Steel is one of the most common materials in modern production. In its composition, it consists of iron and carbon, and to give the material special additional qualities, additional impurities are added, the proportions of which vary depending on the final purpose. St3 steel is becoming increasingly widespread. It is used in the manufacture of a fairly wide range of designs, but most people know it as a material for making pipes for heat supply systems. As part of this material, we will look at the features and characteristics of steel 3.
Main details
St3 steel is currently one of the most in demand due to its operational features. It is most widespread in the industry of manufacturing pipes for heating systems, as well as many other items for everyday use.
Galvanized circle made of steel St3
In most cases, St3 steel is classified as ordinary quality carbon steel.
Chemical composition of steel St3
The area of use and functionality of each type of steel is determined by its chemical composition, since it determines the specific properties of the material, as well as the potential difficulties of heat treatment.
Due to its chemical composition, this type of steel is the most widespread on the market, and many construction works cannot be imagined without its use. The main chemical properties in this case can be identified as follows:
- Iron concentration is 97%, carbon concentration ranges from 0.14 to 0.22%. The hardness of the structure, as well as some of the physical properties, is determined precisely by the carbon content in the material.
- A small amount of alloying elements, namely chromium and nickel. Their concentration does not exceed 0.3%. Copper is added to this brand in the same percentage.
The main requirement for the production of this type of steel is the organization of a strict system for controlling the concentration of harmful impurities, which means phosphorus and sulfur. Excessive amounts of nitrogen should also be avoided.
St3 grade steel is a mandatory material for the construction and construction of above-ground and underground communications, production of transport, as well as various machine tools.
The most important element in the manufacture of st3 is deoxidation, which means the removal of oxygen from the molten raw material, on which the mechanical and physical properties of the alloy will directly depend.
Depending on deoxidation, st3 is divided into the following categories:
- Calm. Aluminum, silicon and manganese are used for deoxidation.
- Boiling. Only manganese is used for deoxidation.
- Semi-calm. Use of aluminum and manganese for deoxidation.
The properties of the ST3 steel alloy are presented in table form.
| Surface hardness | 131 MPa | ||
| Temporary resistance | 360-570 MPa | ||
| Yield strength | 235-245 MPa | ||
| Relative extension | 33% | ||
| Relative narrowing | 59% | ||
| Forging temperature range | 750-1300 degrees | ||
| Unlimited weldability by any possible method | |||
Foreign analogues of markm steel 3sp
| USA | A284Gr.D, A57036, A573Gr.58, A611Gr.C, GradeC, K01804, K02001, K02301, K02502, K02601, K02701, K02702, M1017 |
| Germany | 1.0038, 1.0116, DC03, Fe360B, Fe360D1, RSt37-2, RSt37-3, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235JR, S235JRG2, St37-2, St37-3, St37-3G |
| Japan | SS330, SS34, SS400 |
| France | E24-2, E24-2NE, E24-3, E24-4, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235J2G4, S235JRG2 |
| England | 1449-2723CR, 1449-3723CR, 3723HR, 40B, 40C, 40D, 4360-40B, 4360-40D, 4449-250, 722M24, Fe360BFU, Fe360D1FF, HFS3, HFS4, HFW3, HFW4, S235J2G 3, S235JR, S235JRG2 |
| European Union | Fe37-3FN, Fe37-3FU, Fe37B1FN, Fe37B1FU, Fe37B3FN, Fe37B3FU, S235, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235JR, S235JRG2 |
| Italy | Fe360B, Fe360BFN, Fe360C, Fe360CFN, Fe360D, Fe360DFF, Fe37-2, S235J0, S235J2G3, S235J2G4, S235JRG2 |
| Belgium | FE360BFN, FE360BFU, FED1FF |
| Spain | AE235BFN, AE235BFU, AE235D, Fe360BFN, Fe360BFU, Fe360D1FF, S235J2G3, S235JRG2 |
| China | Q235, Q235A, Q235A-B, Q235A-Z, Q235B, Q235B-Z, Q235C |
| Sweden | 1312, 1313 |
| Bulgaria | BSt3ps, BSt3sp, Ew-08AA, S235J2G3, S235JRG2, WSt3ps, WSt3sp |
| Hungary | Fe235BFN, Fe235D, S235J2G3, S235JRG2 |
| Poland | St3S, St3SX, St3V, St3W |
| Romania | OL37.1, OL37.2, OL37.4 |
| Czech | 11375, 11378 |
| Finland | FORM300H, RACOLD03F, RACOLD215S |
| Austria | RSt360B |
Physical properties
Currently, the scope of use of St3 steel is constantly expanding. Already now, the basis for a huge number of workpieces is precisely this type of steel. This is largely due to mechanical properties, among which are:
- Yield strength;
- Temporary resistance;
- Relative extension;
- Impact strength.
- Tensile strength.
At the same time, the following most important technical characteristics are also highlighted:
- Hardness 131 MPa.
- Heterogeneous density;
- No restrictions on weldability;
- No tendency to temper brittleness.
It is these technical characteristics that determine the active use of St3 steel in the construction industry.
Decoding the brand
The specifics of decoding any grade of metal are determined by the relevant regulatory documents, as well as GOSTs. For example, according to GOST 380, the following types of metal are available: steel St3SP, St3PS and St3KP.
Indexes are mandatory for any marking. This is an important note for the preparation of any documentation and descriptions in this type of activity.
When deciphering a brand, the following principle should be used:
- St is a formal designation used to indicate the common quality of carbon steel.
- 3 – digital value showing the conventional number of the alloy grade. According to current accepted numbering rules, stamps from 0 to 6 can exist.
- G is a symbol that is not used in all markings. Indicates the presence of manganese impurities.
- Sp is the degree of deoxidation of the material. The most important parameter of steel grade. The additional designation “ps” means “semi-calm”, and “kp” means “boiling”.
It is worth noting that this particular approach to deciphering markings began to be used relatively recently after the introduction of new standards. Before this, other approaches were used to create steel markings, which were additionally divided into various groups.
Features of processing steel with mechanical tools
One of the most important aspects of drawing up the correct technological process for processing parts made from ST3 is the choice of cutting modes and the choice of the right tool.
For turning and milling, a cutting tool is used, which is made of hard alloys VK8, T5K10. Taps and dies can also be used, which are made from P18 and P6M5. When cutting threads by hand, it is recommended to use castor oil, which will greatly simplify the process.
Depending on the type of processing, as well as the available technical parameters of the machine equipment, a specific choice of processing speed is made.
Total information
| Substitute |
| Steel: 09G2, 09G2DT, 09G2T, 10G2S. |
| Type of delivery |
| Long products, including shaped steel: GOST 19281-73, GOST 2590-71, GOST 2591-71, GOST 8240-72. Thick sheet GOST 19282-73, GOST 5520-79, GOST 5521-76, GOST 19903-74. Thin sheet GOST 17066-80, GOST 19903-74, GOST 19904-74. Strip GOST 103-76, GOST 82-70. Forgings and forged blanks GOST 1133-71. |
| Purpose |
| Various parts and elements of welded metal structures operating at temperatures from -70 to +425 °C. |
Use of St3 steel
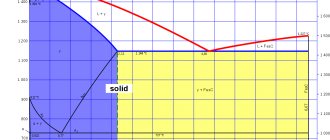
Deoxidation is a key factor for this grade of steel. Depending on it, specific possible operating conditions and processing features of a given metal are determined. The chemical and physical properties of the metal will deteriorate as the total amount of oxygen increases.
Steel can also be classified depending on its silicon content:
- Boiling. Silicon level not less than 0.05%.
- Semi-calm. Silicon levels range from 0.05% to 0.15%.
- Calm. Silicon level is above 0.15%.
During the production of boiling steel, additional gas saturation occurs. However, such steel is classified as non-deoxidized, and therefore is less valued.
The quiet variety of steel has the highest final cost. This is explained by the fact that it is this type of steel that undergoes the most thorough purification from oxygen to ensure the greatest hardness and strength. As a result, this metal is most resistant to negative environmental influences.
Angles made of steel St3
The quiet version of this steel is used to create rolled sheets, railway elements, suspended structures, fittings, and pipelines.
At the same time, the semi-quiet variety of steel contains about 1% oxygen. It is characterized by less hardness and ductility than the calm variety, but has also become quite widespread. It is necessary for the production of pipes with different diameters and wall thicknesses, hexagons, angles and squares of load-bearing structures, as well as sheet metal.
Features of ST3 production
All chemical and physical properties of the finished material will be determined by the components that are included in the composition, and therefore largely depend on the technologies used in the production of the alloy.
The basis of the steel alloy is ferrite, which is a component of iron-carbon alloys. At its core, this element is a solid solution of carbon and alloying components. This alloy is also infused with carbon to increase its strength.
Phosphorus, sulfur and their derivatives are considered harmful impurities, since they impair the ductility of the alloy and also increase its brittleness when exposed to cold.
Areas of application
Areas of application:
- Manufacturing of parts that are subject to heavy loads - metal corners, channels, axles, beams.
- Assembly of vehicles, industrial equipment, construction of metal structures. Due to their resistance to different temperatures, the structures can be used in different climatic conditions.
- Application in the chemical industry. The material is resistant to chemicals.
- Manufacturing of poles, fences, frames for public benches, gazebos, swings, children's slides, horizontal bars.
- Production of heating equipment, steam boilers, machines for agricultural activities.
To use the material in other areas of industry, various alloying components are added to its composition.
Advantages and disadvantages of ST3 steel
The main strengths of this steel grade are:
- Excellent weldability under any heat treatment.
- Possibility of obtaining a large variation in mechanical properties.
- Low cost with a large number of operating options.
- Possibility of hardening using high-frequency current.
- No tendency to temper brittleness.
The main disadvantage, which is inherent in all such carbon analogues, is the increased susceptibility to corrosion. Other disadvantages include the impossibility of using the alloy in northern climates, as well as increased fragility due to its coarse or medium-grained structure.
The demand for boiling alloys is explained by their high availability, since they have the lowest price, and their structure is easiest to further process. Thus, if it is necessary to use active heat treatment, this variety will be the most suitable, although it is worth considering its reduced performance characteristics due to high oxygen levels.
Comparison with another steel grade
For example, for 09g2s and st3 the difference is determined primarily by the carbon content. For St3sp it is 10-20 times higher than what is found in the low-alloy alloy.
St3sp – refers to carbon alloys. This grade of steel is characterized by high brittleness and rapid destruction at low temperatures. If the brand being described has a lower limit of -70 degrees, then the object of comparison is only -20.
The quality of St3sp is ordinary, which indicates a likely high presence of sulfur and phosphorus. Then, like 09g2s is high quality. All other advantages are already in the previous description. It only remains to note that the cost of this brand is significantly higher than the price of St3sp.
Video about low alloy steels: