Drilling machines can be classified as equipment with universal capabilities. At the same time with the ability to drill holes of various diameters, cleanliness and accuracy, with their help it is possible to perform numerous operations in accordance with the technological process of surface treatment. The use of this category of equipment is optimal if the technology provides for the following actions:
- drill, bore holes of various diameters;
- countersink the drilled holes to the appropriate parameters, countersink the necessary recesses to accommodate the protrusions of the fasteners;
- expand the surface of the holes within specified limits;
- roll out holes using ball and roller mandrels to a given level of roughness;
- perform internal thread cutting;
- trim (chase) the ends of parts in order to align them.
There are also other possibilities for using equipment in this category.
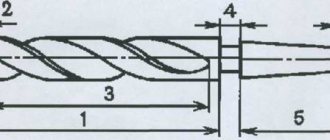
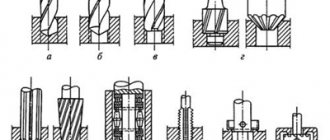
Rice. 1. Work performed on drilling machines
a – drilling; b – drilling; c – countersinking; g – countersinking; d – deployment; e – rolling; g – cutting internal threads; h – cutting (countering) the ends
Tools
To solve these problems, a series of special tools have been developed with different characteristics and design solutions for cutting surfaces, edges, for which special cutting angles, helix length, configuration of recesses for chip removal, etc. are provided. Depending on the cutting operations performed and the technical qualities of the processed materials, tools are used with the corresponding parameters:
- drills of various diameters;
- sweeps;
- countersinks;
- countersinks;
- taps, etc.
In order to obtain the required purity and precision of processing, there are special devices used for:
- fastening the tool in the machine spindle;
- placement and fastening of the workpiece;
- holding fasteners on the machine table, etc.
Auxiliary Tools
The mounting of the cutting tool listed above in the machine spindle is carried out using auxiliary tools:
- adapter drill bushings;
- drill chucks;
- mandrels, etc.
In cases where the size of the cone in the machine spindle does not coincide with the cone of the tool shank, the tool is fastened using adapter conical bushings. If the production does not have the required bushing number, it is possible to use several bushings, however, the accuracy of the part may suffer. Most often, adapter bushings with a Morse taper are used (No. 0...6).
Fastening cutting tools with a cylindrical shank on drilling machines is also done using two- and three-jaw drill chucks. In a three-jaw chuck, cage 3 with nut 2 is rotated by key 4. When the nut rotates, the cams 1 connected by it move downward, clamping the shank of the cutting tool. By rotating the key in the opposite direction, the cams unclench, releasing the tool.
Rice. 2. Drill chuck for holding straight shank drills:
A – general view of the chuck with a key for clamping the workpiece; b – cartridge device; 1 – cams; 2 – nut; 3 – clip; 4 - key
The two-jaw chuck contains jaws that move along T-shaped slots in accordance with the rotation of the key and clamp the tool shank. Small-diameter drills are easily secured in collet chucks, and to save time, it is convenient to use quick-release chucks for tools with tapered shanks, into which tools can be installed and removed without stopping the machine. Drills with a diameter of up to 10 mm with cylindrical shanks are mounted in a chuck with a Morse taper using an adapter conical split sleeve.
In order to ensure exact alignment of the centers of the holes when performing several successive operations, it is most advisable to use self-aligning chucks.
Rice. 3. Quick-change drill chuck (a) and conical bushing for fastening drills with cylindrical shanks (b):
1 – cartridge body; 2 – replaceable bushing; 3 – balls; 4 – coupling; 5 – ring; 6 - mandrel
Thread cutting is an operation that requires maximum precision. In order to ensure accurate parameters during its execution, the taps are mounted in safety chucks, which also ensure the safety of the tool, protecting it from breakage. During the threading process, a tight connection is ensured between the driving coupling half 5 and the driven coupling halves 2.4. Upon completion of the operation, the coupling half 5 slips, the tap is removed from the hole by reverse rotation of the spindle. In cases where the machine is not equipped with a reverse system, they resort to the use of reversible chucks, which ensure the reverse movement of the tap from the threaded hole.
