A drill is a common cutting tool that is used not only to produce through holes by drilling, but also to increase the size of existing ones.
Technically, the products are attachments for hand drills, hammer drills and various machines.
Drilling itself involves removing material through the rotational movement of a sharp cutting edge.
The instrument is divided into a huge number of types according to its shape and purpose.
Drill characteristics
The main characteristic of any drill is its strength, which should exceed this indicator for the material being processed.
The tool, depending on the conditions of use, has different sizes and shapes.
The sharpening angle of the cutting part, color, etc. also differ.
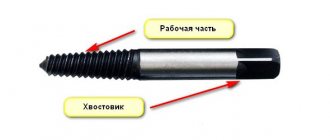
Each product has a shank, the type of which must match the chuck of a drill, screwdriver or machine.
Material
For the manufacture of drills, alloys with different characteristics are used.
In this case, the so-called “high-speed” steel grades P18, P9, P9K15 are used.
If the diameter of the drill exceeds 8 mm, a welding method is used in its manufacture, for example: carbon steel for the shank, high-speed steel for the working part.
For materials with high hardness (mainly metal), cobalt drills are usually used.
Their peculiarity is that the working part is made from high-speed steel R6M5K5, VK6M with the addition of cobalt.
NOTE
After the letter “K” in the marking there is always a number that indicates the amount of cobalt in the parts.
Carbide Pobedit drills are used for drilling concrete, stone and brick.
The tip of such a tool is tipped with pobedite, an alloy of tungsten (90%) and cobalt (10%), developed in the USSR. There are more than ten modern modifications of this alloy.
IMPORTANT!
The pobedite tip does not cut the material, but crumbles it, so it is not suitable for working with metal, plastic and wood.
In addition to tungsten and cobalt, chromium, molybdenum, and vanadium are found in the alloys, and their percentage is indicated in the marking.
Coating
To extend the life of drills, their body has one of the following coatings:
• Oxide film – significantly increases resistance to overheating from friction.
Also protects the product from rust.
The service life naturally increases.
• Diamond coating is the most durable coating available.
It is mainly used on those products that are used when working with extremely hard materials, including stone and porcelain stoneware.
• Titanium coating is a general name indicating that the material contains a chemical compound of titanium - TiN (titanium nitride), TiAIN (titanium aluminum nitride), TiCN (titanium carbonitride).
Coloring
The color of the drill is very important.
It indicates the coating used or processing method:
• Gray is the native color of steel.
Indicates the absence of any processing.
The cheapest and most short-lived products are gray in color.
• Black is the color of steel that has been exposed to superheated steam during finishing.
Black products are much more durable than the previous option.
• Yellow is the color of steel that has been tempered (processing of metal to relieve its internal stress).
It speaks of the high hardness of steel, and its brittleness is greatly reduced by tempering.
• Golden – the color of titanium nitride. Bright golden tools are very durable, and they also have reduced friction against the workpiece.
Dimensions and weight
Manufacturers of cutting tools offer an impressive range of drills of every possible “caliber”, depending on the design and purpose.
Let's look at the most common spiral products according to GOST:
- Short: 20 – 131 mm in length, 0.3 – 20 mm in diameter (GOST 4010-77);
- Extended: 19 – 205 mm in length, 0.3 – 20 mm in diameter (GOST 10902-77);
- Long: 56 – 254 mm in length, 1 – 20 mm in diameter (GOST 886-77).
As for the exact weight, it depends not only on the design of the products, their sizes, but also on the material of manufacture.
The weight of ordinary twist drills usually ranges from several units to several tens of grams.
Processing accuracy
For twist drills there is such a characteristic as accuracy class:
- A - increased accuracy (10 - 13 qualifications);
- B1 – normal accuracy (up to 14 qualifications);
- B – normal accuracy (up to 15 qualifications).
Quality is a characteristic of accuracy that determines the tolerance values.
Blade Hole Making Tools Types of Holes
The holes used in machine parts have different cross-sectional and longitudinal sections: cylindrical, conical, stepped and shaped. The holes can be through or blind, that is, they do not have an exit from the other side of the part.
Holes are also distinguished by size, required accuracy and quality of the machined surface (roughness parameters).
Hole Machining Methods
Using a blade tool, holes can be drilled, reamed, countersinked, reamed, bored, and pulled.
