- home
- >
- Catalog
- >
- Categories by equipment type
- >
- welding equipment
- >
- Resistance welding machines
- >
- Butt welding machines
- >
- Resistance butt welding machines for wire/rod (steel or copper, aluminum, brass)
- >
- Butt welding machines (DS) for intermittent and short-term operating modes (joining wire coils)
- DS - list of models for welding copper, aluminum, brass wire (7)
- DS - list of models for welding steel wire (8)
DS - resistance butt welding machines for wire (rod) made of steel, non-ferrous metals (copper, aluminum, brass, tungsten)
- Name
- Purpose
- Technology and job description.
- Ranges
- Modifications and equipment
- Links
- Announcement!!!
- Specifications
Technology of butt electric welding of metals
It should be taken into account that butt welding is a special case of contact welding. That is why both technologies involve the use of almost the same equipment. The welding machine used is characterized by the following features:
- Electric current is generated by installing a high-power transformer.
- Electric current is transmitted through a stationary electrode.
- The design also has a movable electrode through which energy is supplied.
- To move the main element, a different drive can be installed.
- There is also a process control system.
Design features are determined by exactly how butt welding is carried out. It is worth considering that the butt welding scheme is characterized by the following features:
- There is no need to generate large current. This is due to the fact that the consumable material used ensures the maintenance of a stable arc.
- The method involves only local heating of the surface. Due to this, the efficiency of the process is significantly increased and the costs of the amount of current consumed are reduced.
Resistance butt welding diagram
In general, we can say that the technology is characterized by a fairly large number of features that must be taken into account. The power welding transformer generates voltage from 2 to 10 volts.
Consumables
Electrodes that are subject to the greatest wear in welding machines are constantly subject to mechanical and thermal loads. They are made from pure copper, or from copper alloys with aluminum, zinc, cadmium and other metals that increase the strength and elasticity of the product. Such alloys are divided into several types:
- To operate at high temperatures (about 500 degrees Celsius) and continuous current supply, such electrodes are made of bronze with the addition of nickel, silicon, zirconium or chromium;
- To work at temperatures up to 300 degrees, welding non-ferrous alloys, low-alloy steels, MS (alloyed with silver) and MK alloys are used;
- Alloys of bronze with chromium and cadmium are suitable for working at low temperatures (up to 200 degrees Celsius).
Conical and cylindrical electrodes wear out the fastest, while flat and wide ones, used in projection welding machines, wear out the slowest.
Manual welding process
Today, welding is performed using the technology in question to obtain high-quality products. Features of the process include the following points:
- Before starting work, the workpieces are placed in special fixtures. Electrodes act as such elements.
- The clamps used closely follow the shape of the future product. Due to this, you can get a quality product.
- Special consumables are used as electrodes, which are characterized by good resistance to mechanical stress.
- Due to a special drive, both workpieces are brought closer to each other. The transmitted force can be quite large, thereby improving the quality of the connection.
After firmly clamping the connected workpieces, the transformer turns on. Through the electrodes, current is supplied to the part of the workpiece being processed. The high current provides local heating of the metal.
Manual Hydraulic Butt Welding Machine
The above information indicates that resistance butt welding can be carried out using special equipment. Due to their features, it is possible to automate the process and improve the quality of the resulting products.
Resistance welding designation in the drawing
The designation in the drawing of a visible weld, regardless of the welding method, is made with a solid main line, and an invisible one - with a dashed line. The visible weld point is made with solid main lines, the invisible one is not marked in any way. From the image of a seam or point, if they are visible, draw an extension line that ends with a one-way arrow.
Designation on the drawing of a resistance welding seam
Advantages
The technology in question has a fairly large number of advantages, which has determined its spread. An example is the information below:
- There is no need for careful preparation of the processed edges.
- In conventional welding, in some cases it is necessary to perform thermal surface preparation. This is due to the fact that local exposure to high temperature allows you to achieve the best result.
- The resulting connection is characterized by increased reliability and strength. As practice shows, if all recommendations were followed during the work, the connection can last for a long period.
- The method under consideration is characterized by simplicity and ease of implementation. That is why the master does not have to have special skills.
- The thermal and mechanical effects provided ensure the production of a homogeneous metal. That is why it is possible to obtain metal with high strength.
- Under certain conditions, it is possible to automate the process.
- High performance value.
Welding pipes for storm drainage
A fairly large number of advantages of resistance welding determine its spread. However, it is necessary to take into account some disadvantages of the technology, which we will discuss in more detail later.
