Most car owners treat their four-wheeled friend with due reverence, trying to prevent scratches and other noticeable exterior defects. At the same time, enemy body number 1 always acts secretly, gradually, destroying the metal gradually. In many cases, corrosion processes begin from the inside or under the paintwork layer, so noticing them in time is not an easy task. There are many methods to combat rust - covering problem areas with a special anti-corrosion compound, timely painting over paint chips/scratches, but in many cases the most adequate action will be galvanizing the body. Some automakers perform a similar operation on the entire body; with independent processing, we can only talk about partial galvanization of the vehicle.
Method of galvanizing a body at home.
What is galvanizing
This operation refers to the coating of body parts/assemblies with a thin layer of zinc. Many metals are resistant to corrosion, but only zinc is characterized by relative ease of application to a metal surface, which allows ferrous metal structures to be treated both for protection against corrosion and as a protective layer against exposure to a wide range of chemically active substances. Unfortunately, not all automakers galvanize passenger car bodies at the factory, so in many cases the protection of body parts that are most exposed to moisture (the bottom, the inside of the wings, sills) has to be done independently.
Causes of corrosion
First, let's figure out why corrosion processes occur. The fact is that there are four types of corrosion of metal surfaces - electrochemical, chemical, hydrogen and oxygen. In the context of rusting of an automobile body, only the first two types occur.
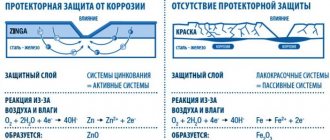
Electrochemical corrosion occurs due to the fact that two materials with different reducing properties interact through an electrolyte (any non-distilled water is such). Since iron has low reducing properties, it is significantly susceptible to rusting. Chemical corrosion occurs due to the interaction of the metal surface and a corrosive environment. The latter role can be played by oxygen at high temperatures. Understanding the essence of the emerging processes gives us the basis for searching for methods to combat corrosion.
Advantages and disadvantages of galvanizing body elements
Galvanization can hardly be called a panacea, but the advantages of this method of anti-corrosion treatment are obvious:
- a thin layer of zinc well protects ferrous metal from exposure to oxygen, moisture, and salts, preventing the spread of corrosion areas;
- galvanization, depending on the application method, can last on body parts for 5-25 years;
- Coating iron parts with zinc is more reliable and much cheaper than using tin.
Unfortunately, such protection is not eternal - on average, the zinc layer thins by 1-5 microns every year. Disadvantages include higher cost compared to treatment with a special primer. But if you do it yourself, the procedure will not be so burdensome financially.
Popular rust removers
Currently, there are dozens of different rust converters in auto stores, and their range may vary in different regions of the country. Therefore, it makes no sense to give recommendations regarding the purchase of this or that product. But we will still give as an example several names of popular compounds that are common among car owners. So:
Popular remedy "Tsinkar"
- "Tsinkar";
- "Movil";
- Hi-Gear line of rust converters;
- "Chain mail";
- Sonax;
- "SF-1";
- Runway;
- Permatex;
- Bitumast;
- "Phosphomet".
It must be remembered that with the help of any converter you can fight rust, the layer of which does not exceed 0.1 mm. In addition, the active components only fight stubborn rust. It is better to remove its loose component mechanically (using sandpaper, a knife, a metal brush, sandblasting, and so on).
The choice of one product or another should be based on the range, its composition, and price. Fortunately, they are inexpensive, so if the purchased product turns out to be ineffective, you can always buy another one.
Types of galvanizing metal surfaces
Currently, there are several methods for applying a thin layer of zinc to a metal surface. All of them are used in industry with varying degrees of success:
- cold/hot galvanizing;
- gas-thermal galvanizing;
- galvanic method;
- thermal diffusion treatment.
Each of these methods uses different physical and chemical technological processes to apply zinc coating. Let's look at them in more detail.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3S_wa0BbnWw
Hot galvanizing
It is considered one of the most effective galvanizing methods. Zinc applied in this way lasts much longer, protecting metal parts for the longest possible time. Among the main disadvantages of this method, one can highlight the environmental component - the use of a chemical method of applying a layer of zinc contributes to environmental pollution. The hot-dip galvanizing method involves the use of the following technological chain:
- at the preparatory stage, metal surfaces to be galvanized are degreased, after which they are etched with acid;
- after such treatment, the part is washed in water and dried thoroughly;
- then the product is placed in a container filled with molten zinc.
In addition to harm to the environment, hot-dip galvanizing has other disadvantages:
- such processing requires the use of expensive special equipment;
- There are also restrictions on the dimensions of the parts being processed (it will not be possible to process the entire car body).
Cold galvanizing
This method of anti-corrosion treatment is one of the simplest. Its essence is to paint a metal surface with a special paint that contains zinc. It does not matter what method is used to apply the coloring composition: it can be a roller, a spray gun or a brush. The combination of powder paint and a spray gun allows galvanizing of any parts, regardless of their size, which is why it is often used as an alternative to hot-dip galvanizing. In particular, the entire vehicle body is galvanized using this method. Cold galvanizing also allows for the re-application of a protective layer on a previously galvanized surface.
Galvanic processing method
Galvanizing a car body using the galvanic method involves treating metal surfaces susceptible to corrosion through electrochemical action. The advantages of this method over cold galvanizing are the possibility of applying a more uniform and very thin layer of zinc. Its essence is to place the part in a tank filled with water, in which a zinc plate is placed. After applying electricity, the process of diffusion of zinc atoms begins, which are transferred from the plate to the workpiece, forming a very thin protective layer. As in the case of hot-dip galvanizing, galvanic treatment is considered an environmentally very dirty method, and also quite expensive - in particular, a lot of money is spent on waste water treatment.
Gas thermal galvanizing
This method is not perfect, but with its help it is possible to process very large parts. It involves blowing the surfaces with a gas stream containing zinc. This is how the bodies of large vehicles are galvanized, but in this case the zinc layer is applied unevenly, requiring additional painting of the body parts. Of course, this method is characterized by the use of specialized equipment, so it is certainly not applicable in garage conditions.
Galvanizing method using “white powder”
For more efficient processing of metal with zinc, soldering acid is used instead of phosphoric acid. This is hydrochloric acid diluted with water with zinc dissolved in it. According to craftsmen, galvanizing with a similar composition lasts longer and penetrates deeper into the metal surface. Soldering acid is sold in radio equipment stores in small bottles. It can also be made by diluting zinc chloride, a white powder that is sold by weight.
Main stages of work
First, you need to pour zinc chloride into a strong container, pour in distilled water to get a clear liquid. Approximately 2.5 liters are needed per kilogram of product. You can put the entire part into the finished soldering acid, creating a galvanic bath. Before starting work, you should clean the product from rust with sandpaper or a grinder, and then activate the metal - remove the oxide film from its surface.
Metal activation
During activation, the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the part, the negative terminal is connected through a 20-watt light bulb to the electrode (an iron bolt wrapped in a cotton rag and soaked in soldering acid). As current is applied, the product will be cleaned of the oxide film. Only after its removal is the metal immersed in a galvanic bath and galvanizing is carried out in a similar way.
Self-galvanizing the car body
As a rule, the better the galvanizing method, the more complex it is. It is for this reason that galvanizing a body at home is carried out using only cold or galvanic technology for applying a protective layer. All other methods require the use of specialized equipment, the cost of which is too high even for the average volume of such work, not to mention artisanal operations.
Safety precautions when galvanizing a car in a garage
Since galvanizing a car body at home involves the use of chemical methods, increased attention should be paid to safety precautions when carrying out such work. The following recommendations must be followed:
- the room in which the work is carried out must have good ventilation, therefore it is more preferable to carry out galvanizing in the open air, that is, outside the room;
- working with electrolyte requires the mandatory use of personal protective equipment: safety glasses, a respirator, rubber gloves;
- When making your own electrolyte, you must take into account that it is accompanied by the release of hydrogen, which can cause a fire/explosion if there are flammable objects in the workplace.
