The demand for semi-automatic welding machines in the welding equipment market continues to grow every year. This is due to their obvious advantages: affordable cost, wide range of operating modes, ease of setup and operation. However, it is not always possible for a novice master to figure out how to use a semi-automatic machine correctly. The first thing you need to know is the structure and operating principle of the unit, as well as basic recommendations for choosing wire for welding.
Semi-automatic welding is
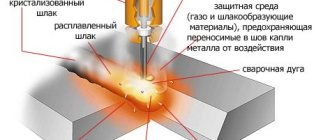
A type of arc welding, during which the welding process occurs due to the simultaneous automatic supply of the electrode wire with the influence of a shielding gas on it.
The shielding gas used during welding completely protects the heated and molten base and electrode materials from exposure to air, which both slows down the welding process and can completely stop it.
Next, we will look at the basic principles of working with a semi-automatic machine, the selection and preparation of this type of tool.
Operating principle of semi-automatic machine
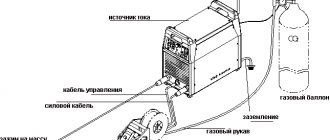
Semi-automatic welding machines are mostly simple equipment. Its main parts are an adjustable direct current source, which supplies the welding voltage, as well as a special mechanism designed to feed the welding wire into the welding arc zone, and the feed is performed at an adjustable speed.
The arc has reliable protection thanks to the gas flow created by the burner, where it enters from a cylinder with the same gas. The electrode feed speed and welding voltage are adjusted simultaneously.
As already mentioned, the welding wire must be fed into the arc zone at a strictly defined speed. Only in this case will the welding process proceed stably. Otherwise, at the slightest break in the wire feed, the arc breaks, and this leads not only to a decrease in the quality of the weld, but also to other more serious consequences, which include, first of all, burn-through of the seam, melting of the electrode tip and other failures and defects.
For high-quality feeding, it is necessary to check the drive rollers before work. It is necessary that the feed roller has a V-shaped groove, the size of which must match the size of the wire, and that this groove is in good condition, that is, not worn out.
Often when people experience poor feed, they will increase the clamping force on the drive rolls, which can only make the feed worse as the wire can become deformed. In addition, the burner guide channel can be damaged for the same reason.
During operation, the welding wire passes through the torch through a guide channel, which over time tends to become dirty and wear out. As a result, the resistance of the electrode feed increases, until the wire stops completely.
This should not be allowed; it is better to notice these changes in time and replace the guide channel with a new one, installing which you need to be very careful, since if its length, external and internal diameters do not match, serious feeding problems may arise. In other words, the whole point of replacement is lost and normal welding is still not possible.
In order to reduce wire contamination, as well as premature wear of the guide channel, it is better to choose a semi-automatic machine with a closed feed mechanism. This approach to wire feeding significantly better protects it from dust, moisture, oxidation, etc.
Now a few words about the contact tip of the torch, through which the actual welding current is supplied to the electrode (welding wire). It is clear that for high-quality welding, the wire must have high-quality and reliable contact with this tip. It is necessary to monitor the degree of wear of this part of the semi-automatic welding machine in order to replace it in a timely manner.
All these seemingly little things are of great importance for high-quality welding performed using a semi-automatic machine. Good condition of equipment is the key to success, and poor care of it is the first and surest step to the occurrence of all kinds of malfunctions.
Semi-automatic arc welding machines and their main components
⇐ PreviousPage 11 of 33Next ⇒
Currently, mechanized welding is widely used. This is explained by the high maneuverability of semi-automatic machines and the ability to weld in hard-to-reach places. Mechanized welding is widely used on conveyor lines in mechanical engineering when welding the bodies of all types of vehicles and building structures during their preliminary assembly and welding, etc.
Semi-automatic machines for consumable electrode arc welding are classified according to several criteria in accordance with the standard.
According to the method of protecting the welding arc
The following classification of semi-automatic devices has been adopted:
in active protective gases (G);
in inert gases (I);
submerged (F);
open arc (O).
According to the method of regulating the electrode wire feed speed
Semi-automatic devices with smooth, step and combined control are produced. Semi-automatic machines are also distinguished by the method of feeding the electrode wire: pushing, pulling, universal.
By burner cooling method
They produce semi-automatic devices with natural burner cooling (up to 300 A) and with forced cooling (500 A). The service life of semi-automatic welding machines is 5 years with a change of welding torch every six months. In semi-automatic machines, only the supply of electrode wire is mechanized, which is fed into the arc burning zone through a flexible hollow hose, which is why such semi-automatic machines are called hose-type.
