Home craftsmen who make and repair various technical devices with their own hands often have to deal with pressing equipment. You can buy it on the modern market without any problems, but you can go the other way and make a functional and effective press with your own hands from a jack. By choosing this option for equipping your workshop with pressing equipment, you can manufacture a device at minimal cost that will fully meet the requirements for it, both in terms of technical and operational characteristics, and in size.
The press can be used for various purposes: for pressing bearings or bending metal. The design will be similar in any case, the only difference is the size and working attachments
Using a manual press made from a jack, which can fit in every workshop, you can successfully perform many technological operations at home, such as installing and dismantling bearings, pressing in and out of various bushings and shafts, and carrying out bending and simple stamping operations.
The main element of a homemade press
Why is a hydraulic jack used to make homemade presses? This is due to the operating principle of such a device, based on one of the fundamental laws of physics. According to this law, a liquid, unlike a gas, does not compress under the influence of pressure and, accordingly, does not reduce its volume. A hydraulic jack makes it possible to transfer the force applied by the user of such a device to the object to be processed without loss of power.
The design of a hydraulic jack consists of two cylinders and pistons of different diameters. It is designed in such a way that the force created by the device on its working element is much greater than that which the user of such a device applies to its control element. This allows the use of hydraulic jacks to lift loads of even very significant weight, and in cases where such a device is installed on a hydraulic press, to create with its help a large compression force. It is also important that the efficiency of hydraulic jacks can reach up to 80%, which is a very good indicator.
Portable press device with a lower jack position
Meanwhile, if you decide to make your own press based on a hydraulic jack, take into account the disadvantages that lifting devices of this type have. The most serious disadvantage of a hydraulic jack is that when using it, it is impossible to accurately determine the height to which the rod of such a device is lowered. If this drawback is not particularly critical when lifting a load, then when using a hydraulic jack as the main working body of the press, after each working cycle the pressure in the jack chamber must be released in order to then re-approach the rod of the device to the workpiece.
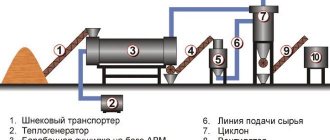
Production of oil stations
The website's electronic catalog presents ready-made pumping stations with various technical characteristics. However, at the customer's request, we can assemble equipment according to an individual plan. The client decides which key installation parameters he needs. If you have previously installed an imported station, you can simply collect documentation for it and transfer it to our specialists. They will create a similar installation, in no way inferior to the original. Thus, you can significantly save on the purchase of industrial equipment.
Which jack to choose
For the manufacture of a press from a jack, single-rod bottle-type devices are optimally suited, which are distinguished by a simple design and high reliability. Presses made on the basis of such a jack have higher power when compared with equipment whose main working body is lever, crank, screw or eccentric mechanisms.
Press with hydraulic jack
Various models of hydraulic jacks are capable of creating a force, the value of which varies in the range from two to one hundred tons, which allows them to be used as a very effective power mechanism.
Hydraulic jacks, along with high power, are distinguished by fairly compact dimensions, which allows them to be used for the manufacture of presses that will not take up much space in a workshop or garage, but at the same time will be highly efficient.
Principle of operation
Hydraulic oil stations have a number of other names - “hydraulic drives”, “hydraulic stations” or “hydraulic units”. However, no matter what such a device is called, its purpose always remains the same and is to convert energy by controlling the pressure and flow of the working fluid. The type of energy converted, as mentioned above, determines the type of prime mover, which is the main part of any oil station.
Hydraulic diagram of the oil station
If we briefly describe the principle by which the hydraulic station works, it is as follows.
- The prime mover of such a device, consuming a certain energy in accordance with its type, transmits torque from its shaft to the shaft of the hydraulic pump.
- The running hydraulic pump begins to suck the working fluid from the storage tank through the suction filter.
- The working fluid flows through the pipeline system to the corresponding elements of the system. They ensure the distribution of fluid, determine its pressure, and supply it to a hydraulic cylinder or hydraulic motor, which do the main work.
- The working fluid, which has already passed through all the required sections of the system, returns to the storage tank, having previously passed through the drain filter.
What is needed to make a press
The drawings of such a device allow you to make a press from a jack with your own hands. They are easy to find on the Internet in the public domain.
Drawing of a homemade press from a hydraulic jack
To make a hydraulic press from a jack, you should also prepare:
- the hydraulic jack itself is of a single-rod bottle type (for a press that will be used at home, a jack that develops a force of up to 10 tons is also suitable);
- inverter with a set of electrodes;
- hacksaw for metal;
- grinder with a set of discs designed for cutting metal;
- a section of channel size 8 and above, 4 m long;
- square or rectangular profile pipe with thick walls;
- equal-flange metal corner No. 50;
- steel strip having a thickness of more than 10 mm;
- a piece of pipe 10–15 mm long, the diameter of which should match the size of the jacking rod;
- metal plate measuring 25x10 cm and thickness 9–10 mm;
- two springs that are needed to return the stop to its original position (springs from car seats, doors, etc. are suitable).
Channel blanks
Recommendations for selection
In order for an oil station for a press, for equipping a lift or any other equipment to effectively cope with the assigned tasks, you should know how to choose it correctly. The modern market offers a wide variety of such devices, the prices of which depend on the following factors:
- the type of prime mover used;
- created pressure and power of the device;
- distribution equipment;
- degree of device mobility;
- manufacturing company.
Typical configurations of hydraulic circuits
The main characteristics of devices of this type include:
- oil station performance or its rated power;
- the volume of the storage tank and the pressure created by the working fluid.
In addition, when choosing hydraulic stations, you need to pay attention to the following parameters:
- drive operating pressure;
- working volume of the piston part of the device;
- speed of the working stroke and its magnitude;
- drive type and equipment configuration options.
When choosing an oil station, take into account the fact that the volume of its storage tank should be one quarter greater than the volume of all channels of the hydraulic equipment that will be connected to such a device.
If the oil station that you are going to purchase will be simultaneously used in conjunction with several actuators, then it is better to choose a multiport pump or a multiport valve as such a device.
When choosing an oil station based on the amount of flow it can provide, this parameter should be compared with the characteristics of the actuators. If the feed amount is insufficient, the actuator will work too slowly; if it is too large, it may simply fail.
Sequencing
Having decided to make a hydraulic press with your own hands, pay special attention not only to the choice of the jack with which such a device will be equipped, but also to the manufacture of a strong supporting structure. It must be understood that the same forces are exerted on the press platform as on the workpiece being processed, therefore this assembly of a homemade pressing device must have very high strength. Otherwise, it will collapse after a short period of use.
To make a platform for a hydraulic press with your own hands, which will be highly durable and rigid, you should use thick-walled U-shaped profiles. Profiled rolled products of square or rectangular cross-section are also suitable for this. To create a platform for a hydraulic press, you will need 4 pieces of a U-shaped profile or profile pipe, the lengths of which must correspond to the drawing. Sections of profile pipes or profiles prepared for the press platform are welded to each other on their sides, and the welds are made on all sides of the joint being created, which will provide the manufactured structure with the required rigidity.
Before welding, the parts are placed in place and secured with clamps.
After the press platform is completely ready, you can begin to create the lower stop and vertical posts of the device, for which a profile pipe is used. When selecting blanks for the vertical stands of the press, it is necessary to take into account that their length should be equal to the sum of the height of the jack body, the largest output of its rod and the thickness of the future removable stop. For the lower stop, a section of profile pipe is prepared, equal in length to the support platform.
Bolting workpieces together
The press platform, its vertical posts and the lower stop are welded into a single frame structure, and it is important to ensure that a right angle is strictly maintained between the joined elements. To make the assembled press frame structure more rigid and resistant to loads, it should be strengthened using metal plates that are welded diagonally to the side posts and the press platform.
Assembling the upper part of the frame
To make the jack press operational, it must be equipped with a removable stop, which, moving vertically along special guides, will exert pressure on the part being processed. Such a structural element of the press is made from several metal plates more than 10 mm thick, which are assembled into a block and welded together on both sides. The length of the plates from which the removable press stop is made should be slightly less than the distance between the side posts of the device.
Since the stop of a homemade press, which exerts pressure on the workpiece, must, if necessary, be replaced with an element of a different size and shape, quickly be removed from the device, holes must be drilled in it with the help of which it will be connected to the base of the jack. Such holes are also needed to install guide plates that will prevent lateral movements of the removable stop. The length of these plates, which are located on both sides of the vertical posts of the press, must be at least 10 cm longer than the length of the removable stop itself.
The next thing you need to do when making a homemade press is to weld a piece of pipe 10–15 mm high exactly in the center of the lower surface of the support platform. The diameter of such a pipe, which will serve as a retainer for the jack rod, must correspond to the cross-sectional size of such a rod.
Welded piece of pipe for the jack rod
The plate with the rod is fixed on the movable part of the press
To enable the jack to return to its original position after the work cycle with its use is completed, two springs are used, which are fixed at an equal distance from the center of the support platform in any way between it and a removable stop. Thus, when the jack is activated and the removable stop of the press is lowered, the springs are stretched, and at the end of the working cycle and the pressure is released from the working chamber of the lifting mechanism, they are compressed, returning the removable stop to its original position.
Securing the return springs
Locking pin
After completing all the steps described above, in order to make the hydraulic press operational, you need to install the main element on it - a jack. To carry out this procedure, you need to pull down the removable stop and install the jack in the gap between it and the support platform so that the end of its rod is fixed in the pipe ring welded to the bottom of the support platform. After this, all that remains is to connect the base of the jack with a removable stop using bolts, washers and nuts, and you can begin to use the freshly made hydraulic press.
Jack installation
All that remains is to clean off the rust, prime and paint
Appearance of a finished homemade press
So, it is quite possible to make a hydraulic press yourself at home. This does not require large labor costs or serious financial investments.
Types of hydraulic presses
Platform press
There are many different types of hydraulic presses; each has its own set of applications, although there is some overlap. Presses that use a plunger and a strong, stable surface are classified as plate presses .
C-Frame Hydraulic Press
The C-shaped hydraulic press is named for its C-shaped frame; This frame is narrow but strong and allows the press to take up less floor space than others. As presses that can be designed for manual or automatic use, C-frame presses can be used for a variety of industrial operations, including forming, straightening, punching, stamping, drawing and riveting.
H-Frame Hydraulic Press
The H-frame press is also named after its frame; This is a welded H shape. Similar to C-frame presses, this type of press is used for industrial applications such as embossing, crimping, bending, stamping and trimming. However, unlike C-frames, H-frames can handle multiple operations.
Extrusion press
Extrusion presses are a type of press that metalworkers and other manufacturers use to extrude parts and products. Extrusion extrusion is a process in which a press forces a die through the material to create a fixed cross-sectional profile.
Lamination press
Laminating presses are manually operated compression presses One is used for heating and the other for cooling, which speeds up the lamination process by simultaneously cooling one board and heating the other.
Vacuum press
Vacuum presses have several specialized applications, such as applying films to various materials, as well as sealing layers of materials in plastics for the electronics industry, credit cards and ID cards.
Stamping press
Stamping presses , like laminating presses, have specialized applications and are used for two main purposes: forming or cutting materials by deforming with a die for the metalworking or automotive industries.
Transfer Press
Transfer presses operate by automatically feeding flat plastic, rubber or metal blanks into the right end of the press. From there, the feed rod fingers pick up the part and move it from die to die. They are used for stamping and molding of plastic, rubber and metal, for example in the medical and aerospace industries.
Press brake
A press brake is used to bend, fold, or otherwise cold process sheet metal. It usually consists of two C-shaped frames on the sides, a movable beam at the top and a lower tool mounted on a table.
The hydraulic press brake differs from other types of press brakes by having two synchronized hydraulic cylinders on C-shaped frames; they move the beam. In automatic mode, this type of press is known as a CNC press brake.
Hydraulic Forging Press
Forging presses are used only for metal. They force metal blocks into shape using closed or open molds, force, pressure, and sometimes heat. This combination stretches the metal to its yield point without breaking or cracking. Forging presses are most popular in automobile production.
Non-hydraulic presses
A standard industrial hydraulic press is a type of power press. Power presses can be pneumatic, hydraulic or mechanical. Alternatives to hydraulic presses include mechanical presses, electric presses, and pneumatic presses.
Mechanical press
Mechanical presses are driven by a flywheel that stores energy and then releases it, thereby transferring the energy to the main caliper through mechanisms such as a crank, cam, pivot joint, or tumbler. In a mechanical press, the stroke of the slide is adjusted within the limits of daylight.
In addition, strokes are also classified by the number of guides or pistons, which can be single, double or triple acting.
Fully electric press
All-electric presses are a relatively recent development that offer more efficient drive systems by mechanically linking the plunger to the drive motor. This ensures that the controller can provide a signal to the motor for a specific speed.
If the motor is not overloaded, this speed will be achieved. Additionally, eliminating hydraulic fluid fluctuations is beneficial because hydraulic fluid changes over time and temperatures, which can even change within a single day.
Pneumatic press
Pneumatic presses serve applications similar to hydraulic presses, including broaching, metalworking, crimping, stamping, bending and punching. They can have stroke cycles up to 400 beats per minute.
Even at high stroke speeds, pneumatic presses can provide controlled flow rates, making them ideal for applications where material flow or piston speed is critical.
Pneumatic presses do not convert rotary motion into linear motion, so they have fewer moving parts than hydraulic or machine presses.
However, pneumatic presses use compressed air to produce motion and are not capable of the extremely high pressures of hydraulic presses.
Hydraulic press device
The basic form of a hydraulic press consists of the basic components used in a hydraulic system and consists of a set of double-acting cylinders, pistons, also called punches, hydraulic pipes and a stationary support or die.
One cylinder is small and the other is large. The pair are called the slave cylinder and the master cylinder, respectively.
Pistons are mechanical devices that provide pushing or thrusting motion. Finally, the anvil or die is the preformed part that gives the substrate its final shape.
Advantages of hydraulic presses
The force achieved with hydraulic presses is unmatched; the same force cannot be achieved by either mechanical or pneumatic presses. However, these are not the only advantages of hydraulic presses. Others include:
- Low initial investment and operating costs - Because hydraulic presses are simple and have few moving parts, they are inexpensive to purchase and easy to maintain and troubleshoot, especially compared to other available options. If any parts break, they can be easily replaced without disassembling the machine. In addition, hydraulic equipment and consumables can be easily accessed worldwide, meaning less downtime and lower maintenance costs for you.
- Operation - Unlike presses that only transfer full power from the bottom, hydraulic presses can transfer full power at any point during the stroke. This eliminates the need to purchase an unnecessarily heavy press, such as a 200 ton press , only to provide less force, such as 100 tons, throughout the entire stroke. This benefit is especially useful when drawing.
- Ease of Operation and Built-in Safety - A hydraulic press rated for 100 tons or less will produce that much pressure regardless of any mistakes made in the setup. In this regard it is reliable. In addition, you as an operator do not have to worry about overloading, die breakage and press failure. These presses are designed in such a way that when the hydraulic press reaches a set pressure, it opens the safety valve at that limit; therefore there is no danger of overload.
- Control and Flexibility – You can control and adjust many things in a hydraulic press to suit your needs. Examples include: duration of pressure retention, direction, force of impact, speed, and force release.
- Lower operating noise – Because hydraulic presses do not have flying wheels or many moving parts, they produce much less noise than mechanical presses. In fact, modern hydraulic presses with a properly installed pumping system exceed current federal noise control standards.
- Long machine life - Built-in overload protection is also good for tools. Since the pressure is always the same, there is no danger of damaging the instruments due to overload. The absence of shock, vibration and impact helps auxiliary equipment such as press brakes and machine guards last longer.
Hydraulic press loads
Most machines are designed to handle extremely heavy loads, measured in tons. However, hydraulic press manufacturers have complete control over this and can design presses to handle any size load.
For example, while they can design presses that can withstand a maximum load of 3,500 tons, they can also design machines with a maximum load of only 15 tons.
Presses are typically made from stainless steel and other durable materials such as high-strength steel alloys, aluminum and brass.
They are available in both single and multi-station configurations. Single-position presses consist of a single set of pressing tools, a die and a punch, located inside the table.
Multi-station presses have multiple sets of pressing machines that either perform the same operation on many materials or perform different pressing operations on the materials as they move between stages.
To customize your machine, manufacturers can change the press ton limit, increase or decrease the length by mm, increase or decrease the fold by mm, die shape, hydraulic fluid type and much more.
Safety and Compliance Standards
What to consider
Maintenance plays a big role in keeping hydraulic equipment running optimally and efficiently. To keep your car in great shape, take the following precautions.
- Avoid Leaks - It is a fact that a leaky machine operates well below its capacity. For best results, your operator should regularly check seals around O-rings, press cylinder, hydraulic lines, hose end fittings and valve seats.
- Don't exceed your load limits - it's pretty simple; Do not use a heavier ton load than your press is designed for. If you exceed your hydraulic press's ton limit, you risk stress on the machine, breakdown, or even injury to workers.
- Keep the machine well oiled. To ensure smooth operation and reduce wear, hydraulic machines must be adequately lubricated, especially around the seals. Also make sure that the hydraulic fluid you use is the same type as specified in the operator's manual.
- Check the speed of pressure build-up - a press in good condition can create working pressure in half a second. Alternatively, if the press takes more than two to three seconds to generate the set pressure, the press has a problem with either the pump or the relief valve. The problem is mainly due to insufficient pump revolutions per minute. Occasional valve problems include dirt in the line and an opening that is too wide.
- Listen to unfamiliar machine sounds - You should immediately investigate any unfamiliar sound, find the source and correct it. The most common source of noise during press operation is valve movement. Noises also sometimes occur due to insufficient lubrication.
- Checking the electronic elements of the machine . The most common electrical problems with hydraulic presses involve coils and relays. Please note that they have a finite life cycle and need to be replaced from time to time. (Coils have a life cycle of 3 million strokes, and relays are rated for 1 million strokes.) Replacement reduces troubleshooting effort and downtime. A record should be kept using an hour meter and a cycle counter that is not reset because they help in servicing the machine.
- Check other parts of the machine - You also need to take care of fittings, loose wires and hoses, as worn hoses and improperly crimped fittings can cause plumbing failures in any machines.
- Maintain Oil and Temperature During Operation - The easiest way to extend the life of hydraulic presses is to maintain oil and temperature during operation. If the press machine is running with low oil levels and/or dirty oil, you risk damaging it or shortening its life. The best way to determine if there is dirt in the oil is to test the oil. If there are dirt particles in the oil, the filter should be replaced. Ideally, the operating temperature of the press is about 120 ° C; if it gets higher, the operation starts to break down. To maintain optimal temperatures, use air and water coolers. Take proper care of these units, especially the radiator, which tends to collect dirt.
Additional settings
When using a homemade hydraulic press, users often have a question about how to make the jack rod move a shorter distance. This will allow you to spend less time processing parts using a homemade press. There are several ways to solve this problem.
- A rectangular or square profile pipe is mounted on the lower fixed stop of the press (either a removable version or fixation using a welded joint is possible).
- A height-adjustable lower stop is installed on the press, which is fixed to the side posts of the device with bolts. To install such a stop at different levels, holes are made in the side posts of the press at the required height.
- The distance between the press stops can also be reduced by using replaceable pads or anvils installed on the surface of the lower stop of the equipment.
Overall dimensions of the working space of the P6334 press
Specification of components of the P6334 press
- Press control - P6334A.41A.001
- Slider - P6334A.32A.001
- Bed - P6334A.11.001A
- Working cylinder - P6334A.31.001G
- Pipeline - P6334A.81.001
- Hydraulic unit - P6334
- Electrical cabinet - P6334A.93.001A
- Electrical equipment - P6334A.91.001A
- Electrical panel - P6330.92.001
- Working table - P6334A.61.001
- Striker - P6334A.62.001
- Short stroke mechanism P6330.42D.001
- Straightening device - P9.00.001A
Technical characteristics of the P6334 and P6330 press
| Parameter name | P6330 | P6334 |
| Basic parameters of the press | ||
| Nominal press force, kN (t) | 1000 (100) | 2500 (250) |
| Maximum stroke of the rod, mm | 500 | 500 |
| The greatest distance between the table and the rod is the open height of the press, mm | 750 | 800 |
| Distance from the rod axis to the frame (reach), mm | 400 | 400 |
| Rod speed - stroke, mm/sec | 12,5 | 4.5 |
| Rod speed - idle, mm/sec | 80 | 29 |
| Rod speed - return stroke, mm/sec | 18 | 70 |
| Table dimensions, mm | 800 x 630 | 1000 x 630 |
| Dimensions of the opening in the table, mm | 200 x 415 | 200 x 415 |
| Dimensions of removable leveling table, mm | 2000 x 420 | 2500 x 600 |
| Weight of removable leveling table, kg | 960 | |
| Weight of straightening tool, kg | 195 | |
| Table height above floor level, mm | 745 | |
| Nominal operating fluid pressure, kg/cm2 | 250 | |
| Electrical equipment | ||
| Number of electric motors | 1 | 1 |
| Main drive electric motor, kW | 22 | 18,5 |
| Dimensions and weight of the press | ||
| Press dimensions (length width height), mm | 2250 x 900 x 2720 | 1250 x 2170 x 3150 |
| Machine weight, kg | 5500 | 10940 |
- Banquetov A.N., Bocharov Yu.A., Dobrinsky N.S. and others. Press-forging equipment, 1970
- Bocharov Yu.A., Prokofiev V, N. Hydraulic drive of forging and pressing machines, 1969
- Belov A.F., Rozanov B.V., Linz V.P. Volumetric stamping on hydraulic presses, 1971
- Zhivov L.I. Forging and stamping equipment, 2006
- Kuzmintsev V.N. Forging with hammers and presses, 1979
- Rozanov B.V. Hydraulic presses, 1959
- Titov Yu.A. Equipment for forging and pressing shops, 2001
- Shcheglov V.F. Forging and pressing machines, 1989
- Berlet Development of forging drawings, 2001
- Rudman L.I. Sheet Forming Equipment Handbook, 1989
- Romanovsky V.P. Handbook of Cold Forging, 1965
- Okhrimenko Ya.M. Technology of forging and stamping production, 1966
- Kuzmintsev V.N. Forging with hammers and presses, 1979
- Meshcherin V.T. Sheet stamping. Atlas of circuits, 1975
Bibliography:
Related Links. Additional Information
- Directory of enterprises producing forging and pressing equipment in Russia
- Classification and designation of hydraulic and crank presses
- Mechanical presses
- Hydraulic presses
- Automatic forging and pressing machines
- Bending and straightening machines
- Guillotine shears, press shears
- Hammers
- Repair of hydraulic systems of metal-cutting machines
- Designations of hydraulic circuits of metal-cutting machines
- Repair of gear hydraulic pumps
Home About the company News Articles Price list Contacts Reference information Interesting video KPO woodworking machines Manufacturers