Application area
The ultimate goal of cutting is to obtain workpieces of the desired size by separating the metal into parts. In mass production or when it is necessary to cut thick material, metal cutting using electric arc welding is used. Since the method is not highly accurate, it is successfully used for dismantling large structures, such as pipelines. The simplicity of this method is attractive.
There is no requirement for a highly qualified welder. For welding and cutting equipment, a welding machine is required, and for tools, a special electrode is required.
Description of technology
Arc cutting of metal is performed using a welding inverter. It is, in fact, a transformer that produces a current of a certain strength sufficient to form a welding arc. This technology appeared quite a long time ago, thirty to forty years ago. While not ultra-modern, like plasma, it continues to be popular and widely used due to its ease of use, efficiency and ease of use.
Operating a welding machine, including cutting metal with a conventional or special electrode, is not particularly difficult and does not require professional knowledge and skills. But at the same time, it is necessary to take into account safety requirements, since welding work is associated with electrical voltage.
Technological process
The technologies of electric arc welding and metal cutting begin in the same way. The welding machine is connected to the network. It is connected to the part with one cable, and with the second to the holder with the electrode. The current value is set depending on the thickness of the material and the size of the electrode. By tapping the electrode on a metal surface, an arc is initiated. The metal begins to melt under the influence of high temperature.
When it comes into contact with oxygen in the air, oxidation of the metal that begins to harden occurs. This can lead to defects in the form of oxides. To avoid this, use an inert shielding gas. Most often, argon and helium play this role. The gas that is used for cutting and welding metals is supplied to the weld pool.
Cutting has three types:
- Dividing . It assumes the possibility of molten metal flowing out of the resulting cut. The diameter of the electrode is larger than the width of the sheet. If the sheet is located in a vertical plane, then welding is carried out using the top-down method. The electrode is placed perpendicularly and moved along the intended line. If through holes must be made, then you should start with them.
- Superficial . It is used when it is necessary to lay various types of grooves on the metal surface, as well as to remove defects in the form of sagging. To obtain wide grooves, the electrode performs transverse oscillatory movements. The movement is done when the electrode is slightly immersed deep into the metal.
- Cutting holes . First make a small hole and then expand it to the desired size. A slight deviation of the electrode from perpendicular to the surface towards the circle is acceptable.
How to learn to use a welding machine?
Operating the equipment is not difficult, the main thing is to fulfill all the operating requirements, which are easy to find in the instructions. After everything is carefully prepared, you can start welding the metal.
To weld metal correctly, it is recommended to follow the following algorithm:
- To begin with, grounding is installed on the part that is intended for welding.
- Next, the welding current is selected, which will correspond to the diameter of the desired electrode.
- After completing the two steps described above, you can begin the welding process.
Cutting electrodes
When welding and cutting metals, special electrodes are used. The difference from conventional electrodes is the greater amount of heat generated by the welding arc and the increased heat resistance of the coating.
Cutting metals using welding can be done with different types of electrodes:
- Non-melting . Made from tungsten. When using a non-consumable electrode process, the cut is quite rough. The process requires a protective gas environment. Used for alloy steel and non-ferrous metals.
- Melting . To obtain a neat appearance, consumable electrodes are used.
- Coal . Otherwise they are called graphite. Carbon electrodes are used for non-critical parts. Their advantage is slower melting. The peculiarity is that they do not melt, but burn. This reduces the amount of slag and produces a cleaner cut. Another feature is the ability to heat up to very high temperatures with low current.
- Tubular . Tubular electrodes are used when cutting occurs using the oxygen-arc method. The basis of the electrode is a special tube with thick walls, hollow on the inside.
When deciding how to cut metal by welding, you should make a choice between these types of electrodes. Cutting can also be carried out with conventional electrodes. In this case, the current should be increased by 30-40%. This will require more electricity consumption, and accordingly, will increase the cost of the process.
Required tools and equipment
Before cutting metal with a purchased welding inverter, you need to prepare the equipment and tools required for this:
- the welding machine itself (presented on the construction and industrial equipment market in various versions from a variety of manufacturers);
- hammer and brush;
- electrodes. Until recently, metal cutting by arc welding was carried out using the most common electrodes. Nowadays, special electrodes are used more often, used for cutting by electric welding and designated as OZR. They are characterized by high heat resistance of the coating, which ensures faster cutting, increased productivity and cut quality. The use of special OZR electrodes allows the material to be cut in such a way that a much larger amount of heat is released, and the arc is stable and stable.
For safe work, the purchase of protective equipment is required, including:
- special suit (robe);
- mittens (gaiters);
- protective mask equipped with a light filter;
- boots whose soles are made of rubber;
- when working in a confined and small space, use a respirator.
Welder equipment
All of the above equipment, materials and equipment are available and can be easily purchased at almost any specialized store.
Principle of operation
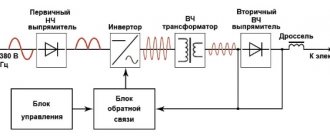
A welding inverter for manual welding converts the mains voltage (220 or 380 to 50 Hz) into a voltage suitable for maintaining the electric arc. This transformation takes place in three stages:
- AC input voltage is rectified,
- this direct current powers the high-frequency generator, it creates alternating current with a frequency of 20-50 thousand Hz.,
- the transformer reduces the voltage to 70-90 volts, the current in the working winding reaches 100-300A.
READ Is it possible to cut a car
Triple conversion makes it possible to reduce the size and weight of the device several times compared to conventional welding transformers. In addition, thanks to automatic adjustment of electronic circuit parameters, the device provides high stability of output current and voltage. The inverter is not affected by voltage surges in the supply network, and it itself does not cause such surges.
In semi-professional and professional models, systems are also installed that facilitate ignition of the arc and prevent sticking of the electrode.
The operating current flows through a circuit formed by:
- electrode and mass cables,
- electrode,
- electric arc in the air gap,
- workpiece
The electrode wire is connected to the holder, the ground wire to the cleaned area on the part.
Welding work for the repair of special equipment
Special equipment includes various vehicles used in construction and road work - cranes, excavators, bulldozers, loaders, etc. Initially, this equipment is made to be durable and wear-resistant, but due to active use in difficult conditions, even it fails. Among other repair activities, special equipment is repaired by welding. They are needed if there are kinks or cracks in the equipment, if it is necessary to correct a defect in the welds, or when it is necessary to weld a new element to the structure. Welding work can be electric or gas. The place of work can also be different - it is either welding at the place where the equipment is working, or working with certain of its elements in special welding workshops.
How to cut metal with a welding inverter? – Metals, equipment, instructions
- Date: 06/20/2015
- 619
- : 47
The need to create reliable connections of various types of metal products periodically arises in almost any household. In most of these situations, welding is the best solution. For beginners, as practice shows, the easiest way to learn how to cook is with an inverter.
Such a device makes it possible to obtain much more reliable connections when compared with the results of its immediate predecessors, especially in the absence of proper experience and skills.
It is not difficult to cook various metals with an inverter; you just need to fully study the instructions and follow the recommendations received in everything.
Welding inverter device.
Equipment, equipment, safety precautions
Safety precautions. Welding production is associated with electrical voltage, or in common parlance - current. The current is invisible, but can kill a person.
We check the welding cables for serviceability and connect them to the inverter equipment. Return cable with a clothespin on metal to the negative connector. Cable with electrode holder to connector Insert the electrode into the electrode holder.
When connecting the device to the network, visually evaluate the current-carrying cables for serviceability. After making sure that the cables are in good condition, we plug in the plug into the socket and the toggle switch on the device, having previously set the current regulator to the lowest value. If the cooling fan starts working smoothly, without crackling or noise, then everything is fine.
Metal weight. When connecting heavy structures, take precautions. If multi-ton products collapse, they can lead to death or disability.
Equipment. Welding production involves high temperatures. The welder must have:
Is it possible to cut with a welding inverter?
- canvas mittens (gaiters);
- robe (special suit);
- mask with a light filter;
- respirator for work in confined spaces;
- boots with rubber soles.
Gaiters are used when welding at heights, when arms are raised up, and mittens in other cases.
- welding machine;
- hammer;
- brush;
- electrodes.
Electrodes are selected according to the metal (carbon content, additives) and diameter, depending on the thickness of the metal and the technical characteristics of the inverter.
Stages of production of structures using welding
Studying drawings - we are ready to work on your sketches or start developing them from scratch; Material preparation - we work only with high-quality steel: carbon and alloy; Welding work is the process of joining parts itself; Testing is testing a structure or product for strength.
Welding current
What about welding current? As you, I hope, have already understood, the higher the welding current, the more energy is transferred to the welding zone, the stronger and deeper the metal melts and the thicker the products you can join. And to transmit a greater current, a thicker conductor is needed. Accordingly, we can reach a direct relationship: metal thickness - electrode thickness - current strength. Welding machines are often marked with signs corresponding to the thickness of the electrode and the welding current. I recommend that you do not take such tables as dogma - they are just a starting point to guide you. For household use, a current of up to 160A is sufficient, which allows you to use a 4 mm electrode. In my memory, I very rarely used this diameter of electrodes. Basically it is 2 and 3 mm. There is also a diameter of 2.5 mm for electrodes of the UONI-13/45, 15/55, NIAT-3M brands (types for carbon steels). Approximately the strength of the welding current can be determined by the formula: I=Kdel. Where K is an experimental coefficient equal to 40-60 mm for electrodes made of low-carbon steel and 35-40 mm for electrodes with a rod made of high-alloy steel, and del is the diameter of your electrode.
| Metal thickness, mm | 2 | 3 | 4 — 5 | 4 — 5 | 5 — 10 | 5 — 10 |
| Electrode diameter, mm | 2 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Welding current strength, A | 40 — 80 | 80 — 120 | 100 — 150 | 160 — 200 | 160 — 210 | 180 or more |
Features of thin metal
Workpieces of small thickness are welded with a current of reverse polarity, using the method of guiding the electrode at an angle forward. The diameter of the electrodes needs to be chosen smaller.
Particular care must be taken when igniting: at this moment it is easy to burn the sheet.
At the end of the seam, do not sharply lift the electrode - a crater may form. To ensure that a thin part does not move during welding, it should be securely fixed in the equipment or grabbed after 10-15 centimeters by spot welding.
Features of welding non-standard products
Non-standard metal structures are products that are manufactured individually according to a pre-agreed sketch. These can be shelving for warehouses, suspended ceiling elements of unusual design, advertising billboards, frames and decorative elements for stairs, ramps, podiums, metal products for landscape design and interior design. The welding process is part of the formation and processing of products of this type. But before making complex connections between elements by welding, the master and the customer first prepare a sketch of the future structure and make accurate calculations. And then, strictly according to the drawing, specialists weld and connect the elements of the product. The peculiarity of this process is that the work is performed not only mechanically, but also creatively.
Pipeline welding
The work of welding pipeline elements is scrupulous, so only an experienced craftsman performs it. The strength, reliability and longevity of the metal structure will depend on the quality of welding. Before welding, it is necessary to prepare metal pipes. Markings are applied to the metal products to thoroughly fit them to each other. Then the chamfer is removed (2-3 mm). Immediately before starting welding, the surfaces of the pipes must be joined, leaving a small gap between them - for the future seam. During welding, the master makes sure that no pores are formed and that all elements are tightly welded to each other without shifting. Finally, the surfaces of the metal pipes are cleaned of pores and cleaned until smooth and shiny. In a perfectly welded pipeline there is not a hint of roughness, grooves, or other defects.