The word “shavings” is the most common concept in the Russian language. But the types of shavings in people's understanding are different. Some even attribute edifying meaning to the shavings. After all, they say about a strict boss that he takes the shavings off his subordinates. At the same time, they mean that he reprimands workers for wrong actions, improper attitude to work, and tries to eradicate bad practices.
Something similar happens in the manufacture of parts: an extra layer is removed from the workpiece, obtaining the required product. And shavings, they are shavings - ordinary industrial scrap. It is collected and sent for processing.
What are shavings?
Chips are a small fraction of any material, including wood, plastic, metal, which is a narrow filigree layer removed from the workpiece using planing equipment, knives or other tools. In metal manufacturing, shavings are a by-product. Its waste is expected. Unnecessary scraps of non-ferrous, ferrous and even precious metals are formed as a result of mechanical processing on drilling, milling and lathes. As a rule, the structure of the chips remains identical to the regulated material of the product. In exceptional cases, a mixture of alloys differing in chemical composition is detected. This is possible after welding, soldering and similar manipulations.
Features of processing cast iron parts
Processing cast iron by turning has some difficulties, but the demand for the material is worth it to understand all the intricacies. The popularity of alloy cast iron is growing, as parts made from this material can withstand heavy loads. As a result, we obtain reliable mechanisms, machines and equipment.
Specifics of turning cast iron
Each turning operation is carried out in several passes. When it is necessary to remove most of the volume of the entire workpiece, cast iron castings are usually used. Work on computer-controlled machines is carried out using rods of different sections made of alloy gray cast iron.
Processing of workpieces must be carried out with super-hard tools. It is best to use a coated tool to avoid abrasive wear. In most cases, it is possible not to use coolant during processing. During work, it is important to monitor the uniformity of the allowance on the castings.
Some recommendations for working with cast iron
It is better to know the following features of mechanical and other types of processing of cast iron before you start working.
- When manufacturing parts in large volumes, it is necessary to use plates with special coatings to remove heat. Suction off dust and chips. Thermal expansions can change the size of the workpiece. The ideal option for roughing operations is CBN cutting.
- When stripping cast iron castings, the entire layer down to bare metal must be removed in one pass so that the cutter remains within the casting crust.
- If you use replaceable carbide inserts from foreign manufacturers, the optimal turning speed is from 200 to 450 m/min.
- To remove metal dust, it is best to use an air injector or an industrial vacuum cleaner. In an ordinary household unit, the motor may fly due to dust.
- To prevent sand and other inclusions typical of cast iron alloys from damaging the tool, use inserts that combine wear resistance and low brittleness.
The wrong choice of insert or cutting mode causes rapid dulling of the cutting edge, and, as a result, poor surface finish. Anyone who masters the technology of turning and other types of processing of cast iron will be able to produce pump housings, engine cylinder blocks and other parts of complex shapes.
Types of chips
The metal cutting process (MMT) is carried out under given parameters using tools and materials with different properties. Depending on this, forces arise in the cutting zone that affect the quality of processing and chip formation. Research professor I. A. Thieme identified the following main types of shavings:
- fracture chips – characteristic when processing cast iron, consisting of small fragments and grains;
- drain shavings - smooth, curled, most often formed when processing copper;
- chipping shavings (chipping) - fragments of material remaining from the metalworking of hard steels and pobedits.
By the type and color of the chips one can judge the quality of the surface obtained as a result of OMR and the manufacturability of the process as a whole.
Why are shavings dangerous?
A wide variety of industries use a large amount of metal-cutting equipment (lathes, drilling, milling and other types of machines). When cutting metals on these machines, chips are formed. Read about the dangers of chips and how to protect yourself from injury from chips in the article.
Why are shavings dangerous?
In the process of cutting various materials, depending on the type of material being processed, cutting modes and other factors, the following main types of chips can be formed: continuous (continuous), chipping (elemental) and fracture.
Types of chips: a - flush, b - chipping, c - fracture
IT IS IMPORTANT! The greatest danger to workers is the drain chips that are formed during turning and drilling of tough metals. It usually comes off the machine as a continuous strip.
Types of chips, their danger.
