up to 2 mm will turn on. | over 2 mm | ||
| K260V | 260-380 (27-39) | 25 | 28 | 26 | 29 | d=0 (without gasket | d=a |
| K270V | 270-410 (28-42) | 24 | 26 | 25 | 28 | ||
| OK300V | 300-480 (31-49) | 21 | 23 | 24 | 26 | ||
| K310V | 310-440 (32-45) | 23 | 25 | 24 | 27 | ||
| K330V | 330-460 (34-37) | 23 | 24 | 24 | 25 | ||
| K350V | 350-500 (36-51) | 22 | 23 | 23 | 24 | ||
| OK360V | 360-530 (37-54) | 20 | 22 | 22 | 24 | d=a | d=2a |
| OK370V | 370-530 (38-54) | 20 | 22 | 22 | 24 | ||
| K390V | 390-590 (40-60) | 19 | 20 | 20 | 21 | ||
| OK400V | 400-680 (41-69) | 17 | 19 | 19 | 21 | No | No |
| K490V | 490-720 (50-73) | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 | ||
There should be no tears, cracks or delaminations at the bend. Hot-rolled steel is produced by heat treatment, cold-rolled steel is produced by heat treatment and tempering. Hot-rolled steel from continuous rolling mills may be produced without heat treatment. Hot-rolled steel is produced with both pickled and unetched surfaces. Sheets must be cut on all sides. Sheets obtained from coils rolled on continuous rolling mills may be manufactured with uncut edges, except for cases specified in the order. Rolled products are produced with unedged and trimmed edges. Defects are not allowed on the edges, the depth of which exceeds half the maximum deviation along the width of the rolled product, and which would take it beyond the nominal width size. Rolled products should not have ends and edges turned at an angle of more than 90 degrees. The length of part-width rolls should not exceed the width of the roll. The depth of the hole during the extrusion test must comply with the requirements of Table 4
Table 4
| Rolled thickness | Hole depth, not less, for rental, mm | |||
| deep drawing strength groups | normal drawing of strength groups | |||
| K260V, K270V | K310V, K330V, K350V | K260V, K270VA | K310V, K330V, K350V | |
| 0,35 | 7,5 | 7,2 | ||
| 0,4 | 8,0 | 7,5 | 7,4 | 7,4 |
| 0,5 | 8,4 | 8,0 | 8,0 | 7,6 |
| 0,6 | 8,9 | 8,4 | 8,5 | 7,8 |
| 0,7 | 9,2 | 8,6 | 8,9 | 8,0 |
| 0,8 | 9,5 | 8,8 | 9,3 | 8,2 |
| 0,9 | 9,9 | 9,0 | 9,6 | 8,4 |
| 1,0 | 10,1 | 9,2 | 9,9 | 8,6 |
| 1,1 | 10,4 | 10,2 | ||
| 1,2 | 10,6 | 10,4 | ||
| 1,3 | 10,8 | 10,6 | ||
| 1,4 | 11,0 | 10,8 | ||
| 1,5 | 11,2 | 11,0 | ||
| 1,6 | 11,4 | 11,2 | ||
| 1,7 | 11,6 | 11,4 | ||
| 1,8 | 11,7 | 11,5 | ||
| 1,9 | 11,8 | 11,7 | ||
| 2,0 | 11,9 | 11,8 | ||
The surface of cold-rolled steel must be free of films, through breaks, blistering bubbles, rolled bubbles, adhesion-welding spots, cuts, tears, rolled-in scale, over-etched, under-etched, cold-working stripes, rolled-in metal and foreign particles. Layering is not allowed. The same is true for hot-rolled steel. An unetched surface may retain a non-removable layer of scale, allowing surface defects to be identified. Characteristics of the quality of surface finishing are given in Table 5.
Table 5
| Finishing group | Mode of production | Characteristics of surface finishing quality | |
| II | cold rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds 1/2 of the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness and taking the rolled product beyond the minimum dimensions in thickness, as well as tarnished color at a distance exceeding 50 mm from the edges. On the front side (the best surface quality) scratches and scratches longer than 50 mm are not allowed. | |
| III | cold rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds 1/2 the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness, and which do not take the rolled product beyond the minimum thickness dimensions. | |
| IIIa: tarnish colors are not allowed at a distance of more than 200 mm from the edges | IIIb: tarnish colors are allowed over the entire surface of the rolled product | ||
| hot rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds 1/2 the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness, and which take the rolled product beyond the minimum thickness dimensions. | ||
| IV | hot rolled | Defects are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product, the depth of which exceeds the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness and that would take the rolled product beyond the minimum dimensions in thickness. | |
Characteristics of the quality of surface finishing are given in Table 6.
Table 6
| Surface condition | Characteristics of the state of surface finishing | Surface quality characteristics |
| glossy | roughness no more than 0.6 microns | Defects are not allowed on the front side of the rental. Individual risks and scratches longer than 20 mm are also not allowed. |
| matte | roughness 0.8-1.6 microns, roughness density no more than 0.20 mm | Defects are not allowed on the reverse side of rolled products, the depth of which does not exceed 1/4 of the sum of the maximum deviations in thickness |
| rough | roughness more than 1.6 microns | Spots of dirt and tarnished colors are not allowed on both sides of the rolled product. |