Analogs of steels. Structural steel.
| CIS GOST | USA AISI, ASTM, ASME | Germany DIN | Japan JIS | China GB | UK BS | Italy UNI | France AFNOR NF |
| 03Х17Н14М3 | 316L SA-240TP316L | X2CrNiMo18-14-3 | SUS 316L | 00Cr17Ni14Mo2 00Cr17Ni14Mo3 | 316S13 LW 22 | X2CrNiMo 18-14-3 X2CrNiMo1713KG | Z 3 CND 17-12-03 |
| 03X18H11 | 304 L SA-240TP304L | X2 Cr Ni 19 11 GX2 Cr Ni 19-11 | SUS304L | — | 304S11 LW 20 LWCF 20 S 536 304 C12 (LT 196) 305 S 11 | X2 CrNi 18 11 X 3 CrNi 18 11 GX 2 CrNi 19 10 | Z 1 CN 18-12 Z 2 CN 18-10 Z 3 CN 19-10M Z 3CN 18-10 Z 3 CN 19-11 Z 3 CN 19-11FF |
| 03ХН28МДТ 06Х28МДТ | — | X3NiCrCuMoTi2730 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 06X18H11 | 305 3008 | X4CrNi18-12 | SUS 305 SUS 305J1 | — | 305S17 305S19 | X7 CrNi18 10 X8 CrNi 19 10 | Z 5 CN 18-11FF |
| 07Х16Н6 | 301 A 167 301 A 240 301 A 666 301 | X12CrNi17-7 X10CrNi18-8 | SUS 301 | — | 301 S 21 301 S 22 Cr Ni 17/7 | X10CrNi18-8 X12CrNi17-07 | Z 11 CN 17-08 Z 11 CN 18-08 Z 12 CN 18-09 |
| 08kp | A 622 | St 50-2 | SPHE | — | BS 1449 1HR | — | 3C |
| 08X13 | 403 409 410 S 429 SA-240 TP 410S | X6 Cr 13 X7 Cr 14 | SUS 403 SUS 410S SUS429 | — | 403 S17 | X6 Cr 13 | Z6 C13 Z8 C12 Z8 C13FF |
| 08Х17Н13М2Т 10X17H13M2T | 316 Ti A 167 316Ti A 213 F316H A 240 316Ti A 368 316Ti SA-240 TP 316Ti SA-479 316Ti | X6CrNiMoTi 12 122 X 10 CrNiMoTi 18-12 | SUS 316Ti | 0Cr18Ni12Mo3Ti 1Cr18Ni12Mo3Ti | 320 S 33 CrNiMo 17/12/2 1/4 Ti | X 6 CrNiMoTi 17 13 | Z6 CNDT 17.12 |
| 08Х17Т | 430Ti 439 | X 6 CrTi 17 X3CrTi17 | SUS 430LX | — | — | X 3 CrTi 17 X 6 CrTi 17 | Z 4 CT 17 |
| 08X18H10 | 304 304 H SA-240 TP 304 | X5 Cr Ni 18 10 | SUS 304 | — | 304S11 304S15 304S16 304S17 304S31 LW21 LWCF 21 | X 5 Cr Ni 18 10 | Z4 CN 19-10 FF Z5 CN 17-06 Z6CN18.09 Z7 CN 18-09 |
| 08Х18Н12Б | 347 A 167 347 A 240 347 A 313 347 A 580 347 | X 6 CrNiNb 18 10 X6CrNiNb18-10 | SUS 347 | 0Cr18Ni11Nb 1Cr18Ni11Nb 1Cr19Ni11Nb | 347 S 20 347 S 31 ANC 3 Grade B Cr Ni 18/9/Nb CrNi 18/9 0.10C/Nb | X 6 CrNiNb 18 11 | Z 6 CNNb 18-10 |
| 08YA | A 620 | DC 04 DC04+ZE Fe P04 / St 14 St 14 St 4 | SPCE | — | DC 04 / FeP 04 HR 1 HR 2 | DC 04/FeP 04 | DC 04 / FeP 04 |
| 09G2S | A 516-55 A 516-60 A 516-65 A 561 Gr70 | — | SM41B SB49 | — | — | — | — |
| 09Х17Н7У | — | X 7 CrNiAl 17 7 X7CrNiAl17-7 | SUS 631 | 0Cr17Ni7Al | 301 S 81 | — | Z 9 CNA 17-07 |
| 10 | C1010 A 108 1010 A 29 M1010 A 510 1010 A 575 M1010 SA-29 M1010 | C 10 C10E Ck 10 | S 10 CS 9 CK SACM 1 | 10 | 040 A 10 045 M 10 En2A En32A HS 10 | 1 C 10 2 C 10 2 C 15 C 10 | C 10 RR XC 10 |
| 10Х13СУ | A 268 TP405 | X10CrAl13 X10CrAlSi13 | — | — | — | X 10 CrAl 12 | Z 13 C 13 |
| 10X23H18 20X23H18 | SA-240 TP 310S | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12K | A 201 Gr AFx | ASt 35 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12X13 15X13L | 410 430 A 183 F6 A 193 B6 A 479 410 | X 10 Cr 13 X12 Cr13 GX 12 Cr 12 | SUS 410 | — | 410C21 410S21 ANC 1A | X 10 Cr13 X 12 Cr13 | Z10C13 Z12C13 |
| 12Х17 | 430 A 182 F 430 A 240 430 SA-182 Grade F 430 SA-240 Type 430 | X6Cr17 | SUS 430 | 1Cr15 1Cr17 ML1Cr17 | 17Cr 430S17 430S18 | X 6 Cr 17 X 8 Cr 17 | Z 8 C 17 |
| 12X18H10T 06Х18Н10Т 08X18H10T 09Х18Н10Т | 321 A 213 TP321H SA-240 TP 321 | X6 Cr Ni Ti 18 10 X10 Cr Ni Ti 189 | SUS 321 | — | 321S12 | — | Z6 CNT 18.10 |