Preparatory stage
Regardless of the method used for self-processing of body parts, the car must first be prepared for galvanizing. This procedure includes the following activities:
- removal of old paintwork. Usually, for these purposes, a hand-held sanding machine with sandpaper of different fractions is used (coarse - for rough processing, fine - for finishing);
- if pockets of rust are found under a layer of paint, it must also be removed using abrasive materials;
- straightening of body parts is also carried out at the preparatory stage;
- The final operation is degreasing of body parts, and the use of traditional solvents (white spirit/acetone) is not recommended due to the increased content of heavy resins in them, which prevent the fixation of zinc on the metal.
Please note that galvanizing of the car body, including its individual parts, must be started immediately after degreasing, without long pauses, otherwise the last preparatory stage will need to be done again.
And one more important point: do not use aggressive chemicals to remove the paint layer, but if you cannot do without it in certain areas, immediately after use, wash off their residues from the surface to be treated with an ordinary solution of baking soda, after which the area should be thoroughly dried.
Self-galvanizing a vehicle using the cold method
Despite its rather low efficiency, the method of cold processing of body parts is considered the most affordable and easiest to implement. Another advantage over galvanizing is the ability to process much larger parts, which is not possible when using an electrolyte. That is why, if there is a need to process such large body elements as the hood, pillars, trunk lid, doors or roof, there is no alternative to the cold method when performing this operation independently. Let's look at the order of the procedure and start with the list of necessary materials/tools. We will need:
- spray gun, roller or brush;
- special product for cold galvanizing (sold ready-made; products from the brands Zinga, Galvarex, Zinol, Galvanol are quite in demand);
- PPE (gloves, goggles, respiratory bandage).
As you can see, the list is minimal, which suggests the simplicity of this method. If you have considerable experience working with a paint brush, then galvanizing a car will not be an irresistible task for you. So, the algorithm for galvanizing a body or its individual parts using the cold method is as follows:
- As with regular painting, but more carefully and smoothly, we apply a layer of the composition to the surface to be treated. Using a spray gun is preferable, since it demonstrates good results even in the absence of basic skills, but in some cases you cannot do without a paint brush, and here the accuracy of the work depends entirely on your experience. In any case, you should try to ensure a uniform and thin layer of galvanization;
- after finishing the work, it is necessary to allow the zinc composition to dry completely - at a temperature of 20ºC and higher, this will take approximately 30-60 minutes;
- the second layer is applied in the same way;
- After complete drying, you can begin finishing - applying a paint layer, although for some parts this is not required.
How to tell if your car is galvanized
Currently, most car manufacturers, both domestic and foreign, subject their products to galvanizing by one method or another. If you purchase a car from an official representative of the brand, then the dealership will definitely tell you whether your new iron horse is protected from corrosion. But what if you buy a car from the previous owner, and he is not sure about the availability of zinc coating? And if at the same time the car is of a low price category and is more than 15 years old, then it becomes even more difficult to establish this.
Is it possible to check this yourself?
It is impossible to determine by eye whether there is a protective layer of zinc on the surface of the body. For this you will need professional equipment. It is completely unprofitable to purchase one for use at home, since the cost of the device will not pay off in one test. Not even every service station can afford it. If you do find a service station that will carry out such a procedure for you, then its cost will be quite high. Therefore, it is better to purchase a car whose galvanization you are sure of.
So how can you tell if your car has been galvanized?
- The easiest way to find out whether the manufacturer galvanized a car is to look at its technical documentation. If you find the phrase “full galvanized” there, you can rest assured that your car is protected from rust. However, there is a high probability that the manufacturer cheated and galvanized only certain parts of the machine. In this case, you will not find the word “complete”.