Drain chips have a complex trajectory of movement during processing and, with their sharp edges, can cause serious injury to the worker’s face, arms and legs. At high cutting speeds, these chips have a high temperature, which in some cases reaches 600-700 ° C and when touched, severe burns are possible. In addition, drain chips quickly clog the workplace, move outside the machine, and are extremely inconvenient to remove from the machine and transport from the workshop. Failure to promptly remove drain chips from the machine operating area can result in injury to both the employee and others.
Chip protection methods
In order to give the drain chips a safer and more convenient (for removal and transportation) form, it is necessary to use technological methods of chip control: curling the chips into a continuous spiral or crushing them using the appropriate cutter geometry, cutting mode, or using chip breakers.
Welded or soldered plates on cutters are used as chip breakers for grinding drain chips; overhead plate or spring chip breakers, which are thresholds (protrusions). Protection of the worker from injury from flying chips and at the same time automatic removal of chips from the machine is ensured by the use of chip removers, chip collectors and dust collectors.
Chipping chips are formed during turning and drilling of brittle metals, as well as during milling and planing of various metals. Chip chips can fly away from the cutting site over long distances, sometimes even in the form of a torch, and pose a danger, as they can injure and clog the eyes, cause burns to the face and hands. At the same time, it is easy to remove chipping chips from the processing site: from the machine and from the workshop.
To protect workers from injury from flying chips, it is necessary to use safety glasses, masks, shields and screens.
Goggles are designed to protect the eyes; must have side walls to prevent chips from getting into the eyes from the sides. Transparent shields protect the entire face; their use is advisable for high-speed cutting, when chips flying off with great force, the temperature of which reaches 600-700 ° C, can injure not only the eyes, but also the face. The shield, made of organic glass, is mounted on the rim, with which it has a hinged connection, and can be raised upward if necessary.
At particularly high cutting speeds, exceeding 500 m/min, glasses and shields cannot always protect the eyes and face from injury from chips. In these cases, screens are used. Screens protect the cutting area, protect against injury from chips and at the same time provide good visibility of the processing area. The design of the screens may be different, but they are subject to general requirements: they must move easily and move away from the support, which is necessary when changing the cutting tool, measuring the product and turning the tool holder.
Fracture chips are formed when cutting brittle metals, such as gray cast iron, bronze, and brass. Such shavings consist of separate, almost unrelated elements. However, when processing cast iron, a large amount of graphite dust is formed, which is very harmful for the worker. In such cases, it is necessary to install dust extractors on the machine.
A serious problem that is constantly faced at all metalworking enterprises is the removal of metal shavings and sawdust from the workplace. And it's not just a problem of keeping the workplace clean. Statistics of diseases among workers at metalworking enterprises show that the greatest burden of diseases is caused by injuries to the hands on the sharp edges of metal shavings.
To remove metal shavings and sawdust from the workplace, as a rule, various hooks and sweeping brushes are used. These brushes wear out very quickly, the bristles fall out and are cut by the sharp edges of metal shavings. As a result, the workplace becomes even more clogged, now with brush bristles.
To clean steel shavings, you can use a modern device called a magnetic mop, magnetic brush, or magnetic magic stick. This is a 300 - 400 mm stainless steel rod with a handle protected by a plastic or rubber guard. The rod is magnetic, and metal shavings from the most inaccessible places stick to it.
But it is enough to pull the shank protruding from the end of the handle, as the rod loses its magnetic properties, and the chips fall into the container intended for it. Convenient, simple, safe.
Safety requirements when working with chips are regulated in the following regulations.
Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for working with chips
Document. Sanitary norms and rules “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in mechanical processing of metals”, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus on November 21, 2012 No. 182 (hereinafter referred to as Resolution No. 182).
It is prohibited to use compressed air on existing equipment for blowing cutting tools and cleaning machines in metal machining shops. Blowing of products (parts) with compressed air should only be carried out in specially equipped chambers (cabinets) provided with local exhaust ventilation (clause 38 of Resolution No. 182).
When using high-speed methods of metal cutting using oil and water-soluble cutting fluids and TC, the processing zones must be equipped with shelters and devices for mechanized removal of chips. (Clause 39 of Resolution No. 182).
Metal shavings from workplaces and machines should be stored in containers in specially designated areas. (Clause 59 of Resolution No. 182).
