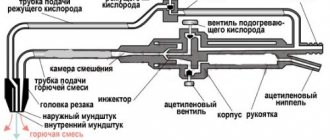
Design and features of a gas burner
The cutting torch consists of the following elements:
- tube for supplying gas and oxygen;
- head with two replaceable special mouthpieces;
- 3 valves (for flammable gas, regulation and direct supply of the necessary oxygen);
- lever;
- mixing chamber in which the necessary mixture of cutting and fuel gases is formed.
The listed elements are the main components of this tool, since its design may include a larger number of other parts.
Principle of operation
Metal cutting occurs due to its melting under the influence of a directed stream of oxygen on the line of the intended cut. After melting, the same jet blows out the oxides formed in the cut zone.
The use of gas cutters is effective in the following cases:
- If it is necessary to cut metal structures before subsequent melting during the sorting process.
- To correct defects formed during welding work.
- To eliminate the consequences of accidents.
- In foundry production to correct external defects on finished ingots.
- In metallurgy for cutting metal sheets and rolled products before installing metal structures.
- If necessary, preparation work before welding.
- When dismantling steel structures.
According to the method of mixing oxygen and gas, a gas burner cutter is
- Injection – the nozzle for a gas cutter mixes the gas inside, which ensures high safety of the device. This is due to the fact that gases pass separately through special channels and are mixed into a combustible mixture directly in the mixing chamber.
- Injectorless - it does not have a mixing chamber. Oxygen enters through two special tubes, and gas through a third. Mixing occurs in the middle of the head. A three-pipe oxygen gas cutter requires a significantly higher pressure of combustible gas compared to an injection burner.
Homemade for household needs
If it is necessary to carry out a small amount of work related to cutting thin sheets of metal (thickness within 1.0 mm) or melting copper wires, home craftsmen are able to make a compact portable gas cutter of simple design with their own hands. The cutter diagram is shown in Fig. below
Diagram of a homemade gas cutter.
To make such a simple product you need:
- dropper;
- needle for inflating nipple soccer balls;
- gas cartridge used in lighters;
- aquarium air compressor or plastic bottle.
The sequence of manufacturing a mini-cutter is as follows:
- A cut is made on the nipple ball needle.
- The needle from the dropper is bent at an angle of 45 degrees. And a ball needle is inserted into the incision.
- Both needles are tied together with wire, then the wire tie is fixed with solder.
- Dropper tubes are placed on the ends of the needles, acting as gas hoses.
- The protruding end of the dropper needle acts as a nozzle.
- The air supply will be provided by an aquarium compressor or a plastic bottle slightly modified to match an external air source (tube, tire, etc.).
- Gas will be supplied from a gas cartridge.
- To regulate the outlet gas and adjust the flame, dropper limiters are used, acting as valves.
With proper flame adjustment, the temperature can exceed 1200-1300 degrees. C. Users of this mini-cutter claim that it can successfully serve for several years.
According to the combustible gas used, cutters can be divided into propane, acetylene and universal
- Propane cutters use propane as the cutting gas. These burners are considered very reliable and safe to use, as well as durable.
- An acetylene gas cutter – in which the working gas used is acetylene, is capable of creating a high flame temperature (up to 3300 °C). This tool is used for cutting thick metal workpieces. It is also equipped with special valves for adjusting high-speed gas supply.
- In a universal cutter, combustible gas can be used in different types. Moreover, their price is not much higher than a propane or acetylene cutter.
Selection rules
When choosing a cutting torch, you need to consider a number of recommendations. You should pay attention to the following factors:
- Comfort is an important indicator that determines how long a technician can work with the device without fatigue. It is advisable to hold the burner in your hands. This will help you understand how comfortable it will be while working.
- Mouthpiece material - the outer part of this burner element should be made of chromium bronze. Pure copper with a red tint is acceptable.
- Connecting tubes must be made of brass.
- It is advisable to choose a burner without a decorative coating. The paint will cover possible defects in the assembly of the device.
- When working with oily or painted surfaces, you need to choose long cutters (up to 800 mm). This length will protect the brush from injury from the flame.
- Choose an aluminum handle. Plastic is less durable and wear-resistant.
- Flame temperature and gas flow rate affect the cutting thickness of metal parts. The cutting depth is indicated by special markings. For example, if you need to cut sheets up to 10 cm thick, the machine will be designated P. To cut sheets thicker than 10 cm, you need to select the P3 marking.
It is important to check the equipment before leaving the store. To avoid unnecessary problems in case of possible breakdowns of the gas burner, it is necessary to obtain a guarantee.
Main advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of burners with intra-nozzle gas mixing include:
- Stable flame without backfire or popping.
- The ability to cut a thick layer of metal (up to 300 mm), which directly depends on the operating parameters of the modification.
- High cutting performance.
- The ability to cut metal in any direction, regardless of thickness.
- Long service life and easy maintenance.
There are also disadvantages to this tool:
- When thin sheet metal is heated strongly, the cut parts may become deformed.
- The large cutting width of metal with this tool requires adherence to allowances when marking.
- Low cut quality - the edges remain uneven with scale and oxides. This may require pre-treatment before carrying out other work,
- The high cost of the oxy-fuel metal cutting process.
What is the difference?
The main difference between Acetylene and Propane is that Acetylene has a triple bond between two carbon atoms , whereas Propane has no double or triple bonds between carbon atoms other than single bonds.
Acetylene is denoted as C2H2, while its chemical name is Ethine. It is also a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne that exists as a colorless gas. Propane is denoted as C3H8, and it is a simple alkane that has no unsaturation (no double or triple bonds). It also exists as a gas. However, it is often liquefied.
Acetylene is the gas of choice for industrial cutting methods, all industrial thermal cutting processes, but when propane (LPG) was introduced to the market, the entire thermal cutting process changed and the battle between propane (LPG) and acetylene began.
Content
- Overview and main differences
- What is Acetylene
- What is Propane
- What is the difference between Acetylene and Propane
- Conclusion
What is Acetylene?
Acetylene is the simplest alkyne, having the chemical formula C2H2. The chemical name of this compound is Ethine. Moreover, it is a colorless gas at room temperature and normal pressure.
It can be classified as a hydrocarbon because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms with bonds between the carbon atoms. Acetylene gas is widely used for welding, cutting, as a fuel and building material for the synthesis of various chemical compounds.
There is a triple bond between the two carbon atoms of this molecule. Moreover, the valency of one carbon atom is 4. Therefore, each carbon atom is bonded to a hydrogen atom through a single bond. The molecule has a linear geometry and it is a planar structure. Each acetylene carbon atom is sp-hybridized.
What is Propane?
Propane is a simple alkane with the chemical formula C3H8. It is a colorless gas at room temperature and in its pure form this gas is odorless. Its molar mass is 44.10 g/mol.
Propane tank
To make propane easier to detect in the event of a leak or spill, manufacturers add various chemical compounds to give it a distinctive odor.
This compound is widely used for welding, cutting and as a fuel. LPG (liquefied petroleum gas) contains liquefied propane gas.
However, there are some other gases that are used as LPG. Example: butane, propylene, etc. This gas is produced as a by-product of two processes, natural gas processing and petroleum refining.
What is the difference between Acetylene and Propane?
Acetylene is the simplest alkyne, having the chemical formula C2H2. Its molar mass is 26.04 g/mol. It is an unsaturated compound because it has a triple bond between two carbon atoms. Propane is a simple alkane with the chemical formula C3H8. The molar mass is 44.01 g/mol. It is a saturated compound because it has only single bonds between atoms, there are no double or triple bonds.
Difference in combustion temperatures in oxygen:
- The flame temperature when burning propane in oxygen is 2800 degrees Celsius.
- The flame temperature when burning acetylene in oxygen is 3100 degrees Celsius.
Acetylene and Propane for welding
First, propane cannot be used for gas welding. When acetylene burns in oxygen, it creates a reduction zone that cleans the surface of the steel. Propane does not have a reduction zone like acetylene and therefore cannot be used for gas welding.
Acetylene and Propane for soldering
Propane and acetylene can be used for soldering. For capillary soldering (silver soldering), a result of equal quality is obtained. For “welding” solder (high-melting alloys for soldering), acetylene will be an advantage
Acetylene and Propane for cutting
Both Propane and Acetylene can be used for cutting. If you are cutting with acetylene, you usually place the tip of the inner flame cone on the metal (1mm from the surface of the plate). If you do the same with propane, you'll be waiting a long time. If you raise the burner so that the outer cone of flame is used, the preheating process will begin faster. Propane produces only a small portion of the heat in the inner cone of the flame (less than 10%), so most of the heat in the flame is in the outer cone. Acetylene releases almost 40% of its heat in the inner cone of the flame.
Pre-setting the torch cutting tool
When starting to work with a new tool, you need to connect it correctly and check its functionality. Configuration of this equipment is carried out by the manufacturer and is the final stage of its assembly. In this case, interference with its design is strictly prohibited.
Before starting work it is necessary
Carefully read the equipment operating instructions and perform all actions in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Connect the cutter to special cylinders with cutting and flammable gases, which must be equipped with certain reducers: propane - red, and oxygen - blue. Rubber hoses are screwed onto the threads of special gearboxes, which ensures gas supply and are tightened with clamps for reliability.
- Check the cutter and its integrity, the presence of all necessary gaskets, and the absence of oily traces near the oxygen valve.
- Blow out the hoses and adjust the supply of the necessary oxygen and gas. To purge, open the valve on the burner, and after the sound changes, close it. To set up the oxygen supply, you need to set the pressure to 2 atm, then blow out the hoses using the valves on the cutter and reducer.
- It is also prohibited to change the hoses for supplying propane or acetylene and oxygen with each other and to blow the hose for acetylene or propane with oxygen.
When working, you should use the necessary personal protective equipment, which will help you ensure additional safety:
- gloves (mittens);
- special glasses;
- special work shoes;
- pants and jacket with fire-resistant properties.
In general, a gas cutter is excellent for high-speed cutting of various types of steel, and the variety of existing types of this tool will help you complete the work you need.
Differences
The main difference between a propane burner and an acetylene burner is based on the different calorific values of the gases and different proportions when creating the working mixture . The proportions of oxygen and acetylene are 1:1, oxygen and propane are 3.5:1. In an acetylene burner, the combustion rate of the mixture is significantly higher.
Accordingly, the cross-section and shape of the injection channels, working chamber and nozzle differ.
When propane is supplied to an acetylene burner, unstable combustion is observed, the torch power decreases, and backfire is possible. This type of use is unacceptable and may result in a serious accident.