For welding low-carbon and low-alloy steels with a consumable electrode in a carbon dioxide environment in all spatial positions, except for the ceiling, semi-automatic machines of the PDG series are widely used. Stabilization of the output parameters of the power source together with stabilization of the electrode wire feed speed makes it possible to obtain high-quality welded joints.
Semi-automatic machines in this series consist of a feeding mechanism, a DC or pulsed power source, a welding torch, gas equipment and flexible connecting hoses. The semi-automatic machine includes a welding torch of the GDPG type. The semi-automatic machine is controlled by a special unit BUSP-2 (control unit for semi-automatic welding machines) (Fig. 26).
Rice. 26. Semi-automatic PDG complete with main components:
1
– replaceable gas burner;
2
– hose for supplying electrode wire;
3
– feeding mechanism;
4
– cassette for electrode wire;
5
– control unit BUSP-2;
6
– gas hose;
7
– power supply;
8
– gas equipment;
9
– control circuit wires;
10
– welding cable
In setup mode, the control unit performs the following operations:
turning on the gas supply to adjust its flow or dosage;
setting a given wire feed speed;
selection of the working cycle for welding long, short and spot seams.
In welding mode, the control unit ensures the execution of commands to start and stop welding.
When the welding start command is received, the gas supply is turned on, then the power source and after 0.5 s the wire feed is turned on. When a command is received to stop welding, the electric motor of the feeding mechanism is turned off and it is braked, the power source and the supply of shielding gas are turned off; the control unit returns the circuit to its original position.
Semi-automatic machines of the PDI type provide welding in a pulsed mode.
The semi-automatic device PDG-516 (PSh-13) can weld with both solid steel and flux-cored wire. For welding in various spatial positions, some types of semi-automatic machines of the PDG series are equipped with a console-rotating device. Such devices make it possible to increase the productivity of welding work both on stationary installations (Fig. 27) and mobile ones.
The technical characteristics of some semi-automatic machines are given in table. eleven.
Due to the unification of the main components of semi-automatic machines, universal semi-automatic machines (quickly reconfigurable) are becoming more widespread.
One of these semi-automatic devices is PSh-112. The semi-automatic machine is designed for welding with self-shielded and flux-cored wire, but can be easily and quickly converted to carbon dioxide welding with solid wire.
Rice. 27. Stationary installation for mechanized welding of large-sized products:
1
– console;
2
– monorail;
3
– trolley;
4
– semi-automatic welding machine;
5
– flexible hose
Table 11
⇐ Previous11Next ⇒
Recommended pages:
Use the site search:
Rules for working with a semi-automatic machine
We list a number of requirements, or rather rules, that should not be neglected when using an automatic welding machine:
- Before starting to operate the semi-automatic welding machine, you should carefully study the operating instructions;
- when welding, you need to ensure strict polarity - “plus” should be on the torch, and “minus” should be on the part being welded;
- To avoid unpleasant situations associated with human injury, when threading wire into the torch, you should not point the nozzle at yourself or other people. Here you need to be very careful, because the end of the wire can pierce your palm or other part of the body;
- It is strictly forbidden to move the semiautomatic device during operation by pulling it by the burner or cable; there are handles for this;
- in order not to damage the eyes and other parts of the face, you should work with a semi-automatic welding machine only in a special protective mask that has a light filter, the marking of which must correspond to the current range used in welding, and for additional protection you should use glasses with glass lenses, since glass does not transmit ultraviolet radiation;
- for long and trouble-free operation of the device, it is necessary to clean all its insides from dirt and dust twice a year;
- if, during an external inspection of the device, damage was discovered in the cable or burner sleeve, they must be immediately eliminated using insulating tape or heat-shrink tubing, and it is better to replace worn parts with new ones;
- the shape of the groove must clearly correspond to the electrode material: V-shaped smooth is used for solid steel wire, V-shaped with notches for flux-cored wire, U-shaped for alloys and soft metals;
- during operation, it is prohibited to touch the live parts of the semi-automatic welding machine, as well as to work with its covers removed;
- the room in which welding is performed must be well ventilated, since aerosols released during work are extremely harmful;
- Fire safety rules should be strictly observed;
- We must not forget that during welding the welding seam heats up to very high temperatures, so it is strictly forbidden to touch these places;
- It’s no secret that a semi-automatic machine, like any welding machine, is a source of electromagnetic radiation, which has an extremely harmful effect on human health. Not all people can work in such conditions, so you must first undergo a medical examination;
- It is strictly forbidden to weld vessels and pipelines together with liquids, as well as vessels in which flammable and flammable liquids were previously stored;
- do not overload the semi-automatic machine, work only under the conditions specified in the operating instructions, since this, firstly, is dangerous to the health of the operator, and, secondly, reduces the service life of the semi-automatic machine itself;
- since a person is a carrier of static electricity, touching the elements of the electronic board is strictly prohibited, in this case they may breakdown;
- The lid of the feed mechanism niche must be tightly and securely closed during operation so as not to become a source of injury to the operator;
- welding should not be performed in a continuous mode, it should be alternated with regulated breaks, the duration of which and the intervals between them should be selected in accordance with the manufacturers' recommendations;
- while operating the semi-automatic welding machine, it is strictly forbidden to switch the stages of the transformer installed on the welding power source;
- all welding work should be performed only in clothing specially designed for this purpose, in addition, clothing must be completely dry in order to protect yourself from possible electric shock;
- The flow rate of the shielding gas, which can be argon, helium, carbon dioxide or mixtures thereof, must be calculated optimally, since it forms a protective environment in the arc zone; in addition, the gas must be selected in accordance with the type of material being welded, as well as its thickness. The cylinder must be secured horizontally and securely enough.
Safety precautions when working
When working with welding equipment, the following safety precautions must be observed.
- The welder must protect all areas of the body from splashes of hot metal. For this purpose, special clothing is used that tightly covers exposed areas of the body, as well as protective gloves. Clothing should be made of dense material that can withstand hot splashes. Under no circumstances should clothing be made from synthetic fibers, which begin to melt when exposed to high temperatures. Such material burns through instantly, which can cause burns to the welder.
- Since welding produces hard ultraviolet radiation, it is necessary to protect your eyes from it using a mask with tinted glass. Not long ago, masks with chameleon glass, which darkens when exposed to bright light, appeared on sale. Other areas of the body should also be protected from ultraviolet radiation.
- Shoes must be closed to prevent hot splashes from getting into them.
- The room where welding work is carried out must have forced or natural ventilation (the presence of windows that can be opened). Inhalation of vapors and smoke generated during the welding process has a detrimental effect on human health.
Semi-automatic welding without gas
Among the vast number of types of welding, welding without the use of gas is becoming the most promising and in demand.
Semi-automatic welding of this type is carried out using flux-cored wire or, as experts call it, flux-cored welding wire.
Flux-cored wire is a steel tube, but inside this tube there is a special powder - welding flux, similar to the coating of conventional electrodes.
By exposing the flux-cored wire to high temperature, the flux is burned, which provides a protective gas cloud at the welding site. The process itself is very similar to conventional electrode welding.
The main advantage of this method is the absence of the need to carry gas cylinders with you, a huge selection of materials with different types of chemical compositions, with the help of which you can form the necessary arc properties and change the characteristics of the seam.
Since semi-automatic welding is similar to conventional electrode welding, slag from the burnt flux gets into the welding zone, so it is necessary to ensure sealing of the welding surface. To do this, you need to put a few more new ones on top of the finished seam.
Flux-cored wire has low rigidity, so it must be fed to the welding zone with a slight increased pressure; bends in the semi-automatic welding hose are simply unacceptable.
It is extremely necessary to observe the polarity conditions of the phase wire and the “ground”
On the left you see the polarity of welding without using gas, and on the right with using gas when welding.
In order to start the process, you need to connect the power source in the following way: minus to the torch holder, and plus to the surface to be welded. In the case of welding using shielding gas, the connection occurs in the reverse order.
This method of power connection provides a high temperature for melting the flux and the formation of a protective gas environment.
The main advantages of gasless welding:
- Easy welding process
- No need for a gas cylinder
- Fast speed of work
Advantages and disadvantages of semi-automatic welding
The advantages of semi-automatic welding include:
- The ability to relatively easily obtain a high-quality welded connection, including for thin-walled welded structures.
- High productivity of welding by this method compared to manual arc welding, gas welding, etc.
- Mechanized welding in shielding gases can be performed in all spatial positions: bottom, horizontal, vertical and ceiling.
- No fluxes and coatings, and therefore no operations to clean the seam from slag.
- The arc when welding in shielding gases is more concentrated, so the heat-affected zone is minimal.
- Welding is accompanied by minor stresses and deformations.
- Possibility of full automation of the welding process.
Disadvantages of this method:
- When welding outdoors or in a draft, the likelihood of gas protection violation increases.
- Spattering of electrode metal during welding, especially when using carbon dioxide.
- When welding in high-power modes, there is a need to use water cooling systems due to the strong heating of the equipment.
Semiautomatic welding machine for gas environment
Semi-automatic welding machine designed to work in a protective gas environment is a new type of welding that is gaining popularity. Over the past 20 years, the use of this type of welding has reached a large scale.
This type of welding involves two types of work:
MIG (Metal Insert Gas) - welding occurs under the influence of an inert gas, for example argon, as well as other types of gas mixtures.
