Device
To perform the functions assigned to it efficiently, planing machines must include the following components:
- bed;
- control unit;
- a support with one or more tool holders;
- frame (on large machines the frame has a portal configuration, on smaller ones it is made in the form of a console);
- mechanism for moving the table and/or support;
- work table with T-shaped slots for precise positioning of the product;
- electric motor;
- pumping station for supplying lubricating and cooling media to the planing zone;
- a cross member that connects the elements of the frame and gives it the necessary rigidity;
The general classification index for such equipment includes an alphanumeric designation of the type XXXX. The first digit indicates the group number according to the classification tables. For planing machines, this is number 7. The second number indicates the type of machine (1 - single-column longitudinal planing; 2 - two-column longitudinal planing; 3 - cross-planing; 4 - slotting; 5 - broaching horizontal; etc.) . The third and fourth digits indicate the largest size of the workpiece.
Schemes of metal processing by planing
The last two digits of the marking indicate the main technological parameter of the equipment. As a rule, this is the largest dimension of the processed product in decimeters. For example, brand 7310 will indicate that this unit is a cross-planing unit and is intended for processing metal with a maximum plane length of up to 1000 mm. The letter in the designation (for example, 7A110) indicates a modification of the base model (for example, the presence of a hydraulic drive, an additional clamping unit, etc.). The presence of the letter F in the designation indicates that this equipment is equipped with a CNC system.
Planing equipment should be used in technological campaigns for the processing and production of various types of parts. The initial types of workpieces undergo a multi-stage processing process on machines of a certain type. The equipment produced at a machine-building enterprise uses parts of different configurations and dimensions.
Types of metal planing machines
A classic metal planer carries out controlled removal of material of a certain thickness from the surface of the workpiece. It is distinguished by both the accuracy of the process and the technological schemes.
The main difference between planing machines and milling or turning machines is the configuration of the workpiece and the principle of operation. It does not have a rotation shape - its sides are often flat. The cutter processes one or more sides of the part, which is rigidly fixed on the work table.
Depending on the manufacturing technology, the following types of equipment are distinguished:
- Longitudinal planing machines (“1” – single column, “2” – with two columns). They can be used to give a certain shape to large samples. As an option, several medium-sized workpieces can be processed simultaneously. The cutter (there may be several of them) is fixed, and the blank, fixed on a special platform (table), moves with it.
- cross-planing (“3”). The cutting part moves, but the workpiece remains motionless. Used for the manufacture of large-sized parts. In addition, several types of operations can be carried out simultaneously to increase production speed. This depends on the number of cutters installed in the spindle slots of the cutter - from one to four. As a result of processing, recesses, grooves and recesses of a given shape are formed.
In addition, there are special-purpose machines. They perform similar operations, but differ in the form of influence on the workpiece:
- slotting (“4”). They make holes, select metal for grooves, protrusions, recesses, splines, grooves, that is, they are used for specific operations. Their working tool is called a “cutter”, the teeth of which perform the function of traditional cutters. The head can be rotatable, which allows processing in several planes, at an angle.
- Lengthy (“5” – horizontal; “7” – vertical). Mainly for removing chips from long workpieces.
- Shaped-planing machines (“9”). For processing curved surfaces (punches, bays of railway cars, etc.) or with ledges, when individual surface segments are located in different planes.
Elements that have the shape of a body of revolution are processed on some machines, and body objects are processed on others. The longitudinal combustion method is used when processing shaped and flat products. To achieve the highest level of cleanliness and surface quality of the product, it is worth using separate tools and technological processes.
Inferior to milling and turning models in productivity and price, this equipment wins in the low cost of the attached working tool and in the ease of sharpening it. For this reason, such machines are recommended to be purchased if you need to remove scale or form precise grooves and grooves in flat and shaped workpieces in a minimum number of passes
Planing machines
Planing machines are presented on our website in a wide range, which will allow you to choose and buy the equipment that is most optimal in price and functionally suitable for solving new problems posed in your production, or for replacing planing equipment, the operation of which at your enterprise becomes impractical due to moral or physical wear and tear.