| 12XM | A 182 grade F12 A213 Grade T12 A 335 Grade P12 A 387A,B,C | 13CrMo-44 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12X2M | A 182 Grade F22 A335 Grade P22 387 Grade D | 10CrMo910 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 12Х1МФ | — | 14MoV63 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 14G2 | A414 Gr F,GA 515 Gr70 A516 Gr70 | 17 Mn4 | SB 46 SB 49 SG V 46 SG V 49 SP V 32 | — | — | — | A 48CP |
| 15 | C1015 A 108 1015 A 512 1015 A 576 1015 | C15 C15E Ck 15 | S 15 CS 15 CK | 15 H15A ZG200-400 (ZG 15) | — | — | C 18 RR XC 15 XC 18 |
| 15kp | A 621 FS Type AA 621 FS Type B | DD 11 (StW 22) | SPHD | — | — | — | 1 C |
| 15ps | A 29 1015 | QSt 38-3 | SWRCH15A SWRCH16R | ML15 | — | CB 15 | — |
| 15N2M 15HM | 4615 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15X | — | 15Cr3 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15X5M | A 182 Grade F5 A 193 Grade B5 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15X25T 15X28 | A 268 TP446 | 10CrAl24 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15XФ | 6117 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 15ХМ | A 182 grade F12 A213 Grade T12 A 335 Grade P12 | 13CrMo-44 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 16K | A 414 Grade E | H II St42-2 C22N ASt41 P 265 GH | SG 295 SG 30 SM 53 B SM 53 C SPV 315 SPV 32 SPV 355 SPV 36 | — | P 265 GH | Fe 410 KW P 265 GH | — |
| 17GS | — | S355J2G3 / Fe 510 D1 St 52-3 St 52-3 / S355J2G3 St 52-3 G | SM 490 A SM 520 C SM 53 C | 16Mn | — | Fe 510 Fe E 420 S 355 J 2 G 3 | S 355 J 2 G 3 |
| 18ХГ | SA-29 Grade 5115 | 16 MnCr 5 | — | 15CrMn 20CrMn | 527 M 17 590 H 17 590 M 17 | 16 MnCr 5 | 16 MC 5 16 MnCr 5 RR |
| 20 | C1020 A 105 Gr1 A 106 GrA,BA 659 CS Type 1020 A 794 CS Type 1020 | C 22 C 22N C 22.3 Ck 22 St35.8 St45.8 | S 20 CS 20CK | — | 040A20 070 M 20 070 M 26 1 C 22 C 22 En3A En3B En3C En3D | C 20 C 21 C 22 | C 20 XC 25 |
| 20K | A 283-CA 285-A,B,c A 414 Grade EA 515-5 A 515-60 A 515-70 | H II P 265 GH | SG 295 SG 30 SM 53 B SM 53 C SPV 315 SPV 32 SPV 355 SPV 36 | — | P 265 GH | Fe 410 KW P 265 GH | — |
| 20ps | A 29 1020 | — | SWRCH17R | ML20 | 0/4 | — | — |
| 20H2M 20HM | 4621 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 20X | 5120 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 20HF | 6120 | 22CrV4 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 20Х13 | 420 A 276 420 A 580 420 | X 20 Cr 13 | SUS 420J1 | 2Cr13 | 420 S 37 En56C | X 20 Cr 13 | Z 20 C 13 |
| 20Х17Н2 | 431 A 493 431 A 580 431 SA-479 Type 431 | X17CrNi16-2 X17CrNi16-2 (X 20 CrNi 17 2) | SUS 431 | 1Cr17Ni2 ML1Cr17Ni2 | 431 S 29 En57 | X 16 CrNi 1 | Z 15 CN 16-02 Z 15 CN 16.02 CI |
| 20Х25Н20С2 | 310 314 | X15CrNiSi25-20 X15CrNiSi25-21 | SUS Y 310 | 2Cr25Ni20 | — | X 16 CrNiSi 25 20 | Z 15 CNS 25-20 |
| 20ХМ | 4130 SA-29 Grade 4130 | 4130 SA-29 Grade 4130 | SCM 420 SCM 430 | ML30CrMo ML30CrMoA | 25 CrMo 4 | 25 CrMo 4 | 25 CrMo 4 |
| 20XH | 3120 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 22K | 1022 1518 | 20Mn5 | S Mn C 420 | — | 120M19 | — | 20M5 |
| 25 | C1025 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 25G | 1025 A 108 1025 A 510 1025 A 512 1025 A 513 1025 A 576 1025 | GS-Ck 25 | S 25 C | 25 25Z ZG230-450 (ZG 25) | 070 M 26 080 A 25 | — | — |
| 25X1MF | A 193 B14 A 540 B21 | 24CrMoV55 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 30 | C1030 A 29 1030 SA-29 1030 | — | SWRCH30K SWRCH33K | ML25Mn ML30 | 1/1 | — | — |
| 30X | 5130 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 30XM | 4130 A 302 Gr BA 304 | 25CrMo4 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 30Х13 | 420F | X30Cr13 | SUS 420J2 | 3Cr13 | 420 S 45 En56D | GX 30 Cr 13 X 30 Cr 13 | Z 30 C 13 Z 33 C 13 |
| 30ХМ | — | 34 CrMo 4 GS-34 CrMo 4 | SCM 435 SCM 435 H | 35CrMo | 34 CrMo 4 | 34 CrMo 4 | 34 CrMo 4 |
| 30G2 | — | 36 Mn 5 | SCMn 3 SMn 438 SMn 438 H | — | 150 M 36 En15 En15A | — | 40 M 5 |
| 35 | C1035 C1034 A 107 | C 35 Ck 35 | S 35C | — | 080M36 | — | XC 38 |
| 35X | 5132 | 34Cr4 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 35XM | — | 34CrMo4 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 40 | 1040 | C40 Ck40 | S 40C | — | 080A40 060A40 | — | XC 42 |
| 40X | 5140 | 41 Cr 4 | S Gr 440 | — | 530A40 530M40 | — | 42C4 |
| 40Х13 | — | X38Cr13 X39Cr13 X46Cr13 | SUS 420J2 | — | 420S45 | X 40 Cr 14 X 46 Cr 13 | Z 38 C 13 MZ 40 C 13 Z 40 C 14 Z 44 C 14 Z 50 C 14 |
| 40Х2Н2МА | 4340 SA-29 Grade 4340 | 40 NiCrMo 6 | SNCM 439 STPT 38 | 40CrNiMoA ML40CrNiMoA | 818 M 40 | — | — |
| 40XH | 3135 3140 | 40Ni Cr 6 | — | — | 640M40 | — | — |
| 40ХН2МА | 9840 | 36 CrNiMo 4 | — | — | 36 CrNiMo 4 | 36 CrNiMo 4 | 36 CrNiMo 4 40 NCD 3 |
| 45 | 1045 A 107 A 29 1044 SA-29 1044 | C 45 Ck 45 Cq 45 | S 45C SWRCH45K | ML45 | 080M 080M46 | — | XC48 |
| 45G | 1045 A 108 1045 A 29 1045 A 311 1045 A 576 1045 SA-29 1045 SA-311 1045 | C45E Ck 45 GS-Ck 45 | S 45 CS 48 C | 45 ZG310-570 (ZG 45) | C 45 E | C 45 E | C 45 E XC 45 |
| 45X | 5145 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 50 | С1050 A 108 1050 A 29 1050 A 311 1050 A 510 1050 A 576 1050 SA-29 1050 SA-311 1050 | C 50 E Ck 50 | — | 50 | 080 M 50 C 50 E | C 50 E | C 50 E XC 50 |
| 50X | 5147 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 55 | С1055 A 29 1055 A 576 1055 SA-29 1055 | C 55 Ck 53 | S 55 CS 55 C-CSP | — | 070 M 55 C 55 En9 En9K | C 55 | AF 70 C 54 C 55 |
| 60 60G | C1060 A 29 1060 A 576 1060 SA-29 1060 | C 60 | S 58 CS 60 C-CSP S 65 C-CSP | — | 060 A 62 C 60 CS 60 HS 60 | C 60 | C 60 |
| St0 St1kp | A 283 Grade A | S185 / Fe 310-0 St 33 | SS 330 | Q195 Q195-F Q195-Z Q195-b | HR 15 | S 185 | — |
| St2ps St2sp | A53 Gr A A192 Gr A | St 35 | — | Q215B Q215B-F Q215B-Z Q215B-b | S360 | — | — |
| St3kp | A 107 A 283 Grade C SA-283 C | USt 37-2 USt 37-2 G RSt37-2 | — | A3 Q235A Q235A-F Q235A-Z Q235A-b | — | — | — |
| St3sp | A 414 Grade AA 570 Grade 36 | S235J2G3 / Fe 360 D1 St 37-3 St 37-3 G UZSt 37-2 | SS34 | — | HS 37/23 S 235 J 2 G 3 40C BS4360 | S 235 J 2 G 3 | S 235 J 2 G 3 E 24-2NE |
| St5sp | A 570 Grade 50 | St 50-2 | SS 50 | — | — | — | A 50-2 |
| St6ps St6sp | A 572 Grade 65 | E335 / Fe 590-2 St 60-2 St 60-2 G | SM 570 SM 58 | — | 55 CE 335 | E 335 Fe 590 | E 335 |
| steel grade | Analogues in US standards | ||
| CIS countries GOST | Euronorms | ||
| 10 | C10E | 1.1121 | 1010 |
| 10XGN1 | 10 HGN1 | 1.5805 | — |
| 14 ХН3 М | 14 NiCrMo1-3-4 | 1.6657 | 9310 |
| 15 | C15 E | 1.1141 | 1015 |
| 15 G | C16 E | 1.1148 | 1016 |
| 16 HG | 16 MnCr5 | 1.7131 | 5115 |
| 16XGR | 16Mn CrB5 | 1.7160 | — |
| 16 CGN | 16NiCr4 | 1.5714 | — |
| 17 G1 S | S235J2G4 | 1.0117 | — |
| 17 ХН3 | 15NiCr13 | 1.5752 | E3310 |
| 18 HGM | 18CrMo4 | 1.7243 | 4120 |
| 18 X2 N2 M | 18CrNiMo7-6 | 1.6587 | — |
| 20 | C22E | 1.1151 | 1020 |
| 20 XM | 20MoCr3 | 1.7320 | 4118 |
| 20 HGNM | 20MoCr2-2 | 1.6523 | 8617 |
| 25 | C25E | 1.1158 | 1025 |
| 25 XM | 25CrMo4 | 1.7218 | 4130 |
| 28 G | 28Mn6 | 1.1170 | 1330 |
| 30 | C30E | 1.1178 | 1030 |
| 34 X | 34Cr4 | 1.7033 | 5130 |
| 34 X2 N2 M | 34CrNiMo6 | 1.6582 | 4340 |
| 35 | C35E | 1.1181 | 1035 |
| 36 HNM | 36CrNiMo4 | 1.6511 | 9840 |
| 36 X2 N4 MA | 36NiCrMo16 | 1.6773 | — |
| 40 | C40E | 1.1186 | 1040 |
| 42 XM | 42CrMo4 | 1.7225 | 4140 |
| 45 | C45E | 1.1191 | 1045 |
| 46 X | 46Cr2 | 1.7006 | 5045 |
| 50 | C50E | 1.1206 | 1050 |
| 50 HGF | 50CrV4 | 1.8159 | 6150 |
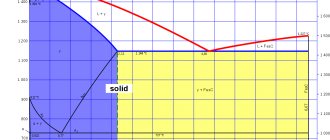
Temperature of critical points of steel 45
As previously noted, to improve the performance properties of the metal, heat treatment is carried out. It involves exerting a certain influence on the structure, after which the crystal lattice is rearranged and the qualities change. When carrying out heat treatment, critical points are often taken into account. Processing of steel St 45 is carried out taking into account the following factors:
- Temperature conditions. It is important to choose the right temperature, since too low will cause incomplete heating of the structure and complete restructuring of the structure will not occur. Too high an indicator causes overheating of the metal, as well as the appearance of scale. A variety of settings can be used to ensure that the required temperature is applied. An example would be blast furnaces or electrical installations. Melting temperatures that are too high determine that it is quite difficult to harden the steel in question at home.
- Rate of temperature increase. The heating rate can also determine which qualities will be transferred to the processed product. Modern equipment allows you to control the heating rate with high precision. For example, HDTVs have an electronic control unit; electrical energy is converted into magnetic energy, which causes heating of the structure.
- The length of time between exposure to different temperatures. When heat treating all metals, the presence of three critical points is taken into account and taken into account. The holding time may depend not only on the chemical composition of the material, but also on the size and shape of the workpiece.
- Features of the cooling process. The quality of the resulting product largely depends on the conditions under which the cooling process took place. For example, it is possible to use oil or water, as well as various powders as a cooling medium.
Quite often, HDTV is used to change the qualities of a metal. It is characterized by high efficiency in application, as well as ease of use. Today there are models that, if desired, can be installed in a home workshop.
Critical points are considered to be temperatures at which restructuring of the structure occurs. There are three main temperature points that are displayed on the plotted diagram.
Attention is also paid to choosing a more suitable cooling medium. For example, it is possible to carry out cooling in water. However, such an environment leads to uneven cooling, which leads to scale and other problems. For higher quality, oil is used. Large workpieces can be cooled in the open air, since it takes a long time to reduce the temperature.