Drilling is a method of processing blind and through holes in solid material with a drill.
Drilling is a method of processing existing holes using drills.
When drilling and reaming, holes are obtained with an accuracy of 13-12 quality and a roughness of Rz = 10–30 microns.
Countersinking processing method:
— a previously obtained hole by casting, piercing or drilling;
- cylindrical recesses with holes for the heads of screws, bolts and nuts;
— conical holes for the heads of screws and rivets;
— center holes;
— end surfaces and bosses near holes and chamfering.
Spiral cylindrical countersinks are used for processing through cylindrical holes.
This increases the accuracy of the hole shape, corresponding to quality 11, and ensures surface roughness with Rz = 20–40 μm.
Conical countersinks and countersinks are used for processing holes for screw and rivet heads, center holes and chamfering.
Cylindrical countersinks with a trunnion or counterbore are used to process cylindrical recesses with holes for the heads of screws, bolts and nuts.
End countersinks with a trunnion or counterbore are used to machine the end surfaces of protrusions and bosses near holes.
Reaming is a method of processing holes with reamers in a material with a hardness of HRC40.
At the same time, the accuracy of the shape and size of the hole increases to 6-5 quality grades and the surface roughness decreases to Ra = 2.5–0.15 microns.
Reaming is mainly performed after boring or countersinking holes, and sometimes after drilling.
Boring is a method of processing a previously obtained hole by casting, drilling or some other method. In this case, boring cutters, blocks and heads are used.
Fine boring ensures hole accuracy of 6-5 grades, surface roughness Ra = 0.25–0.18 microns, shape error (ovality, taper) is 0.003–0.004 mm.
Broaching is a method of processing pre-formed holes with broaches, which usually have a complex shape (cylindrical, slotted, square, shaped and other shaped holes) with a diameter of 10 to 300 mm.
In this case, the holes receive an accuracy of 6-5 grades and a roughness of Ra = 0.15–0.08 microns.
DRILL
A drill is an axial cutting tool with two teeth. The drill carries out the technological operation of drilling and reaming.
Drill classification
Twist drills, the most common, are distinguished:
Drills made of alloy (9ХС) and high-speed (Р6М5) steels with conical and cylindrical shanks, diameter 0.1-80 mm.
Solid carbide drills, diameter 0.2 – 12 mm;
Drills with soldered carbide plates (VK6, VK6-M, VK-8, VK10-M, etc.), with a diameter of 1.2 - 12.4 mm.
Special drills. Currently, more than two thousand types of drills are used (feather, ejector and centering drills, single-sided cutting and annular drills, combined drills, etc.). They differ in design and geometric parameters, which is due to the variety of structural materials, as well as the geometric shape and requirements for the quality of the holes.
Classification of drills according to their purpose. Drills are divided into groups:
- Drills for hard and especially hard materials of high strength;
- Drills for non-ferrous metals and their alloys;
- Drills for light alloys;
- Drills for drilling marble, glass.
- Drills for drilling deep holes;
- Drills for precise holes.
studfiles.net
Types of drills
Products are divided into several groups according to design and purpose.
This allows you to quickly select a tool for specific tasks.
BY FORM
Based on the shape of the drill, it is quite easy to determine what material it can be used for:
Spiral
Classic instrument.
The working part has two teeth, which are twisted in a spiral.
The tool, biting into the material, pushes the chips to the surface with its grooves.
The shape of the tip depends entirely on the material for which the tool is intended.
As a rule, the diameter of products does not exceed 80 mm.
Screw
A modernized previous version, which has a more advanced form of grooves that remove chips.
Another difference is that such products are longer.
Feather
The product is flat in shape, the cutting part is made in the shape of a sharp peak, the outlines of which turn into a wider blade.
Other names are flat cutting drill, which is dictated by its shape, feather drill.
Builders call it perka.
Used where you need to get a deep and at the same time wide hole.
Ring
For those cases when you need to drill a hole with a large diameter without preliminary preparation.
More commonly known as a crown.
The shape of the tool resembles a hollow cylinder, and on the axis of rotation there is a centering twist drill.
The part that cuts the material is made either in the form of teeth, carbide tipped, or has a coating of diamond chips.
Conical (tapered)
Its shape resembles a cone with a sharp tip.
Suitable for working with metal whose thickness does not exceed 0.5 cm.
