Polypropylene fiber is an artificially created material that was first used in the 70s of the last century in the USA as additional reinforcing agent, preventing the formation of microcracks on the concrete road surface. The experience was so successful that cracks from temperature differences stopped appearing in concrete sections with reinforcement, which was especially important during severe frosts.
Ten years later, this polymer has become an integral part of any construction process, where reinforcement at the micro level has become a priority. Already in the 80s, in many European countries, fiber gradually replaced metal mesh for semi-dry concrete screed, gaining increasing popularity.
The technology, which uses polypropylene fiberglass as reinforcement (the price of which is much lower than stainless steel mesh), came to the territory of the former Union after 2000. Now there is a significant increase in the use of polymers in domestic construction, both in the professional and domestic segments.
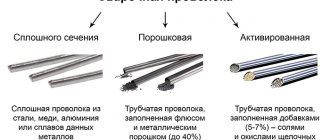
Many people often ask the question: “Fiber for concrete – what is it and what does it look like?” We answer: externally the material is chaotically mixed white fibers of different lengths and with a translucent structure. Each fiber has a length from three to eighteen millimeters (depending on the brand) and a diameter of around 20 microns.
What is fiber fiber
Concrete has specific characteristics that define it as a brittle substance with a heterogeneous structure. Its ultimate deformation value is much lower than, for example, glass, steel or polymer composites.
To increase elasticity, it became necessary to use fibrous additives (fiber) as micro-reinforcement for concrete structures. This feature has found wide application in the technology of construction processes, such as the preparation of cement mixtures, the production of high-strength materials, etc.
Fiber is a material in the form of lengths of threads or narrow strips of organic or inorganic origin. The mechanical characteristics of fiber-reinforced concrete depend on the number and arrangement of fibers in the solution.
The method of dispersed reinforcement of concrete provides for arbitrary and directional orientation of the fibers.
Directional involves the use of thin continuous threads, woven and non-woven meshes, strands and other similar materials. Free (free) occurs when using rolled materials in the form of mats, canvases, veils.
What is fiber?
Fiber is thin fibers or strips made from different groups of materials. It can be organic or inorganic. The size and profile of these fibers depend on which variety you choose. It could be a few millimeters, or it could be several centimeters. And all this “trifle” is carefully mixed into the solution at the stage of diluting it with water. Filling the entire volume, it then serves to increase the strength of your structure.
At first, only polypropylene fiber was available, but now steel, glass, and basalt are used, depending on the initial tasks.
Photo: beton-house.com
The dosage of adding fiber to concrete depends on the loads the structure will be subjected to. For example, if we mean a garden path along which a gardener will walk with a bucket, that’s one thing, and under minor loads the fiber can be left out or mixed in in a low dosage. But if we are talking about, say, a strip foundation, it’s a completely different matter, and many zealous owners want it to be fiber-reinforced concrete, and powerfully reinforced with a microframe.
Main components of the supplement
The technology for manufacturing additives depends on the type of reinforcing components used. Not all fibers meet the requirements for reinforcement cages.
Metallic and non-metallic threads of different lengths and cross-sections are used as fibers:
- In terms of construction, the greatest effect is obtained from the use of steel fibers, the deformability modulus of which is 6 times higher than that of concrete.
- The use of polypropylene can reduce the risk of cracking during plastic shrinkage of mixtures by 60-90%.
- Glass fiber has low alkali resistance and is used only for preliminary reinforcement in the manufacture of gypsum products or wall blocks made of cellular concrete.
- Basalt fiber is resistant to alkaline processes. The elastic modulus is 15-20% higher than that of glass fibers.
- Asbestos fibers are neutral to the aggressive effects of cements and are characterized by high strength and fire resistance.
A rational choice of additives for concrete reinforcement makes it possible to obtain products that are resistant to mechanical loads.
Fiberglass has low alkali resistance.
Steel additive for concrete
Steel fiber for concrete consists of pieces of wire. Their length can vary, from 25 to 60 mm, with a diameter from 0.7 to 1.2 mm. The uneven, rough surface of the starting material provides excellent adhesion to concrete ingredients, sand and cement. Metal fiber with curved ends is often used. Although, its form can be any:
- straight;
- arcuate;
- triangular section;
- wave;
- smooth or rough metal structure.
Advantages
The widespread use of fiber-reinforced concrete is due to the fact that its physical and mechanical properties are several times better than those of traditional materials. At the same time, the performance characteristics of the products comply with the standards.
Strengthening the screed
To strengthen coatings, it is recommended to use steel fibers with a length of 35-75 mm and a diameter of 0.3-1.0 mm. Heavy concrete of class B25-B35 with a coarse aggregate size of no more than 20 mm is chosen as a cement matrix.
The use of dispersed reinforcement with steel fibers will enhance the performance properties, strengthen the top layer of the base, increase wear resistance, bending strength, crack resistance and durability of the structure.
Prevention of defects
The occurrence of defects in concrete pavements is associated with a violation of the technological process. This is explained by thoughtless savings, non-compliance with the norms and rules provided for this type of structure. Such negligence leads to the appearance of cracks, chips, and potholes on the surface.
As practice has shown, the most effective means for preventing and eliminating defects that have arisen are repair solutions reinforced with various types of fibers. The use of steel or polypropylene fiber makes it possible to avoid the delamination of mixtures during the laying period, and subsequently premature wear and destruction of coatings.
Improved adhesion and water resistance
The water resistance of concrete can be improved using dispersed reinforcement. Since the properties of fiber-reinforced concrete depend on the characteristics of the fibers used, by choosing a material with the necessary characteristics, you can successfully solve the problem.
For example, the use of steel and basalt fibers will increase the water resistance of products several times. To obtain better adhesion of fibers to the cement matrix and uniform distribution of fibers, it is necessary to correctly select the optimal length and diameter of the segments used.
Cost-effective and anti-corrosion properties
The use of fiber for reinforced concrete structures, when part of the frame is replaced with dispersed fibers, allows one to obtain tangible benefits, since the price of modifiers is much lower than the cost of rod reinforcement.
Another big advantage of using steel fiber is that it is protected from corrosion by a dense cement coating.
With proper use of additives, you can obtain an economically useful product with improved performance properties.
Material consumption
Before using fiber, you need to determine the consumption of metal additives for concrete. And this will largely depend on the loads to which the structure will be subjected in the future. If they are insignificant, then a consumption of 15 to 30 kg per 1 cubic meter of concrete is sufficient. For medium loads, the value should be increased to 40 kg. If we are talking about high pressure on the elements, then a fiber consumption of 40 to 75 kg will be required. At even more critical loads, this value can reach 150 kg of metal filler consumption per 1 cubic meter of concrete mixture.
The amount of fiber used to prepare concrete can be seen in the instructions attached to the original packaging. The best result of using the additive will be achieved with the correct ratio of the amount of this material per 1 m3 of concrete, cement or dry mix. In the production of prefabricated products or during monolithic construction work, fiber consumption can vary significantly.
Here are the consumption rates for fiber fiber in commonly used building mixtures:
- For the preparation of concrete, foam concrete or other porous structures, the average consumption of metal fiber ranges from 500 g to 900 g/1 m3.
- When the additive is included in dry plaster mixtures - from 600 g to 1 kg.
- In preparing the composition for casting decorative stones for facade cladding, as well as gypsum products, it is allowed to use from 400 g to 800 g of fiber.
- Concrete mixture for roads includes metal raw materials from 1 to 1.5 kg/m3.
- For screeds for paving slabs and the production of small architectural forms, you can use from 1.5 to 2.5 kg.
Based on the list above, it can be seen that the average fiber consumption is 0.4-1.5 kg per cubic meter of concrete.
Types of fiber fiber for concrete and its properties
The introduction of modifiers in the form of fibers into concrete helps to improve operational and performance characteristics. The mechanical properties of fiber reinforced composite materials depend on the type of additive, volume and size of the elements.
Steel fiber
Metal fibers used as reinforcement cages are produced by various methods:
- electromechanical;
- mechanical;
- from molten metal by molding.
The most widespread are mechanical methods, using which the following types of materials are obtained:
- Wire fibers, which are pieces of thin wire 10-50 mm long.
- Sheet fibers are produced by milling a thin sheet of metal.
- Ultra-thin ones are made by melt extrusion and subsequent drawing through diamond filters.
Steel fiber.
Advantages of dispersed reinforcement with metal fibers:
- resistance to dynamic and static loads increases;
- crack resistance;
- wear resistance;
- seismic resistance;
- frost resistance.
With a fiber content of 0.5% or more, the workability of the mixtures increases. With an increase in the volume of the additive in the range of 02-0.8%, an improvement in tensile-compressive strength is observed.
Glass fiber
This group of additives is produced from silicate materials and molten volcanic rocks. Glass fiber has a length of 20-40 mm and a diameter of 10 microns. Its main feature is its high tensile-compressive strength (1500-3000 MPa). The elastic modulus of such modifiers is several times higher than that of concrete.
For cement matrices, glass threads woven into bundles are used. The harness is divided into segments of equal length, the exact dimensions of which are specified by the technological map.
Asbestos fiber
To reinforce concrete, sections of fibers, veils, canvases and materials in the form of non-woven meshes are used.
Asbestos fibers have the following qualities:
- high strength (300 kgf/mm²);
- fire resistance (up to 1500 °C);
- resistance to alkaline environments (9.0-10.1 pH);
- low electrical and thermal conductivity (0.045-0.065 W/m∙K);
- durability.
When reinforcing concrete, sections of fibers and materials in the form of non-woven meshes are used.
The tensile strength of asbestos fiber exceeds the similar properties of steel.
Basalt fiber
Basalt fiber is equal length pieces obtained from molten natural stone of volcanic origin.
The introduction of additives improves the following indicators:
- crack resistance - 2 times;
- frost resistance - up to 500 cycles;
- impact resistance - 5 times;
- elastic modulus - by 30-40%;
- by 20-50% - compressive strength;
- waterproof - 50%.
Basalt fibers provide high adhesion to the cement matrix, do not corrode and do not ignite under the influence of open fire.
Polypropylene fiber
Polypropylene fiber is an alkali-resistant material, compatible with cement and gypsum binders.
It is a synthetic fiber with a diameter of 0.02-0.038 mm. Fiber is made from polypropylene film by cutting and twisting into bundles. The tourniquet is divided into segments 0.3-0.5 mm long. In the concrete solution, the weave opens up and creates a network structure.
The use of polypropylene fiber allows you to:
- increase water resistance;
- frost resistance;
- tensile bending strength;
- increase fatigue and impact strength;
- heat resistance;
- wear resistance;
- improve the quality of the base of concrete products;
- strengthen the ability to withstand alternating loads;
- prevent mixtures from separating.
Polypropylene fiber reduces the risk of cracking by 60-90% and reduces shrinkage of concrete.
Construction of houses
0 votes
+
Vote for!
—
Vote against!
Fiber is an auxiliary building material, which is a synthetic fiber used for micro-reinforcement of concrete structures. Often, fiber is also added to dry mixtures and solutions in order to improve their properties and characteristics. With the advent of this material, developers got rid of most of the hassle associated with pouring concrete, now numerous processes have been significantly accelerated and simplified, and finished objects have become more reliable and durable. What is fiber for concrete, what types exist, how is it used correctly and what are its advantages?
Why is fiber used for concrete?
In modern construction, such a universal and proven material as concrete is widely used. This is explained by the properties of concrete, such as:
- strength;
- durability;
- the ability to use for the construction, installation and finishing of a wide variety of objects;
- low cost.
Concrete is good in many ways and no analogue has yet been invented. Despite the abundance of new materials, it still does not go out of use and will be in demand for many more decades. But concrete also has its disadvantages. Under constant and intense loads, under the influence of weather factors, wind and moisture, with temperature changes and shrinkage, this material is susceptible to mechanical damage, such as cracking and destruction. Particularly affected are the edges and joints of concrete structural elements. To increase the strength of concrete, improve its structure and extend its service life, microfiber fibers are added to the solution - thanks to this, an excellent building material becomes even better.