Flaws
There are also several significant disadvantages to consider when considering the resistance welding procedure. They are as follows:
- Quite high electrical costs. This is due to the fact that a high voltage current must be supplied to melt the material.
- There are high demands on the dimensions of the elements to be connected.
- The equipment used is characterized by high cost. Therefore, it is practically impossible to carry out the work in question at home.
Such shortcomings determine that the technology has become widespread.
Welding defects and quality control
Defects that occur during resistance welding are of two types:
- Defective welded joints. There may be several reasons for this: excessive heating of the docking area, excessive mechanical pressure, malfunctions of the device itself. The dimensions of the weld point are controlled using special templates and measuring instruments;
- Weld defect. This happens if the area where the parts are joined is too narrow, or, conversely, wide, if it contains irregularities, burrs, and gaps. Such defects can be determined by visual inspection - with the naked eye, through a magnifying glass, using a probe or probe. If necessary, the seam is x-rayed.
Prevention of defects is competent work not only during welding, but also before it, which includes leveling and cleaning the contact edge.
Butt welding methods
It is worth considering that there are several different butt welding methods. The most widespread are:
- Reflow welding.
- Resistance method.
All technologies are characterized by their own specific features that need to be taken into account.
Resistance butt welding
The common resistance butt welding is characterized by quite a large number of features. They are as follows:
- The workpieces are exclusively pressed against the electrodes with special jaws. This ensures rapid passage of current through the materials being processed.
- The use of special sponges eliminates the possibility of parts slipping between the electrodes used, through which voltage is applied to the surfaces being treated.
- The next step is to apply electrical current. Due to this, the metal in the treated area is heated.
- After this, sediment is applied, due to which the buildup is reduced. The next step is to apply a strong current to heat the surface as much as possible.
With electrical resistance, parts with a small cross-section can be processed. The maximum cross-sectional thickness is 40 millimeters. In this case, a strong connection is formed at the joint without melting the metal.
Flash butt welding
The technology in question has also become widespread. To heat the ends of parts, special equipment is used, which makes it possible to obtain a high-quality seam. Among the features of contact welding, the following points can be noted:
- The connected elements are brought together at low speed.
- The voltage remains constant throughout the entire process.
- Due to the uniform supply of the elements being connected, all micro-irregularities are leveled out.
- The surface is melted to ensure maximum contact area.
- There is no need for thorough surface preparation.
Reflow welding
Exposure to high temperature leads to the appearance of a high-quality connection, which is characterized by strength and reliability.
1. Continuous fusion welding is carried out when the welded rods come into contact, as a result of which a melting hole is formed. After heating the joint, the pressure rises to sedimentary pressure. Flash welding does not require well-fitting surfaces; it is possible to trim the ends using press shears, autogenous, etc. This welding is used on non-automatic machines.
2. Flash welding with heating is carried out with intermittent, often repeated approach of the rods until they touch, during which alternating heating and melting occurs during the arc process. It is suitable for welding rods with a cross-section of more than 1000 mm2, and if the power of butt machines is insufficient, the cross-section should be smaller.
Institute of Electric Welding named after. E. O. Paton developed a fundamentally new method of butt welding by pulsed flashing, combining continuous flashing and flashing with intermittent heating. The melting speed program is set by a throttle regulator, and a special vibrator is provided to apply vibration pulses of the reciprocating movement of the electrodes with a given frequency and amplitude. The K-724 docking machine works using this method.
For welded rods, the ends must be cleaned of burrs, scale and dirt using emery grinding machines. To obtain high-quality joints, it is necessary to accurately install and securely fasten the rods in the clamps of the machine, observing their centering and release length, avoiding distortions and displacements of the rods. Approximately the output of each rod is 1.5d (d is the diameter of the welded rod).
For butt contact electric welding of reinforcement, the following machines are used: ASP-10 (MS-301), MS-502, MC-I602 (MSR-100), MS-2008 (MSMU-150), K-724. For welding reinforcement of large sections, more powerful machines MSGU-300 and MSGU-500 are used.
The ASP-10 (MS-301) butt welding machine is designed for resistance butt welding with preheating and continuous fusion of rods made of low-carbon steel and non-ferrous metals.
A lever-eccentric fixed clamp is installed on the body, and a movable clamp is mounted on a swinging lever. The machine clamps are manual with an eccentric mechanism and radial movement of the movable jaws. The axes allow you to obtain two final distances (4 and 14 mm), at which the welded rods will be coaxial.