Just one tool can make holes of different sizes.
It all depends on the initial and final diameter of the cone, as well as on the immersion depth.
On the opposite sides of the drill there are special grooves with sharpened edges.
Stepped
A type of cone version.
The cone is divided into steps with increasing diameter, which have their own size.
The tool is convenient in that it allows you to monitor the diameter of the hole being formed during operation.
Spear-shaped
The shape resembles the tip of a spear, hence the name.
Used when working with hard, but at the same time fragile materials, such as glass and tiles.
Ballerina (ballerina)
Circular drill, which is used when working with wood and tiles.
It all depends on the installed cutting part.
Designed in such a way that the output is a perfectly smooth hole of large diameter.
The tool has a cross-shaped shape with cutters, the distance to which from the center can be adjusted.
This sets the diameter of the required hole.
The central part is a spiral drill, around which the cutters rotate.
Single cut drills
The cutting edges are located on one side relative to the axis of the tool itself.
In turn, they are divided into cannon type (the front end of the rod-shaped form is half cut off, which forms an outlet channel for chips)
and rifle-type (a compressed tube with a cavity through which coolant is supplied, and a groove angle of up to 120 degrees).
Tubular
Similar to crowns, but with a longer working part.
Forstner designs
An improved version of the spiral tool, but with additional cutters.
Zhirov's designs
A subtype of screw tool that has three cones on the cutting part, which is why its length is increased.
The design is also supplemented with a jumper with a groove, which is sharpened by a third of the cutting edge.
Designs by Yudovin and Masarnovsky
A tool with a large groove angle and a special shape, which distinguishes it from other types.
Countersinking
A monolithic cylinder having several cutting edges forming a cone.
Used for countersinking holes for screw heads.
BY PURPOSE
The instrument is divided according to its purpose, which is the reason for its special shape in each specific case.
The following drills are used in construction, at home and in production:
Universal
As the name implies, they cope with most materials.
They have a special sharpening, which received the corresponding name - universal.
On wood
These include spiral and feather, ring and screw.
Forstner drills and ballerina drills work well on wood, among others.
For metal
Conical, crown, stepped, as well as classic spiral.
On concrete
Crowned with carbide tipped, impact spiral and screw.
They have different shanks for hammer drill chucks.
For ceramics
Crowns, spear-shaped and ballerina.
The first ones are produced without teeth.
The cutting function is performed by a special diamond coating.
When working on glass, these are the types that are used.
For plastic
Special spiral options and crowns that can pass through material without breaking it.
There is a specialized tool that is used strictly to perform a specific task:
For deep drilling
Spiral tool with through channels.
Their purpose is to supply coolant directly to the cutting part.
This includes rifle and cannon subspecies.
Single-sided cutting
A tool whose main purpose is to create precise holes.
Subtype - ejector drills designed for drilling machines.
As the name implies, the cutting edges are offset to one side of the axis around which the tool rotates.
Centering
A specific tool capable of making only center holes in parts, but nothing more.
What do woodworking tools look like and how do they differ from metal drill bits for a drill?
By their appearance, metal twist drills for drills can be easily recognized and distinguished from analogues for woodworking. Tools of the second category come in two types.
Standard twist (screw) drill bits for wood
Standard screw drills for wood look like this.
Photo No. 2: twist drills for wood
Visually, they differ from metal drills in two parameters of the working parts.
- Woodworking tools have special peaks at the ends. They make centering much easier and make the machining process more precise.
- Drills for wood and metal can be distinguished by the angle between the cutting edges. For instruments of the first type, it varies from 90 to 100°. The angle between the cutting edges of metal drills is 110–140°.
- Tools for woodworking may have special scorers.
Image #3: Design of standard twist drills for woodworking
Screw drill 7 for wood 110 rub.
Add to cart
Screw drill 11 for wood 163 rub.
Add to cart
Screw drill 12 for wood 163 rub.
Add to cart
Lewis twist drills
Lewis twist drills look like this.
Photo No. 3: Lewis twist drills
They are designed for drilling perfectly smooth deep holes of small and large diameters in wood. In design, they are visually significantly different from standard ones.
Image #2: Lewis twist drill design
The main elements of such drills are the central rod and the massive Lewis spiral surrounding it. It is also called an auger. To facilitate centering, such drills have special threaded tips. Another difference between tools in this category is the small angle of inclination of the groove.