Planing machines are divided into longitudinal planing (single and double column) and transverse planing. The main movement in longitudinal planing machines is imparted to the workpiece, and in transverse planing machines - to the tool. The machines are effective when processing long narrow surfaces, especially through, straight grooves and grooves; They also receive shaped linear outer surfaces. The advantage of planing machines compared to milling machines is the simplicity of the tool design, which is important for single and small-scale production.
1. Longitudinal planing machines
The dimensional characteristics of longitudinal planing machines are the largest dimensions of the processed parts (width x length x height). The industry produces machines from 630 x 2000 x 550 to 5000 x 12,500 x 4500 mm. Machines with dimensions up to 1600 x 6300 x 1250 mm inclusive are available in a single-column design. In longitudinal planing machines, the moving part is a table with a workpiece fixed on it. Depending on the design of the crossbar, single-column and double-column machines are distinguished. The former are used for processing large parts, the width of which exceeds the distance between the columns of two-column machines.
Longitudinal planing machines are used for processing horizontal, vertical and inclined planes of large parts (beds, bodies, frames, etc.) or for simultaneous processing of several sequentially fixed small parts. The length of the surface to be processed is 1.5-15 m. In these machines, the workpiece performs a reciprocating motion, and the cutter performs a periodic feed in the transverse direction.
A single-column longitudinal planing machine is shown in Fig. 1. The main components of this machine are the table (3), bed (2) and traverse (5). Two vertical supports (4) and (6) move along the traverse, and a side support (1) moves along the vertical guides of the frame. The main working movement is communicated from the electric motor (9) using a rack and pinion gear to the table (3), and the feed movement is communicated to the calipers.
The movement of the supports along the guides of the traverse and frame is carried out by separate electric motors provided for this purpose. The traverse (5) has accelerated movement up and down the frame, carried out by an electric motor (7). The control of the machine is concentrated on the remote control (8), mounted on a flexible hose, which can be placed anywhere.
A two-post longitudinal planing machine is shown in Fig. 2. The machine consists of the following main components: bed, table, portal, table drive, cross member, supports, feed boxes, lubrication system and electrical equipment. Two posts are attached to the frame - right and left, fastened together by a crossbar. Two posts and a beam form a portal. The crossbar lifting mechanism is mounted on the crossbar.
The cross member moves along the guides of the racks. The right and left upper supports are installed on the cross member guides. On the right end of the cross member there is a feed box for the upper calipers, on the left end there is a box for duplicating the control of the upper calipers; A crossmember clamping mechanism is mounted behind the crossmember.
The carriage on which the side support and its feed box are mounted moves along the guides of the right rack.
Rice. 1 Single column planer
Rice. 2 Double column planer
2. Cross planing machines
The characteristic size of cross-planing machines is the stroke length of the slide, which is 200 - 2400 mm. Machines with a large slide stroke (over 1500 mm) do not have a movable table, machines with a stroke length of 700-1000 mm are hydraulically equipped.
Cross-planing machines are used in single and small-scale production for processing the surfaces of small workpieces. Vertical, horizontal and inclined planes, rectangular and shaped grooves on planes and cylinders, and other combinations of planes and ruled surfaces are planed on workpieces.
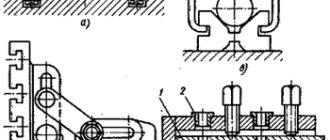
The layout of cross-planing machines is simple and compact, in which the workpiece being processed is motionless during the cutting process, and the cutter, fixed in the slide, makes a reciprocating movement. The general view of the cross-planing machine is shown in Fig. 3. All components of the machine are installed and secured on bed 1. A slider 7 moves along the horizontal guides of the frame, making a reciprocating movement using a rocker mechanism or from a hydraulic cylinder. At the left end of the slide there is a support 6, consisting of a turntable, a slide, a rotary and folding board 5 with a tool holder. The support together with the cutter can move in a vertical or inclined direction. Inclined movement is ensured by rotating the caliper relative to the horizontal axis. The tool holder can be tilted under the influence of the hinge, thereby ensuring free sliding of the cutter along the workpiece when the slide is idle. Crossbeam 4 with table 3 is installed on the vertical guides of the frame in accordance with the height of the workpiece. The table is used to place the workpiece being processed on it; it moves along the traverse in a horizontal plane and imparts a transverse feed to the workpiece. For greater rigidity, the table is additionally secured in rack 2.
