Purpose and principle of operation of the scraper
A scraper is a metal-cutting tool designed for scraping metal products.
This process makes it possible to achieve a minimum degree of surface roughness of parts and give them precise geometric parameters.
Using the tool in question, uneven surfaces are scraped off, resulting in a leveled surface, giving it maximum smoothness.
Depending on the type of operations performed, a classic flat scraper can be used:
- For rough processing of products, through which risks and traces of previous manipulations are removed. In this case, a tool is used with a sharpening angle of the cutting part of 70 - 75° with a width of 20 - 30 mm, which allows you to remove a layer of 0.02 - 0.07 mm.
- For semi-finishing, a tool with a width of 12-15 mm is suitable for removing 0.01 - 0.02 mm of microrelief in one pass.
- The cutting edge of models for finishing is made at an angle of 90° with a width of 5 – 10 mm. A tool with a pointed angle of 90 – 100° is used. For each pass, very thin layers (8 - 10 microns) of metal are removed.
In essence, a scraper is a tool for finishing metal products, through which microburrs are removed, the surface is leveled, work hardening is removed, and the geometry of the workpiece is precisely adjusted by removing a thin top layer of material.
You can scrape both flat and curved (including concave) surfaces and edges.
The principle of final processing with a scraper is to scrape off a layer of material similar to working with a chisel, while allowing movements of the tool both “from yourself” and “towards you”. The latter method is considered preferable due to higher productivity.
In addition to purely technical use, there is also a finishing use for the scraper.
In this case, the tool is used to create a design or pattern on metal.
NOTE:
When decorative scraping (inducing frost) the surface accuracy does not increase.
Scrapers are also used by auto mechanics to remove cotter pins, old gaskets, radiator hoses, and adjust parts to the required dimensions.
Table of contents
1. General Provisions
2 Control of the appearance and markings of instruments
3 Control of dimensional parameters and parameters characterizing the roughness of tool surfaces
4 Control of parameters characterizing coatings, hardness and strength of tools
5 Performance tests
| Date of introduction | 01.01.1987 |
| Added to the database | 01.09.2013 |
| Update | 01.01.2019 |
This GOST is located in:
- Ecology section
- Section 25 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
- Section 25.140 Hand Tools
- Section 25.140.30 Hand Operated Instruments
- Electricity section
- Section 25 MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
- Section 25.140 Hand Tools
- Section 25.140.30 Hand Operated Instruments
Organizations:
| 27.01.1986 | Approved | USSR State Committee for Standards | 202 |
| Published | Publishing house of standards | 1994 | |
| Published | Publishing house of standards | 1986 |
Fittter tools. Acceptance rules
For free
download this document in PDF format, support our site and click the button:
What material can the scraper process?
Scrapers are produced in different types, each of them has its own purpose.
Processing surfaces using the scraping method implies a tight, hermetically sealed fit between the tool and the workpiece, therefore it is used when working only with:
- Metal – guides of machine tools, surfaces of sliding bearings, fixtures and tools, individual parts of devices for the repair of units and components.
- Wood - well-sharpened models of a certain shape are required, depending on what result is planned to be obtained: rectangular, “swan neck” type and others.
- Plastic – allows you to process and clean the surfaces of plastic products of various shapes.
NOTE:
When working with metal parts, scraping technology, as well as the configuration of the tool, is determined, among other things, by the hardness of the material being processed.
For example:
- for aluminum and other soft metals such as brass, the sharpening angle of the working part should be within 35 - 40 degrees;
- for steel – 75 – 90 degrees;
- for bronze and cast iron products – 90 degrees or more.
Making at home
You can invent a scraper at home with your own hands. The main thing is to know a few tricks. To make this device we will need the following tools:
- Square rod measuring 15 mm.
- T5K10 plate.
- Emery.
- Vise.
- Bulgarian.
- Bolt with washer.
