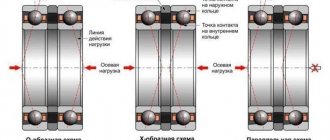
In order to remove the bearing from its installation location, use a puller. It has grips with which the bearing is grabbed and pulled together by the force of the spindle.
Always keep in mind that the force must be applied to the bearing race that is installed with interference.
Pullers are either mechanical or hydraulic, depending on the type of spindle used. As a rule, if necessary, the spindle can be replaced with another one.
Range of bearing pullers
Types of pullers by type of grip
There are 4 main types available for different types of gripping and dismantling:
- External puller Designed for external dismantling, when the inner ring of the bearing is installed on the shaft, and the outer ring can be grabbed from the outside.
- Internal puller Designed for internal dismantling, where the outer race of the bearing is installed in the housing and the hole in the inner ring can be grasped from the inside.
- Separator puller Designed for dismantling with gripping the bearing from behind using a tension separator, when its rear part is adjacent to the surface and the external type is not suitable.
- Puller with grip between rings Designed for dismantling bearings that are installed simultaneously on the shaft and in the housing, and all other types are unsuitable.
Purpose and features of the device
If a hum or noise appears in the area of the car wheels that confuses you, this indicates that the wheel bearing has broken. It is not recommended to delay repair or replacement of this unit. If you are not a specialist in this field, then contact the nearest service station as soon as possible, where the car will be inspected and given a consultation.
However, it is not always possible to use the services of professionals; in some cases you have to act on your own. One of the most difficult repair operations is the dismantling of bearings. This requires special tools.
The most primitive wheel bearing puller is an item consisting of the following elements:
- metal rod;
- gripper arms (2 pieces) with ends curved inward.
The device has a movable connection and the gripping distance can be easily changed. The paws can be used to remove and fix the following:
- rings;
- ball bearings;
- gears.
If the tool has three gripping paws, then it has more possibilities, since the paws can be deployed and used to remove internal elements. It is called an internal bearing puller.
The most versatile device is the combined pressing tool, which has the properties of both a two-legged and a three-legged tool. Its design includes special clamps through which damaged particles can be easily removed.
Mounting and dismantling bearings requires applying manual pulling force to seat or remove one or another element. The success of your work, as well as your own safety, depends on how correctly you choose the tool.
External bearing pullers
They work like this - the spindle tip rests on the shaft, and the claws cling to the outer ring.
To select the appropriate size external puller, you first need to determine the width and depth of the grip, and the required width of the grip jaws. Next, you need to evaluate the expected conditions of use in order to select its type.
If different grip depths and widths are required, you need a universal puller with movable parallel grips. The width is set by shifting the grips in the guides, and the depth by the axial position of the spindle. We offer tools with a working width range from 90...120 to 250...650 mm and a maximum working depth from 100 to 500 mm.
If the same operating conditions are expected, a puller with self-centering grips is suitable.
When different grip depths are planned, the best choice is a puller with articulated grips
For external gripping of bearings adjacent to the back of the surface, or if there is a risk of the jaws slipping, you should choose a puller with a side clamp that tightens the jaws together during operation.
Specifications
These tools differ in different parameters. So, according to the principle of activation, they are as follows:
- mechanical type internal bearing puller - it works by manual force and is designed to work with not particularly tight joints;
- Hydraulic bearing puller - used for hub devices and has a hydraulic drive, which helps to unscrew stuck particles and ease the operator’s efforts.
They have different devices and different operating ranges . They have two meanings:
- maximum working space width;
- maximum length.
The higher these indicators are for the front hub tool, the better it is. The working range can be different, for example, 185/225 mm or 290/380 mm and more.
Mechanical Bearing Pullers
Mechanical pullers are of the following types:
- internal;
- two-grip;
- three-grip.
Double-jaw tools are reliable and simple designs made from high-strength alloys through forging. It also ensures decent control over the entire work process.
They are used as wheel bearing pullers. Some modifications are designed for 1 diameter. They are more reliable because they have a monolithic design. But universal pullers are the most common and can be adjusted to any diameter. But this option has a slight backlash when performing a tightening force.
