CNC lathes are well-proven equipment designed for mass production. Thanks to it, it becomes possible to make parts with high precision, which is important for lathes.
CNC allows it to improve its operation without human intervention, making it almost ideal for turning work and giving it autonomy.
Purpose of the CNC device
Numerical control (CNC) is designed for cutting threads on workpieces, turning parts from them, etc., without human intervention to avoid defects in production.
Thanks to fairly flexible settings, they have proven themselves much better than humans, and due to the fact that they have minimal defects, machines equipped with such a system are simply irreplaceable in mass production, where it is important to produce many parts that meet the quality. There are also types of turning work that only numerical control can handle.
If we divide CNC machines into types, then we need to take into account the purpose and the work they perform. In this case, they can be divided into five types:
- vertical and horizontal milling;
- console;
- longitudinal;
- widely versatile;
- instrumental.
Main advantages
Compared to manual machines, those equipped with CNC are four times more productive. Although the performance range varies from the specified settings and can be from one and a half to five times.
Due to the fact that a CNC machine combines the flexibility of universal equipment and the high productivity of an automatic machine, the problem of using such technology in both serial and individual production is solved.
Important!
Thanks to the latest electronics and the best computer technology, mechanical engineering, namely the production of parts for automobiles, is reaching a predominantly new level.
Due to the fact that the process is becoming almost completely automated, the need for qualified workers to operate the machines is falling. However, this cannot lead to unemployment, since craftsmen are now required who will monitor the serviceability of the CNC machine. Thanks to this, the quality of work improves without consequences.
The time required for fitting work is significantly saved due to the fact that the parts are made, one might say, according to one template, so they are interchangeable.
Due to the fact that all programs for the production of new products are recorded in the computer, there is no need to retrain personnel before switching to working with new products. You just need to turn on the desired program.
Parts that are made on a CNC machine are produced much faster. In addition, due to the absence of a person, the level of defects and unfinished work is significantly reduced.
Area of use
CNC machines and machining centers are widely used in the following areas:
- Metalworking. They are capable of providing 2D and 3D milling, engraving, threading, turning, drilling complex holes, creating complex volumetric parts with high precision, manufacturing injection molds and other processing of parts of almost any complexity. The machines provide one-time, small-scale and industrial (large-scale) production with high repeat accuracy.
- Electronics. In the electronics industry, machines are used in the manufacture of instrument panels, printed circuit boards, cooling radiators, and machining holes in equipment.
- Aerospace industry. Machine tools are used to produce high-precision parts from difficult-to-cut materials. They are capable of machining chassis components, titanium skins, bushings, fender parts, manifold pipes, gear components and connectors.
- Telecommunications and telecommunications. The machines are used in the manufacture of radiators, parts of antenna masts, casings, and corrugated horns.
- Healthcare. The medical industry uses CNC machines in the production of pacemakers, joint and bone prostheses, and medical instruments.
- Automotive industry. Machining centers are actively used in the manufacture of engine parts, internal panels, cylinder heads, drive axles, gearboxes, and other components.
- Furniture manufacturing. The machines are used in the production of complex furniture facades, cutting sheet materials (chipboard, fibreboard, MDF), parquet tiles, wooden rosettes of complex shapes, curved cutouts in doors and windows, panels, artistic carving, production of exclusive furniture parts and doors.
- Advertising. The equipment is widely used for cutting sheet plastic and composite materials, making logos, emblems and letters, engraving inscriptions and drawings, creating templates, patterns, price tags, stands, trays, applying images to glass and plexiglass.
- Modeling. On CNC machines you can create various models, prototypes, new architectural forms, stamps, cliches.
It is difficult to find areas of human activity where CNC machines cannot or are pointless to use. They are actively used in woodworking, metallurgy, the military-industrial complex, construction, production of agricultural machinery and equipment, and jewelry. They are capable of processing almost any materials: ferrous and non-ferrous metals, including high hardness, plastic, wood, glass, fiberglass, stones, concrete, etc.
What metal operations can be performed
Thanks to the fact that the human factor has been reduced to a minimum, metal operations have become much easier and result in less waste. It turns out this way because of the program that is embedded in the computer.
It is a kind of template by which the computer understands whether the part is ready or not. This section will talk about the operations that a CNC machine can perform on metal.
External and internal turning of parts
Everything is simple here, at least for the car. The installed workpiece, which in the future will become a part, is fixed on the machine. It can be secured manually or, if the appropriate equipment is installed automatically (most often the automatic option is used).
Afterwards, external turning of the part begins using either a laser or a blade that is installed on the machine. Gradually cutting off the excess, the workpiece takes the shape of the desired part. This is how external turning of parts is done on a CNC machine.
With the internal everything is about the same, only with changes. After installing the workpiece, the machine begins to drill, or as it is called differently, drill a hole at the base of the workpiece.
Once the hole is ready, the computer will compare it with the template that is written in the given program. If there are any flaws, he will analyze whether it can be corrected (as a rule, yes, because machines rarely make mistakes). Afterwards the workpiece is polished and the part is ready.
Longitudinal processing of the workpiece
Longitudinal processing is a method that is used for the manufacture of strips, strips, tapes. Depending on the program that is installed on the computer.
Such work on a CNC machine is carried out mainly using a laser, as this allows you to get rid of defects and speeds up the work process. After installing the workpiece, the numerical control on the machine will process it in accordance with the specified algorithm of actions. The laser portal is driven by stepper motors on which it is mounted.
Roughing and finishing
To begin with, what is this anyway? Roughing of metal consists of adjusting the part to the desired size by removing layers of metal.
Typically, in a CNC machine, this role is performed by the computer after the part has already been cut. Finishing comes next and consists of polishing the surface of the product. The machine performs all this according to given algorithms.
Adjusting the length of parts
The program that is given to the computer clearly states the dimensions of the part. The blanks are also given in suitable sizes. Before inserting a part, the machine adjusts and sets itself up for production.
After that, he begins to do the work, after which he compares the size with those given by the person. If there are no deviations, the part is ready. If there is, the CNC machine begins to grind the part, removing layers of metal and adjusting the length.
Making grooves, recesses and holes
Grooves and recesses are holes that are made into a part. Such holes can serve either to allow another part to fit into them, or for installation to some device. A CNC machine makes such holes using a laser, making high-precision cuts.
They can be rectangular, T-shaped, dovetail, shaped, through, open, closed and others. What shape the hole will be depends on the part and the program that the person has installed in the numerical control.
Inch and metric thread cutting
Almost everyone has seen this type of carving. It is used mainly so that one part can be screwed to another. The main parameters in the manufacture of such threads are pitch and size. In this case, a step means:
- outer diameter, measured between the top points of the threaded ridges located on opposite sides of the pipe;
- internal diameter as a value characterizing the distance from one lowest point of the cavity between the threaded ridges to another, also located on opposite sides of the pipe.
All parameters need to be entered into the machine’s computer, after which it will cut out an excellent and even thread using a laser.
Reference! In any case, the parameters for making threads on a product are entered by a person into the computer of the machine, and the latter, acting according to an algorithm, uses a laser to make an excellent thread.
Purpose
CNC lathes are modern versions of standard machine analogues, equipped with a number of additional functions, one of which is the presence of a CNC system. Such devices are designed for processing metal workpieces by turning, but can also be used to work with other materials. Thanks to this, lathes have become universal devices used in various fields. The main area of application is in factories and at home.
Using CNC machines:
- External and internal turning of parts is carried out;
- cone-shaped elements or having other complex shapes are manufactured;
- longitudinal processing of the workpiece is performed;
- roughing and finishing processing is carried out;
- the length of the parts is adjustable;
- grooves, recesses, holes are machined;
- Inch and metric threads are cut.
This machine is able to cope with a task of almost any level of complexity. Therefore, the scope of application of CNC machines for turning work is in enterprises engaged in the serial production of parts. Also, the use of lathes is noted in frequent production in small businesses.
Design and principle of operation
Lathes equipped with a CPU are of three types - contour, positional and adaptive. Each has its own advantages and may be suitable for different types of work.
The first type of machine cannot be called maximally independent, since human intervention is necessary for its operation. It works only along the trajectory specified by the operator.
The second type of machine can perform work on a part in a point-by-point manner.
The third type is universal. It can perform the work of both machines, while having the same functionality, so this type is the most expensive and most useful in the production of various parts.
Compared with older analogues that are already outdated, the latest machines with an installed numerical control system have increased rigidity, which allows reducing production time even for quite complex types of work. This level is ensured by the design features of the machines.
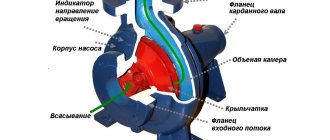
The CNC lathe consists of:
- beds;
- spindle or headstock;
- calipers;
- feed boxes;
- electrical part;
- turret heads.
The bed is one of the main parts of any machine, since it is on it that all other parts of the machine are located. The spindle (or headstock) has two parts of the machine: the spindle itself and boxes for changing speeds on the machine.
Another important part is the caliper. It is he who regulates the rotation speed of the workpiece, which is fixed in the lower and upper carriages. The caliper is controlled using one of the spindle parts, namely the gearbox.
Turrets are also very important for the operation of the machine, as they automatically replace worn-out equipment. The workpiece is installed in the machine, and then it does the work itself, using a program pre-written by the operator.
Principle of operation
Operation of CNC lathes depends on the characteristics of the device used. The choice of machine depends on:
- permissible thickness of the workpiece being processed;
- the maximum distance that can be set between the central parts of the headstocks;
- permissible diameter of the part installed above the support.
The tailstock is used to install a cutter or other working tool. The movement of the headstock is carried out along the trajectory of the rails located on the frame. The length of movement is equal to the dimensions of the workpiece. The working tool moves along the workpiece, the movement of which depends on the carriage. The caliper is responsible for ensuring that its position does not get lost during turning.
The single holder is used for simple machining. More complex tasks are accomplished with heads that can accommodate multiple cutters. The largest number of incisors is four.
The use of parts using such a device should be preferred when working with complex shapes.
The electric motor uses a belt drive. It is capable of providing high performance. The disadvantage of this transmission is that the belt stretches. To maintain performance at a high level, the belt is periodically tightened.
How to write a control program
Programs for operating CNC machines are made in three steps, each of which determines what the new part will look like:
- Creation of a three-dimensional model. This stage is the creation of a model of the workpiece with which the work will be carried out. This is mainly done not by operators, but by designers, since not everyone understands so well how to make a good three-dimensional model.
- Instructions. Having a three-dimensional model, the operator sets the parameters that the machine will have to perform when working with the workpiece in order to get the part.
- Test run. It is necessary to check whether the program was written correctly to work. After all, if you run a bad program on a machine right away, without a test, it will ruin all the workpieces. Therefore, the operator looks to see whether the machine is performing the job correctly with the given program, and then looks at the result and decides whether modification is required or not. Most often it is, of course, required, but it cannot display any critical errors.
Once the program has been installed, the machine is ready for use. There are five special applications for writing such programs:
- AutoCAD.
- T-FlexCAD.
- NanoCAD.
- ArtCam.
- SolidWorks.
Now we will talk about each one separately.
AutoCAD
This program was developed by Autodesk specifically for automatic design of turning operations. AutoCAD has 3D modeling functions, as well as the ability to work with 3D scan data, which allows you to save money on designers. But, due to the lack of three-dimensional parameterization, this program is not the best choice.
T-FlexCAD
This program was developed to develop different types of work with lathes. It has all the necessary functions, but it is not the best choice and is not popular.
NanoCAD
This program can work with both three-dimensional and two-dimensional models. With its help, work calculations can be carried out, 3D and 2D models, various drawings and much more can be prepared. Thanks to this program, the work of operators is greatly facilitated.
ArtCam
This program is needed exclusively for creating a three-dimensional model. Calculations of work or anything similar cannot be done on it, but the models are of very high quality.
SolidWorks
This is not just a program, but a whole software complex. It was released back in 1995, but is still considered one of the best among the development of programs for lathes using a CNC system. True, this software package costs a decent amount, but it perfectly demonstrates the principle “price equals quality.”
A little history
However, the modern stage in the history of CNC machines began only a century and a half after the invention of Jacquard, in the United States of America. After the end of World War II, in the late 40s, John Parsons, the son of the owner of Parsons Incorporated, tried to control the machine using a special program that was entered from punched cards. Parsons did not achieve any positive results, so he turned to specialists at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology for help.