Having prepared these tools, we take the grinder in our hands and saw off thirty centimeters from the rod. This part will serve as the housing for our homemade device. Next, we clamp it in a vice and make a cut. Its depth should be three centimeters. Then we make a groove for the cutting surface one centimeter in size and drill a hole for the bolt that will clamp the structure.
Now the cuts need to be sanded and the plate installed in the groove. All that remains is to tighten the bolt and the device for removing roughness is ready.
Now let's look at how to make a scraper from a file.
The width of the device from which the device will be made must be at least ten millimeters. The length is equal to the length of the palm, and the handle should fit comfortably in the hand. Now we begin to manufacture a device for removing roughness on metal.
We transform the working edge into a part of a future device for working with metal. If you are going to do rough work with it when removing it, then you need to make a straight line, but if you are going to finish it, grind it out round.
After this, sharpen until a notch of 1 centimeter appears. We make the end flat and the sides rounded. Now it needs to be secured in a vice. Sharpened on an abrasive stone. It must first be filled with diamond paste.
The main advice when scraping metal is to select the right device. This is the only way to scrape the part perfectly and not ruin the scraper. Many professional workers in this field have entire sets of such tools. However, if you are an ordinary hobbyist, then you can buy a universal tool that allows you to change plates for each part.
Never attempt to clean metal that has serious defects over a large area. Such a part is subjected to rough processing on a milling machine. It is necessary to cover with a light layer of paint to determine the places where you need to start scraping the metal. It is necessary to paint after each scraping cycle.
A tool such as a scraper is known in various industries. Not only the locksmith, but also the manicurist knows what it is. Of course, we are not talking about exactly the same device, but their operating principles and design are similar. Let's find out more.
Device and characteristics
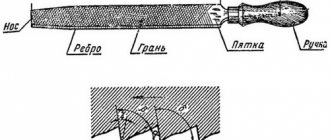
In its simplest form, a scraper is a hand tool, which is a metal rod, on one side of which there is a handle for easy holding and safe operation, and on the opposite side there is a cutting part with a certain sharpening angle.
The end faces, if we talk about a flat tool, are its cutting edges.
In addition to one-piece versions, there are also composite models with a holder equipped with a clamping screw for fixing replaceable cutting inserts.
This design is designed for the use of attachments of various shapes, which allows you to solve a wide range of problems with one tool.
In industry, along with hand tools, the following are most often used:
Pneumatic scraper (pneumatic scraper) - in a small body there is an impact mechanism with a piston, which transmits translational movements of a certain frequency to a removable attachment - a chisel. The tool is powered by compressed air, and therefore a compressor pneumatic hose is connected to its back. On average, the operating frequency reaches 2.2 - 4.5 thousand vibrations per minute, air flow is about 100 - 115 l/min.
An electric scraper (electric scraper) is a tool with a built-in electric motor, powered by a battery or mains. Can be used as an electric chisel or chisel. The average power consumption, depending on the model, is 150 – 350 W.
Among the classic scrapers, there are double-sided versions, where the working elements are located on both sides of the handle.
Also, for processing wide surfaces, a disk tool is used, where a sharpened carbide disk acts as the working part.
Material
The shaft of a hand tool is usually made of tool steel.
The working part is a carbide cutting element.
The material for the handle is plastic or wood.
Composite scrapers are equipped with replaceable plates, the raw materials for which are often alloys with high hardness values (64 - 70 HRC).
To work with soft materials and plastics, ceramic versions of the tool are used, equipped with a one-, two-, or even three-component handle.
As for pneumatic models, their body is made of lightweight but durable materials that can withstand high loads, such as aluminum alloys.
Electric versions usually have a plastic housing, rubberized where it is held by hand.
Dimensions and weight
The dimensions of a hand scraper depend on its purpose and the configuration of the cutting part, as a rule, they are within the following limits:
- Length: 190 – 550 mm.