The organizational and technical equipment of workplaces where mechanical processing and smelting of metals are carried out must meet the requirements of ergonomics, technical aesthetics, occupational safety and ensure compliance with the following requirements: - workplaces of machine operators intended for standing work must be equipped with shields (grids) for protection legs from metal shavings, an auxiliary work seat (chair, folding seat) for short-term rest. (Clause 55 of Resolution No. 182).
Safety precautions when working with chips
Document. Intersectoral general rules on labor protection, approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Republic of Belarus on June 3, 2003 No. 70 (hereinafter referred to as Intersectoral Rules No. 70)
In production premises, metal boxes with tightly closing lids are installed to collect metal shavings, cleaning materials, sawdust and other production waste (clause 62 of Interindustry Rules No. 70)
Cleaning (cleaning) of equipment, machines and products by blowing with compressed air is prohibited (clause 132 of Rules No. 70)
Special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment issued to employees must correspond to working conditions and ensure labor safety. (clause 292 of Rules No. 70)
Personal protective equipment must meet the requirements of technical regulations. (clause 293 of Rules No. 70)
Workers who have received personal protective equipment must be instructed on how to use and care for them.
Employees are required to correctly use the special clothing, special shoes and other personal protective equipment provided at their disposal, and in cases of their absence or malfunction, report this to their immediate supervisor (clause 294 of Rules No. 70).
Personal protective equipment is made available before work begins. (clause 295 of Rules No. 70)
It is prohibited to carry out work without the necessary personal protective equipment or with faulty personal protective equipment.
The employer is obliged to replace or repair personal protective equipment that has become unusable before the expiration of the established wear period for reasons beyond the control of the employee.
Personal protective equipment is subject to periodic control inspections and tests in accordance with the established procedure. (clause 296 of Rules No. 70)
Document: Inter-industry rules on labor protection during cold processing of metals, approved by the resolution of the Ministry of Industry of the Republic of Belarus and the Ministry of Labor and Social Protection of the Republic of Belarus on July 28, 2004 No. 7/92. (Hereinafter - inter-industry rules No. 7/92)
To ensure occupational safety when carrying out cold metal processing processes, the employer is obliged to monitor the use of safe work practices by employees, compliance with the requirements set out in the rules and instructions on labor protection, as well as the correct use of collective and individual protective equipment. (clause 6 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
. Cleaning of workplaces, driveways and passages must be carried out throughout the working day and after each shift. (clause 33 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
At each workplace near the machine there should be wooden ladders on the floor for the entire length of the working area, and a width of at least 0.6 m from the most protruding parts of the machine. (clause 159 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
It is allowed to use other types of protective devices that provide effective fencing of the processing area (for example, sliding curtains made of elastic materials that are resistant to coolant and hot chips). (clause 247 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
Guards should not limit the technological capabilities of the machine and cause inconvenience during operation, cleaning, adjustment, or lead to contamination of the floor with chips and coolant when they are opened. If necessary, they must have handles and brackets for ease of opening, closing, removal, movement and installation. (clause 249 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
The shape of the equipment and its elements (beds, tables, fixtures) must ensure convenient and safe removal of chips and coolant from the processing zone, as well as removal of chips from the surfaces of the equipment. (clause 340 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
. To remove chips from the surfaces of the machine manually, workers are provided with sweeping brushes and hooks. Hooks should have smooth handles, without eyes. To protect your hands from injury from chips, the hook is equipped with a protective screen. Removing chips may only be done with the equipment stopped and wearing safety glasses. ( (clause 343 of intersectoral rules No. 7/92)
Automatic machines whose operation produces more than 20 kg of chips during a shift are equipped with automatically operating conveyors for its removal. In special automated machines and automatic lines, chip removal schemes are agreed upon with the consumer (clause 344 of Interindustry Rules No. 7/92 )
Equipment on which, when processing materials (for example, during abrasive processing, cutting cast iron, graphite, plastic and other non-metallic materials), dust, small chips, aerosols harmful to health, gases are formed, the concentration of which in the working area exceeds the maximum permissible standards, must be equipped with devices including dust and gas receivers and suction devices (aspiration units), ensuring complete removal of contaminated air from the processing area and its purification. (361 Intersectoral Rules No. 70 )
After turning off the equipment, aspiration units must continue to operate for 5-10 seconds and prevent the creation in the air of the working area of concentrations of harmful or dangerous substances exceeding the maximum permissible standards.
