Scratches on a new car always upset its owner. However, the only thing worse than the unaesthetic appearance of a brand new paint coating is rust, which slowly but surely covers an increasing area of the damaged surface of the car. Of course, this can be combated by timely removal of scratches and application of anti-corrosion primer. But sometimes, due to lack of time or finances, a motorist simply does not have the opportunity to have the car repaired or paint it himself. In such situations, fully galvanizing the car can save the day.
The benefits of galvanizing the machine body
Despite the presence of factory protective coatings on the car body, road dirt, salts, reagents, constant temperature changes and humidity cause damage to parts. Galvanizing, or galvanizing, helps stop or prevent metal corrosion that occurs when a machine is used for a long time in difficult conditions.
Body galvanizing is the process of coating metal with a layer of zinc to protect it from rust. Typically, metal is applied to the bottom, wheel arches and some other vulnerable areas of the car. As a result of manipulation, a galvanic couple is created, where zinc is a more active metal and a strong film is obtained on the surface of the iron. Galvanizing a car allows you to form a reliable anodic protection that “saves” the body from physical and chemical damage. Even when scratched, the zinc layer will be the first to be damaged, while the iron will remain intact.
Types of corrosion control
There are two main ways to protect a car body from corrosion. The first is barrier protection. It does not allow physical interaction of the surface of vulnerable metals with the external environment. This is expressed in the use of paint and varnish coating and various mechanical means and protection. The second is tread protection. An example of this is galvanizing, because zinc has a more negative potential than iron. Accordingly, if you connect them, then in such a pair the iron will be reduced and the zinc will corrode. However, since there is an oxide film on the surface of zinc, this process occurs very slowly.
As mentioned earlier, there are three main types of car corrosion control:
Corrosion Removal Brushes
- Passive.
- Active.
- Electrochemical.
The passive control method involves the use of paintwork on the body. The car owner’s task in this case is to maintain the integrity of the paintwork. Do not allow small chips or scratches to appear on its surface. This method also includes periodic washing of the car, as well as the use of additional protective agents - wax, liquid glass, and so on.
Types of galvanization
There are different types of metal galvanizing:
- Galvanic. Zinc from a zinc-containing electrolyte is deposited on the surface of the body during electrochemical processes.
- Hot (thermal). The machine body is lowered into molten zinc. Zinc can also be applied to a metal sheet, which is then rolled, or sprayed from a special gun (shooping). The hot method is considered the most expensive, but the most effective type of galvanizing.
- Cold. It is most often used at home, as it is easy to carry out. It involves applying zinc to the metal surface in a manner similar to painting with conventional polymer paints.
- Diffuse. Zinc powder is used to process (sherardize) parts at a temperature of +290...+450 degrees or immerse them in zinc vapor at +800...+900 degrees.
Based on the completeness of processing, galvanizing is classified into complete, partial or partial. In the latter case, metal is applied only to individual components and connections. When purchasing a new machine, the type of galvanization performed can be clarified in the accompanying documents, which also indicate the thickness of the created coating and its warranty period. Professionals, even without documents, know which car models are galvanized at the factory and exactly how the metal is applied to body parts.
Hot-dip galvanized vehicles
Initially, this type began to be used at the Volkswagen and Audi factories, with the first galvanized production model being the Audi A80. Next, Porsche, Volvo and other automakers began to process car bodies using the hot method. Due to the high cost of hot galvanizing technology, it is used for premium machines. Among the inexpensive models that have received such reliable protection, we can point out:
- Chevrolet Lacetti;
- Chevrolet Epica;
- Opel Astra;
- Opel Vectra;
- Ford – Sierra, Mondeo, Escort;
- Fiat Albea;
- Fiat Marea.
During processing, a durable coating with a thickness of 2–10 microns is created (depending on the model and the specific manufacturing company), protecting the body from rust.