The MS-502 machine is designed for resistance butt welding of reinforcement with a diameter of 3-8 mm. Welding is performed using the resistance method. Spring pressure drive with pedal control. The machine is equipped with clamping and feeding mechanisms. It has control equipment and is equipped with a welding transformer. The machine clamps are lever driven and pedal driven. When you press the pedal, the welded rods are clamped and their ends are compressed. Upsetting is carried out automatically under the action of springs as the rods heat up. The welded joint is annealed in special clamps. The machine has clamps and scissors for preparing the ends of the rods and filing the burrs.
MCP type machines are designed for flash butt welding of reinforcement with a diameter of 40 mm using the heated flash method. Like the MS-502 machine, they are equipped with a welding machine; transformer; clamping and feeding mechanisms and control equipment are mounted on the housing.
The MS-1602 (MSR-100) machine has a manual lever drive for draft. On the bed frame there are two cast iron plates with copper contact inserts, to which the secondary turn of the welding transformer is connected. The left fixed plate is isolated from the machine body, and the right movable plate is mounted on two guides moving in bearings. The gap between the plates is closed with protective shields and a trough, which protects the transformer and other machine components from splashes of molten metal and scale.
Manual screw clamps. They are easily removed and can be replaced. It is possible to adjust the position of the contact jaws horizontally and vertically. The welding transformer is turned on and off by an electromagnetic contactor. For maintenance safety, the control circuits operate at reduced voltage (36 V) from a step-down transformer. It is turned on automatically at the beginning of upsetting by a switch located near the feed lever.
The MS-2008 (MSMU-150) machine is used for automatic welding of reinforcing bars with a diameter of up to 60 mm using the continuous reflow method. In semi-automatic welding, the heated reflow method is used. The main components of the machine are: a clamping frame with a pneumatic device, an electromechanical upsetting drive, a welding transformer, a contactor and a step switch.
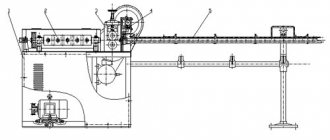
Rice. 2. Machine MS-502 for butt welding: 1 - body; 2 — adjusting spring; 3 - handle; 4 — contact block; 5 - vice; b - scissors; 7 — stage switch; 8 - pedal
The welding rods are installed in the contact jaws of the clamps and are held by lever devices and pneumatic cylinders. The operation of the clamps is controlled by trigger buttons connected to an electro-pneumatic valve. When welding using the continuous reflow method, after installing the rods and pressing the start button, the electromagnetic contactors are automatically activated and the welding transformer and the movable clamp movement drive are simultaneously turned on. As the ends of the rods come closer together, they melt with increasing intensity. After reaching the required heating, the welding transformer automatically turns off and the rods are upset. The rate of melting and upset is determined by the profile of the drive cam. It is adjusted using a friction adjuster. After upsetting, the welding cycle ends, the drive motor turns off, the clamps open, and the machine returns to its original position for the next welding.
The MSGU-300 and MSGU-500 machines are produced according to the same design and differ only in their power. They are used for butt welding of rods with a diameter of up to 70 mm using continuous flashing and flashing with preheating. The machines consist of: a frame, clamps with a pneumohydraulic device, a hydraulic upsetting drive, a welding transformer with a contactor stage switch. The rods are clamped using pneumohydraulic clamps. The reinforcement is installed in the clamps and its lifting after welding is carried out manually or using an electric hoist.
Rice. 3. Machine MS-1602 (MSR-100) for butt welding: 1-3 - screws; 4 — clamping device; 5 — emphasis; 6 — lever; 7 - contactor; 8 — bolt for grounding; 9 — lever
Rice. 4. Electrical diagram of the MS-1602 machine: 1 - stage switch; 2 — power contactor; 3 — terminal board; 4 - control circuit transformer; 5 - intermediate relay; 6 - limit switch; 7 - power button
Welding control is automatic using time relays, limit switches and electro-pneumatic valves.
Automatic welding occurs after pressing the “welding” button. The contactors are activated, the welding transformer and the drive for moving the movable clamp are turned on. Subsequently, the welding process occurs in the same way as with the MSMU-150 machine.
When flash welding with heating, after clamping the rods, pressing the “welding” button turns on the welding transformer and hydraulic displacement drive, which automatically performs a reciprocating movement and the ends of the rods periodically come into contact, heating them with welding current. Regulation of the duration of the welding cycle and the duration of individual operations is carried out by appropriately setting the electronic time controller.