MAG (Metal Active Gas) is a process of welding metal using an active gas, for example carbon dioxide.
The use of gas cylinders does not allow mobile welding in any conditions, however, when used stationary, this type of welding is the best and has no analogues.
The welding process is carried out by feeding electrode wire, which contains silicon and manganese, into the welding zone together with carbon dioxide.
This creates a protective environment for the electrode and welding surface from the effects of the environment.
The advantage of this welding is the ability to control the process; also the advantages of welding in a gas environment include saving time, because when gasless welding it is necessary to change the electrodes and clean the welding seams from slag.
The quality of work using a protective gas environment is much superior to gasless welding, but there are small nuances here too.
Let's look at them using the example of seam quality. When using CO2 active gas, the seam will have a scaly appearance and burrs, i.e. effect of stuck balls. At the same time, when using a mixture of argon gases in the amount of 80% and carbon dioxide 20%, respectively, the seam has a smooth and even surface that does not require additional processing.
In recent years, for the operation of semi-automatic welding machines, the use of inverter types of power sources instead of an alternating current source has become widespread. This is due to such advantages as:
- Light weight of the device
- Smooth voltage regulation, which means safe work performance
- Low load on the electrical network, which in turn leads to uninterrupted operation of other electrically consuming devices in the room.
How to choose a welding machine
Like any equipment, the welding machine has its own design and it consists of:
- Burner, differing in type of power and cooling methods
- Wire feed mechanism. It includes feeding method, speed regulation and number of pinch rollers
- Hose that varies in diameter
- A gas reducer, which must have two pressure gauges.
When choosing a semi-automatic welding machine, you should take into account the thickness of the metal that will be exposed to welding, the length of the seam the machine produces, as well as the conditions for performing welding work.
Before purchasing, you need to clarify all the above parameters, as this will help you choose the device that is right for you.
It is necessary to select a welding machine using the following method:
- The choice begins with clarifying the tasks for which the device is purchased
- When choosing, pay attention to the quality of the welding machine, read information about the manufacturer and study reviews about it and the machine. Also pay attention to the cost, which cannot be lower than average.
- If you choose a low-power device, then you should take into account that it is capable of processing only small surfaces.
- At the place of purchase, find out the specifics of the warranty, the availability of service centers and the availability of consumables and spare parts for the device, such as conductive tips, torch nozzles, insulating sleeves, feed spirals and rollers.
Feeder
There are several options for delivering wire to the welding zone. Each of them works quite simply. The first, the so-called “push” method, is that the wire feed mechanism pushes it to the torch through a hole in the base of the semiautomatic machine.
The second method, called pulling, ensures the supply of the filler product through a channel equipped in the handle (holder) of the burner. And finally, the combined option involves the integrated use of both methods.
In this case, a special feed unit ensures coordinated movement of the filler material. The combined method is most often used for supply channels of considerable length.
The diameter of the wire fed into a semi-automatic welding machine usually ranges from 0.6 to 2.0 mm. It itself is located on rotating reels, which significantly facilitate its supply to the welding zone.
When using a special flux-cored wire with an internal cavity for flux, there is no need for additional protection, since the gas shell is formed due to the combustion of the flux filler.
There are several varieties of electrode filler material used in the operation of semi-automatic welding machines (steel, copper-plated and aluminum wires).
Each of the names is used in different conditions for fusion of workpieces, under which the welding process usually takes place.
Preparing the welding machine for work
Like any type of activity, carrying out welding work requires compliance with the rules of preparation for the process, this will ensure the safety and quality of the process itself.
Before starting work, you need to prepare the welding surface to avoid the appearance of pores. To do this, you need to remove dust, debris, dirt, moisture, oil, as well as rust up to 30 mm from the edge of the gap from the surface.
The surface can be cleaned with a metal brush, a steel brush for metal, rags, or a sandblaster, then it must be degreased and etched.
It is also necessary to prepare the welding machine; for this, the following preparation steps must be followed:
- Check the grounding of the device. Any cooking equipment must be checked for connection to the grounding conductor. Missing or malfunctioning jeopardizes the safety of the welding process.
- Checking the network voltage. Many devices are sensitive to power surges and may fail. Therefore, the voltage in the network must be stable.
- Select the welding machine mode. Modern semi-automatic machines have many welding modes and its adjustment. With their help, you can adjust the welding to the material being welded and the nature of the welding.
- Before starting work, you need to adjust the diameter of the tip; it should be several millimeters larger than the size of the wire.
- Check the adjustment of the tip and feed mechanism. If these elements are upset and configured incorrectly, this can lead to operational errors or damage to the material being welded.
- Checking the quality of the wire. It should be smooth without burrs, dents and various kinds of scratches.