Fig.3 Cross-planing machine
At the Stanochny Mir company you can buy new planing machines from domestic and foreign manufacturers at competitive prices. Our sales team will be able to select the most suitable option for you.
Cutters for metal planing machines
Manual planer
Planing machines for metal processing are used to complete technological lines with high productivity and repair shops. Their advantage is relatively simple setup and maintenance.
The main factor in the correct processing of the workpiece is the choice of the appropriate cutter. It must be designed to perform a specific operation or have a universal application. To do this, in the production process of cutters, high-speed steel blanks are used or carbide brazing is made.
Types of cutters for planing equipment
Cutters used for processing parts on a metal planing machine are divided according to a number of characteristics:
- In the direction of delivery; (left and right)
- According to the shape of the head; (straight, bent, with a retracted head)
- By manufacturing method; (solid and composite)
- By type of work performed (through roughing and finishing, shaped, cutting, grooving, etc.)
The process of planing metal occurs only with a working cutter, or on tables with a firmly fixed workpiece.
At the moment when the cutting tool is tightly fixed in the folding holder, its process of wear and exhaustion will take much longer, since during the return stroke it begins to fold back and move freely over the entire surface.
Main criteria for choosing a cutter model:
- type of equipment - for longitudinal or transverse operations;
- cutting edge material. Affects the speed and accuracy of work;
- cutter shape. Depending on this parameter, grooves, holes or grooves will be formed on the surface of the part.
There are several types of operations carried out on a longitudinal planing machine. They can be pass-through, finishing, shaped, trimmed or cut-off. To increase the service life of cutters, it is recommended to use equipment with a folding locking head. After initial processing, the cutter returns to its original position. During the return stroke, it should not come into contact with the surface of the workpiece.
The most common are longitudinal planing machines. They are characterized by relatively small dimensions and ease of operation. Particular attention should be paid to the quality of cutting tools. To ensure an uninterrupted technological process, it is necessary to have a small supply.
How to choose a planing machine
Criterias of choice:
- desktop area;
- installed engine power;
- speed of movement of the cutter relative to the workpiece;
- available cutting methods;
- table configuration;
- possibility of positioning the cutter: angle of inclination, trajectory of movement;
- degree of protection of the housing from dust and moisture;
- maximum permissible weight of processed parts;
- manufacturer, warranty period, availability of additional options to expand functionality.
Equipment configuration (Photo: Instagram / kubanzheldormash)
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages of planing machines:
- versatility of application - processing of various types of metals;
- selection of optimal cutting speed;
- wide selection of cutting tools;
- the possibility of roughing or finishing to obtain the desired level of surface roughness;
- high strength of the body, capable of withstanding increased loads from the cutting tool and the weight of the part;
- convenient control;
- formation of surfaces of complex shape;
- high reliability of installed components and assemblies.
Flaws:
- loss of time moving the cutter relative to the workpiece;
- inertia of moving mechanisms;
- high level of vibrations;
- engine noise;
- the difficulty of obtaining high engine speeds under load or at idle in a short period of time.
Cost and manufacturers
In Russia, machines are produced at the following enterprises:
- Sverdlovsk Machine-Building Plant LLC (SMZ);
- Ryazan Machine Tool Plant LLC (RSZ);
- OJSC "Orenburg Machine Tool Plant" (OSZ);
- OJSC "Astrakhan Machine Tool Plant" (ASZ);
- Lipetsk Machine Tool Company LLC;
- Verkhnevolozhsk Machine Tool Plant.
Cost of machines, depending on their types:
- slotting - from 100 thousand rubles;
- compact - from 35 thousand rubles;
- combined - from 600 thousand rubles;
- transverse - from 65 thousand rubles;
- industrial longitudinal planing machines - from 7 million rubles.
Slotting and planing machine (Photo: Instagram / krasnyi_mehanik_)
Review of the best models of cross-planing machines
Planing equipment with a reciprocating movement of the cutter and a stationary workpiece mounted on the feed table has a limited scope of application and is used primarily in small-scale and one-time production. Nevertheless, it has its advantages and is considered worthwhile when it is necessary to perform roughing and finishing operations for planing and preparing grooves in relatively small metal workpieces with a flat and shaped shape.
The model range of these machines is limited, but all offered devices are valued for their simplicity of layout, high processing accuracy, reliability and unpretentiousness.
Purpose of the machine
During longitudinal planing, the movement is transmitted to the table on which the workpiece being processed is located, and the cutter is stationary, and has only technological movements associated with the constantly increasing depth of removal of the metal layer. In this case, this equipment unit moves at different speeds: lower during the working stroke and higher during the return stroke. The speed of the main movement cannot be adjusted. The feed movement to the cutter, which is fixed in the tool head, is performed at the end of the idle stroke.
Desktop view
Increasing the productivity of longitudinal planing (which in its absolute values is inferior to milling of similar products) is possible only by installing several semi-finished products of the same size on the table, technologically grouped according to the parameter of metal removal. This can slightly increase processing productivity. In general, planing machines of the design in question are used for small-scale and single-piece production. Indications for the use of longitudinal planing technology are:
- impossibility of milling due to rapid wear of cutters, for example, with increased hardness of the surface of the product;
- possible thermal deformations of the part during its milling, when thermal deformation is likely, due to which the product will lose its geometric dimensions required by the drawing;
- the presence at the enterprise of highly qualified workers who can carry out longitudinal planing of high-duty products with very high accuracy;
- reduction of specific energy costs during processing, which has a positive effect on the cost of the final product.
Scope of application
This equipment is not highly productive; due to the idle reverse motion and the inadmissibility of high cutting speeds due to inertia, the dimensions of the workpieces processed are limited; longitudinal planing machines are practically not used for mass production of metal products. But they are the best when it is necessary to form complex grooves and profiles using cutters or the use of rotating cutters is inadmissible.
A wide variety of working tools are fixed in the support assembly of such machines, including passing, trimming, slotting and shaped cutters, which allow roughing and finishing planing operations to be performed with their inherent accuracy (average deviations do not exceed 0.03 mm per 300 mm length of the metal workpiece).
In particular, the cross-planing machine is successfully used:
- When planing horizontal planes with the help of universal cutters, vertical ones with scoring cutters complete with stops.
- Processing of parallel planes with division of the process into two stages and sequential execution of work
- When planing inclined planes by installing the support at an angle and ensuring its feed in a parallel direction. The maximum effect is achieved when it is necessary to process a narrow strip (10-30 mm); with such parameters, all the advantages of fixing a wide and non-rotating cutter are manifested.
- When making grooves and grooves, including keyways.
- When planing chamfers using concave, convex and similar cutters. In the manufacture of gears, couplings and cams (subject to the use of additional specialized and dividing devices).
Inferior to milling and turning models in productivity and price, this equipment wins in the low cost of the attached working tool and in the ease of sharpening it. For this reason, such machines are recommended to be purchased if you need to remove scale or form precise grooves and grooves in flat and shaped workpieces in a minimum number of passes.
Types of devices
A planing device for a metal surface can be of two types at once: longitudinal planing and transverse planing. The principle of processing such parts on equipment will differ significantly .
Longitudinal planing machines are designed to work with a fairly short surface. That is why in them the movement occurs on the table to which the part being processed is attached. While the cutter itself will be installed by the cutting head of the support, and also relative to the bed, the machine will not carry out any movement.
In a cross-planing machine, the work occurs in a completely different way: the cutter produces movement, and the semi-finished product installed on the table remains stationary.
Planing types of machines are significantly inferior to milling machines in their functioning, since they have an idle stage, while the workpiece or the same cutter moves to a new position. In this case, the drive will not be very energy-intensive , since the process of rotational movement of the working device (as in a milling machine) will require significantly greater costs from the drive electric motor.
Design and principle of operation of the equipment
The layout of the units is simple and includes several large elements:
1. A foundation slab with a stable frame secured with bolts. The metal planing machine is a fairly massive structure and weighs at least 1800 kg.
2. A slider with a built-in support that holds and regulates the position of the planing cutter and its feed mechanism.
3. Cabinet or casing with a motor (mostly asynchronous) and electrical equipment and drive. Planing types of machines are equipped with rocker, crank, gear, portable or hydraulic transmission mechanisms, the first group is the most common, but has a relatively limited stroke length of the slide (up to 700 mm), varieties with movement within 700-1000 mm are usually hydraulically powered and have a separate drive for accelerated return of the caliper.
4. Work table with stands for additional fastening and increased rigidity and guides for horizontal movement. In improved modifications it is inclined.
Transverse planing in these machines is carried out using a reciprocating slider with a fixed cutter with different sections and shapes; during contact with the tool, the workpiece itself remains motionless.
The removal of metal or the formation of a groove is carried out during the working stroke of the caliper assembly, followed by its idling (usually accelerated several times) with a return to its original position. Upon completion of each return operation, the machine moves the table feed in a transverse direction relative to the main stroke.
The main dimensional characteristic is the stroke length of the slider, varying from 200 to 2400 mm, with an average range of 500-700. The support with the cutter is capable of moving in the longitudinal and vertical direction and rotating around a horizontal axis. The speed of its movement, along with the dimensions and feed parameters of the table, have a direct impact on the functionality and dimensions of the workpiece being processed. The devices are powered by a three-phase network and have simple controls.
Types of planing units
After analyzing the geometric dimensions of the workpiece, as well as the properties of the metal from which it is made, the surface finishing is carried out on a longitudinal or transverse planing unit.
The fundamental difference between these metal cutting machines is determined by the method of moving the cutter. A table moves on the longitudinal planing unit, with the workpiece fixed on it.
Large blanks are processed in this way. When cross planing is performed, the cutter moves and the workpiece is fixed on the table. This method is used when processing medium-sized parts. In each specific case, cutters of the appropriate configuration are selected.
The same class of metal processing equipment includes slotting, broaching and shaped-planing mechanisms.
Using cutters of various shapes, such machines perform operations of selecting recesses and grooves, turning channels and cutting holes.
One of the features of a metal planer is the number of cutting tools installed.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: Do-it-yourself machine for bending profile pipes
Some models are designed for simultaneous fastening of several cutters at once.
The following machine models are produced according to these parameters:
- one-sided;
- double sided;
- four-sided.
The more cutting tools installed on a planer-type device, the higher its productivity.
Construction of a longitudinal planing unit
As prescribed by the technical characteristics, longitudinal planing machines are used for processing surfaces on body and asymmetrical parts cast from cast iron or alloys of non-ferrous and ferrous metals.
The dimensions of the workpiece being processed are determined by the technical capabilities of the planing unit. The initial workpiece to be processed is placed on the table.
The table is capable of performing reciprocating movements. In this case, the cutter fixed in the support remains motionless.
When the table is idling, the support moves to the side, allowing the table to move freely to its starting point.
This complex movement allows you to process large workpieces with several cutters at once.
A longitudinal planing machine for the production of metal products is composed of a frame, a table, supports, a cross member, electrical equipment, a lubrication system and other components.
Each model has its own length and width of the working surface of the table. A common element for all models is the control panel.
When processing parts with complex geometric dimensions, several cutting tools can be installed on the support. This technique reduces the time for processing the product.
Design of a cross-planing unit
A cross-type metal planing machine is installed in production lines where small and medium-sized parts are processed.
The unit is used for planing horizontal, vertical and inclined surfaces.
As in any metalworking machine, the main elements of the cross-planing unit are the bed and the base.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: The design of a machine for sharpening saw blades
All components and devices that are designed to ensure fastening and movement of the corresponding elements are attached to this support. The part is fixed on the table at the specified coordinates.