Twist drill 8x450 mm/D-07559 for wood MAKITA RUR 1,070
Add to cart
Twist drill 8x230 for wood 162 rub.
Add to cart
Twist drill 10x600 for wood RUR 234
Add to cart
Twist drill 10x450 mm/D-07565 for wood MAKITA RUR 1,168
Add to cart
Twist drill 12x600 for wood 435 rub.
Add to cart
Twist drill 12x200 mm/D-07266 for wood MAKITA RUR 1,180
Add to cart
How to choose a drill
When choosing a good drill for your home, you should focus on the color of the product, its size, and manufacturer.
As for shanks, one of the following options occurs:
- Cylindrical (for drills);
- Conical (Morse shank);
- SDS type (for rotary hammers);
- Triangular (for hand drills), tetrahedral, hexagonal (hex for screwdrivers and drills).
When choosing a drill for professional activities, the following will be useful:
• Marking is a combination of letters and numbers indicating such parameters as diameter, steel hardness, impurities in the alloy, place of production and its technology.
NOTE
The marking is placed on products whose diameter is more than 2 mm.
• Sharpening angle – differs for different materials and is the angle between the cutting edges.
The ease of drilling and speed depend on it.
Drill color and marking
Black metal drills are characterized by increased wear resistance, since superheated steam was used in their finishing. If the finished drill has been tempered, which helps relieve internal stress, it will have a light golden color.
Elements of a twist drill
The highest quality metal drills have not only increased strength, but also the ability to reduce friction during their work. These properties are possessed by a tool of bright golden color, the working surface of which is coated with a layer of titanium nitride.
If you want to choose an inexpensive metal drill, pay attention to those that have not been subjected to any additional processing. Such a tool, the service life of which is very short, is gray in color.
The marking of drills is determined by the diameter of their working part. Instruments with a diameter of up to 2 mm are not marked at all. On drills with a diameter of 2–3 mm, their size and steel grade are indicated; over 3 mm, the manufacturer and accuracy class are indicated.
At the beginning of the marking of any metal drill there is the letter P, which indicates that it is made from high-speed steel. If the material from which the drill is made contains additional alloying elements, then its marking contains the first letter of their name and a number indicating their percentage content.
What you need to know about drills
Morse taper type shanks are usually found on tools intended for installation in industrial machine tool chucks.
Since these shanks are available in sizes from KM0 to KM7, and the machine chuck is designed to work with one option, special sets of adapters are produced.
In addition to monolithic drills, drills with removable tips (feather drills) are produced.
As a rule, they are installed on universal CNC drilling machines.
The tips are made of various shapes from hard alloys or powder steel.
Important!
Drills coated with titanium nitride (TiN) cannot be sharpened.
Otherwise, all its strength indicators come to naught.
When do you need a special tool for drilling wood?
The question of how and what is the best way to drill a hole in a product made of chipboard, MDF, plywood or solid natural wood is relevant not only for carpentry specialists and those who professionally make furniture, but also for home craftsmen who prefer many jobs around the house do it yourself. The choice of drills for wood in such cases is made depending on what type of holes need to be drilled:
- blind, without an exit from the opposite side of the product (intended for mounting hinges on interior doors or on doors that are equipped with furniture structures);
- through (threaded connection elements (bolts and studs) are placed in them; without such holes it is impossible to install door handles and locks).
The main purpose of feather drills is to quickly make through holes of small depth. When drilling blind holes, be aware of the protruding tip of the drill bit.
For woodworking, you can purchase an expensive tool (such as a disk cutter). However, its use is not justified in all cases. For most situations where wood needs to be drilled, a tool that is easier to use and significantly less expensive will do the job. These are, for example, feather drills, which, despite their affordable cost, are highly efficient in use. A wood drill bit can be used in combination with either an electric drill or a regular screwdriver.
Drill manufacturers
Modern, time-tested manufacturers:
- Bosch is one of the top three brands in the world for construction tools;
- Ruko – good value for money;
- Bison is a manufacturer with a good pricing policy and tool durability;
- Haisser – powerful tools for industrial needs.
Particular attention is paid to Soviet-made drills, as the most reliable and durable.
Today it is difficult to find such a tool, however, every professional knows that a tool marked “Made in the USSR” is always preferable.