Analogs of steels. Structural carbon steel.
| CIS countries (GOST 1050-88) | Foreign analogues | ||
| Germany (DIN) | USA (ASTM) | ||
| 10 | 1.0301 | From 10/Sk 10 | 1010 |
| 15 | 1.0401 | S15/Sk 15 | 1015 |
| 20 | 1.0402 | From 22/Sk 22 | 1020 |
| 30 | — | — | 1030 |
| 35 | 1.0501 | From 35/Sk 35 | 1035 |
| 40 | 1.0511 | From 40/Sk 40 | 1040 |
| 45 | 1.0503 | S 45/Sk 45 | 1045 |
| 50 | 1.0540 | From 50/Sk 50 | 1050 |
| 55 | 1.0535 | S 55/Sk 55 | 1055 |
| 60 | 1.0601 | From 60/Sk 60 | 1060 |
Properties of steel St 45
When purchasing metal products, you need to know the properties of the material from which they are made. The type of steel the product is made from affects its cost, strength, and reliability. This also determines the service life and possible scope of application.
In this case, you will find information about steel grade 45, which is often used for the manufacture of a variety of metal products. It is considered structural carbon quality. To purchase rolled metal products made from 45 steel, check out the company’s catalogs and contact our managers.
It is supplied in the form of long and shaped products. You can find an extensive list of products for which it is used. For example, silver, sheets of metal of different thicknesses, rods with different types of surface treatment, forgings and forged blanks, long wire products, tapes and strips, as well as pipes.
Analogs of steels. Alloy structural steel
| CIS countries (GOST, TU) | Foreign analogues | ||
| Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | ||
| 12ХН3А | 1.5732 | 14NiCr10 | — |
| 12Х2Н4А | — | — | E3310 |
| 15ХМ | 1.7335 | 13CrMo44 | — |
| 17G1S | 1.0570 | St52-3 | — |
| 18ХГ | 1.7131 | 16MnCr5 | 5120 |
| 20ХМ | 1.7218 | 25CrMo4 | 4130 |
| 27ХГР | 1.5526 | 30MnB4 | — |
| 30Х3МФ | 1.8519 | 31CrMoV9V | — |
| 30Х2Н2М | 1.6580 | 30CrNiMo8V | — |
| 34Х2НМУ | 1.8550 | 34CrAlNi7V | — |
| 38Х2Н2МА | 1.6582 | 34CrNiMo6 | 4330 |
| 40X | 1.7045 | 42Cr4 | 5140 |
| 40ХГМ | 1.7225 | 42CrMo4 | 4140 |
| 40ХН2МА | 1.6565 | 40NiCrMo6 | 4340 |
| 40ХГНМ | 1.6546 | 40NiCrMo22 | 8640 |
| 45G | 1.0912 | 46Mn7 | — |
Analogs of steels. Carbon tool steel
| CIS countries (GOST, TU) | Foreign analogues | ||
| Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI/ASTM) | ||
| U 7 | 1.1620 | C 70W2 | — |
| U 7A | 1.1520 | C 70W1 | — |
| U 8 | 1.1625 | C 80W2 | — |
| U 8A | 1.1525 | C 80W1 | W 108 |
| At 10 | 1.1645 | C 105W2 | — |
| U 10A | 1.1545 | C 105W1 | W 110 |
| U 11 | 1.1654 | C 110W | — |
| U 13 | 1.1663 | C 125W | W 112 |
Analogs of steels. Alloy tool steel
| CIS countries (GOST, TU) | Foreign analogues | ||
| Germany (DIN/BOHLER) | USA (AISI/ASTM) | ||
| X12 | 1.2080 | Х210Cr12 | D3 |
| Х12В | 1.2436 | Х210CrW12 | — |
| Х12МФ* | 1.2379 | Х155CrVMo12-1 | D2 |
| H12MF4-MP | — | K190RM | — |
| 95HF | 1.2210 | 115CrV 3 | L2 |
| 9Х1Ф | 1.2067 | 102Cr 6 | L3 |
| 9G2F | 1.2842 | 90MnCrV 8 | O2 |
| 95ХГВФ | 1.2510 | 100MnCrW 4 | O1 |
| 3Х3В9Ф | 1.2581 | Х30WCrV9-3 | H21 |
| 95Х5ГМ | 1.2363 | Х100CrMoV5-1 | A2 |
| 95ХМ | 1.2303 | 100CrMo 5 | L7 |
| 95Х18 | 1.4125 | Х105CrMo17 | A473 (440C) |
| 5ХНМ | 1.2713 | 55NiCrMoV 6 | L6 |
| 5ХВ2СФ | 1.2550 | 60WCrV 7 | S1 |
| 5Х3М2Ф | — | — | S7 |
| 5ХН2МФ | 1.2714 | 56NiCrMoV 7 | — |
| 3Х3М3Ф | 1.2365 | Х32CrMoV3 3 | H10 |
| 4Х5МФС | 1.2343 | Х38CrMoV5-1 | H11 |
| 4Х5МФ1С | 1.2344 | Х40CrMoV5-1 | H13 |
Analogs of steels. High-speed tool steel.
