Welding is an important stage in the creation of new objects and their elements. The performance characteristics of the connections depend on the correctness of the process. Welded structures are created in several ways, using different materials and apparatus. The choice of technology depends on the required characteristics of the seams.
Welding is an important stage in the creation of new objects and their elements.
Total information
Metal structures are used everywhere: industrial and civil buildings, production facilities and equipment, parts of transport routes, etc. There are different ways to connect metal structures, they are distinguished:
- Rivet connections;
- bolted connections;
- welded joints;
Welding is becoming a common solution when choosing a method for connecting metal elements, since a welded structure has a number of advantages:
- Relative ease of manufacture;
- High speed of work;
- Large selection of materials and equipment for welding;
- Ability to create structures of complex configuration;
- Creation of an equally strong hermetic connection;
- Connection of metal meshes and reinforcement cages.
Let's talk in more detail about welded metal structures.
Weld quality control
The state standard regulates the mechanical properties of the welded joint, its individual sections, as well as the resulting material. In order to determine how high quality a product is, it is necessary to test it.
GOST prescribes the following methods for determining quality:
- Static
. This method involves a gradual increase in load. It takes a long time to determine quality, since it is necessary to create a constant, prolonged tension. - Dynamic
. In this case, pendulum pile drivers are used. There is no need for long-term observation. A load of maximum force is created in a short period of time. - Fatigue
. The load is created repeatedly. Its strength has different meanings, the number of cycles can reach several million.
Recommended articles
- Welding electrodes: which ones to choose for the job
- Capacitor welding: process features
- Weld defects: we understand the causes, eliminate the consequences
To determine the hardness of weld sections, the Rockwell, Brinnell, and Weckler methods are used.
.
To determine acceptance quality without destructive force, the following methods are used:
- Visual and measuring control
. To assess quality, an external inspection is performed. - Ultrasonic method
. Quality assessment occurs using ultrasonic waves. If there are defects in the material, the defective areas will not reflect the wave. - Capillary method
. In this case, liquids with coloring pigments are used. If the material has microcracks, the liquid will penetrate into them and reveal the presence of a defect through staining. - Pneumatic method
. The presence of defects is determined by supplying air under pressure and a soap solution. Poor quality will be indicated by the formation of bubbles. - The hydraulic method
is similar to the capillary method. Here, too, liquid is poured in, then time is waited. If there are microcracks in the material, they will be filled. Then the specialists will tap the surface with a hammer. If the metal leaks, it means the material has defects. - The magnetic method
is used to control the quality of steel elements. During the test, the material is magnetized and then metal powder is sprayed. If there are no defects, the powder will fall according to the pattern of magnetic fields.
GOST 23118-99 and Consolidated Rules SP105-34-96 indicate the quality requirements for metal products and various types of welds. All parts are examined for the following defects:
- inhomogeneities;
- cracks;
- shells;
- fistulas;
- chips;
- lack of penetration;
- folds
Knowledge of the basic types and connections of welds, as well as the methods and principles of their application, makes it possible to choose the required welding method as competently as possible.
Classification
Classification of welded metal structures is divided into:
According to the materials of the workpieces from which they are made:
- Pipe
- Leafy
- Profile
- Rod
According to the material from which the structure is made:
Metal:
- Made of black steel;
- Made from low, medium and high alloy steel;
- From non-ferrous metals;
- From alloys;
Non-metallic:
- Polyethylene;
- Polypropylene;
- Composite;
According to the type of industrial facility on which they are mounted:
- Oil;
- Gas;
- Thermal power;
- Nuclear power structures;
- Ship;
- Aviation;
- lifting structures.
Types of welded metal structures
Metal structures are something without which it is very difficult to imagine the most modern construction industry. Along with reinforced concrete, they are the most common solution for industrial, public and civil buildings and structures, mechanical engineering and other industries. The most common types (groups) of building metal welded structures are steel:
- Columns.
- Beams.
- Connections
- Shells.
- Cases.
- Rod.
- Lattice.
- Farms.
- Welded supports (for pipelines or equipment).
- Leafy.
Let's talk in more detail about some welded structures, their features during manufacturing and installation. Their production is carried out at enterprises that manufacture metal structures and directly at the construction and repair site.
Metal welded trusses
Welded steel trusses are a flat lattice system of metal elements that allows you to span large spans of buildings and structures.
A truss is a structural element of a building that serves to support the roofing system (purlins, decking, roofing pie) and transfer the load from it to columns or walls.
Metal trusses are often used in the construction of industrial buildings, since the technological process often does not allow the installation of intermediate racks.
Also, steel trusses are most widely used in the construction of social and administrative buildings. Such as: shopping centers, cinemas, stadiums, swimming pools and many others.
It is such buildings that are characterized by the presence of large free internal space. The metal welded truss consists of:
- Knots of the upper belt.
- Raskosov.
- Stoeck.
Braces, in turn, are divided into supporting and ordinary. Support braces are located at the point where the truss is supported. They carry heavy loads, so their cross-section is often larger than that of ordinary braces (or the grade of steel is higher).
Farms can be homogeneous or combined. Because they can combine elements made from different grades of steel.
It is combined metal structures that are an effective solution; their use is most rational in cases where the loads on the elements are significantly different. The braces, as well as the truss posts, are connected to the lower as well as the upper chord directly or using gussets. Their elements can be made from:
- Square pipe.
- Rectangular pipe.
- Round pipe.
- Corner.
- Various profiles.
Steel trusses are the most common solution. Trusses are developed for a specific construction project or selected according to a series, having performed the appropriate calculations.
Truss drawings are developed in the KM and KMD section, where basic instructions for the production and installation of structures are also prescribed.
Requirements for welds
Welding today is recognized as the most popular method for the production of various metal structures. Its popularity is explained primarily by the reliability and strength of the final connection. It is quite obvious that welding is widely used in the production of metal products that will bear heavy loads.
But it is worth noting that not all types of welds have durability; the promised durability can only be guaranteed by connections in the manufacture of which all the requirements specified in GOST were met.
The main document that prescribes quality criteria for various types and types of welds is GOST 23118-99. Some additional requirements are specified in the following rules and instructions:
- SP 105-34-96 - consolidated rules that prescribe quality criteria for welds, and also dictate the algorithm for carrying out welding activities;
- VSN 006-89, VBN A.3.1.-36-3-96 – instructions on the technology of welding work;
- VSN 012-88 is an instruction, the content of which consistently indicates all measures to control the quality of work performed.
VT-metall offers services:
The above regulatory documents apply to various welding methods and to various types of seams in welded joints.
How to weld metal trusses
Welding is carried out either in the factory or at construction and repair sites. In the factory, production of critical structures, such as trusses for covering public and industrial buildings, as well as objects.
As a rule, large-span metal trusses are divided into shipping marks (KM section), which are delivered to the construction and repair site. There they carry out enlarged assembly of shipping stamps, as well as installation according to the developed technology.
The length of shipping stamps usually does not exceed 12 meters; this is necessary for the safe transportation of the shipping stamp by road or otherwise.
Less critical ones, such as trusses for entrance canopies and awnings, are made at the construction site. You can make a simple farm with your own hands, for example for a garage, or for a greenhouse. On the website mrmetall.ru you will find useful information on the choice of steel, selection of electrodes, as well as all the necessary equipment.
Key Benefits
The positive qualities of steel structures include:
- Increased load-bearing capacity. Despite its small size, the structure can withstand high loads. This is due to the increased strength of the metal.
- Increased reliability. At the preliminary stages, accurate calculations are made, which helps to obtain the required performance characteristics.
- Easy to install and transport. Metal elements are much lighter than concrete or stone ones.
- Integrity of metal or seams, allowing the formation of sealed pipelines and tanks.
- Possibility of assembling structures both in industrial conditions and at home.
- Ease of use. As loads increase, the products can be strengthened. They can easily be reconstructed and repaired.