Rice. 5. Machine MS-2008 (MSMU-150) for butt welding: electric motor; 2 - body; 3 — variator; 4 - gearbox; 5 - lower lips; b - upper lips; 7 levers; 8— guides; 9 - pneumatic cylinder; 10—replaceable gears
The K-724 welding machine is used for pulse butt welding of fittings of classes AI...AV with a diameter of 12-40 mm. The machine includes a hydraulic pump station and control cabinets. The drive of all mechanisms is hydraulic. The cantilever-type machine body allows for axial and lateral supply of reinforcement. The welding transformer of the machine is located outside the machine, and the current flow is connected to the upper clamping electrodes. The machine provides automatic welding in continuous fusion and vibration fusion modes. The reflow rate program is set by the throttle controller.
During contact butt welding, a veil is formed at the joint, which must be removed, as it prevents the movement of rods between the electrodes of welding machines. To remove it, devices with sanding wheels located in a line after the butt welding machine are used.
The Kherson Design and Technological Institute has proposed a special rotary crimping machine for deburring (Fig. 18.20). The burr is compressed using four special cams installed in a rotating machine with a frequency of 450 min. head, which provides 48 compressions in 1 s. As a result, compaction occurs (forging) and the burr is leveled flush with the rod. The electric drive power of the machine is 4.5 kW.
Rice. 6. Rotary crimping machine for deburring: 1 — casing lock; 2 — V-belt; 3 - electric motor; 4 - bed; 5 - casing; 6 — rotational crimping head
Table 1 Technical characteristics of machines for resistance butt welding of reinforcement
—
Machines for butt welding of reinforcement, complete with cutting machines, are widely used in semi-automatic lines for waste-free butt welding and cutting.
The ASP-10 (MS-501) machine is designed for electric contact butt welding of reinforcement with a diameter of 3-8 mm. Welding is performed using the resistance method. Spring pressure drive with pedal control.
Rice. 7. ASP-10 machine for butt welding 1 - body; 2— stage switch; 3 - pedal; 4—scissors; 5 - vice; 6 — contact block; 7 — handle; 8 - adjusting spring
The clamping and feeding mechanisms are mounted on the machine body. The machine has control equipment and is equipped with a welding transformer. The machine clamps are lever driven and pedal driven. When you press the pedal, the welded rods are sequentially clamped and their ends are compressed with the required welding pressure. Upsetting is carried out automatically under the action of springs as the parts being welded heat up. The welded joint is annealed in special clamps. Clamps and scissors are mounted on the machine table for preparing the ends of the welded rods and filing the burr.
MCP type machines are designed for electric flash butt welding of reinforcement with a diameter of up to 40 mm using the heated flash method. Like the ASP-10 machine, they are equipped with a welding transformer; clamping and feeding mechanisms and control equipment are mounted on the body.
The upper part of the body of the MCP-100 machine is a rigid frame formed by two traverses, tightened by guide ties, along which the middle traverse, carrying the right movable clamp, slides. The left clamp is attached to the left crossbar.
Rice. 8. MSR-100 machine for butt welding 1-3 - screws; 4 - lanyard; 5 — emphasis; 6 — lever; 7 - contactor; 8— bolt for grounding; 9 - lever
The MCP-100 machine is equipped with manual screw clamps. The design of the clamps provides the ability to adjust the position of the contact jaws in the horizontal and vertical directions to compensate for their wear and correct the position of the welded rods. Pressure drive is manual, lever. The distance between the clamps is adjusted with a lanyard. Single-phase armored type welding transformer. Regulation of the secondary voltage is achieved by switching sections of the primary winding of the transformer.
The electrical circuit of the MSR-100 machine is shown in Fig. 9.
Rice. 9. Electrical diagram of the MSR-100 machine 1 - stage switch; 2 — power contactor; 3 — terminal board; 4 - control circuit transformer; 5 - intermediate relay; 6 - limit switch; 7 - power button
The MSMU-150 machine is designed for butt welding of reinforcement with continuous flashing and flashing with intermittent preheating of reinforcement with a diameter of up to 50 mm.
The machine consists of a body, an electric motor, a variator, a gearbox, pneumatic cylinders, guides, upper and lower jaws.
The rods to be welded are clamped using pneumatically driven lever clamps and removed from the clamps manually after welding.
The movement of the movable clamp during melting and upsetting is carried out by an electromechanical drive. The variator allows you to smoothly change the reflow rate (within 1:2).