If necessary, the treatment area should be covered with a casing to which the air duct of the suction system is connected.
To reduce injuries from cuts from strip (drain) chips, it is necessary to use devices for crushing or curling chips. When machining brittle materials and producing small steel chips, it is recommended to use chip removal devices. (clause 426 of Intersectoral Rules No. 70 )
The processing area of parts in universal cantilever milling machines, as well as in machines with a cross table, must be protected by a protective device (screen). (clause 441 of Intersectoral Rules No. 7/92 )
Personal protective equipment when working with chips
Document: Rules for providing workers with personal protective equipment, approved by Resolution of the Ministry of Labor of the Republic of Belarus dated May 28, 1999 No. 67 (hereinafter referred to as Rules No. 67)
The personal protective equipment used must ensure the protection of workers from hazardous and harmful production factors under existing technology and working conditions. (Clause 809 of Rules No. 67)
The procedure for using personal protective equipment must be set out in labor protection instructions, taking into account the specific conditions in which they are used. Workers must be trained in the use of personal protective equipment. (clause 810 of Rules No. 67)
Personal protective equipment used in this technological process must be indicated in the technological documentation. (clause 811 of Rules No. 67)
Alexander Zhuk , occupational safety specialist.
Turning parts
The most common OMR technique, which allows obtaining a part of the desired configuration and roughness, is turning. The essence is to cut off the unnecessary layer of metal from a blank or workpiece. By acting on the layer being removed with the front surface, the cutter deforms it. As a result of compression of the metal, its compressed element breaks off and dislocates with the front surface of the tool upward. Then the algorithm is repeated: the chips are chipped, separated and curled into beautiful springs.
There are no different types of chips encountered during turning. The following factors influence:
- the degree of cohesion of metal elements sequentially chipped during processing (drain chips, fractures and chipping);
- cutting modes: spindle rotation speed, caliper feed rate, cutting depth;
- use of cutting fluids.
Pereosnastka.ru
The concept of the process of chip formation
Turning
The concept of the process of chip formation
Machine parts are made from blanks. The layer of metal that is cut off from the workpiece during processing is called allowance. A workpiece is a production item from which a part is made by changing the shape, size, surface roughness and material properties.
The cutting process is accompanied by complex physical phenomena (plastic and elastic
low deformations of the workpiece, heat generation, and the formation of build-up on the cutting part of the tool), which have a great influence on the operation of the cutting tool, labor productivity and the quality of processing. To carry out the cutting process on a lathe, two movements are required: the main movement and the feed movement. The main movement is the rotational movement of the workpiece; it consumes most of the machine's power. If you bring a cutter to a rotating workpiece, it will machine a circular groove, and in order to process the workpiece over the entire cylindrical surface, it is necessary to move the cutter along its axis.
The feed motion is the forward movement of the cutter, ensuring that it continuously cuts into new layers of metal.
The following surfaces are distinguished on the workpiece being processed: - processed - the surface from which the metal layer must be cut off; - processed - the surface obtained on the workpiece after cutting off the metal layer (chips);
- cutting surface - formed on the workpiece directly by the cutting blade. The cutting surface can be conical, cylindrical, flat (end) and shaped, depending on the shape of the cutting edge of the cutter and its location relative to the part.
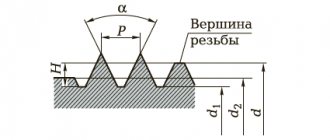
Various cutting tools are used in mechanical engineering, but the principle of their operation is basically similar. The simplest cutting tool is a chisel. Its cutting part is a wedge-shaped body, which, under the action of force P transmitted by the working mechanism of the machine, cuts into the surface layer of the workpiece, compressing it (Fig. 5).
Internal stresses arise in this compressed layer. When, with further deepening of the cutter, the internal stresses exceed the adhesion forces between the metal molecules, the compressed element 2 breaks off and moves upward along the working surface of the cutter. The subsequent movement of the cutter compresses, chips and shifts successive elements of the metal, forming chips*.
