The use of high arc temperatures during welding is a technology widely used in many areas for joining metal structures. However, it cannot be used for all alloys, since many of them, when heated to high temperatures and melted in the open air, oxidize and lose their technological properties. Therefore, special argon welding is used for them, in which, in addition to heating with an electric arc, neutral argon gas is used to protect the metal.
Features of argon arc technology
Like arc welding, argon welding technology is based on melting the area where metals are joined using an electric arc. It can be carried out using melting and non-melting electrodes.
Non-consumable electrodes are usually products made from tungsten, since it is distinguished by its refractoriness and can withstand the temperature of the metal melt. The official designation for welding with non-consumable tungsten electrodes in a neutral gas environment is TIG.
In this case, the metal joining zone is filled with filler material. To do this, use metal wire made of an alloy alloyed with the same elements as the metal being welded. The main rule when choosing it is not to deteriorate the properties of the base metal of the weld. Therefore it is important:
The percentage of alloying elements in the filler wire should not be less than in the metal parts being joined.
The diameter of the wire is selected in accordance with the parameters of the weld and the thickness of the product.
When using consumable electrodes, wire or rod is used as their material, which also, according to the requirements for the chemical composition, must correspond to the base metal of the product and, when melted, must not deteriorate its properties.
Argon arc welding with blowing can be carried out in three ways:
- in full automatic mode;
- in automatic wire feed mode;
- in manual mode of the process.
In automatic mode, the entire welding process is fully automated: both the movement of the electrode and the supply of filler wire are controlled by an automatic machine.
In semi-automatic mode, the welding machine is controlled by a person, and the feed of filler wire is adjusted automatically.
In manual mode, the entire welding process is carried out by a welder.
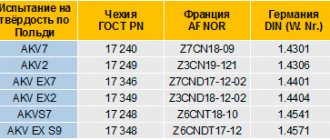
Neutral gas in the welding zone has two functions. It serves as a protective medium against the aggressive action of air components and regulates the passage of a current pulse through ionization by the arc.
In argon arc welding, these functions are provided by argon gas. It prevents the molten weld metal from interacting with air components, since it is significantly heavier than air (38%) and therefore squeezes it out of the weld zone, filling the working space and reliably isolating the melt from contact with the atmospheric environment.
For what purposes is the protective environment used? The fact is that when high temperatures are reached, many high-alloy steels and alloys of non-ferrous metals easily react with oxygen and nitrogen present in the air, forming compounds that harm their strength and deprive them of resistance to corrosion. Argon is a neutral gas; it does not react to the components of heated metal alloys, therefore it serves as a kind of curtain that prevents contact of the heated metal with air, preventing it from interacting with aggressive air gases.
Sometimes, especially during bath welding, a small volume of oxygen (3-5%) is added to argon to eliminate the formation of porosity in the welded metal. It takes on the role of a liquid melt cleaner, interacting with its surface harmful inclusions, which subsequently burn out or float to the surface of the melt in the form of slag.
In addition, inert gas has an increased tendency to ionize, and this affects the nature of the passage of directed electrons of the welding arc to the surface of the metal, and, consequently, the parameters of the welding current.
TIG welding - how to avoid problems
The advantage of TIG welding is a much larger range of welded metals and alloys - stainless, nickel alloys (Monel, Inconel, etc.), titanium, aluminum, aluminum and magnesium alloys, copper, bronze and even gold. It is possible to join dissimilar metals, such as copper with brass and stainless steel with low-carbon steel with thicknesses ranging from tenths to tens of millimeters.
Blades welded together using TIG welding
TIG welding is a clean process
For high-quality welding, the product being welded must be cleaned of dirt, scale, paint, oil and other contaminants. For welding, filler metal is used, which also needs to be pre-cleaned. Welding must be done with clean leather gloves. The purity of the process is not at all exaggerated, especially for aluminum, aluminum and magnesium alloys, which are more susceptible to pollutants than ferrous metals.
Attempts to TIG weld aluminum on an unprepared surface
It would be fair to note the fact that competent preparation and processing of the material takes much more time than welding itself.
An example of high-quality TIG welding
Let us briefly describe the production of a custom stainless steel exhaust and the common mistakes that we have encountered:
Material selection
As for the material for the main pipeline, everything is more or less clear - heat-resistant stainless steel grades 304, 321 and others, depending on the purpose and capabilities. Pipe suppliers are known to everyone and it is difficult to come up with anything here. However, when it comes to flanges, many craftsmen turn on saving mode. The client is informed that everything will be made of stainless steel on the assumption that no one will check with a magnet under the car. As a result, the flanges are cut out of ferrous metal, reducing the whole point of using a stainless steel pipeline to nothing, because after some time the flange and welded joint will rust again and will require another repair.
Ferrous metal flange connection
Hint: When accepting the exhaust system, ask the technician for a magnet and walk along the entire length of the pipeline. Stainless steel is not magnetic, or is very weakly magnetic (grade 304).
Corrugation
The next bottleneck is where many workshops prefer to save money due to the elementary unavailability of positions on site, and often simply due to ignorance.
There are two main types of corrugations - Interlock and Inner Braided.
Inner Braided - 3 layers, braided on top, then corrugated layer and braided again inside. Most often they are made of ferrous metal and are presented on the market as universal.
Inner Braided Black Metal
Ferrous metal corrugation has the same number of disadvantages as flanges:
Rusted corrugation
Inner Braided Stainless Steel. The material was chosen correctly, but the type of corrugation was wrong
Interlock - 4 layers (reinforced). It differs from Inner Braided by the presence inside of an additional layer similar to a layer of rings connected to each other.
Stainless steel interlock
Hint: When choosing components for your exhaust system, and especially for cars equipped with a turbocharger, do not skimp on a good corrugation. Interlock made of stainless steel will cost you 2-3 times more, but it is worth it in order to avoid the “surprises” that Inner Braided can present.
Blowing
This point, or rather its absence, is a favorite of many workshops. You can check whether the root of the seam was blown or coated with flux during welding only by being next to the welder, or by dismantling the entire exhaust system for the purpose of inspection, because the outer (visible) part of the seam when welding with and without blowing can be equally beautiful, but here Things are not so rosy inside. The notorious desire to do it faster and cheaper forces us to play not by the rules, as a result of which the quality of welded joints suffers greatly, not to mention a decrease in the efficiency of the exhaust system.
Welding stainless pipe without blowing
In our work, we always blow or coat with a special flux when welding pipelines and any containers to achieve the highest quality of connections and their durability:
Welding a stainless steel pipe with blower
The main advantage of welding a blown exhaust system is better gas dynamics. The exhaust gas flow does not have unnecessary resistance in the form of porous welding slag in its path, resulting in no turbulence that reduces the efficiency of the entire system. When pressurized, the structure of the weld becomes homogeneous and has better strength characteristics, which means trouble-free operation.
Hint: When coordinating welding work, ask the foreman a direct question about how the seam inside the pipeline will be protected. There can be three possible answers: a) argon or another inert gas b) special coating c) what kind of “protection”?
In the end, you make the final choice, but do not forget that the result can be completely different:
Something clearly went wrong