Three-grip options are more advanced in design and have three gripping arms. They are made from carbide tool steel by forging. They are used as bearing pullers on the front hub. The reliable gripping system allows them to also be used as generator bearing pullers.
Be sure to consider the build quality of its components when choosing a tool. In particular, there should be no unnatural play, and the hooks can be made at an angle to the base to properly secure the puller to the shaft.
Using internal pullers, ball or needle roller bearings are removed, as well as brass couplings of various shafts, crankshafts in particular. And similar pullers are needed for dismantling bushings and bearings with a tight fit.
There is another type of this tool - a special one, which is used for pressing out bearings of various automotive devices:
- generator;
- motor;
- cylinders and more.
These devices are manufactured to specific diameters and sizes, only this ensures their reliable operation.
Hydraulic pullers
The hydraulic method of installation or dismantling involves the use of special tools for seating or semi-automatic removal of bearing elements. Hydraulic traction is used here.
A hydraulic puller is a nut whose internal cavity presses on a special piston, which transmits forces to the part that is being removed or installed. Using this puller, you can remove wheel hub bearings from cars of different brands. It is also used as a puller for pulleys.
Hydraulic pullers are used for mounting and dismantling bearings of trucks and large vehicles. Their internal parts are quite massive, and human strength is limited.
How to work with a hydraulic device
To prepare the puller for work , you need to do the following:
- We check all its parts for serviceability. If there are cracks, deformations or signs of severe wear, it should not be used;
- accurately estimate the axial force required to remove the part from the shaft. If the force of the hydraulic cylinder is small, it cannot be used; select the option that is most suitable for this;
- operating temperature should be up to 45 degrees.
Then we proceed directly to the work itself:
- Place the grippers over the part to be removed. Screw the hydraulic cylinder of the puller into the nut with legs so that the end of the rod rests against the shaft with the part. The conical nozzle on the rod should fit into the centering hole of the shaft;
- screw the pressure release screw all the way;
- Using the handle, we pump oil from the tank into the hydraulic cylinder, and the rod should rest against the end of the shaft, and the part will move. When removing a part, you need to monitor the position of the working platforms of the paws relative to it so that they do not fall off;
- Depending on the model of the tool, the stroke of the rod should be 50−70 mm.
Many people are interested in how to properly maintain the tool and whether there are any guarantees for it from sellers and suppliers.
Thus, hydraulic oil will lose its properties over time and become contaminated. During operation, you may need to add oil or replace it entirely. Oil is added directly into the rubber container of the tank, located under the steel casing. To change the oil in the puller, the steel casing must be removed, then the oil is drained, but the rod cannot be pulled out. The working fluid is special hydraulic oil.
It is strictly forbidden to allow water to get on the tool, and its parts must be lubricated in a timely manner.
As for warranties, suppliers provide it for a period of 12 months from the date of purchase, but only if the consumer follows the rules for using the device as set out in the manual.
Suppliers accept all claims only if there is an instruction manual, as well as with a note on the date of purchase and the stamp of the company that carried out the sale.
Such warranty obligations do not apply to tools with mechanical damage caused by improper use, as well as attempts to repair them yourself, as well as if there is no oil in the tank or if the oil in the tank does not correspond to that recommended by the manufacturer.
Product quality must be controlled. Each instrument must undergo a series of special technical tests. Especially when it comes to hydraulic products. Such pullers can develop a force of 15 tons or more. Their production is controlled using special devices that carry out spectral and ultrasonic analyses.
Internal bearing pullers
They allow you to grab the bearing by the hole in the inner ring and pull it out of the housing. When choosing, it is necessary to determine the diameter of the bearing bore and select the type of spacers - three-jaw, segment or for needle bearings. We offer pullers for hole diameters from 5 to 200 mm.
Next, if there is a supporting surface on the body for a stop, you need to choose a puller with a counter support and a spindle.
Otherwise, you need a puller with a reverse hammer.
Types of universal pullers
There are two types of universal pullers - mechanical and hydraulic. The former are easier to operate, cheaper and more effective. They create a load on the spare part approximately equal to the strength of a person. This tool consists of a central rod on which there is a universal thread, and 2 or 3 legs. Mechanical tools are used for bearings and similar parts.