- Study the warranty card. There you will find information about the warranty period for body corrosion protection. From 5 to 10 years of warranty speak about the cold galvanizing method, 10–20 - about the galvanic method, and 20 and above - about the thermal one.
- Pay attention to the cost - if it seems too low to you, and the word “galvanization” is present in the documents, there is a risk that we are talking about a cold method, which is not highly efficient.
- You can obtain information about the presence of galvanization and the method by which it was performed using the VIN code of the car. It contains encrypted information about the technical characteristics of the car.
- If you are buying a car not from a store, but from the previous owner, then carefully examine the body. Few people manage to avoid scratches. If you see only a slight darkening where the paint is chipped, and there is no rust, then a protective layer is most likely present.
Which cars are galvanized at the factory?
Today, almost all major manufacturers galvanize cars. European and Asian brands prefer the galvanic method. However, there are companies for which the quality and durability of their products are a priority, so they use thermal galvanization. This is typical for cars of the Volkswagen Group and some other brands:
- VolksWagen;
- Audi;
- Cadillac;
- Ford;
- Porsche.
At the same time, the Audi brand is a pioneer in the field of serial galvanization of cars. In 1986, the famous Audi80 rolled off the production line with a completely galvanized body. This event gave rise to the mass galvanization of mid-size cars.
Photo gallery: hot-dip galvanized cars
Chevrolet Corvette C7 hot zinc plated
Audi A80 is the first production galvanized car
CADILLAC CTS Coupe is a hot-dip galvanized vehicle
The galvanic galvanizing method is used by such manufacturers as:
- Mercedes Benz;
- BMW;
- Toyota;
- Skoda;
- Honda;
- Mazda;
- Mitsubishi;
- Peugeot;
- Seat;
- Chrysler.
Photo gallery: galvanized cars
Honda Civic 9 galvanized
Mini Cooper 3 is protected by galvanization
The Mitsubishi brand prefers the galvanic method
Skoda Yeti also has a protective zinc layer
BMW 7 f01 has galvanic zinc coating
Full or partial galvanization of the car is also found in some models of the following brands:
- Chevrolet;
- Opel;
- Buick;
- Fiat;
- Volvo.
Most Hyundai cars are galvanized using a less reliable cold process. The Russian manufacturer VAZ is also doing the same with the latest generation models.
Photo gallery: cold galvanized cars
The old generation Daewoo Matiz M100 was cold zinc coated
The Hyundai brand uses the cold galvanizing method for its cars
Lifan Solano has an unreliable cold zinc coating
The South Korean company Kia prefers zinc metal in the manufacture of its cars.
Photo gallery: cars made of zinc metal
Kia Forte is made of zinc metal
Kia Rio 3 is made of zinc metal
Kia Soul 2 is made of zinc metal
The situation with determining the presence of a zinc layer is further complicated by the fact that in different years manufacturers could use different galvanizing methods. So, at the beginning of this century the cold method was more common, but now it has been replaced in most models by the galvanic method.
Despite all this, it is very easy to find out if your car is zinc coated. There are special resources for this on the Internet. All you need to do is enter the make, model and year of your vehicle. After this, you will know not only the method that was applied to your car, but also an approximate forecast of the condition of the protective layer.
On a special resource you can find information about the method of galvanizing your car
What are the advantages of cold galvanizing
- Simplicity.
You can easily carry out galvanizing yourself, even if you have never done it before. In addition, the solution dries very quickly - in most cases half an hour is enough. - Versatility.
Cold galvanizing is used to process hard-to-reach parts. In addition, the solution can be applied in any way convenient for you: roller, brush, spray gun. Some small parts can even be immersed in a zinc-containing solution. In addition, the material interacts with any solvent (solvent, xylene). Remember that this is the method that can be used to process wet metal. - Durability.
Cold galvanizing lasts about three times longer than heat treatment.