The support, with the cutter fixed in it, is given movement within certain limits.
In the process of metal processing, parts assemblies and structural elements perform complex movements, the purpose of which is to carry out a given program.
The planing unit for metal of the cross type can operate under manual control or according to a given program.
The main one is the reciprocating movement of the slider on which the cutting tool is attached.
Auxiliary is the movement of the table on which the workpiece is fixed. The speed of movement of the slider is controlled using a special gearbox, like in a car.
Before processing any part, all mechanical components of the unit must be lubricated with machine oil.
Overview of the machine range
The main developer and manufacturer of planing equipment of this group is the Orenburg SZ; many domestic companies offer to purchase ready-made, repaired or modernized devices, Pressmash, Stanochny Mir); among used machines, the products of the Gomel SZ have good reviews. The models have a generally similar design, the differences are manifested in the dimensions, power and parameters of the workpiece being processed. The main indicators of the most common of them are presented below:
7305T
The basic model of a cross-planing machine, supplied without a slotting head at a price of 680,000 rubles and used for processing flat and shaped metal products in all planes, including inclined.
| Characteristic | 7305T | 7307GT |
| Slider stroke, mm: | ||
| largest for planing | 500 | 710 |
| largest for chiselling | 200 | 250 |
| Dimensions of the upper working surface of the table, mm | 500x400 | 710x450 |
| Slider stroke frequency, stroke/min | 13,2-150 | 10,6-118 |
| Table feed, mm/double stroke: | ||
| Horizontal | 0,2-5,0 | |
| Vertical | 0,04-1,0 | |
| Main drive power, kW | 5,5 | |
| Weight 7305T machine (without accessories) kg, max | 1980 | 2770 |
| Overall dimensions of the machine, mm | 2380x1085x1560 | 2790x1375x1665 |
| Overall dimensions of packaging, mm | 2400x1306x1620 | 2800x1400x1740 |
This equipment is distinguished by its increased rigidity of the frame and guide and has a good power resource (up to 5500 W), facilitating the precise performance of finishing, roughing and fine planing.
The machine is equipped with a 500×400 rotary table with 25 feeds and three T-shaped slots for gripping workpieces with a slide stroke of up to 510 mm and an outreach of up to 560; the maximum distance between the horizontal plane and the guides is 40 cm.
7307TD
Expanded modification 7305T with a slotting head and a slider stroke increased to 710. By analogy with the previous one, this cross-planing machine is recommended to be purchased when processing flat and shaped workpieces made of hard materials (the permissible cutting force reaches 19.6 kN); with equal power and table movement speed, it wins in functionality and increased working space.
This affects the price; in new condition, this model can be purchased from 800,000 rubles and above. At the same time, its optimal scope of application is enterprises with single and small-scale production conditions.
7B35
Planing equipment for processing with a cutter workpieces with a length of up to 500 mm inclusive and forming grooves and grooves in them with different shapes and depths within the cross-section of the working tool 20×32 mm. The model was developed for installation in repair, mechanical and tool shops of mechanical and instrument manufacturing enterprises with relatively small production volumes (single and small-scale production of metal parts).
In the basic version, 7B35 has a fixed table with 20 feeds and manual, mechanical and root movement; models with universal rotary structures are made to order. The machine is equipped with a centralized lubrication unit and a chip collector; the estimated costs for purchasing it in basic configuration and in good condition are 600,000 rubles.
7M36 and 7M37
The cross-planing machine of the Gomel SZ is the base for models with a universal rotary table and copying devices, used for processing their metal surfaces with a slide length of up to 700 mm inclusive. At the moment, the model has been discontinued from main production and replaced with improved slotting analogues, but thanks to the reliability of the components and hydraulic drive, it is still used in machine shops of machine-building enterprises and is sold in used condition at a price of 140,000 rubles and above.
The machine has 2 electric motors (the main one ensures the start of all components, the auxiliary one ensures rapid movement of the worktable with dimensions of 450×700 and 560×1000 mm, respectively), the lubrication of its frame and slider guides is carried out automatically, the same applies to the feed of the support and cutter.