Machines with galvanic type galvanization
The cost of machines subjected to galvanic treatment is much lower than with the hot-dip galvanizing method. This coating method is used by Japanese, European, and American manufacturers. Since the protection will be worse, leading auto companies have introduced some improvements. Here are the main ones:
- zinc layer thickness – 9–15 microns;
- use of high-alloy steel without impurities;
- a durable layer of specially selected primer and paint.
Among the cars that have been galvanized using this method are some models of Honda, BMW, Mercedes, Alfa Romeo, as well as:
- Skoda Octavia;
- Skoda Fabia
- Renault Logan;
- Renault Espace 3;
- most from the Toyota lineup;
- Chrysler 300M;
- Mitsubishi Lancer.
Domestic cars
AvtoVAZ products were once made from foreign steel, which had already been galvanized. Due to the too high cost of imported material, the company switched to domestic steel, and the bodies began to be cold galvanized, which provides a low degree of protection. In Russian cars, not the entire body is galvanized, but only individual parts and components. Some compounds are processed by cataphoresis without the use of zinc.
Among Russian cars we can name:
- VAZ 2110 (approximately 50% of parts);
- Lada 4x4 (cataphoretic priming without galvanization);
- first generation "Kalina" (up to 52% of parts);
- second generation “Kalina” (galvanization of the entire body, except the hood, roof, side members);
- "Lada Priora" (100% body in modern models);
- "Lada Granta" (hatchback - galvanized wings, doors, sedan - no galvanized);
- "Lada Vesta" (fully galvanized, except for the thresholds);
- "Lada XRAY" (fully galvanized, except for the roof).
Since the protection created by cold galvanizing is not 100% reliable, during prolonged use it is broken and the metal begins to rust. If the impact is unfavorable, this process can begin within just a few years of driving a new car.
Trouble-shooting
Often there is no fundamental difference which engine is installed in a vehicle - the reasons that the engine stalls will be the same. In carburetor-type engines, a common reason for the engine stopping at idle may be an unadjusted drive, a dirty needle valve, or other problems. To eliminate such malfunctions and improve engine performance, change the fuel filter regularly. If the solenoid valve fails, the speed twitches or drops completely.
When the characteristic clicking sound is not heard when connecting, it is better to replace the valve. In diesel engines, the main role is played by the high pressure fuel pump. If this unit fails, the quality of the fuel, the condition of the electrical wiring, glow plugs and other parts are checked, and the fuel filter is changed. In injection engines, the air filter is first cleaned; it is possible that it will have to be replaced. If vibration is felt at idle, it is recommended to replace the gasket. Also, to eliminate the causes of engine shutdown, the injectors on the engine or on a special device are washed.
Is there galvanization or not - how to find out in practice
Before galvanizing a passenger car with your own hands, it is advisable to determine whether the procedure was done initially. If information about a new car can be found in documents (although not always), then with a used car the situation is much more complicated.
If you have documents indicating the technical characteristics of the machine, you should carefully read all the information. In the absence of the words “galvanizing” or “galvanizing”, we can confidently say that the metal was not processed. Only the expression “full galvanization” means the presence of high-quality anti-corrosion protection. Most manufacturers of economy-class cars use partial galvanization, so many body parts are still susceptible to rust.
It is impossible to determine for yourself whether galvanizing has been performed. You will have to contact a specialized center, because in simple auto repair shops such a technique is not practiced due to its high cost and complexity. The cost of research is high, so it is not always advisable. It is better to look for information about galvanizing a specific model on the Internet, although you cannot be 100% sure.
A new super product and method that will protect your car from rust and corrosion
This is a kind of super “Tsinkar” - a new galvanization of the car body, only using a unique method. In this way, metal protection is done much faster and more reliably.
Craftsmen and car enthusiasts who have already used such a device and used this method in practice praise it - it does not rot or rust. They say he is greatly underrated!
Self-galvanizing the body
Removing rust using galvanizing and protecting the body can also be done in a garage. Of course, the quality of the created zinc film will be worse than that of the factory one, but the metal will still last an order of magnitude longer and will not suffer from rapid corrosion. A similar procedure can be carried out to protect other metal products in everyday life.
Preparatory work
The procedure involves the use of phosphoric acid with dissolved zinc. To operate, you need to stock up on a salt battery or several batteries (depending on the volume). To treat a large area, you should buy the largest batteries, print them out, and remove the entire braid. The internal contents (soot, graphite rod) can be left, although they will not be required.
A cotton circle should be attached to the body of each cleaned battery, and on the reverse side - a power wire connected to the car battery. The easiest way to connect the wire and cotton wool is with a rubber band. You should also prepare the metal product to be processed - clean it from dirt, rust, degrease, and dry.
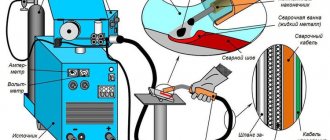
Galvanizing process
First you need to connect the minus and plus of the battery to the components of the galvanizing process. The negative terminal is connected to the desired part of the body, and the positive terminal is connected through a wire to the battery. Next, the order of work will be as follows:
- draw acid with dissolved zinc into a syringe (or a ready-made product, for example, “Zinkar”);
- soak a cotton pad on the battery case with acid;
- start the system, periodically moving the nozzle over the treated area, but always without stopping (otherwise the layer will not be uniform).
On sale you can find kits for galvanizing, which already include all the necessary tools and accessories, and the role of acid with zinc powder is performed by a ready-made composition.
Popular rust removers
Currently, there are dozens of different rust converters in auto stores, and their range may vary in different regions of the country. Therefore, it makes no sense to give recommendations regarding the purchase of this or that product. But we will still give as an example several names of popular compounds that are common among car owners. So:
Popular remedy "Tsinkar"
- "Tsinkar";
- "Movil";
- Hi-Gear line of rust converters;
- "Chain mail";
- Sonax;
- "SF-1";
- Runway;
- Permatex;
- Bitumast;
- "Phosphomet".
It must be remembered that with the help of any converter you can fight rust, the layer of which does not exceed 0.1 mm. In addition, the active components only fight stubborn rust. It is better to remove its loose component mechanically (using sandpaper, a knife, a metal brush, sandblasting, and so on).
The choice of one product or another should be based on the range, its composition, and price. Fortunately, they are inexpensive, so if the purchased product turns out to be ineffective, you can always buy another one.
Galvanizing method using “white powder”
For more efficient processing of metal with zinc, soldering acid is used instead of phosphoric acid. This is hydrochloric acid diluted with water with zinc dissolved in it. According to craftsmen, galvanizing with a similar composition lasts longer and penetrates deeper into the metal surface. Soldering acid is sold in radio equipment stores in small bottles. It can also be made by diluting zinc chloride, a white powder that is sold by weight.
Main stages of work
First, you need to pour zinc chloride into a strong container, pour in distilled water to get a clear liquid. Approximately 2.5 liters are needed per kilogram of product. You can put the entire part into the finished soldering acid, creating a galvanic bath. Before starting work, you should clean the product from rust with sandpaper or a grinder, and then activate the metal - remove the oxide film from its surface.
Metal activation
During activation, the positive terminal of the battery is connected to the part, the negative terminal is connected through a 20-watt light bulb to the electrode (an iron bolt wrapped in a cotton rag and soaked in soldering acid). As current is applied, the product will be cleaned of the oxide film. Only after its removal is the metal immersed in a galvanic bath and galvanizing is carried out in a similar way.
Car anti-corrosion treatment technology
The method of complex anti-corrosion treatment of the body is used, which includes several stages:
- Anti-corrosion treatment of hidden cavities, such as side members, sills.
- Anti-corrosion treatment of the bottom and arches
- Processing of the external contour and engine compartment.
The wheels, arches, bottom, hidden sections and other parts of the car are subject to examination.
Before you start processing, for example, the bottom, you need to wash it thoroughly and then dry it completely. Some dealerships offer floor drying for the underbody. That is, this is not spot drying with tena, but the entire surface of the bottom is dried at once. This drying method will not keep you waiting long. When preparing a surface for anti-corrosion treatment, the main thing is quality and care. After all, even a speck of dust can become the start of corrosion.
Until your car “blooms”, get acquainted with the solutions to problems in this article. There are many rust converters on the auto chemical market, but we suggest choosing one of them - with zinc.
Even experts in the field of anti-corrosion services were interested in a product called “Galvanization” or “Rust converter with zinc. Why does this phrase cause increased attention and heated debate among specialists? If everything is clear with conventional rust converters: iron oxide, also known as rust, reacts with orthophosphoric acid and produces harmless phosphates. But with galvanization everything is much more complicated. Yes, it would be great to not only defeat rust with one procedure, but also prevent further corrosion. But the fact is that zinc is completely omorphic in an acidic environment. That is, the same orthophosphoric acid that fights rust is essentially a zinc neutralizer. Some brands have even gained notoriety for adding zinc to their product. But he didn’t work there at all.
You need to choose a rust remover that says “galvanized” on the package. That is, we are not talking about the zinc content in the product, but about a full-fledged chemical process. The manufacturer does not play with concepts, but promises a complete result.
Galvanizing a car body with a battery in a garage
Self-galvanizing with a salt battery using the technology described above is popular among drivers. Usually it is made for the bottom and wheel arches, which deteriorate from rust faster than other body elements. A battery with cotton wool soaked in soldering acid is moved over the metal, pressing tightly to the surface. As a result, a film of silvery plaque is created.
Upon completion of work, acid residues must be neutralized by washing the part in a baking soda solution. This will reduce the risk of corrosion and enhance the protection created, extending the life of the machine.
Zinc as protection for steel
Galvanizing is the most widely used method of protecting iron and steel products from corrosion caused by natural (moisture, temperature) and artificial (aggressive chemicals) factors. In fact, more than 40% of the zinc mined annually in the world is used for protective coatings.
This situation is due to the high efficiency of several protection mechanisms characteristic of galvanized steel products:
- Formation of barriers. Zinc quickly forms films of oxide or other compounds that are chemically passive to the effects of various substances. As a result, the access of reagents that provoke corrosion to steel products is limited, Zn compounds act as a sealant formed in place.
- Electrochemical protection. Due to the difference in electrochemical potentials (-0.441V - Fe, -0.763V - Zn), the latter, deposited on the surface of iron or steel parts, acts as an electrochemical protector. In fact, corrosion processes occur in the protective layer without affecting the base material. Protection extends even to areas that do not have a coating (within the radius of the tread) - even if the integrity of the zinc layer is partially damaged, the protective properties are preserved.
- Partial regeneration. The potential difference between the materials also causes the transfer of Zn particles to the unprotected surface of the base material, allowing for self-healing of minor defects or damage.
Problems of galvanizing technological processes:
- Ensuring the required level of adhesion - adhesion of the zinc layer to the surface of the material.
- Obtaining a given thickness. With the annual rate of destruction of galvanizing from 0.85 (minimum) to 6 microns, a thickness of 2-5 to 10-20 microns is required for a 5-15 year warranty on the body.
- Protection of complex parts.
Galvanic method
Galvanic galvanizing does not work well under all conditions. Below we present the optimal set of conditions and electrolyte composition.
Electrolyte composition.
- Zinc sulfate 200–300 g/l.
- Aluminum sulfate 20–30 g/l.
- Sodium sulfate 50–100 g/l.
- Dextrin 8–10 g/l.
- DCU 0.5–1 g/l.
Surface preparation.
Applying any coating to a car body requires careful preparation of the surface. You can’t do without it even before galvanizing. Before immersing a car part in a container with electrolyte, its surface must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt and oxides. Degrease and pickle with a special compound. If the surface of a body part is planned to be painted after galvanizing, it should be phosphated. For this, a 30-second treatment with a solution of the drug Majef is suitable, which must be diluted to a concentration of 30–40 g/l with the addition of 30–60 g/l zinc nitrate.
Of course, it is hardly possible to galvanize the entire car body at home. Therefore, cold galvanizing is more suitable for galvanizing a car body with your own hands at home.