Chip tarnish color
In mechanical engineering, in particular metal cutting, there is such a thing as tarnish color. It can be compared, for example, to the iridescent stains of gasoline on the surface of a puddle after heavy rain. It turns out that by the color of the tarnish and the unusual appearance of the chips, knowledgeable machine operators can easily determine the degree of heating in the cutting zone and understand that something has gone wrong: perhaps the cutter has become dull, which needs to be urgently sharpened or replaced.
The nature of this phenomenon on the surface of a hot metal is the formation of a thin layer - a tarnished film. The degree of heat of the chips determines the color of the film. The color range varies from a slightly yellow tint at 200 0C, passing purple and dark blue at 270-290 ℃, to light gray, almost white at 400 0C.
How to make tuna flakes?
To make tuna flakes
, the fillet of this fish is thoroughly boiled to remove excess fat.
Then the fat-free fillet is smoked for a long time and dried until completely solid. The tuna flakes
themselves are obtained by grating the fish on a special board, which is placed in a special box.
Interesting materials:
How to reduce latency on OBS? How to reduce latency on stream? How to reduce stream latency on Twitch? How to reduce the volume in Discord? How to wash your face after yellow peeling? How to wash your face with colored eyebrows? How to organize icons on iPhone? How to use emulsion liqueur? How to eat daikon? How to manage bookmarks in Google Chrome?
Creative shavings
Students of mechanical engineering educational institutions, who came to the workshop for the first time to practice, admire the fresh shavings with genuine interest. Snakes, beads, rings, nests - what enthusiastic young people can’t see in ordinary shavings.
The different shapes, colors and intricacies of the shavings inspire some people to get creative. For example, one of them took many photographs with beautiful metal shavings and called the unusual gallery “Shavings, you are space!” Another author, Vladimir Kargin, a lover of creating three-dimensional panels, produced a number of paintings made from various types of shavings. All the themes of his paintings are related to nature.
Classification of metal shavings
According to the generally accepted classification, chips are divided into three main types:
- chipped;
- drain;
- broken.
As the name implies, the type of chip is determined by the amount of cutting force and the processing method. Indicative in the process of determining chips is the work of the planing cutter . During operation, the cutter moves in a certain direction, and it is in this place that the workpiece is affected. Under the influence of this influence, tension is formed in the cut layer, leading to deformation of the material. The degree of deformation will be highest at the point of contact of the cutter with the workpiece; the further the cut is located from the cutter, the weaker the deformation will be.
By-product of production
Waste of all types of metal shavings, including non-ferrous ones, is disposed of and sent for recycling. This process is labor-intensive: it includes sorting chips, oil extraction, crushing, briquetting and transportation for remelting. Briquetting is necessary to minimize waste when melting chips in furnaces. Mechanisms used for processing chips:
- centrifuge for extracting oil;
- crusher for crushing chips;
- briquetting (baling) presses for compact compaction of chips.
All machine operators know that when cutting metals, they need to protect their eyes and hands: work with glasses or with protective shields installed on the machines, and remove wound and stuck chips with a hook. The shavings often look beautiful, but they are always dangerous because they can be sharp, hot, or prickly. Take care of yourself.
Plastic deformation and its consequences
Plastic deformation leads to changes in the mechanical characteristics of the material - the hardness and brittleness of the metal increases. As a result, cracks may appear, which are called advanced cracks. The main reason for the appearance of cracks is an increase in the fragility of the material with a simultaneous increase in pressure on the same area. It is impossible to predict the direction of movement of a crack; it can go deeper and thereby worsen the quality of processing.
If you work in such a way that the resulting chips are thin, the processed surface will be cleaner. The second consequence of constant stress in the upper layer is the shearing of elements from the main mass. This occurs when the tension exceeds the adhesive force between the individual elements. The direction of the chip is determined by the angle, and this indicator can vary from 3 to 35 degrees . Frequent chipping can cause deterioration in the quality of processing, therefore, when organizing the production process, great importance is given to creating optimal conditions for fast and efficient work with metals.
When processing ductile metals, the processing speed fluctuates within high limits, so the likelihood of chipping is reduced to a minimum. At the moment when a chip should form, the cutter manages to reach the point of highest stress and cuts the metal, thereby preventing spalling. This process is continuous, since in production conditions metal processing is carried out coupled with high temperature exposure and elevated pressure. These factors ensure that chipping does not occur, so the treated surface remains clean and undamaged.