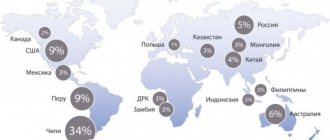
Deposits on the world map
The largest ore reserves are located in Chile - 34% of the world's total. The USA and Peru each have 9% of fossil deposits. Eastern Siberia, the Urals and the Kola Peninsula account for 5% of the deposits.
The world's copper deposits are located on the African continent, South America, Canada, and Australia. Of the European countries, Poland is the richest in them. There are known deposits in China and Mongolia.
Porphyry and vein deposits are located in the Western Pacific belt and Mediterranean regions. Kazakhstan, Armenia, and Uzbekistan have them.
Map of copper deposits in the world
Reserves
The USGS distinguishes the following two categories:
- A reserve base is that portion of an identified resource that meets specific minimum physical and chemical criteria for current extraction and production methods, including grade, quality, thickness and depth. Publication of data on the storage base was stopped by the USGS in 2009.
- Inventories are that portion of the supply base that can be economically produced or produced at a given time. This term does not necessarily mean that the exhaust systems are installed and operating. Reserves contain only substances suitable for use.
The reserves of the countries with the largest production are listed here.
Figures in thousands of tons (2018)
| classify | a country | promotion | Reserves | Share base (2009) |
| 1. | Chile Chile | 5 830 | 200 000 | 360 000 |
| 2. | Peru Peru | 2,440 | 87 000 | 120 000 |
| 3. | Australia Australia | 920 | 87 000 | 88 000 |
| 4th | Russia, Russia | 751 | 61 000 | 30 000 |
| 5. | Mexico Mexico | 751 | 53 000 | 50 000 |
| Sixth | USA USA | 1,220 | 51 000 | 70 000 |
| 7th | Indonesia Indonesia | 651 | 28 000 | 38 000 |
| 8th. | People's Republic of China People's Republic of China | 1,590 | 26 000 | 63 000 |
| 9. | Democratic Republic of the Congo DR Congo | 1,230 | 19 000 | k. A. |
| 10. | Zambia Zambia | 854 | 19 000 | 35 000 |
| Other countries | 3 540 | 220 000 | 110 000 | |
| World | 20 400 | 870 000 | 1,000,000 |
Varieties of copper ores
Ore classification according to genetic and geological characteristics:
- stratiform - these are sandstones and shales;
- pyrite - vein copper and nuggets;
- hydrothermal - it is called the porphyry copper form;
- skarn rocks;
- igneous - this ore contains nickel;
- carbonate - have an iron-copper and carbonatite composition.
Natural minerals containing copper
Bornite. Sulfide ore, its composition is determined by the expression Cu5FeS4. There are two polymorphic types - low-temperature and high-temperature. The melting point of which, respectively, is less than or greater than 228 degrees.
There is an early unstable sulfide that is easily destroyed by water and wind. The other type is endogenous, and has a variable chemical composition due to admixtures of elements such as galena, pyrite, chalcocite, and chalcopyrite. Bornite is called variegated pyrite. The characteristics of these minerals depend on their origin.
Chalcopyrite. The formula CuFeS2 determines its composition. Known as copper pyrite. Refers to polymetallic. It can exist in the form of skarns and mountain greisen.
Chalcocine. Contains 79.8% copper and 20.2% sulfur. Very beautiful, the mirror surface has a grayish tint, sometimes black.
There are rare fossils containing copper elements:
- cuprite (Cu2O), an oxide, is seen among deposits of malachite and nuggets;
- covellite, contains 66.5% of the main element and sulfur. First found surrounded by the Vesuvius volcano. Mined in the USA, Greece, Chile;
- malachite. A stone that is used for various crafts. Polymetallic ore. Nizhny Tagil is the place of large deposits of this mineral;
- azurite This is azure, a blue stone. The main places of its production are Africa, Australia, England, and the Balkan countries. Occurs near sulfide deposits.
Porphyry copper forms include molybdenum, gold, chalcopyrite, and pyrite. They are found in deposits of poor rocks. They have the form of veined stockwork-type inclusions.