Hydraulic devices can withstand loads of up to several tens of tons. They have a hydraulic cylinder and do more serious work than power tools. Often used in cases where the spare part is located deep and it is necessary to avoid damage to third-party parts.
Design features
The hydraulic system of the device acts on the support rod. To fix the puller relative to the part being removed, different support platforms are used:
- clamping claws;
- sites;
- other.
First of all, a hydraulic puller is installed on the structure with a bearing (another element), and then the rod is positioned. The hydraulic system provides pressure on the part being removed, and it is squeezed out of its socket.
Our device allows you to remove the following structural elements:
- bearings;
- pins;
- bushings;
- gear transmissions;
- couplings;
- brake discs;
- crankshafts.
Pullers are used at car service stations and repair shops. They are quite simple in design and can work without electricity , compressed air, etc.
With swivel grips
They are more varied in design. The grips in them are locked with bolts.
A puller with two rotating double-sided jaws has stops that have different widths at both ends of the jaws. It comes with three rotating one-sided grips; the reach of the grips can be changed by rearranging them. There is also a model that can be used with either two or three rotating single-sided grips. There are 4 points on the body of the puller for installing grips.
Some can be used with an impact (inertial) puller. They can also be used as internal ones, but then the clamp can no longer be used to secure the grips. Crossed grips allow you to change the grip over a wide range. A small (working width up to 50 - 70 mm) tool of simple design, originally intended for removing the ends of battery cables, but is widely used for dismantling various small parts.
Homemade puller
After familiarizing yourself with the industrial versions of the special tool, it is easier to understand how to make an oil filter puller on your own. To do this, you need to choose a simple device design and copy it for personal use. The main nuances are:
- Making Crab and Cup parts at home will be more expensive than buying a tool in a store;
- Usually scrap materials, waste from cutting rolled metal, fasteners, used tow rope tape and consumable belts are used;
- the device should be easy to use, then you can unscrew the filter quickly;
- there is no need to copy the entire linear series, because a specific internal combustion engine uses one filter size.
The most popular homemade options are discussed below.
Chain
To build a chain oil filter puller on your own, you will need the following materials:
- a piece of double-row chain, for example, a bicycle chain, slightly longer than the diameter of the filter (2 - 4 plus links);
- hexagon 5 - 7 cm long of any size for a standard key.
The chain can be welded to the hexagon or first rivet it into a loop, weld a piece of rolled metal from the inside anywhere. The work will take 15 - 30 minutes, you will need a hammer and a welding machine.
Chain and hex tool
In the absence of a piece of rolled metal, you can take an adapter shank for a cone drill. In this case, you will have to turn the top part turnkey.
Homemade chain tool
A piece of tube flattened at one end will eliminate the need for welding. To do this, insert the edges of the chain into the flattened end of the tube, drill a hole to fix it inside, for example, with a nail or screw through.
Chain attachment with tubular handle
Belt
If you use a belt loop, you can pull out the oil filter yourself even faster:
- a piece of belt, preferably with transverse slots, wraps around the filter with the smooth side;
- the ends are passed through the hole of a spanner wrench of a suitable size;
- When rotating, the belt splines prevent it from slipping into the key eye.
Homemade belt wrench
The material has sufficient roughness and elasticity to transmit torque without tearing or twisting.
If you make a slot in the socket head and place a similar piece of belt in it, you will get a more convenient device for working in confined spaces.
Belt key from head
Tape
In the garage, unscrewing the oil filter consumable element can be done with a piece of used tow rope made of nylon tape. In principle, the handles of bags and backpacks are suitable, which allows you to avoid investing additional funds in repairs.
The characteristics of the tape are slightly inferior to the belts, but they have a similar shape, so it is logical that all keys are made using the same technologies. The most popular end puller is:
- a groove is cut in the hexagon, bolt, socket head;
- 2 through holes are drilled for screws;
- The edges of the tape are laid and fixed with screws or rivets.
Homemade band wrench
The adapter for a cone drill already has a groove, but in hardened metal it is difficult to drill holes for fixing the belt with screws, so you can sew a ring from this material, pass one edge through the hole, and insert an improvised fastener made of a nail or wire on the other side.
This will not change the principle of operation of the key; it’s just that at the moment of selecting free play, this locking element must be held until the tape is fully tensioned.
Clamping
This homemade device is copied from the Cup. However, at home it is difficult to make slots on the inside of the pipe, so the tool is secured to the filter body with a clamping screw. The top arcuate plate is welded to the tubular spool to secure the hex socket/wrench nut.
Homemade clamp puller
Due to the simple design of the key, a drawing is not required; it is enough to cut a piece of pipe with an internal diameter slightly larger than the filter, about 5 cm long. If the nut is located at the top, you can use a homemade puller, even in a confined space.
With conical jaw lock
They have two or three grippers and are intended for use in cases where it is necessary to eliminate the asymmetrical load application during dismantling. They provide automatic centering of the jaws using a conical nut that is hand-tightened when the puller is installed. Sometimes this nut is spring loaded.
For external and internal use of such a puller, grippers of different shapes are usually used. Less commonly used is a specially shaped nut that allows the jaws to be reversed so that the puller can be used as an external or internal puller. They are often included in kits along with impact pullers.
Types of hydraulic pullers
The designs and technical characteristics of devices can be very different. To choose the optimal model, carefully analyze the operating conditions. At a specialized service station, for example, mobility, the ability to install in hard-to-reach places and reliability are important.
The first step is to find out the maximum force that the hydraulic system provides. For work in a car service, models with a pressure of up to 15 tons are sufficient. When it is necessary to dismantle large bearings, more powerful pullers are selected.
Depending on the design, the following selection parameters are distinguished:
- A type of pump that can be built-in or remote. In the first case, the compactness of the model increases. To work with complex structures, it is recommended to choose a hydraulic puller with a remote hydraulic system.
- Type of clamp - paws or platform. The platform is used when it is possible to make mounting holes. The paws are used for installation on the structure without violating the integrity.
- Method of increasing pressure in a hydraulic cylinder. This can be done manually or using external devices - hydraulic pumps or compressors. These devices allow you to quickly create the required pressure in the device.
Increased functionality of some models is achieved through the ability to install clamps. In addition, the mobility of the device is taken into account. Stationary models allow bearings or similar units to be removed after the structure has been installed in the machine. Mobile models are mounted on the hub or other element of the car.
The applied force is monitored by a built-in dynamometer. This helps prevent damage to the element being removed.
pullers
The times when most plumbing operations were carried out, as they say, “on the knee” are long gone. Foreign-made vehicles, as well as structurally relatively simple domestic cars, having received imported components and assemblies, now require a qualified approach to their maintenance and repair using special tools and devices. This is dictated by the requirements for the quality and timing of certain operations specified in the regulations for the maintenance and repair of equipment.
Since mechanics do not use this type of locksmith equipment as often as conventional locksmith tools - wrenches, socket heads, wrenches and extensions, the owner of a service station or the manager of a repair area of a large ATP is tempted to save money and buy cheaper pullers. Fortunately, tool manufacturers from China, India and Turkey have literally flooded the market with analogues, or even exact copies of devices from famous companies. But not all servicemen realize that the price of a puller includes not only materials, but also the technologies with which it is made.
In other words, two tools that are absolutely identical in appearance will have different consumer properties. We’re not even talking about the service life of a cheap tool. It's frankly small. The second extreme is the unreasonably inflated price for products manufactured under the famous brand of a manufacturer of commercial vehicles and/or components and assemblies. Manufacturers of commercial vehicles will never independently develop special tools and equipment. They delegate tasks for the production of these devices to companies that specialize in this. In addition, these firms produce the same devices for the free market.
To produce devices for both markets, these companies do not skimp on the quality of the materials from which they make their products. The technologies are also the same. It turns out that the consumer must pay more for tools and equipment that are identical in quality only because they have a special mark. It’s no wonder that prudent business owners adhere to the “golden mean” rule. Let's consider pullers from companies from this very middle.