Advantages of combining concrete with microfiber
When concrete is reinforced with fiber, it gains the following valuable qualities:
- plasticity and viscosity, which makes working with it more convenient, quick and easy;
- frost resistance;
- waterproof;
- no deformation after hardening;
- abrasion resistance;
- strength and durability.
In what areas is fiber used?
The areas of application of fiber are almost unlimited - just like concrete.
- It is used for the construction of concrete road surfaces and platforms, hydraulic structures (swimming pools, drains, water canals and reservoirs), bridges and piles for them, pouring foundations, gunite and plastering, construction of monolithic structures and industrial premises (hangars, warehouses, sales areas) .
- It is also used in the manufacture of figured cast products of any shape and size, which allows you to create more original architectural designs for decorating buildings.
- Often, a solution containing polypropylene, glass, basalt or other fibers is used to decorate the facades of a building, since concrete does not change its appearance at all, but at the same time becomes more plastic, holds its shape better and does not collapse for a long time. The use of fiber can prevent warping, cracking and chipping at the edges of concrete joints and precast structures.
What types of fiber are there?
Depending on the raw material and size, the following varieties are distinguished.
- Glass fiber . This type is used only for finishing and decorative work, as the fibers quickly become brittle and are not able to withstand heavy loads in concrete structures. When adding these glass fibers to the solution, the consumption of cement and water is significantly saved - by 15 and 20%, respectively. Consumption per square meter of concrete is an average of one kilogram.
- Basalt fiber . The main advantages of this variety: non-flammability of the material, non-toxicity, resistance to aggressive chemicals. The peculiarity of fibers is that when combined with cement, they completely dissolve in it and increase its strength. Due to its characteristics, basalt fiber can be used for the construction of heat-resistant concrete structures. For one square meter of concrete, 1.5 kg of material is consumed. The consumption of cement and water is also reduced by 15 and 20% when using basalt fiber.
- Polypropylene fiber for concrete . This type of material has excellent technical characteristics, significantly increases the strength of concrete, does not form cracks and is very durable without compromising its properties and qualities. Most often used for dry screeding of floors, installation of walls and foundations. Material consumption per square meter is approximately 1 kg.
- Steel fiber for concrete . The most popular and frequently used type of material, as it can provide unlimited possibilities in construction. Gives buildings and structures high strength and resistance to external influences, reliability and durability. Material consumption per square meter is from 30 to 40 kg.
- Anchor fiber . This material consists of pieces of wire, added to concrete if it is necessary to shape the curves of buildings and other structures, and gives the structure additional strength. One square meter of concrete requires from 20 to 40 kg of material. Consumption of cement and water is reduced by 15 and 20%.
Also, depending on the purpose and scope of use, fiber comes in different sizes - 6, 10, 12, 18 and 20 mm in length and from 0.3 to 0.5 mm in diameter. Various types of fiber are designed to work with various materials - concrete, plaster, dry mixtures and mortars.
How and where fiber is used depending on the length
It was not in vain that manufacturers developed several different length options for this material.
- Small fiber - 6 mm - is used to increase strength and improve geometric shape when working with mixtures such as cement, sand, gypsum, in plaster and grout mixtures, as well as when working with foam concrete.
- Concrete fibers measuring 12 mm are used to strengthen and increase the strength of various floor slabs, non-autoclaved gas and foam concrete, for self-leveling concrete floors and foundations, piles, hollow concrete structures, and hydraulic structures.
- The largest fiber with fibers 18-20 mm is intended for working with heavy and especially heavy concrete, which is mixed with the addition of coarse filler - crushed stone, gravel, coarse sand. Indispensable for the construction of bridges, laying road surfaces and other large structures that require increased strength and resistance to mechanical stress.