What ores do copper come from?
Copper is extremely rare in the form of nuggets. It is always mined with additional impurities. The largest nugget was found in the USA. It weighs more than 420 tons.
A total of 20 types are used in heavy industry. The most famous and widely used of them are chalcocite, chalcopyrite and bornite. What are their properties?
- Chalcocite is the most concentrated copper. Here its concentration can be up to 80%.
- Chalcopyrite is copper, which is part of polymetals and has hydrothermal origin.
- Bornite - this type has a bluish tint due to impurities of iron and silver. Concentration - more than 60%.
- Kovelin belongs to the hydrothermal group, like chalcopyrite. The concentration is 64%.
It is from these ores that most of the metal is obtained, which is then used by humans.
Mineral extraction methods
In Russia there are deposits such as shale and sandstone. Copper pyrite, copper-nickel and porphyry copper forms occur here. The mining industry uses various methods to extract minerals from the depths of the earth.
Depending on the depth of occurrence, ore is mined using open or closed methods. There are standards that determine the feasibility of the depth of excavation of soil layers and the use of technologies that reduce their costs.
The work technology includes the following:
- use of self-propelled equipment;
- production of ore extraction directly;
- filling the resulting voids with materials to make further work safe.
With the open method, fossils are selected in layers, this ensures their fullest use. For deep quarries, the technology of cyclic-flow operations is suitable, it depends on the characteristics of the layers.
Negative consequences of mining
When the formations occur at a depth of 500 to 1000 m and deeper, the closed method of copper mining is convenient. This requires vibration mechanisms; the rock is completely excavated and delivered to the surface. The voids formed underground are filled using pipes lined with rubber or basalt resin.
It is economically advantageous to locate the mineral processing industry in close proximity to the places of their extraction. It is also necessary to build plants for recycling waste after processing. This can promote the release of various beneficial products. For example, processing sulfur dioxide makes it possible to obtain useful fertilizers containing sulfur.
Production technologies
The mined ore has a low concentration of copper. To obtain one ton of metal, on average, 200 tons of ore will be needed. To extract it, the modern metallurgical industry uses the following technologies:
- hydrometallurgical;
- pyrometallurgical;
- electrolysis.
The pyrometallurgical method of rock enrichment uses chalcopyrite for processing. This common technology uses two stages of operation. The first is oxidative roasting, the so-called flotation. The resulting rough concentrate contains 10–35% pure substance. Then the copper is refined and vitriol is added to the solution. As a result, non-ferrous metal is released with almost one hundred percent purity.
With the hydrometallurgical method, the metal is leached, then sulfuric acid is added. As a result, a solution is obtained in which copper and various metals, which may be precious, are released. This technology is applicable for the production of copper from poor rocks.
For oxidative roasting of minerals with a high sulfur content, the ore is heated to 700–8000 degrees, and the amount of sulfur is halved. The result is an alloy of sulfides. Side airflow in the convector allows you to obtain blister copper of 91%. To achieve a higher purity of the metal, electrolytic refining occurs to obtain a 99% composition.
In industry, this element is practically not used in its pure form. The most famous alloys are:
- brass – an alloy with zinc;
- bronze – with tin;
- various babbits - an alloy with lead;
- cupronickel – nickel is added to the composition;
- duralumin – connection with aluminum;
- jewelry alloys, where gold is added in various percentages.
Stages of pyrometallurgical copper production
There are several methods for processing ore, of which pyrometallurgical is the most economical. This method not only provides high productivity, but also makes it possible to obtain associated metals. A reduced amount of harmful atmospheric emissions should also be considered an advantage of the pyrometallurgical processing method.
Enrichment
From a quarry or mine, ore goes to a processing plant. Here it is crushed by crushing machines. Since the copper content in the ore is low, further enrichment is necessary. For this purpose, the flotation method is used.
The raw materials are loaded into a special container, into which a solution is then supplied, which is water with the addition of flotation reagents. The effect of these substances may be different, but the purpose is the same - they should increase the production of metal.
Air bubbles are passed through the mixture of aqueous solution and ore. Metal particles stick to them and rise to the top, forming foam. Then the separation of sediment - waste rock, foam - released metal, and aqueous solution occurs. The collected foam is sent for further processing.
Burning
The concentrate isolated by flotation contains a large amount of impurities that need to be removed. To do this, the ore is sent to a furnace, where it is exposed to thermal effects at a temperature of about 800 °C.
This method burns sulfur. When exposed to heat, sulfur oxide is formed, which then evaporates. Metal impurities, for example, iron, turn into an easily slag state, which simplifies their further removal.
Melting for matte
The mass obtained after firing is dried. It is then placed inside a furnace where it is melted at temperatures up to 1450 °C. Next, the melt is separated into matte, consisting of metal sulfides, slag, which is oxides, and a gaseous fraction, which is used to produce sulfuric acid.
Melting can be carried out using several technologies. A distinction is made between smelting in a liquid bath and suspended smelting. These processes are autogenous and are primarily used to create mattes. In addition to them, electric smelting, reflective smelting, and shaft smelting are used.
The output is ingots weighing up to one and a half tons. The copper content in them reaches 96%. The rest consists of: iron - 0.04%, sulfur - 0.1%. Another 0.5% are other metals: tin, silver, nickel, gold. The alloy is called “blister copper” and is marked as MCh1-6, where numbers from 1 to 6 characterize the copper content.
Refining using copper cathode
At this stage, pure copper is obtained by electrochemical method. An ingot of rough metal, which is used as an anode, and pure metal plates, which serve as a cathode, are placed in a bath with an electrolyte.
After connecting electricity, copper molecules leaving the rough anode are deposited on pure metal plates. Impurities of other substances precipitate in the form of sludge, which is collected and sent for processing. The whole process lasts about a month, and as a result, a metal with a copper content of 99.99% is obtained.
Areas of use
One area of application is the electrical industry. Cables and electrical wires contain pure metal strands, which increases their electrical conductivity. Alloys with nickel are suitable for instrument making; compounds with tungsten are filaments in light bulbs.
Copper Applications
Brass is used in the food and chemical industries. In agriculture, copper is used as fertilizer. Copper sulfate is known to gardeners; it is used to treat plants to protect them from diseases and pests.
In construction, such alloys are simply irreplaceable. The roof covering with the patina formed on it has a beautiful appearance and is very durable.
The medical industry cannot do without this chemical element. Widely used in medicines.
In mechanical engineering, bronze is used to make bearings, heat exchangers, and various structural elements of mechanisms. The metal is used in powder metallurgy to make friction parts.
World reserves
World proven copper reserves are estimated to range from 654 million to 1,600 million tons.
Copper is a non-ferrous metal that is consumed by many types of industries. The most profitable ore for production is bornite. This is due to its high content and large deposits in the world's subsoil. Rocks containing 0.5–1% of copper are suitable for copper mining. The most common are ores with nickel additives. They make up 90% of all copper-bearing minerals that are economically beneficial for the mining industry.
The largest copper deposits are located in Chile - 34% of all world reserves, which is 140 million tons.
The countries with the largest reserves in the world are: USA - 35 million tons, Indonesia - 35, Peru - 30, Australia - 24, China - 26, Russia - 20.
Global reserves of copper-bearing ores are estimated at 467 million tons. Geologists say that there are about 5 billion tons of deposits of such ore in the world's oceans.
Fundamental Analysis of Copper
Copper is one of the metals that is traded on financial markets. Copper is widely used in production and finds application in the following areas (the share of copper currently directed to these areas is indicated in brackets): 1. Construction (43%). 2. Electric power (20%) 3. Transport (20%). 4. Basic consumer goods (10%). 5. Production equipment (7%).
To fairly assess the cost of copper, it is necessary to consider factors affecting supply and demand, mining and consumption.
Copper production and its global reserves for 2022 according to the United States Geological Survey are as follows:
According to these data, global copper reserves will last for 42.89 years with demand at 2022 levels. The estimated amount of unmined copper on Earth is estimated at around 3 billion tons.
CONSUMPTION.
The main consumer of copper at the moment is China, which consumes about half of all copper produced. Interesting dynamics are observed in the field of transport. If before 2019, about 13% of all mined copper was spent on transport, then in 2019 this number was already 20% and will continue to grow, which is associated with an increase in the production of passenger electric vehicles, which require more copper than conventional cars and, according to estimates a number of experts from the International Copper Association, this could increase copper consumption in the transport sector to 8 million tons per year by 2030 (from 4 million tons per year in 2022). Electric vehicles, power generation and construction will increase demand for copper by 415,000 tons annually.
HISTORICAL PRICES.
Average copper prices and production volumes for the previous five years are shown in the following table:
CONSEQUENCES OF LOCKDOWN.
The lockdown led to a decrease in copper production by large producers and a reduction in investment in new projects. According to Refinitiv data, copper production over the next five years will average 2.2% of earlier forecasts, resulting in an overall decline in supply of 3 million tons of copper over that time period, for an average of 23 million tons per year.
IS IT POSSIBLE TO COPPER DEFICIENCY?
It should be noted that back in 2022, the issue of copper deficiency became acute. According to the statements of the General Director of the Ural Mining and Metallurgical Company Evgeny Bragin, in 2020-2024 there will be an increase in copper consumption by 415,000 tons annually; construction, electric power and the automotive industry (electric vehicles) will stimulate the growth of copper consumption. And given the fact that there are still enough copper reserves in the world, investments in geological exploration become unreasonable, expensive and risky, with the return on risk at copper prices above $10,000 per ton. And in existing deposits, ore depletion is observed. According to the company’s fears, a copper shortage may begin to be felt as early as 2022, and given the lockdown and a decrease in copper production, this date is postponed to 2023-2024.
COPPER RECYCLING.
Recycling of copper. The cost of producing one ton of refined copper from scrap and waste is on average 35% lower than the cost of its production from ore raw materials. In the United States, copper recycled from waste accounts for about 12% of that mined from ore. In Europe this share reaches 50%. In world production this share is 29%. Taking into account the fact that copper can be recycled with very minor losses in its properties, there is wide scope for the development of the processing sector.
WEAKENING DOLLAR.
During 2022, the US dollar is undergoing a significant weakening and is expected to weaken significantly when the QE program is wound down, and sooner or later it will be wound down, it’s only a matter of time. This factor will play in favor of an increase in the price of copper, especially given the fact that in conditions of economic instability, investors seek to place their funds in those assets that will be least susceptible to depreciation. Precious metals are too expensive for these purposes and do not play as significant a role in production as copper, making it one of the most reliable defensive assets.
RUSSIAN COPPER PRODUCERS.
In a small digression, I would like to point out the main copper producers in Russia, there are three of them: 1. Norilsk Nickel (ticket on the Moscow Exchange: GMKN ). 2. Ural Mining and Metallurgical Company (the company is not currently listed on the stock exchange, its subsidiaries were previously available). 3. Russian copper company (the company is not currently listed on the stock exchange). Norilsk Nickel produces about 42% of total production in Russia, UMMC - about 40%, RMK - about 18%. Together, these three companies smelt about 1 million tons annually, of which up to 800 thousand tons are exported. So if you invest not in copper itself, but in a mining company, then among Russian assets only Norilsk Nickel is available, whose performance indicators are slightly beyond the scope of this analysis.
CONCLUSIONS BASED ON THE ABOVE DATA.
Based on historical data, we can say with a high degree of confidence that the minimum copper price level is now $6,000 per ton, which is the average copper price over the previous five years, taking into account inflation and excluding increased demand for it and the current weakening of the dollar. Given the increase in demand and the high cost of geological exploration, it is safe to say that $10,000 per tonne is the long-term growth target for copper over the next five years. Once this goal is achieved, copper recycling will become highly profitable, and the development of new deposits will be more interesting from an investment point of view, which will restrain further growth in the cost of copper.
Persons interested in investing in copper can consider for this purpose the settlement futures contracts of the "Co" series (from the word "Copper" - "Copper"), traded on the Moscow Exchange.
All of the above is not an investment recommendation.
Source