Using electro-pneumatic valves and limit switches on the machine, automatic control of the welding process is possible. The welding transformer is turned on and off using an electromagnetic contactor.
Rice. 10. Machine MSMU-150 for butt welding 1 – body; 2 – electric motor; 3 — variator; 4 – gearbox; 5 – replaceable gears; 6 – pneumatic cylinder; 7 – levers; 8 — guides; 9 — upper lips; 10 - lower lips
The MSGU-300 and MSGU-500 machines are designed for resistance butt welding of reinforcement with a diameter of up to 70 mm by continuous flashing and flashing with preliminary intermittent heating.
Rice. 11. MST-35 machine for friction butt welding 1 - hollow spindle; 2 - clamping device
The machines have a hydraulic drive to move the movable clamp during heating, melting and upsetting. The parts are clamped using pneumohydraulic clamps. Installation of reinforcement into clamps and its removal after welding is carried out manually.
Welding control is automatic using a thyratron voltage relay, an electronic time relay, limit switches and electro-pneumatic valves.
The contact jaws of the machines are processed depending on the shape of the parts being welded. To compensate for the wear of the jaws, it is necessary to periodically check the position of the jaws in height.
It is recommended to measure the ohmic resistance of the secondary circuit at least once a month. When the resistance of the secondary circuit increases by more than 25% compared to the resistance of the machine circuit, the ohmic resistance of individual contacts should be measured and contacts with a sharply increased resistance should be identified. Contactor contacts should be cleaned at least once per shift.
For butt welding of reinforcement, machines using the friction welding method are also used. Friction welding on machines is completely mechanized; only the operations of loading reinforcement and removing finished products are performed manually.
Welding is controlled from a device that monitors the amount of upsetting, or from a time relay.
All friction butt welding machines are structurally identical and differ only in parameters. In Fig. Figure 11 shows a general view of the MST-35 machine for friction butt welding. The main interface of the machine is a hollow spindle through which the rotating part to be welded (rod) passes. The second rod is fixedly fixed in the clamping device coaxially with the rotating one. The machines are equipped with a pneumohydraulic mechanism, powered by an air line with a pressure of at least 0.45 MPa.
Butt welding of plastic pipes
The technology in question is used to connect plastic pipes. Among the features of butt welding, we note the following points:
- It is worth considering that plastic does not allow current to pass through. That is why it is necessary to use special equipment with a contact heater.
- Both elements being connected must fit tightly to each other. That is why the diameter of the pipes must match each other perfectly.
- In order to heat the surface evenly, a special nozzle is used that follows the shape of the pipe.
- At the moment of exposure to heat, the nozzle is slightly compressed. When exposed to pressure, a high-quality connection is formed.
Welding of polyethylene pipes
After the surface has been melted, it takes some time for it to cool. There are simply a huge number of different special tools on sale for obtaining high-quality connections of PVC pipes.
Seam properties
The spread of technology can be primarily associated with the high quality of the resulting seam. It is characterized by the following properties:
- Increased decorative qualities. During conventional welding, a wide shaft can be formed, which must be further processed to obtain a flat surface.
- Reliability and strength of connection. The seam can withstand a wide variety of impacts, including variable loads.
- In the area where the weld is located, the metal does not lose its properties, since local heating of the metal occurs.
As a rule, the quality of the resulting seam is checked visually. On a high-performance line, special equipment can be used for this.
Devices for carrying out the process
Resistance welding equipment can be used to fully automate the process. In most cases, all you need to do is place the workpieces correctly and press one key. Other features of butt welding machines include the following:
- Good performance.
- Possibility of process automation.
- High cost of equipment.
- When carrying out work, the possibility of making an error is eliminated.
Butt welding machine
You can find equipment from a variety of manufacturers on sale. It is recommended to pay attention to products only from well-known companies.
What equipment is used
Since butt welding is a subtype of electric resistance welding, the equipment used for these two processes has much in common. When automating this welding technology, the most important thing is the correct placement of workpieces, tools and pressing one key.
The main welding element is a butt welding machine, consisting of a butt welding machine and a welding transformer. The butt machine allows you to create the necessary axial pressure in the welding zone and consists of:
- bed (body with a supporting surface);
- plates and guides, with the help of which the alignment of the workpieces is ensured;
- clamps (hold workpieces);
- a mechanical or electromechanical drive, which allows you to create the necessary pressure and transmit it to the clamps.