Sequences of operations when welding a metal truss
As when welding any other product, before starting work it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the regulatory documentation for manufacturing and the developed technology in full. With drawings of the KM, KMD section, technological maps, as well as prepare the necessary materials, tools, and organize the workplace.
The connection of individual nodes (made from pipes or profiles) leads from the middle node elements to the supporting ones. First, the existing butt joints of the parts are welded, then they move on to T-joints and corner joints. Next, seams with greater thickness are welded. Assembly is carried out using tacks 25-40 mm long. Seams located next to each other must be made after a technological pause.
Fulfillment of this condition is necessary to reduce deformations. Only after the metal has completely cooled down, where a closely spaced seam will be applied. The end of each longitudinal connection (when connecting braces, racks or other units with a gusset) must be brought out to the end of the welded unit by an amount of 2 cm.
Connections used in welding structures
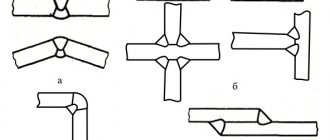
The most common types of seams are:
- Butt joints, characterized by resistance to static and dynamic loads. When forming joints, almost all welding technologies can be used.
- Corner, performing connecting functions. Connections are not capable of transferring workloads. Any welding method is used to form seams.
- Laps used to connect sheet elements. They differ from butt ones in less strength.
- T-bars used when working with spatial structures.
Less common are slotted, end and other connections.
Butt welding joints.
We recommend that you read
Existing types of welded joints
Metal sheet structures.
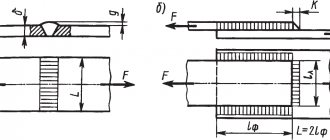
Metal sheet welded structures are most often used in industry, these include: reservoirs, tanks, bunkers, gas tanks, decks, etc. Sheet metal structures are characterized by a combination of load-bearing and enclosing functions.
Automatic, semi-automatic, electroslag welding is often used for sheets. The parts are longer and are subject to more stringent requirements for joint strength and tightness. You can see the sequence of seams in the image.
Additional Information
Each type of welded structure is connected in its own way. Recommended technologies are indicated in drawings and designs. After welding is completed, the object must acquire the required strength. This places the responsibility on the welder for compliance with the rules and regulations of the process. Special requirements are imposed on metal structures subject to high loads. The service life of the entire facility depends on the quality of welding. After completion of the work, the structures are thoroughly inspected.
Welding methods
Another classification is based on the welding method. There are many welding methods, differing in performance conditions. In production (factory), as a rule, they use:
- Semi-automatic welding in CO2 environment.
- Automatic electric welding in a shielding gas environment (for electric current welding of thick metal, submerged arc welding).
- In installation work, use: Manual arc welding. Automatic and semi-automatic (rare); Manual welding in argon with a non-consumable electrode (mainly used for aluminum and stainless steel).
What types of welded joints exist
A seam formed as a result of crystallization or plastic deformation (pressure welding) of the material of the joined elements. It represents a space at the junction. Welds can be divided into:
- Factory ones.
- Assembly.
They have different designations on the drawings, so carefully study the design documentation before starting work on the construction of this welding structure.
Regardless of whether the seam is factory or assembly, it must meet the requirements and ensure equal strength of the connection. There are many types of welded joints, we suggest you visually familiarize yourself with the most used and common:
- Butt joint.
- Gusset.
- T-joint.
- Lap connection
Tolerances are indicated in regulatory documentation, namely in GOST R 13920-2017.
Standards and regulations
Requirements for the working qualities of welded metal structures used in construction are specified in GOST 27772. SNIP II 23-81 is also an important regulatory documentation.
The requirements specified in these acts apply to the work of professionals. However, you need to familiarize yourself with them before performing welding in a home workshop.
When using a hand-held device, take into account the requirements of GOST 5264-80. Standard 14771-76 describes the features of gas shielded welding. Regulatory documentation also regulates the process of preparing the parts to be joined.