| steel grade | Analogues in US standards | ||
| CIS countries GOST | Euronorms | ||
| R0 M2 SF10-MP | — | — | A11 |
| R2 M9-MP | S2-9-2 | 1.3348 | M7 |
| R2 M10 K8-MP | S2-10-1-8 | 1.3247 | M42 |
| R6 M5-MP | S6-5-2 | 1.3343 | M2 |
| R6 M5 K5-MP | S6-5-2-5 | 1.3243 | — |
| R6 M5 F3-MP | S6-5-3 | 1.3344 | M3 |
| R6 M5 F4-MP | — | — | M4 |
| R6 M5 F3 K8-MP | — | — | M36 |
| R10 M4 F3 K10-MP | S10-4-3-10 | 1.3207 | — |
| R6 M5 F3 K9-MP | — | — | M48 |
| R12 M6 F5-MP | — | — | M61 |
| R12 F4 K5-MP | S12-1-4-5 | 1.3202 | — |
| R12 F5 K5-MP | — | — | T15 |
| R18-MP | — | — | T1 |
| CIS countries (GOST, TU) | Foreign analogues | ||
| Germany (DIN) | BOHLER (D-016) | USA (AISI/ASTM) | |
| P18* | 1.3355 | S 200 | T 1 |
| Р6М5* | 1.3343 | S600/S601 | M 2 |
| Р6М5К5* | 1.3243 | S 705 | — |
| R6M5F3 - MP | 1.3342/1.3344 | S 790PM | M 3 |
| R6M5F4 - MP | — | S 690PM | M 4 |
| R6M5F3K8 - MP | — | S 590PM | M 36 |
| R10M2F5K8-MP | — | S 390PM | — |
| R10M3F4K8-MP | — | — | — |
| R12F3 | 1.3318 | — | — |
| R12MF4 - MP | — | S 207PM | — |
| R12K5F4 - MP | — | S 308PM | — |
| R12M6F5 - MP | — | — | M 61 |
| R12MF5K5 - MP | 1.3202 | — | T 15 |
| R0M2SF10 - MP | — | CPM 10V | A 11 |
*possible production by powder metallurgy method
Purpose and use of steel 09G2S
The properties of the alloy make it ideal for the manufacture of welded structures. In addition, the metal is used as a coating in the manufacture of two-layer corrosion-resistant sheets.
Also made steel 09G2S
- parts for carriages;
- steam boilers;
- welded transitions, flanges;
- seamless pipes;
- pressure apparatus;
- equipment for the petrochemical industry.
In addition, steel is very popular among developers, because the high mechanical properties of the alloy and its low weight make it possible to save considerable money on the construction of commercial facilities.
Analogs of steels. Heat-resistant steel
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| 1.4713 | X10CrAl7 | — | — | 10Х17СУ |
| 1.4724 | X10CrAl13 | 405 | — | 10Х13СУ |
| 1.4742 | X10CrAl18 | 442 | — | — |
| 1.4762 | X10CrAl24 | 446 | — | — |
| 1.4878 | X12CrNiTi18-9 | 321H | — | 12Х18Н10Т |
| 1.4828 | X15CrNiSi20-12 | 309 | — | 20Х20Н14С2 |
| 1.4845 | X12CrNi25-21 | 310 S | — | 20Х23Н18 |
| 1.4841 | X15CrNiSi25-20 | 314 | — | 20Х25Н20С2 |
Application of AISI 304 and 12x18n10t, difference
When using these steels for the production of structures and parts, product elements, it is necessary to take into account the comparison of the chemical composition and properties of AISI 304 and 12x18n10t.
Steel grade 12x18n10t, as a chromium-nickel stainless alloy, is used for structures and equipment elements intended to be used in cryogenic areas. For the manufacture of parts for capacitive, heat transfer and reaction technology. It is used to produce elements of steam heaters and pipes for high-pressure pipelines, parts of furnace equipment, muffles, and exhaust system manifolds. When using this steel in production, an important quality is a long service life while maintaining the same basic characteristics.
AISI 304 steel has such a wide range of applications that it is impossible to list everything. This alloy is most in demand for the manufacture of elements for connecting pipelines, fittings, and welded pipes themselves. 304 steel is widely used in construction, for the production of welded columns, transition bridges, floor parts, monorails, etc. 304 steel is excellent for the manufacture of medical instruments, parts of medical equipment, tanks and containers.
This steel is in demand in the automotive and food industries.
Analogs of steels. Corrosion-resistant steel
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| 1.4003 | X2CrNi12 | — | — | — |
| 1.4512 | X2CrTi12 | 409 | SUH 409 | — |
| 1.4000 | X6Cr13 | 410S | SUS 410 S | 08Х13 |
| 1.4002 | X6CrAl13 | 405 | SUS 405 | — |
| 1.4006 | X12CrN13 | 410 | SUS 410 | 12Х13 |
| 1.4024 | X15Cr13 | (410) | SUS 410 J1 | — |
| 1.4021 | X20Cr13 | (420) | SUS 420 J1 | 20Х13 |
| 1.4028 | X30Cr13 | (420) | SUS 420 J2 | 30Х13 |
| 1.4031 | X39Cr13 | — | SUS 420 J2 | 40Х13 |
| 1.4034 | X46Cr13 | (420) | — | 40Х13 |
| 1.4016 | X6Cr17 | 430 | SUS 430 | 12Х17 |
| 1.4520 | X2CrTi17 | — | — | — |
| 1.4510 | X3CrTi17 | 439 | SUS 430 LX | 08Х17Т |
| 1.4113 | X6CrMo17-1 | 434 | SUS 434 | — |
| 1.4509 | X2CrTiNb18 | 441 | — | — |
| 1.4521 | X2CrMoTi18-2 | 444 | SUS 444 | — |
| 1.4589 | X5CrNiMoTi15-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.4310 | X10CrNi18-8 | (301) | SUS 301 | — |
| 1.4318 | X2CrNiN18-7 | 301 LN | SUS 301 LN | — |
| 1.4301 | X5CrNI18-10 | 304 | SUS 304 | 08Х18Н10 |
| 1.4303 | X4CrNi18-12 | (305) | SUS 305 | 12Х18Н12 |
| 1.4306 | X2CrNi19-11 | 304 L | SUS 304 L | 03Х18Н11 |
| 1.4541 | X6CrNiTi18-10 | 321 | SUS 321 | 08Х18Н10Т |
| 1.4550 | X6CrNiNb18-10 | 347 | SUS 347 | — |
| 1.4401 | X5CrNiMo17-12-2 | 316 | SUS 316 | — |
| 1.4404 | X2CrNiMo17-12-2 | 316 L | SUS 316 L | — |
| 1.4571 | X6CrNiMoTi17-12-2 | 316 Ti | SUS 316 Ti | 10Х17Н13М2Т |
| 1.4561 | X1CrNiMoTi18-13-2 | — | — | — |
| 1.4435 | X2CrNiMo18-14-3 | 316 L | SUS 316 L | 03Х17Н14М2 |
| 1.4439 | X2CrNiMoN17-13-5 | S 31726 | SUS 317 | — |
| 1.4539 | X1NiCrMoCu25-20-5 | N 08904 | — | — |
| 1.4565 | X3CrNiMnMoNbN 23-17-5-3 | S 34565 | — | — |
| 1.4462 | X2CrNiMoN22-5-3 | S 31803 | SUS 329 J3L | — |
| Europe (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) | Japan (JIS) | CIS (GOST) |
| steel grade | Analogues in US standards | ||
| CIS countries GOST | Euronorms | ||
| 10 X2 M | 10CrMo9-10 | 1.7380 | F22 |
| 13 XM | 13CrMo4-4 | 1.7335 | F12 |
| 14 HMF | 14MoV6-3 | 1.7715 | — |
| 15 M | 15Mo3 | 1.5415 | F1 |
| 17 G | 17Mn4 | 1.0481 | — |
| 20 | C22.8 | 1.0460 | — |
| 20 G | 20Mn5 | 1.1133 | — |
| 20 X11 MNF | X20CrMoV12-1 | 1.4922 | — |
09G2S – properties
The composition of the alloy provides this material with the following basic properties:
- density 7.85 g/cu. cm.;
- the yield strength, when heated to different temperatures, lies in the range from 255 to 155 MPa.
Parts made of 09G2S alloy can be welded together by any known type of welding used in industry. In this case, there is no need to carry out any additional preparatory operations, for example, preheating the welding site.
This type of steel has found its application in the creation of welded structures. The good weldability of this material is ensured by the low content of carbon atoms.
Many years of experience show that a higher amount of carbon leads to the formation of various defects, for example, porosity, lack of penetration. Moreover, when carbon burns out, hardened micro-sections are formed in the structure of the weld and this leads to a decrease in the quality of the weld.
Among the many advantages of this steel is the fact that it does not acquire additional brittleness after tempering. In addition, its structure makes it possible to ensure resistance to excessive heating and, as a consequence, the appearance of cracks in the weld area.
Several methods are used to produce this grade of steel:
- open hearth;
- electrothermal;
- converter
Cast iron is used as the main raw material. In accordance with GOST requirements, the melt is optimized, that is:
- raise the amount of carbon;
- alloying components are introduced.
Thanks to these measures, the finished product receives the required properties.