Rice. 4. Safety chuck for tapping blind and through holes:
1 – ring for fastening the tap; 2, 4 – driven coupling halves; 3 – clutch cams; 5 – driving cam coupling half; 6 – spring; 7 – mandrel; 8 – adjusting nut
With the help of swinging mandrels used to fasten reamers, it is possible to maintain centering accuracy when machining holes. The issue of removing the main and auxiliary tools from the spindle socket is easily resolved - specially shaped wedges or eccentric keys are used for this.
| Rice. 5. Wedges for removing tools from the machine spindle: a – flat wedge; b – radius wedge | Rice. 6. Eccentric wrench for removing the cutting tool from the machine spindle |
Characteristics
- max. workpiece width per installation: 656mm
- for dowels: ?8mm
- for confirmation: ?7mm
- hole distance: 32mm
- number of holes: 2x20mm
- board thickness: 16~40mm
- maximum error: 0.8mm
Manufactured by CMT (Italy).
"CMT Utensili SpA" (CMT) produces high-quality cutting tools and equipment for processing wood, wood-containing chipboard, MDF, OSB, plastic, aluminum - cutters, drills, circular saws, replacement knives, etc. The history of CMT began in 1962 in Italy, today it is a major production center with divisions in Italy, Spain and the USA. For more than 40 years, SMT has been investing in the most modern CNC equipment, engineering developments, and personnel experience. CMT tools are easy to recognize thanks to the proprietary orange coating CMT ORANGE TOOLS; the products use the best materials: von Moos Stahl AG steel (Switzerland), CERATIZIT hard alloy (Luxembourg), Du Pont coatings.
Devices for fastening workpieces
An important point in metal cutting is the installation on the machine and fastening of the parts to be processed. Parts are installed on special devices, including:
- on a vice - machine, eccentric, screw, pneumatic;
- prism;
- squares;
- stops;
- conductors.
Depending on the speed and strength of fastening, manual (in small production) or pneumatic devices are selected, ensuring high speed of installation and fastening.
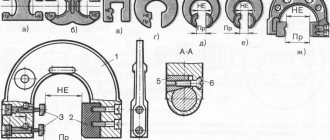
The most suitable for quick installation of workpieces are vices operating on the basis of a lever-cam mechanism. Clamping of the part between the movable and fixed jaws occurs due to the movement of the movable jaw, which is movably connected to a double cam and an eccentric roller. One movement of the handle in the horizontal direction achieves a rigid clamping of the part in the desired position.
Rice. 7. High-speed machine vice with lever-cam clamp: 1 – body; 2 – rotating part; 3 – fixed sponge; 4 – screw; 5 – sponge; 6 – handle; 7 – eccentric shaft; 8 – double cam; 9 - base
Conductors
An important device for precise centering of the axes of the tool and the hole being machined are jigs. The jig is installed above the part with a small gap to remove chips and is mounted on the machine table. In the body of the conductor there are holes, inside of which there are conductor bushings made of especially hard grades of steel that have undergone heat treatment (20X, U10A).
Rice. 8. Conductor bushings: a - permanent; b – quick-change
Permanent and quick-change bushings are used to ensure precise guidance of the cutting part of the tool in accordance with the specified parameters. There are special requirements for the distance between the workpiece and the jig, depending on the material being processed and the quality of the chips during processing. For cast iron parts, a gap of 0.3-0.5 from the diameter of the conductor bushing is assumed. The gap increases and can reach the diameter of the bushing if steel, copper and aluminum alloys, etc. are used as the material being processed.
The design of the conductor includes a body and a plate, which, depending on the purpose, can be:
- Removable (subject to replacement when changing workpiece parameters).
- Suspended, convenient when working with multi-spindle drilling heads. The hanging plate is placed on two rolling pin guides. The drilling head installed in the spindle of the machine is equipped with bushings that align with the upper ends of the rolling pins.
- Lifting ones, which move on rolling pins pressed into the conductor body using a pneumatic drive.
- Rotating (for ease of removal and installation of each subsequent part).
- Permanent (fixed in the conductor body using fasteners or welding).