Fiber mixing technology
- In order to combine fiber with cement, gypsum and other mixtures, in addition to the materials themselves, a concrete mixer or mortar mixer and water are needed. There are several ways to mix the solution. As a rule, the following technology is most often used.
- First, dry raw materials are poured into the concrete mixer - cement, sand, gravel or a mixture of them, fiber fibers - then water is added in accordance with the proportions indicated by the manufacturer on the packaging.
- It is not recommended to violate these proportions. A solution that is too thick will be difficult to work with, while a solution that is too liquid will shrink more, become brittle, and quickly crack. To prepare the solution, 5 to 10 minutes of stirring are required. If it is desired to increase the elasticity of the material, a plasticizer is also added to the mixture. Sometimes the fiber is cured in a plasticizer, rather than in water, before being added to the cement mixture.
- When a small amount of material is required, mixing can also be done using a mixer. Sometimes another technology for preparing the building mixture is used. First, the fiber is filled with water. After the fibers are evenly distributed throughout the entire volume, they are combined with cement.
- The consumption of fiber for concrete depends on the purpose for which the solution will be used. So, for floors 30 kg/m3 is enough, and for walls about 50-55 kg/m3.
Additional Information
- Fiber is available for sale to consumers in bags of various sizes from one to twenty kilograms. Small packages are additionally packaged in corrugated pallets made of dense polyethylene. Bags can be either plastic or paper. If we talk about the use of the material, it is much more convenient to use it in paper packaging. When mixing the solution, it is not necessary to open and remove it, but can be immediately placed in a concrete mixer. In the process of combining the dry mixtures and water and stirring, the paper bag will completely dissolve. Such bags are called water-permeable and are very popular among builders.
- It is convenient to pump the finished mixture, which contains fiber. This method is used when constructing large buildings and structures to speed up the process.
- Sometimes, after hardening, individual hairs can be seen appearing on the surface of the concrete. If no further finishing coat is planned, the hairs are set on fire using a special lamp. If paint or other finishing material is applied on top, it is recommended to leave protruding fibers. Thanks to this technique, increased adhesion of the concrete surface to the outer coating is ensured.
- To obtain a high-quality solution that will provide the required effect after hardening, it is important to strictly follow the dosage prescribed by the special GOST. The duration of mixing also matters. Usually the time is calculated using a very simple formula: another 15% should be added to the time required for mixing cement mortar without fiber in the apparatus if fiber is added. That is, if mixing the base solution should last ten minutes, adding fiber will increase the time by another minute and a half.
- When building large industrial facilities, to save time, the solution is often mixed in automobile mixers. In this case, fiber bags are placed in a mixer along with other components. By the time the car reaches its destination, the mixture will be completely ready. If fiber is added to a ready-made cement mortar in a truck mixer, the mixing time for complete distribution will be from five to eight minutes.
- Polypropylene fiber is often used by architects and sculptors to create small figures and decorative elements cast in molds. With its help you can give additional strength to gypsum products. It is often purchased for artistic creativity at home.
- Thanks to such a versatile material as fiberglass, you can get several other advantages: If the concrete was poured into the formwork, then you don’t have to worry about it deforming or cracking after the formwork is removed. It is much more convenient to control and correct the spreading of cement mortar during shrinkage if fiber of any type has been added to it. And after it hardens, so-called cement laitance is guaranteed to never appear on the surface.
Buy fiber for concrete
- Many people are surprised why the price of fiber for concrete varies so much. The cost is determined, first of all, based on the basis on which the material is made. The most expensive are those for the production of which polypropylene synthetic fibers were used. The most affordable ones are made of steel and wire. But, given the high consumption of the latter, it is unlikely that anything will be saved. Therefore, you should choose the type of fiber not by price, but by its qualities and purpose.
- The manufacturer and region also play an important role. The same variety of different brands can vary significantly in price. If building materials are delivered from afar, their price can increase significantly.
Fiber for concrete of any kind is indispensable in modern construction; today, not a single installation of reinforced concrete and other structures can be done without this material. As a conclusion, we can say that its main advantage is the ability to impart strength to concrete and other materials.
Scope of application
The choice of technical solutions for dispersed reinforcement depends on the type of fibrous materials used.
For example,
basalt fiber
wear-resistant, therefore suitable for strengthening structures used in places with increased requirements for mechanical stress:
- production sites;
- industrial floors;
- pedestrian paths with heavy traffic, etc.
The resistance of basalt fiber to chemical factors and seismic resistance allows its use in the following areas of residential and industrial construction:
- during the construction of hydraulic structures;
- in bank protection works;
- when constructing earthquake-resistant structures;
- explosive objects;
- in the production of chemically resistant reinforced concrete pipes for transporting aggressive liquids.
Basalt fiber is widely used in various areas of residential and industrial construction.
Basalt fiber is an indispensable component in the production of aerated concrete, foam concrete and other products made from cellular concrete, and also serves as a structure-forming material in the manufacture of shaped products for small architectural forms.
Steel fiber reinforced concrete is used
in the construction of structures requiring increased strength:
- Monolithic structures: highways, industrial floors, screeds, etc.
- Dams, breakwaters, irrigation canals, tanks for liquids, tunnels.
- Defensive structures.
- Reinforced concrete structures: production of prefabricated foundations, piles, wall panels, beams, columns, pipelines.
- Construction of road, airfield and sidewalk coverings.
Using polypropylene fiber
recommended when performing the following types of work:
- installation of industrial floors and screeds;
- construction of external walls, insulation based on cellular concrete blocks;
- production of piece decorative products (paving slabs, borders);
- preparation of mortars, shotcrete mixtures, plasters.
Asbestos fibers
used for reinforcing materials with low elasticity:
- roofing wavy and flat coverings;
- free-flow and pressure pipes;
- strengthening modifying additives for the top layer of concrete;
- decorative facade slabs;
- repair compounds, asphalt mixtures.
glass fiber
used for the construction of houses, sewer wells, etc. However, the insufficient resistance of the fibers to the effects of the hydrating cement environment limits its use.
Flaws
There are downsides to this popular metal filler. And above all:
- its presence increases the weight of concrete products;
- there is not always good adhesion strength to cement (more often when using smooth workpieces or using lean concrete mixtures with a large amount of sand);
- it is possible for material to escape from the concrete body under conditions of long-term operation (especially noticeable in road construction during repair work of the road surface);
- applying an additional corrosion or other protective coating leads to additional costs and an increase in the final cost of the product.
These properties, however, do not affect the popularity of such a building material and it is widely used by modern consumers.
Mixing Methods
Do-it-yourself production of concrete structures using the dispersed reinforcement method involves 3 main stages:
- Preparation of fiber reinforcement.
- Preparation of the composite.
- Molding of products.
When using modifiers, the hardness of mixtures increases. As a result, concrete loses its mobility and becomes difficult to place.
Adding polypropylene
An indispensable condition for obtaining compositions with high strength and stability is a uniform supply of fiber fiber into the concrete mixer.
Work order:
- First, filler, crushed stone or gravel is added.
- Then sand is poured in and mixed dry.
- Without turning off the concrete mixer, the required volume of polypropylene fibers is introduced.
- Cement and water with plasticizers dissolved in it are added.
- Continue stirring until a homogeneous mixture is obtained.
Introduction of basalt
To achieve good adhesion and the required reinforcement effect, the optimal diameter and length of the fibers are selected.
Instructions for making basalt fiber reinforced concrete:
- Sand and crushed stone are poured into a concrete mixer.
- Add the required amount of additive and mix.
- When the unit is turned on, pour water into the mixer.
- Cement is added.
- Continue kneading until the desired consistency is obtained.
If products are prepared on the basis of gypsum or cement-sand mortar, then reinforcement is performed last.
Other types of fiber additives
The strengthening component for concrete can be made not only from steel, but also from other bases. Let's take a closer look at each type of fiber fiber.
Polypropylene
This is a synthetic material, it strengthens building mixtures, is economical, affordable and has decent performance characteristics. Aerated concrete blocks, foundations, floor screeds, roadside curbs, and fencing structures are made from solutions with this additive.
Basalt
This additive is odorless (unlike polypropylene), gives strength to structures with a porous structure, is often used in the creation of gypsum products, and is resistant to high temperatures. This fiber has longer fibers than other types, so it is consumed individually. It, for example, is completely unsuitable for architectural forms, since the fibers can appear on the surface of the product.
Advantages of using fiberglass for screed:
Fiber makes the base durable, resistant to cracking and high loads. The material is evenly placed in the concrete. Fibers prevent damage to the floor screed during operation, because moisture is distributed evenly in such a base. Frost-resistant material vibrofiber can withstand many cycles of freezing with further defrosting.
Adding fiberglass to concrete saves money compared to using standard metal reinforcement. A semi-dry screed using fiber makes the drying process of the base faster.
Application of polypropylene fiber
The material is relevant for a wide variety of objects. For example, 100% polypropylene fiber SikaFiber® PPM-12 reliably reinforces screeds, blind areas, and plasters.
The material is convenient to use. The fiber for the solution is supplied in a special bag. The additive can be added at any stage - to dry ingredients or into a liquid mixture. No special equipment is needed; a regular concrete mixer will do.
Fiber fiber for floor screed, wall plaster and other structures is superior in convenience to traditional reinforcement methods.
Compared to metal mesh and steel rods, the fibers are evenly distributed throughout the solution. This reduces the number of internal shrinkage microcracks, and also prevents delamination and rapid abrasion of the outer layers.
To effectively strengthen concrete, you need to use materials from reliable manufacturers. Sika polypropylene fiber has passed laboratory tests and has European certificates - with such an additive, a concrete structure or product will serve for years even in extreme conditions.
Benefits of fiber
Concrete is a popular material for construction because it is very durable and unpretentious in the process. This substance is used both in everyday life and in industry; so far there are practically no alternatives to it. Despite these positive properties, concrete products also have disadvantages:
- Insufficient resistance to stretching and bending;
- Possibility of shrinkage;
- Risk of cracks;
- Poor tolerance to shock loads, reduced viscosity;
- The presence of many pores that perfectly retain moisture, which threatens the gradual formation of mold.
Concrete with fiber fiber Source sevdonstroy.com
Fiber fiber in semi-dry floor screed:
The mixture for semi-dry screed is prepared from cement, sand, fiber fibre, plasticizer with a small addition of water. The finished solution is placed along the beacons, and then they begin to directly level the surface of the solution. After this, leave the surface for several days to dry. Only after this can you proceed to the next finishing stage.
This method is suitable for most buildings, mainly office and industrial, except for structures with thin floors. The small amount of water used when preparing the mixture allows installation without excess dirt.
Adventures of fiber-reinforced concrete at home
What is the situation with steel fiber concrete in our country?
As you know, there are no prophets in their own country, especially in Russia. Even reinforced concrete specialists, if they have heard anything about V.P.’s patent. Nekrasov, about the massive use of steel-fiber concrete abroad, however, no efforts were made to introduce it in the homeland.
The initiative was taken by the management of Kurganstalmost CJSC, an enterprise that produced steel structures for bridges. Having visited Germany, it learned about steel fiber concrete and decided to set up the production of fiber for export to this country, where the demand for it was very high.
And only after some time Russian builders began to purchase fiber. To contribute to this, the plant carried out research work on the effect of fiber on concrete, and developed the documents necessary for its use. Thus, together with the Research, Design and Technological Institute of Concrete and Reinforced Concrete (NIIZhB) (Moscow), “Guiding technical materials (Rgeography)” were developed and are constantly expanding.
The use of steel fiber in cement mixtures intended for the repair of collapsing reinforced concrete products is promising. For this purpose, hard steel fiber, called Emako Fast Fiber, is especially recommended.
A cement mixture with such fiber makes it possible to repair reinforced concrete structures subject to impact or high dynamic loads.
It is also recommended to be used in cases where there is a need to strengthen reinforced concrete structures without installing additional reinforcement.