How to make welds correctly
To perform a weld correctly, firstly, you need to familiarize yourself with the regulatory welding and design documentation. The necessary design documentation is presented in the form of a basic set of drawings of the KM brand, and KMD (metal structures, metal detailing structures). In the album of the KM section you will receive general information about the metal welded structures of the construction site (or part of it):
- General form;
- composition of structures (how many beams, columns, trusses, braces, etc. parts);
- main connection points;
- instructions for performing work;
- information about loads on structures;
- specification of rolled metal.
In the KMD section you will find:
- detailed drawings of each metal element;
- detailed components for connecting elements;
- updated specification of rolled metal products.
Read the notes and instructions for performing work on the drawings. It may contain important points, without which the manufactured metal structure will not meet the requirements applied to it.
Assembly and welding of elements must be carried out only if there is a documented technology for welding work for this structure.
Documentation is carried out in the form of technological maps and (or) a production project (PPSD) for welding work. They reflect in detail all questions about the process and materials.
Welding defects
Disadvantages can be internal or external. The first type includes:
- Hot or cold cracks. The former appear during the heating period, the latter during cooling.
- Pores are gas-filled cavities. Appear when the electrode is moved too quickly.
- Foreign inclusions consisting of tungsten, oxides or slag. They arise due to the destruction of the gas cloud protecting the weld pool. When such defects appear, re-cutting of the edges followed by welding is required.
We recommend reading: How many categories do welders have?
External defects include:
- Lack of fusion or lack of penetration. When multilayer welding, a seam does not form in some places. This reduces the strength of the structure.
- Burns formed when edges penetrate through. The appearance of a defect is facilitated by slowly moving the electrode at a high current.
- Sagging resulting from the contact of the melt on the main surface.
- Craters formed at arc separation sites. Holes appear when novice welders perform work.
- Oxide films or scales that appear when the weld interacts with air.
- Fistulas formed due to improper preparation of parts.
Types and classification of defects
Quality control of connections eliminates such problems. You can see some defects, such as burns or sagging, during the initial inspection.
Welding sequence
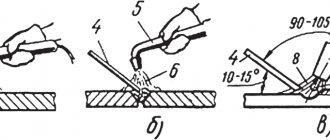
We'll tell you in more detail how to make a seam correctly. To do this, it is important to carry out work in stages:
Stage 1: Familiarization with technical documentation for welding.
Stage 2: Preparation of the workplace, equipment and materials (you can find out which materials to choose for welding on our website mrmetall.ru).
Stage 3: Carrying out the welding work itself.
Stage 4: Non-destructive testing of the resulting seam.
The choice of method depends on many conditions and various factors. The main ones are: the thickness of the elements, the length of the seam made, the type of welding and seam used, the responsibility of the welded structure, etc.
Welding technology for metal structures
For seams of varying lengths, it is necessary to use special welding methods.
Short seams with a length of >250 mm are made “overall”. This is when the welder lights an arc and leads it from one edge of the product to the other without stopping during the welding process.
Seams with a length of 1000 mm are called medium. It is correct to make such seams from the center of the product and move to the edges. The best way to carry out 2 welders in parallel. With this approach, two welders work towards the edge of the seam, trying to do it at the same speed.
Long seams are those whose length exceeds 1000 mm. Several different methods are used to join such long seams.
The first is the reverse step method. When using it, the seam is divided into sections, which are welded by welding 150-200 mm of the seam. Stopping and performing the next seam so that its end comes to the beginning of the previous one.
Welding goes in one direction, and the location of the new section goes in the opposite direction. This is easy to understand by looking at the picture below.
Similarly, using the reverse-step method, welding can be done from the middle of the product to the edges. Two welders perform work on their half of the product. This method can be used to brew either a thin product in one pass or a thick one in several passes.
Each welder's area is divided into smaller areas.
The process, as in the previous case, goes in one direction, and the application of new sutures in the other.
Another way is randomly. The seam is divided into equal sections, 5-6 sections. Next, cook the area in the center.
Also applying short-length seams in the opposite direction from the direction of welding. Next, the most distant areas along the edges are welded and the process of the middle sections of the seam is completed. Each of these methods will significantly reduce structural deformation after welding.