- Width of the working part (depending on the scraping method): 5 – 75 mm
- End thickness: 2 – 4 mm.
For disk versions, the disk diameter is on average 50 - 60 mm with a thickness of 3 - 4 mm.
Hand scrapers weigh about 100 – 600 g.
The dimensions of pneumatic and electric options correspond to the characteristics of medium-sized drills.
Scraping technique
After completing the preparatory processing steps, the first thing to do is apply a special paint to the working surface. Its task is to indicate the lapping pattern, as well as to identify the most prominent areas on the surface. Sometimes large areas are zoned into separate areas depending on the difficulty of bringing them to the desired condition. One way or another, scraping is carried out according to the formed pattern. This means that processing is carried out not over a continuous area, but in a sense, pointwise. The efficiency and quality of the resulting cut are also determined by the frequency with which the stripping is performed. After the planned amount of cutting has been completed, the craftsman performs another coating of the surface with paint, which again reveals bulges and irregularities. In this way, the scraping quality is controlled. By the way, the operation cycle can be repeated several times, depending on how much each session brings the surface of the workpiece closer to the sample.
GOST
State standardization affected scrapers exclusively from the point of view of the rules for accepting this tool and the requirements for metals that can be used in production.
As for the geometric parameters, they are not regulated by GOSTs in any way, however, GOST 1465-80, which applies exclusively to files, is often mistakenly taken for such a standard.
Marking
There is no single marking scheme for scrapers; however, some manufacturers offering tools in sets use color divisions based on the material they are intended to work with.
Typically, handles or their parts (inserts) are painted in the following colors:
- Green – for processing aluminum;
- Red – for cast iron and brass;
- Blue – for steel;
- Yellow – for soft materials, such as plastic.
Separation by color allows the owner to immediately understand the purpose of a particular scraper.
How to learn to scrape correctly ↑
Scraping in home construction does not involve preliminary preparation of surfaces, but scraping metal in industrial conditions requires skill.
To work with a tool with your own hands, you need to know what scraping is - this is the order of operations performed sequentially.
- Lubricate the control plate with scraping paint - a mixture of soot and engine oil.
- Place the part that requires scraping against the plate and smoothly move it back and forth.
- Look at the spots that appear on the surface. White indicates the absence of paint and indicates the deepest places, black indicates the presence of paint and indicates the average depth, gray indicates the presence of protrusions that require scraping.
- Prepare a sharpened tool and start scraping off the rough edges. Hold the scraper at an angle of 30-40⁰, move forward with pressure, and return back calmly. Start with long strokes - from 20 mm, and slowly reduce the amplitude - to 5 mm. Move the tool in different directions - the strokes should intersect at an angle of 45⁰.
- Once scraping is complete, wipe down the part and repeat the staining process. Check the cleanliness of the grinding using a test square.
Mechanics of scraping
The 25x25 mm control frame allows you to determine how deep the scraping has been done. To do this, attach the frame to the part and count the number of spots inside it:
- 5-6 – rough;
- 7-10 – clean;
- 11-14 – exactly;
- from 22 – jewelry.
How to choose a scraper depending on the surface:
- straight - for grinding edges;
- shaped – for bent parts;
- narrow – for hard alloys and materials;
- wide – for scraping soft materials;
- radius – for flat surfaces.
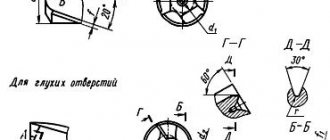
Scraper tip sharpening angle:
- standard – 60-70⁰;
- for bronze and cast iron - about 100⁰;
- for soft alloys – 40⁰.
Types of scrapers and their prices
There are two types of this tool according to the scope of application:
- A metalwork scraper is used when working with metal products, repairing components and assemblies, and cleaning their surfaces from residual sealant and gaskets.
- Construction - used in construction and repair for treating hard-to-reach places, large surfaces, removing paint, old plaster, putty and other materials, scraping dried adhesive from tiles.
The last type is an electric scraper.
Electroscraper
A tool with a body shaped like a cylinder, inside of which an electric motor is hidden.
The working part consists of a holder that moves back and forth at high speed, in which a nozzle of a certain configuration is fixed, depending on the tasks.
Pneumatic scraper
A pneumatic scraper is an analogue of the previous version, the mechanism of which is driven by compressed air.
A scraper for metalworking purposes, in turn, can be classified according to the type of drive:
Manual
A classic version that looks like a chisel.
It has a handle for holding, a base in the form of a steel rod, at the end of which there is a direct working part.
Its average cost is 600 – 1200 rubles.
Mechanical (mechanized)
Designed to speed up and simplify the work, since scraping is a rather labor-intensive and time-consuming process.
This includes electric scrapers, powered by the network, as well as pneumatic models, whose operating principle is similar to a jackhammer, through which fairly deep scraping can be achieved in one pass.
Their price can reach 40 thousand rubles, on average it is from 7 thousand rubles.
Since manual models remain the most common, their design is constantly modified by manufacturers to perform specific tasks, their functionality is expanded, and therefore on the tool market you can find:
Unilateral
Models where the working part is located only on one side of the base rod.
Double sided
They have two working parts of the same or different configurations, located on both sides of the handle.
Both of the above options can be solid (monolithic construction) or with inserted cutting inserts.
Universal
Here the working part of the scraper is equipped with a holder with a fixing screw or other clamp into which different cutting blades are inserted.
Thus, a universal or composite scraper is obtained, which is used to solve a wide range of problems by installing a plate of the required configuration.
The average cost is about 1000 – 1500 rubles.
According to the shape of the working part there are:
- Flat models - used for working with flat surfaces, open grooves and grooves.
- Triangular versions, as well as tetrahedral models, are mainly used for processing cylindrical and concave surfaces.
- Shaped - have a cutting edge that follows the shape of the surface being processed.
There are also semicircular, hook-shaped, spoon-shaped and other types of scrapers designed to perform strictly defined jobs.
In addition to the standard tool, less common variations are also actively used in practice:
- Disc scrapers – for processing wide surfaces.
- Ring – for working with round-shaped products.
Intrinsically safe
These are specialized models; the working part of such scrapers is made from special materials, for example, bronze alloys, copper, beryllium, etc.
Intrinsically safe scrapers are also non-magnetic due to the properties of the materials from which they are made.
Attention!
An explosion-proof tool must be certified.
The cost of specialized scrapers exceeds 12 thousand rubles.
Depending on how the working part of triangular, shaped and other scrapers is located relative to the handle, they are divided into straight and curved (curved).
The latter are convenient when working with soft materials, as well as elements with sharp corners.
Precise scraping of small metal parts requires specialized, suitable tools.
Jewelry (pawnshop)
Numismatists use miniature conical scrapers with a hardness of 50–60 units and a total length of about 115 mm when working with jewelry, and jewelers use miniature conical scrapers when working with jewelry, which is comparable to an ordinary ballpoint pen.
The cost of this jewelry instrument is about 250 rubles.
The manufacturing material is often various hard alloys.
The tool is suitable for restoring small finds of value; it is usually sold in sets of 4–5 units.
When processing soft materials, including plastics, a ceramic scraper is preferred.
It perfectly removes thin layers from flat surfaces and edges of products, and also effectively removes burrs.
Only the cutting part is made of ceramics, which is not subject to corrosion and does not require long sharpening times.
The cost of such a tool can reach up to 2 thousand rubles, depending on the manufacturer and the configuration of the cutting edge.
There are also special scrapers for removing burrs from the edges and corners of the workpiece.
Typically, such scrapers are sold in sets with attachments with different angles of inclination and curvature.
The cost of such sets starts from one thousand rubles.
Manicure
A tool that differs not only in purpose, but also in design.
It is used in cosmetology and is called a pusher; it is a metal rod with a blade having a tapering flat tip, which is used to pry the edge of the pterygium and move it to the base.
This procedure allows you to carefully and evenly cut the skin at the base of the nail using tweezers.
Several recommendations for using a scraper tool
In order for the scraping tool to serve you as long as possible and allow you to obtain high-quality surfaces, you need to follow simple recommendations for its operation. The main one of these recommendations, of course, is the correct choice of tool.
Many plumbing specialists have entire sets of scrapers, from which they select the one that is optimally suitable for solving a specific technological problem. You can do otherwise and purchase a universal tool with replaceable inserts, which can be quickly replaced with those needed in a certain situation.
Homemade head for scraper plates
You should not immediately start scraping if there are large scratches and other significant defects on the surface of the part that needs to be processed. Such a part must first be subjected to rougher processing, for which a milling machine or other equipment can be used.
After the surface is prepared for scraping, it is necessary to identify areas on the part that should be given special attention. To do this, you need to apply a thin layer of special paint to the surface plate and move the workpiece along its surface. As a result of such a simple manipulation, all the protrusions on the surface of the workpiece will be colored. This is where you should start scraping. The surface plate with paint must be used repeatedly, after completing each processing cycle.
Rough (scraping) scraping is used to remove the piled-up top layer from the plane
To perform scraping, the part is securely fixed in a vice, and large-sized products are processed on site. The tool itself is held with both hands in the middle part of the handle and moved towards you. It is very important to maintain the angle of inclination of the scraper in relation to the surface being processed (it should be about 800).
When starting scraping, you should keep in mind that the most convex areas are processed first.
Fitter's tools. Acceptance rules
Date of introduction 1987-01-01
The validity period was lifted by decision of the Interstate Council for Standardization, Metrology and Certification (IUS 11-95)
* REISSUE (January 1996) with Amendments 1, 2, 3, approved in November 1986, August 1987, June 1990 (IUS 2-87, 12-87, 11-90)
DEVELOPED by the Ministry of Machine Tool and Tool Industry**
PERFORMERS**
G.A.Astafieva, A.M.Krasnoshchekova**
INTRODUCED by the Ministry of Machine Tool and Tool Industry**
Deputy Minister V.M. Voevodin**
APPROVED AND ENTERED INTO EFFECT by Resolution of the USSR State Committee for Standards dated January 27, 1986 N 202** ________________ * Information data are given from the official publication, M.: Standards Publishing House, 1986. - Note from the database manufacturer.
This standard applies to metalworking and assembly non-mechanized tools manufactured for the needs of the national economy and for export.
What you need to know about scrapers?
Craftsmen, for whom the use of a scraper is determined by their professional activities, purchase different types of sets of this tool, where each unit is used for a specific purpose.
For periodic use at home, it is more profitable and cheaper to purchase one composite model with several replaceable cutting inserts of the configurations required to solve certain problems.
In some cases, for ease of operation, a longer scraper handle is required; for these purposes, special extension holders can be found on sale.
Manufacturers of scrapers
On the tool market you can find scrapers from well-known manufacturers, as well as homemade versions that have no name, made from low-quality steels, the markings of which are impossible to recognize.
The cost of the latter is noticeably lower, however, the quality of workmanship does not allow them to be used to the fullest; such options are simply useless, since they are not able to ensure the accuracy of the work.
Therefore, it is better to buy high-quality scrapers from reliable manufacturers.
- Hand scrapers are produced by such well-known companies as STEINEL, RENNSTEIG and Narex.
- Among power tools, scrapers from Bosch and SKIL are popular.
- Pneumatic options are produced by Licota, Bosch, Permon, Air Pro and the German company BIAX.
- Manicure instruments are manufactured by Zauber, Merci, Olton, Zinger.
- Among models for jewelry work, options from Zauber are popular.