The employees of the institute's laboratory of servomechanics did not improve the design presented to their attention, and they quickly forgot about Parsons. But about his ideas - no. Having created their own design, they initiated the institute’s purchase of a company that produced milling machines. After which the leadership of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology entered into a contract with the US Air Force. The contract dealt with the creation of a new type of high-performance machines for processing propellers by milling.
The operation of the milling machine, which was assembled by the laboratory staff in 1952, was controlled according to a program read from a punched tape. This design turned out to be too complex, and the desired result was not achieved. However, the story became public, information about the new development was published and aroused great interest from competitors. Several well-known companies simultaneously began their developments in this direction.
The greatest success was achieved by the designers of Bendix Corporation. The NC device released by Bendix has been in production since 1955 and has already been actually used to control the operation of milling machines. The new product took root with difficulty, but thanks to the interest and financial assistance of the military department, over two years more than 120 CNC machines were produced, which significantly increased labor productivity and the accuracy of machine work.
Even then, the undeniable advantages of the NC numerical control system for machine tools were noted: a significant increase in labor productivity and significantly higher precision of surface processing. But truly revolutionary changes in the field of CNC machines took place when specially designed microprocessors and microcontrollers were used as a “smart” module that controls the operation of the machines. The technical term “CNC”, which began to designate these systems abroad, is an abbreviation of the English words ComputerNumericalControl.
Varieties
There are enough varieties of lathes to perform a wide variety of jobs. There are five of them in total:
- horizontal turning-turret;
- tokor-frontal;
- rotary turning;
- multi-spindle;
- turning and milling.
Now we will talk about everyone separately.
Horizontal turning-turret
Designed mainly for mass production of parts. Using a chuck, parts are installed that will process the workpiece before it becomes a part.
Torque-frontal
This machine is used for processing parts whose diameter exceeds the size of the workpiece. These are mainly railway wheels, flywheels and others. It can also remove ends, make cylindrical parts, make grooves, and so on.
Lathe-rotary
Such machines are designed for workpieces that weigh several tons. Also, the workpieces for such a machine have a diameter greater than their height. Thanks to the chuck and the cutting parts installed on it, it is possible to apply threads to the workpiece or drill holes.
Multi-spindle
As the name implies, the design of this machine contains several spindles, which ensure processing of the workpiece to the state of the part in several places, either simultaneously or in shifts after every certain period of time.
Turning and milling
Turning and milling machines with installed CNC are universal. They can perform a wide variety of work with products. Everything will depend on what program was installed in the numerical control computer and what tools were installed on the chucks.
This machine can perform any functions of highly specialized equipment, be it turning, drilling, milling. He can handle any type of work.
Review of modern models of CNC turning machines
Compared to older models, modern lathes have become easier to use and can perform many more functions. The operation of such machines has become faster and better, providing better quality and fewer defective products.
Thus, we can say that CNC lathes are the future. Thanks to him, the number of defects due to human defects has become almost zero, despite the fact that no one has lost their jobs - it’s just that now the specialists who previously worked on the machines now monitor the operation of these machines, correcting breakdowns and giving them new programs.
What is CNC: all about CNC machines
Computer numerical control, or CNC for short, is a modern trend in the development of equipment for various purposes, based on the use of digital electronic devices in the control system. In Russia it is known as numerical control (CNC).
In essence, CNC is a computerized complex that controls the working parts of the equipment and controls the execution of the task. Any movements of the executive bodies are set by a special control program (CP) for this machine. It is composed of the necessary commands written in the CNC programming language (G- and M-codes). The computer stores the program program in its memory, and the operator can always use it to perform a specific job.
The modern CNC system has significantly expanded the capabilities of the previously used NC system. It is based on microcontrollers, programmable logic controllers, and microprocessor-based computers.
Feasibility of use
The CNC system significantly increases labor productivity and contributes to the reduction of workers, but its implementation requires significant costs and specially trained workers, which is not always economically justified. The use of CNC is advisable in the following circumstances:
- Production of high-value products when expensive and scarce raw materials are used. In this case, it is necessary to minimize errors and eliminate defects, which is what CNC provides.
- Production of similar products in large series. A proven program allows you to reduce costs and there is no need to change software, and the initial costs pay off fairly quickly.
- Manufacturing of complex parts requiring numerous technological operations.
- The need to ensure the production of numerous products that are absolutely identical in processing accuracy. The program ensures such production with a deviation of no more than 3 microns.
- Manufacture of products in the design of which minor changes are often made. When using CNC, they are easily entered into the NC from the machine operator console.
Important! Automation of production is a modern approach to its organization, but it requires an economic justification.
Functions
The CNC system is capable of performing the following functions:
- Management of processing processes for parts made of various materials (metals, wood, plastic, etc.). For this purpose, this system provides a machine park (CNC machines).
- Control of asynchronous electric motors. Their smooth adjustment is extremely difficult, and the CNC allows the use of “vector control”.
- Control of industrial robots.
- Management of peripheral devices for various purposes. Typical examples: 3D printers and scanners.
Some equipment is provided by centralized, automated workstations, where the desired program is installed via an industrial network. In this case, CNC allows you to control the operation of not just one machine, but the entire section, workshop (ABB Robot Studio, Microsoft Robotics Developer Studio).
Peculiarities
CNC machines have a number of attractive features:
- High level of automation. The operator only controls the process on the monitor. His participation in the process is kept to a minimum.
- Ensure repeatability. The equipment does not depend on the mood and physical condition of the operator. It produces identical products with consistent high quality for months, or even years.
- One operator is able to operate several machines.
- Flexibility. With minor changes in process parameters, adjustments are made to the program, and with significant changes, a new program is loaded. Such procedures do not take much time.
- Processing accuracy and repeatability. The program ensures the production of many identical parts with the highest accuracy.
- Using CNC machines, it is possible to produce products of complex shapes that can only be done by highly professional workers, and even then using special devices.
Important! CNC machines are versatile and can replace 4-5 simple machines. In this case, there is no need to look for experienced workers in a specific specialty; it is enough to train an operator of CNC equipment.
Classification
CNC machines are divided into several categories. This is reflected in the alphanumeric designation of the brand. The technological category is determined by the purpose of the equipment. It is determined by the possibility of carrying out basic operations. Main types: lathes (group number - 1), milling machines (number 6), drilling and boring machines (number 2), multi-purpose equipment (number 9). This number comes first in the marking.
According to the degree of automation, the following types are established:
- F1 - motion coordinates are set using the computer keyboard (one press - 1 frame of the program). A digital display device is provided.
- F2 - a portion or rectangular control system is used. The first is typical for drilling and boring machines, and the second is typical for milling and turning machines.
- F3 - a contour or continuous CNC system is installed. It allows you to process workpieces of almost any complexity.
- F4 is a multi-operational, combined CNC system. It combines the best qualities of the contour and positioning system.
- C - cyclic CNC. This is the simplest automated system for serial production of fairly simple, similar products.
Machines are also classified according to the method of changing the working tool. The labeling may include the following options:
- R – turret heads are used to change and fasten tools.
- M – a special tool magazine is installed, from where the necessary tools are automatically supplied.
The indicated marking indicates the presence of an automatic tool changer (ATC). In addition to the above modifications, the machines differ in the type of drive control: stepper, stepped, continuously variable.
Main settings
When choosing CNC equipment, main attention should be paid to the following parameters:
- Accuracy class. The permissible error can be determined by the markings: P - increased accuracy, B - high accuracy.
- Operating parameters. They are installed for each technology category separately. So for drilling equipment the maximum diameter of the hole is important, for milling machines - the size of the working area, for boring machines - the spindle diameter, for lathes - the dimensions of the workpiece, etc. Common to all types of equipment include: electric motor power, processing speed ( productivity), supply voltage (220 or 380 V), dimensions and weight of the machine.
- The number of simultaneously controlled coordinates and the accuracy of their setting. Modern machines provide 5-axis control.
Depending on the purpose of the equipment, other important parameters may be set that must be taken into account when organizing production.
Programming principle
The operation of a CNC machine depends on the NC. It can be based on the following programming principles:
- Manual method. The programmer creates the software part of the machine by entering digital information about the coordinates of movement of the working tool, obtained during manual movement. Many points are required, which delays the programming process. This method is used when there are only 1–2 CNC machines used for the manufacture of simple, similar products.