The welding transformer is equipped with an electric motor unit, gearbox, pump, pneumatic and hydraulic unit. The entire work process is managed by a special system.
The main elements of a hand-held welding tool are a heating element and a centering device. To compress heated parts, the operator uses his force through a system of levers and pushers. In the case of using manual equipment, the foreman retains the function of visual control of the process (sometimes, the lack of sufficient experience causes deterioration in the quality of welding seams).
Types of welding wire
When carrying out butt welding, you should correctly select the most suitable wire. It can be used to obtain a quality product. Specialists must distinguish between types of wire and be able to select the most suitable one. The following wire is on sale today:
- Copper has become widespread when joining low-carbon steels.
- Stainless steel suitable for chrome and other alloy steels
- Aluminum is most often chosen when working with sulimins or duralumin.
Copper Welding Wire
In addition, quite a lot of attention is paid to the choice of cross section. It is selected depending on the contact area of the elements being connected.
Resistance welding machines
Welding machines are divided into groups according to the following criteria:
- Purpose: highly specialized machines designed to work with large batches of the same type of parts, or universal ones that process a small number of workpieces, but can be easily reconfigured;
- A type of mechanical unit that compresses and shrinks parts. On this basis, devices are divided into hydraulic, pneumatic, pneumohydraulic, mechanical and others;
- By mobility – mobile, portable, stationary;
- According to the welding method;
- By type of power supply: machines with a rectifier or machines running on alternating current (single-phase, three-phase).
Application areas of butt welding
The spread of this method can be associated with their various advantages. Butt welding is used:
- In construction in the manufacture of monolithic structures. They must be designed to withstand heavy loads.
- In metallurgy, the method is used to join rolled sheets and wires. Butt welding allows you to obtain a continuous high-quality surface.
- In the railway sector, rails are being created without joints. They allow the technology to develop quite high speeds. It takes a relatively small amount of time to connect individual sections.
- In the automotive industry, butt welding technology is used to produce body products. The features of the equipment used make it possible to produce products of complex shapes.
- When creating a cutting part from alloy steel, resistance welding is also used. That is why during operation the cutting edge does not cling to the surface being processed. The strength of the connection is quite high, so the tool can withstand the applied load.
- The connection of steel and plastic pipes is also carried out when using the method in question. By using a special tool, you can obtain a uniform, high-quality seam.
Pipelines for supplying gas and oil products are also created using resistance welding. The technology allows connecting pipes with a diameter of up to 1420 mm. High performance allows you to make a sealed connection within 5 minutes.
In conclusion, we note that resistance welding in most cases can replace the common technology associated with the supply of high voltage current to the workpiece. In this case, the metal does not melt and the basic performance qualities do not change.
Purpose
Butt welding machines
DS wires are designed for butt welding of wire rod spools in
wire/reinforcement production,
butt welding of wire spools in
rope or cold drawn reinforcement production,
to ensure continuous supply of welding wire in robotic or automatic welding (for joining welding wire supplied in spools or barrels), butt welding welding of coils in the production
of measuring rods, cables,
or any other production requiring continuous wire supply.
For welding butt joints of steel wire
DSH/DSF machines of FE modification are intended,
for butt welding wire
from non-ferrous metals (
copper
,
aluminum
,
brass
or, for example,
tungsten
) – NE modification.
This was done for a reason. When welding, non-ferrous metals require different upsetting rates (i.e., different upsetting forces) and a slightly different voltage in the secondary circuit. That is why Ideal-werk does not make “universal” “devices for butt welding of wire” and for
steel
and for
copper/aluminum wire. IDEAL-Werk makes wire butt welding machines WITHOUT COMPROMISE, ideal from the point of view of achieving the result - “perfect welding” of EITHER STEEL WIRE OR NON-FERROUS METAL WIRE.
DSH/DSF machines are not designed
for in-line/continuous butt welding of parts, but only for repeated short-term operating modes in case of wire breakage and butt welding of wire before drawing mills, twisting machines, etc. (For in-line tasks, for example, welding wire rings, welding wire frames, any other parts made of wire - see DSP and DST type machines).
For butt welding of reinforcement of large sections - see flash butt welding machines AS.
DSH butt welding machines are used in the production of:
- for butt welding of wire (including rectangular section), reinforcement, measuring rod;
- in welding production: for butt welding of welding wire, i.e. ensuring its continuous supply when welding with a robot or on an automatic welding installation;
- Cable products;
- Hose reinforcement;
- Welded mesh.