Analogs of steels. Stainless steel
| CIS (GOST) | Euronorms (EN) | Germany (DIN) | USA (AISI) |
| 03 X17 N13 M2 | 1.4404 | X2 CrNiMo 17-12-2 | 316 L |
| 03 X17 N14 M3 | 1.4435 | X2 CrNiMo 18-4-3 | — |
| 03 X18 H11 | 1.4306 | X2 CrNi 19-11 | 304 L |
| 03 X18 N10 T-U | 1.4541-MOD | — | — |
| 06 ХН28 MDT | 1.4503 | X3 NiCrCuMoTi 27-23 | — |
| 06 X18 H11 | 1.4303 | X4 CrNi 18-11 | 305L |
| 08 X12 T1 | 1.4512 | X6 CrTi 12 | 409 |
| 08 X13 | 1.4000 | X6 Cr 13 | 410S |
| 08 X17 N13 M2 | 1.4436 | X5CrNiMo 17-13-3 | 316 |
| 08 X17 N13 M2 T | 1.4571 | Х6 CrNiMoTi 17-12-2 | 316Ti |
| 08 X17 T | 1.4510 | Х6 СrTi 17 | 430Ti |
| 08 X18 H10 | 1.4301 | X5 CrNi 18-10 | 304 |
| 08 X18 N12 T | 1.4541 | Х6 CrNiTi 18-10 | 321 |
| 10 Х23 Н18 | 1.4842 | X12 CrNi 25-20 | 310S |
| 10X13 | 1.4006 | X10 Cr13 | 410 |
| 12 X18 N10 T | 1.4878 | X12 CrNiTi 18-9 | — |
| 12 X18 H9 | — | — | 302 |
| 15 X5 M | 1.7362 | Х12 СrMo 5 | 501 |
| 15 X25 T | 1.4746 | Х8 CrTi 25 | — |
| 20X13 | 1.4021 | X20 Cr 13 | 420 |
| 20 X17 N2 | 1.4057 | X20 CrNi 17-2 | 431 |
| 20 Х23 Н13 | 1.4833 | X7 CrNi 23-14 | 309 |
| 20 X23 H18 | 1.4843 | X16 CrNi 25-20 | 310 |
| 20 Х25 Н20 С2 | 1.4841 | X56 CrNiSi 25-20 | 314 |
| 03 X18 AN11 | 1.4311 | X2 CrNiN 18-10 | 304LN |
| 03 X19 N13 M3 | 1.4438 | X2 18-5-4 | 317L |
| 03 X23 H6 | 1.4362 | X2 CrNiN 23-4 | — |
| 02 X18 M2 BT | 1.4521 | X2 CrMoTi 18-2 | 444 |
| 02 X28 N30 MDB | 1.4563 | X1 NiCrMoCu 31-27-4 | — |
| 03 X17 N13 AM3 | 1.4429 | X2 CrNiMoN 17-13-3 | 316LN |
| 03 X22 N5 AM2 | 1.4462 | X2 CrNiMoN 22-5-3 | — |
| 03 X24 N13 G2 S | 1.4332 | Х2 CrNi 24-12 | 309L |
| 08 X16 N13 M2 B | 1.4580 | X1 CrNiMoNb 17-12-2 | 316 CD |
| 08 X18 N12 B | 1.4550 | X6 CrNiNb 18-10 | 347 |
| 08 X18 N14 M2 B | 1.4583 | X10 CrNiMoNb 18-12 | 318 |
| 08X19AH9 | — | — | 304N |
| 08X19H13M3 | 1.4449 | X5 CrNiMo 17-13 | 317 |
| 08X20H11 | 1.4331 | X2 CrNi 21-10 | 308 |
| 08X20H20TYU | 1.4847 | X8 СrNiAlTi 20-20 | 334 |
| 08X25H4M2 | 1.4460 | X3 CrnImOn 27-5-2 | 329 |
| 08X23H13 | — | — | 309S |
| 09X17H7 Yu | 1.4568 | X7 CrNiAl 17-7 | 631 |
| 1X16H13M2 B | 1.4580 | Х6 CrNiMoNb 17-12-2 | 316Cd |
| 10X13 SJ | 1.4724 | Х10 CrAlSi 13 | 405 |
| 12X15 | 1.4001 | X7 Cr 14 | 429 |
| 12X17 | 1.4016 | X6 Cr17 | 430 |
| 12X17M | 1.4113 | X6 CrMo 17-1 | 434 |
| 12X17MB | 1.4522 | Х2 СrMoNb | 436 |
| 12X18H12 | 1.3955 | GX12 CrNi 18-11 | 305 |
| 12X17 G9 AN4 | 1.4373 | X12 CrMnNiN 18-9-5 | 202 |
| 15X9M | 1.7386 | X12 CrMo 9-1 | 504 |
| 15X12 | — | — | 403 |
| 15X13H2 | — | — | 414 |
| 15X17H7 | 1.4310 | X12 CrNi 17-7 | 301 |