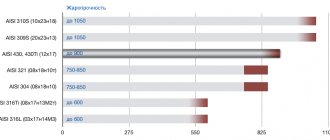
Characteristics of steel grade AISI 430 / SS 430
| Standard | ASTM A182 - Standard Specification for Forged or Rolled Pipe Flanges, Forged Fittings, Valves, and Alloy and Stainless Steel Parts for High Temperature Service ASTM A240 - Standard Specification for Chrome- and Nickel-Chrome, Chrome- and Manganese-Nickel Stainless Steels for Plate, Sheet, and Strip for Pressure Vessels and General Applications ASTM A268 - Standard Specification for Seamless and Welded Ferritic and Martensitic Stainless Steel Pipe for General Applications ASTM A276 - Standard Specification for Fabricated, Unhot or Cold Processed Bars and Blooms, Other than Forged (Recycled) Bars ASTM A314 - Standard Specification Covers Stainless Steel Billets and Bars for Forging Only ASTM A479 - Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Rods and Sections for Boilers and Other Pressure Vessels | ||||||
| Classification | Stainless Ferritic Steel | ||||||
| Application | Sheets, coils, rails, pressure vessels | ||||||
| Other names | UNS | S43000 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A182) | Forged or rolled flanges | A182 F430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A240) | Flat rolled products | A240 Type 430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A268) | Seamless and welded pipes | A268 TP430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A276) | Rods and profiles | A276 Type 430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A314) | Blanks for forging | A314 430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A473) | Stampings | A473 430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A479) | Rods and profiles for boilers and vessels | A479 430 | |||||
| USA (ASTM A580) | Stainless steel wire | A580 Type 430 | |||||
AISI 430 steel is the most popular of the corrosion-resistant ferritic steels intended for general use. It has good properties, characteristics, ease of processing, high resistance to intercrystalline corrosion and oxidation at high temperatures.
Mechanical restoration
AISI 430 stainless steel is relatively easy to process. Machining can be improved by well sharpening the cutting tool to avoid excessive hardening at the machining areas. The impact on the processed surface of AISI 430 steel products should be light, but deep enough to prevent hardening when passing over the surface of the material. Just like when machining austenitic steels, when machining AISI 430 steel it is useful to use coolants.
Mechanical properties of AISI 430 material
| Ultimate strength (temporary tensile strength), min., MPa | 450 |
| Yield strength, 0.2%, MPa | 205 |
| Rockwell hardness, HRB max. | 88 |
| Brinell hardness, HB type. | 160 |
| Magnetic properties | Ferromagnetic |
| Elongation, min., % | 22 |
Which GOSTs regulate
Steel 12x17 according to GOST can be produced according to several standards depending on the type of product. So, for example, calibrated hexagonal rolled products from this steel are produced in accordance with GOST 8560-78, and high-quality round hot-rolled products are produced in accordance with GOST 2590-2006. All GOST standards for this type of steel provide for the same chemical composition of the alloy:
- carbon - 0.12%;
- chromium – 16-18%;
- manganese -0.8%;
- phosphorus – 0.025%;
- sulfur – 0.035%;
- silicon - 0.8%.
In addition to the main components, the metal may also contain harmful impurities in small quantities (fractions of a percent), which arise during steel melting.
Performance at elevated temperatures
| Temperature, °C | 300 | 400 | 550 | 650 | 750 |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 450 | 430 | 220 | 120 | 50 |
| Temperature, °C | 550 | 600 | 650 | 700 | 750 |
| Yield strength, MPa | 50 | 30 | 15 | 5 | 3 |
Corrosion resistance in acidic environments
| Temperature, °C | 20 | 80 | ||||||||||
| Concentration, % by weight | 1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 80 | 100 |
| Sulfuric acid | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Phosphoric acid | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Nitric acid | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Formic acid | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
0
= high degree of protection (corrosion rate does not exceed 100 mm/year);
1
= partial protection (corrosion rate ranges from 100m to 1000 mm/year);
2
= no protection (corrosion rate exceeds 1000 mm/year).
Corrosion resistance
AISI 430 has increased corrosion resistance in most aggressive environments, even in organic and inorganic acids, including nitric acid.
Optimal corrosion resistance of AISI 430 stainless steel is achieved when using polished steel, since in this case the surface in contact with an aggressive environment is minimized.
Like other ferritic (high iron content) alloys, AISI 430 stainless steel has high resistance to stress corrosion cracking.
Scope of application
AISI 430 steel is widely used:
- In the chemical and petroleum industries;
- In mechanical and automotive industry;
- In construction (roofing organization) and design;
- In the food and wine industry;
- In the production of equipment for heat exchangers;
- In the manufacture of furnace equipment;
- In the manufacture of household appliances, dishes, plumbing and kitchen equipment.
Unlike austenitic steel grades containing nickel, chromium grades, which include AISI 430, have low thermal expansion and increased thermal conductivity. High heat resistance allows the use of steel:
- In refrigeration towers;
- In cooling systems for food tanks (cooling with water, glycol, etc.)
It is not recommended to use AISI 430 steel in conditions of cryogenic temperatures and in the construction of structures that are subject to heavy loads.
Welding
AISI 430 / ss 430 stainless steel can be welded by any method. It would be optimal to use arc welding in inert gases.
Welding “from above” is recommended (the welding tool is located above the surface to be welded); the filler material can be 309L welding wire. It is also possible to use electrodes based on ferritic steel AISI 430, AISI 308, AISI 310, AISI 309 or AISI 312.
It is recommended to clean welds from scale mechanically or chemically and then passivate them.
Stainless steel AISI 430 (08x17)
AISI 430 stainless steel is by far the most widely used corrosion-resistant ferritic chromium steel for general purposes (in accordance with ASTM A240), which combines:
- high strength and high mechanical properties;
- high corrosion resistance, including atmospheric. Corrosion resistance is ensured by the high chromium content and low carbon content of the steel;
- excellent machinability (both good plastic deformability and applicability to the processes of stamping, drawing, perforating holes in it, etc.)
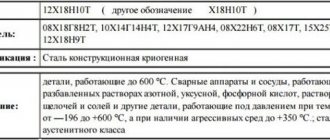
In terms of its performance characteristics, stainless steel AISI 430 is an improved Russian analogue of steel grade 08Х17Т, which, in turn, according to GOST 5632-72 “is recommended as a substitute for steel grades 12Х18Н10Т and 12Х18Н9Т”.
Chemical composition of AISI 430 steel
| Compound % | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr |
| according to ASTM A240 | 0.12 max | 1.0 max. | 0.045 max. | 0.03 max. | 1.0 max. | 16.0-18.0 |
| Typically | less than 0.05 | 0.7 | 0.020 | 0.025 | 0.65 | 17 |
Corrosion resistance AISI 430
| steel grade | NaCl 3.5% (sea water), T=20˚C | C2H2O4 (oxalic acid), 2.5%, T=100˚C | H2SO4 (sulfuric acid), 5%, T=35˚C | CNNO3 (nitric acid), 30%, T=106˚C | |
| 430 | >1.0 mm/year | >1.0 mm/year | >1.0 mm/year | 0.1-1.0 mm/year | |
Characteristics of AISI 430 steel grade and its areas of application
The overall corrosion resistance of this steel grade in many environments is comparable to that of domestic austenitic steel 08x17. In addition, unlike nickel-containing austenitic steels of the “18Cr-10Ni” type, ferritic low-carbon chromium steels are also stable in various sulfur-containing environments. As a result, products made from AISI 430 stainless steel, including, for example, wire mesh, etc., can be used in systems for pumping oil and gas, as well as pure petroleum products, various hydrocarbons. AISI 430 stainless steel is also used in gas and oil refining process plants. Of course, when using this or that steel, it is advisable to conduct individual tests for corrosion resistance, determined by temperature, contact with other materials, load and degree of direct contact with process media, duration of continuous operation, abrasive effects of products, aggressive influence of cleaning and/or disinfectant solutions, as well as other specific conditions.
In general, AISI 430 stainless steel is positioned in terms of its chemical composition as a direct analogue of the domestic steel grade 12X17. However, due to the low carbon concentration in steel, its additional stabilization with titanium is unnecessary, since the actual carbon content at the level of 0.020-0.035% guarantees that the steel is not prone to intergranular corrosion at elevated temperatures (intensive carbide formation in steel 430 begins only at temperatures above 1000 OS) and, in addition, provides excellent weldability. In addition, additional advantages are the fact that, unlike these nickel-containing austenitic grades, 430 steel is insensitive to intergranular corrosion damage in the temperature range of 500-800 °C, and is also much less sensitive to chloride cracking under load.
Due to its low coefficient of thermal expansion, steel is optimally suited for products that experience significant temperature changes, and high thermal conductivity determines the advantages when using this steel in heat transfer systems. Possessing a fairly low thermal inertia (specific heat capacity), grade 430 steel heats up and cools much faster with lower energy consumption, which avoids possible inertial overheating).
Below we present some comparative characteristics of steel grades AISI 430 and 12Х18Н10Т.
AISI 430[/td]
| Name | Thickness, mm | Retail price, rub/t | ||||||
| Steel AISI 430 (sheets, rolls, strips) | 0,4 | 154 990 | steel grade | Specific heat capacity (J/g •K) at 20 °C | Thermal conductivity, (W/m •K) at 20 °C | Thermal expansion coefficient (106 °C-1) average. | Resistance to chloride corrosion cracking, MPa | Magnetic properties |
| 0,44 | 25 | 10 | 350 | Yes | ||||
| 12Х18Н10Т | 0,52 | 15 | 17.5 | 140 | No | |||
AISI 430 steel is widely used in the following industrial sectors:
- civil engineering;
- design and architecture;
- food industry;
- production of kitchen appliances, tables, serving tools, drains, sinks, drums and trays for dishwashers, parts of washing machines, etc.;
- automotive industry (for example, decorative exhaust systems, etc.);
- production of various types of internal and external fittings;
- equipment for heat exchangers;
- and many others.
The use of economically alloyed nickel-free stainless steels (i.e. analogues of steel grade 430) in the food and processing industries is regulated by standards, as well as other regulatory documents.
The main document on stainless steels is GOST 5632, which also regulates the use of chromium ferritic steels of grades 12Х17 and 08Х17Т as substitutes for austenitic chromium-nickel steels 12Х18Н9Т and 12Х18Н10Т, including “for the manufacture of food industry equipment and household items and kitchen utensils.”
Stainless steel type AISI 430 can be used for the manufacture of machine parts and apparatus for the wine industry. These grades have become allowed to be used in direct contact with wine, must, cognac spirit, wine waste processing products, etc. It is allowed to use these steels (08Х17Т) for the manufacture of equipment used in the dairy and meat industries at temperatures of 30-140 °C, etc.
AISI 430 steel is used for the manufacture of technological equipment used at different stages of food production (washing or hygienic processing of raw materials, products and equipment, grinding, separating and sorting products, mixing, heat treatment, packaging and packing, transportation, etc.) .
430 steel can have many types of surfaces, among which the most popular are: matte, honed, grooved and mirror. Recently, a type of surface has also become popular - decorative, which is characterized by decorative properties and is often used in the finishing and decoration of premises and structures.
Steels of the 400 series (including steel 430) can not only be used as substitutes for nickel-containing grades, but also, due to their superiority over the latter in a number of properties, are often indispensable in the production of food industry equipment.
AISI 430 steel complies with sanitary and epidemiological rules and regulations (conclusion of the Department of State Sanitary and Epidemiological Surveillance of the Russian Federation) and is very promising for use in the production of equipment for various sectors of the food and processing industry: meat, oil and fat, bakery, alcohol, beer and soft drinks, alcoholic beverages , confectionery, and many others. Products made from this steel can be used at technological stages of food production, such as washing or hygienic processing of raw materials, products and equipment; grinding, separating and sorting manufactured products; mixing, heat treatment, filling, packaging and transportation. The high corrosion resistance of AISI 430 steel grade is due to the lower carbon content combined with a high chromium content (16-18%).
Since, in comparison with austenitic nickel-containing steel grades, chromium steels have a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and increased thermal conductivity, which predetermines their preferential use and application in such heat exchange structures as cooling towers, etc., a low coefficient of thermal expansion ensures more reliable fitting fastening and ensures rapid heat exchange in cooling systems of food tanks (systems with glycol, water, and other cooling media). Welded structures and pipelines made of chromium steels change dimensions significantly less during temperature fluctuations, which reduces destructive fatigue loads during temperature changes and helps prevent possible leaks from hydraulic connections.
AISI 430 steel has proven itself to be a very resistant material in gaseous environments resulting from the combustion of various types of fuel. These environments can contain both products of complete (carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen, etc.) and incomplete (carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, etc.) combustion. AISI 430 steel is also used for the manufacture of housings and pipes for neutralization, recirculation, capture and exhaust systems.
Properties of AISI 430 steel at elevated temperatures:
AISI 430 steel is not hardened by heat treatment and has good resistance to scale formation up to 850? C, while maintaining its useful operational mechanical properties up to high temperatures.
Tensile strength at elevated temperatures:
| Temperature, °C | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 |
| Tensile strength, MPa | 450 | 430 | 250 | 145 |
AISI 430 steel is classified as heat-resistant when operating at temperatures up to 850 °C. Actual operating temperatures vary depending on environmental conditions.
Welding
This grade of steel is excellently weldable by any known methods. Provided that post-weld pickling/cleaning and passivation operations are undertaken, there will be no loss of corrosion properties at the weld site (including the heat-affected zone).
The best option is to use arc welding in inert gases while maintaining a minimum energy input into the welded seam. Welding “from above” is recommended (i.e., when the surface to be welded is located below the welding tool). Austenitic wire 309L, Sv-07Х25Н13, Sv-08Х25Н13БТУ, etc. is used as a filler material. It is also possible to use electrodes or filler wires based on ferritic chromium steel AISI 430.
In order to guarantee adequate corrosion resistance, it is necessary to remove scale and tarnish by pickling or mechanical treatment with stainless steel brushes and passivate with a cold 10-20% nitric acid solution. Subsequent thorough rinsing with cold water and drying is required.
Our specialists will advise you on any questions you may have regarding the properties, manufacture, application and prices of AISI 430 stainless steel.
Want to know the cost or place an order?
Our specialists will be happy to help you!
+7
Return to main page >>