- Shop-floor – programming from the remote control of the CNC operating system. In this case, the program is compiled using a touch screen and a joystick on the machine stand. The latest machine models use an interactive mode.
- Programming using CAD and CAM systems. The CAD system (AutoCAD, Solid, Catia, Compass) allows you to construct an electronic drawing of the product, and the CAM system (SheetCam, Kcam. MeshCam, CorelDraw) based on it describes the tool trajectory. The graphic file is first converted to DXF, Exeilon, HPGL or Gerber format. The programming process is reflected on the screen. A Cl file is issued. To convert it into a form understandable for the machine, a special program (postprocessor or passport) is used. It provides commands in the form of G- and M-codes.
The program can be loaded onto the machine in finished form from external media (floppy disks, flash media, magnetic tapes, punched paper tapes). It fits in RAM, memory card, hard drive or solid state drive.
Design features
The functioning of the CNC system is ensured by the following main components:
- Operator console, input/output console. This design element is intended for entering the NC, setting process parameters, as well as manual control of the operation.
- Operator panel, display. Allows you to visually monitor the process and make adjustments to the program.
- Controller. This is a computer-type device for putting into operation the software, forming the trajectory of the working body, issuing the necessary commands, carrying out general control, carrying out diagnostics and additional calculations.
- ROM. This is a memory that allows you to store a program for a long time. Information from the ROM is only read.
- RAM. This RAM is intended for programs currently in use, as well as for short-term storage of information.
Industrial ready-made models, embedded devices based on microprocessors, a programmable logic-type controller, and an industrial computer can serve as controllers. The role of actuators is performed by servos and stepper motors.
Types of CNC machines
The most common CNC equipment includes milling and lathes, as well as multi-purpose units. They are selected taking into account what work is planned to be carried out and in what volumes.
Milling machines
CNC milling machines can be used only for milling or with extended functionality (drilling, cutting sheets, processing at different angles, forming grooves, etc.). Main varieties:
- Vertical milling machines. In them the spindle is installed vertically. May have bottom or top drive. Processing is provided on one side.
- Horizontal milling machines. The spindle is installed parallel to the base. The machine can perform all-round processing.
Both types of machines can have 1 or 2 spindles. Control is provided in 3–5 coordinates. According to the control method, the following options are distinguished: with positional, contour, combined control. Basic parameters of the machines: work table dimensions, milling depth, power, spindle speed, transmission type.
Among the design features, we should highlight the presence of a powerful frame, a body with stiffening ribs, a spindle with increased rigidity to eliminate vibrations, and high-precision guide rails. To increase productivity, ASIs are installed in the form of a turret-type spindle head or a tool magazine. A large number of different models are produced for processing wood, metal, plastic and other materials.
Turning
A CNC lathe uses cutters with replaceable inserts. The tool is mounted in a tool holder located in the caliper assembly. To carry out various processes, cassette-type tool holders with the ability to attach up to 12 different cutters are often used.
The most popular varieties:
- Centering machines. Processing is carried out by turning along the contour of the workpiece. Parts of cylindrical and conical shapes, as well as shaped products are manufactured.
- Cartridge machines. They can be used to process both the outside and the inside of the workpiece. Basic operations: threading, countersinking, drilling, turning to install flanges, discs, bushings and gears.
- Combined (chuck-center) machines. Combines the capabilities of both types.
- Carousel machines. They are necessary for processing large parts and irregularly shaped workpieces.
The design features of CNC lathes are: vertical or inclined layout, increased rigidity of elements, ASI system.
Multipurpose
Complex processing of parts is carried out on multi-purpose machines (machining centers) with CNC. For them, special mixed UEs are used. The machines provide the following operations: milling, countersinking, boring, cutting, threading and chamfering. They can belong to the drilling-boring or turning-grinding group.
Multi-tasking machines differ in types:
- Horizontal machines. They carry out one-sided processing of large workpieces.
- Vertical machines. Capable of processing from 3 to 5 sides using a rotating spindle.
Among the design features, the following stand out: the presence of tool stores for ASI, rotary tables for moving workpieces, devices for changing workpieces. Most often, high-torque electric motors with low inertia are used.