Conductors significantly facilitate the work of workers, eliminating the preparatory work on marking and precise reinstallation of parts when performing operations on the equipment of the drilling group, ensuring the accuracy of the direction of the cutting tool. In accordance with the processing technology and production conditions, conductors of various designs are used, called:
- rotary.
- sliding.
- overturned.
- invoices.
The most common devices are overhead jigs, which are applied to the workpiece and fixed with metal fingers in a position that ensures the operation is performed in accordance with the technological map. The part is preliminarily fixed on the work table using an appropriate device that ensures the centering of the guide bushings of the jig with the axes of the holes drilled in the part. Conductors of this type can be mounted on a desktop (fixed), or installed on fixing fingers (unfixed).
Rice. 9. Unfastened overhead jig: 1 and 2 – fixing fingers; 3 – guide bushings; 4 – conductor plate; 5 – base surface of the device; 6 – holes
Rotary equipment
For the convenience of processing parts in accordance with the selected technology, appropriate rotary and movable equipment is used, which significantly facilitates the work without requiring reinstallation of parts for drilling or performing other operations for high-quality processing of holes. In such cases, it is assumed that special racks and tables will be used, including normalized, rotary and mobile ones. These are quite complex structures, which contain removable, including rotary, conductors. In this case, the conductors act as elements that guide the cutting tool during the corresponding operations. The main devices designed to move fixed workpieces on a machine in accordance with the requirements of the technological process are:
- rotary racks with a horizontal axis of rotation of the faceplate in which the workpieces are secured;
- rotary tables rotating around a vertical axis and located in a horizontal position.
Universal devices
Universal prefabricated devices (USP) are used when performing various metal cutting operations. USP are special devices that hold the workpiece in the position necessary to ensure precise machining of parts. Versatility lies in the ability to quickly install the workpiece, and, if necessary, to quickly retool the device.
An important device that provides the ability to perform several simultaneous or sequential operations on machine tools is multi-spindle drilling heads. These devices are used in large industries for drilling holes and their subsequent processing, which leads to a real acceleration of the process of manufacturing parts of complex configurations.
Turret drilling heads can contain a different number of spindles equipped with a cutting tool in accordance with a technological program that provides for sequential execution of operations. In this case, it is possible to set your own rotation speed for each spindle separately. In addition, the tool is fed at a certain speed in the forward and reverse directions. This head design makes it possible to operate and perform programmed operations without readjustment. Turret heads are provided with replaceable spindles with various design capabilities used in the technological process of cutting complex parts with the required accuracy and surface finish.
Rice. 10. Six-spindle turret: 1 – lock; 2 – lock lever; 3 – driving coupling half; 4 – clutch lever; 5 – main body; 6 – rod; 7, 8 – thrust screws; 9 – rack; 10 – gear; 11 – bevel gear; 12 – ratchet mechanism; 13 – serratus vein; 14 – rotary body; 15 – head spindle
The rotation and feeding of tools installed in each spindle is carried out in a programmed automatic mode, for this there is no need to stop the equipment for subsequent readjustment. Servicing machines with such complex devices requires highly qualified machine operators and technologists who develop the cutting process. The sequence of operations is carried out in accordance with the program: rotation of the head and feeding of the tool in the vertical direction is carried out in the required mode and compliance with the speed of rotation and feeding of the tools. After performing a certain operation, the head rises and rotates for the next operation.
Recommendation "Arsenal Master RU"
We recommend for purchase, we will deliver throughout Russia.
Additional information: Drilling adapters CMT400-1 and CMT400-2 (NOT INCLUDED): - have drilling depth locks;
— suitable for various drills and drilling machines; — have a duralumin body with holes for chip ejection; — precision design for precise drilling of holes. CMT400-1: drilling adapter for devices CMT400, CMT656, CMT900 for drilling depths up to 30 mm: 306.030.21 - 306.050.11 - 306.080.11. CMT400-2 (screw connection): drilling adapter for tools CMT400, CMT656, CMT900 for drilling depths from 30 mm to 40 mm: 306.050.11 - 306.080.11 - 307.050.11 - 307.070.11 Video: