Metalworking involves changing the size, shape or quality characteristics of metals and alloys. For each task, a corresponding technique is prescribed. Having divided all methods of influence into large groups, we can distinguish the following categories of metalworking:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- electric;
- thermal;
- pressure treatment;
- welding;
- casting.
The first type is the most common. Each requires appropriate equipment, most often a metal processing machine.
Mechanical restoration
The machining method is based on cutting or cutting off fragments from the surface of the metal to give it the desired shapes and sizes. Mechanical processing is conventionally divided into cutting (turning) and abrasive cleaning. Cutting is a set of processes during which the workpiece is brought to a given geometry by removing excess material using various types of tools. These processes may include:
- milling – shaping surfaces using a milling machine;
- drilling - making holes in metal using special drills;
- cutting - dividing the material into pieces of the required sizes;
- turning – rotary machining using turning tools.
- Abrasive processing is the grinding and polishing of a metal surface using devices that operate with abrasive belts or grinding wheels.
Types of metalworking equipment
Metalworking equipment is classified according to the type of operations it performs with metal workpieces. The following types of equipment are distinguished:
- milling;
- turning;
- drilling;
- thread cutting devices;
- guillotine;
- grinding;
- sheet bending
The most common type of modern metalworking equipment is lathes. These devices rotate a metal workpiece around a spindle. As the tools and cutting edges rotate, they shape or cut the metal into the desired shape. Lathes are available in a variety of options, from small benchtop units to large stationary models. Some of them can be controlled manually, some can be controlled by CNC. Lathes perform a large number of operations, such as: boring and turning cylindrical and shaped surfaces, thread cutting, end processing, drilling holes, and so on. Lathes can be called universal, which explains their demand.
Milling machines are devices that process the surface of a material using a cutter rotating around the axis of a spindle (like a drill) and a work table that can move in several directions. Based on the control method, a distinction is made between manual machines and CNC-controlled machines. The latter can perform a huge number of complex operations, such as cutting grooves, planing, drilling, threading, milling and so on.
Metal cutting machines are used to cut soft and hard metals in one linear direction. According to the control method, this equipment is divided into automatic, manual and semi-automatic.
Bending and forming machines are equipment that allows you to bend metals to give them the desired shape.
Metalworking equipment for drilling, boring, countersinking and reaming of metal parts. Such equipment includes multi-spindle or central machines.
Grinding units are devices designed to make the surfaces of metal products smooth and shiny. They can grind parts both outside and inside.
Top 10 best manufacturers
TOYODA (Japan)
Toyoda was established in 1941 in Japan as an independent subsidiary that is separate from the machine tool division of Toyota Motor Corporation. Initially, the organization produced cylindrical grinding machines. As it developed, since 1968, the manufacturer began to develop and produce high-precision and high-performance machining centers for the serial production of medium- and large-sized parts. The company also specializes in the production of industrial automation equipment, the production of parts for automobile steering and the construction of automated production lines.
Reference! TOYODA is the main supplier of equipment for the TOYOTA automotive corporation. Also, machining centers produced by TOYODA are purchased by other manufacturers to create factory and customer engines of Formula 1 cars.
SMTCL (China)
The machine tool company SMTCL is the largest manufacturer of CNC machines in China (more than 100 thousand units of equipment per year).
The company began its activities in 1964. In 2022, China's largest state-owned concern has 15 machine tool factories and research institutes that develop and produce high-tech equipment.
SMTCL produces more than 300 types of universal and CNC machines. The control systems on the machines are mainly systems NC-100, NC-200, NC-300 (supplied from Russia) and components produced by leading global companies (Siemens, Bullbardi, NSK, Duplomatic, Mitsubishi, Renishaw, etc. .). Purchasing quality parts allows us to produce high-quality and reliable equipment at an affordable price, which is a third or half lower than that of European and Japanese companies.
SMTCL exports manufactured machines to more than 80 countries, including Germany, Great Britain, Italy, Russia, USA, Canada, Japan, Turkey, South Korea and South Africa.
HAAS (USA)
Haas Automation began operations in 1983. It is the largest machine tool manufacturer in the United States, producing a wide range of devices:
- CNC lathes;
- fully programmable rotary tables and indexers;
- CNC machining centers (vertical and horizontal);
- large five-axis and specialized machines.
The Haas company uses 2/3 of its own production machines of the total amount of equipment to produce high-tech equipment. This approach allows us to produce reliable and high-quality devices at a reduced cost.
Reference! California-based Haas made machine tool history with the invention of the first fully automatic programmable collet indexer. This device made it possible to position the parts in such a way that they were processed with the highest possible accuracy.
ANCA (Australia)
Australian manufacturer ANCA Pty Ltd has been designing and manufacturing CNC grinding machines since 1974. The company's headquarters and main manufacturing plant are located in Melbourne, with two other plants based in Thailand and Taiwan.
ANCA designs and also manufactures several types of numerically controlled equipment and tools:
- CNC grinding and milling machines;
- tooling and cutting machines;
- sharpening machines;
- machines for making taps;
- medical and dental drills;
- tools and cutters.
The manufacturer's subsidiary, ANCA Motion, develops computer control systems for ANCA Pty Ltd and also supplies them to other Australian, Chinese and Taiwanese manufacturers.
HEDELIUS (Germany)
The German company HEDELIUS was founded in Bünde in 1967. Initially, the manufacturer specialized in the development and manufacture of woodworking machines. After 9 years, the company's founders began producing machining centers for the metalworking industry and various types of custom-made machines. Since the 90s of the 20th century, the company has been producing the first copies of machining centers. And at the beginning of 2000, the manufacturer began producing new models of three-, four- and five-axis machining centers, which have a combined design and operate in pendulum mode.
Reference! HEDELIUS became famous due to the invention of a new type of machine tools: semi-gantry machining centers with a movable stand. Such equipment was used to produce individual parts and small series of elements using precision cutting.
In the production of machine tools, HEDELIUS uses modern programs for design work and calculations, which allow us to constantly optimize the equipment produced. All work on the production and release of high-tech products is carried out by the development department, which employs qualified engineers, technicians and software developers.
Biglia (Italy)
The Italian company Biglia specializes in the development and production of high-performance turning centers. It has been operating since 1958. The manufacturer produces the following types of CNC turning equipment:
- machining centers;
- centers for processing bar stock;
- turning and milling centers;
- vertical machines.
The quality of Biglia products is confirmed by international certificates of conformity: ISO 9001 and CE Mark. CNC and drive systems for the production of turning machines are supplied by the Japanese company Fanuc. All other parts are produced by the Italian company independently. The produced metal-cutting equipment is successfully used in production in many European countries due to its combination of high quality, functionality, durability and reasonable cost.
AVIA (Poland)
AVIA precision machines have been produced since 1902 in one of the oldest production facilities in the industry in Warsaw. AVIA has been one of the leading manufacturers of metalworking equipment in Poland since the 70s of the 20th century.
The range of equipment produced by AVIA is represented by a wide range of devices with numerical control:
- vertical milling machining centers;
- universal milling machines;
- lathes with inclined bed.
AVIA milling and turning equipment is designed to meet the increased rigidity requirements of heavy-duty cutting applications. For this purpose, the cast bed and the structure of the machining centers are made of high-strength materials. Also, both elements undergo mandatory heat treatment in order to maintain thermal stability during long-term operation.
AVIA machines are developed by highly qualified engineers in our own design office and manufactured in accordance with the ISO 9001 quality control system. Each finished piece of equipment undergoes numerous checks before being sent to the customer. The most popular metalworking equipment made in Poland is in Germany and Western Europe.
TORNOS (Switzerland)
The Swiss company TORNOS began its activities in 1880 in Moitiers. The manufacturer went down in the history of metalworking as one of the first creators of cam-type automatic lathes, which have high flexibility of use and processing accuracy.
The Tornos product range consists of the following types of equipment:
- machining centers for machining parts up to 100 ⨯ 100 ⨯ 100 mm in size, which requires exceptional precision;
- CNC longitudinal turning machines with a movable headstock for parts with a diameter of up to 38 mm;
- multi-spindle CNC longitudinal turning machines for parts with a diameter of up to 32 mm.
Based on its model range, the Swiss company specializes in the development and production of machines that are used to produce parts of exceptional precision and high quality.
Tornos supplies its products to various industries: electrical, automotive, engineering, medical and dental prosthetics.
CIDAN (Sweden)
CIDAN was founded in 1907 in Gothen (Sweden). Subsidiaries of the Swedish manufacturer are based in Denmark and the USA. They are engaged in technological development, service and sale of spare parts in local markets.
CIDAN is engaged in the production of electromechanical rotary beam press brakes, electromechanical guillotine shears, compact modular lines for longitudinal-transverse cutting of thin sheet and coil steel. These types of machines are in demand in any procurement production.
The advantage of the Swedish company among its competitors on the market is its own engineering, technological and design department. They allow an enterprise to develop, implement and patent unique innovative solutions.
CIDAN equipment is designed according to the principles of high environmental friendliness and economical use of materials:
- several operators are not required to operate the machine, which will reduce labor costs and make the worker’s work easier;
- The absence of a hydraulic system will allow you to significantly save on the maintenance of hydraulic elements;
- Energy costs are reduced since CIDAN machines only use electricity during actual operation;
- There is no need to use or replace oil for lubrication, since the machines operate on the basis of a servo-electric drive.
Equipment selection
When choosing metalworking equipment, you should pay attention to several main characteristics:
- Functionality - on the modern market there are machines that perform specific work, as well as entire systems that combine several types of metalworking equipment.
- Degree of automation – for small enterprises, you can choose equipment with manual or semi-automatic control. For manufacturing enterprises, it is more advisable to purchase highly efficient automatic equipment that requires minimal operator intervention.
- Manufacturer - trying to save money and purchasing the cheapest metalworking equipment, mainly made in China, many are faced with the problem of frequent repairs and complex maintenance of devices. As a result, having saved money on purchases, they spend it on restoring the functionality of the machines, and also lose income during downtime. In order for metalworking devices to truly generate income and not fail over a long period of operation, they must be purchased from a reliable manufacturer, whose products are time-tested and have positive reviews from customers. The equipment supplier must be an official representative of a particular manufacturer, otherwise you cannot be sure that you will receive high-quality and durable equipment.
- Warranty obligations - when choosing machines for working with metals, pay attention to what service conditions under the warranty (and after its expiration) the manufacturer promises, as well as the possibility of upgrading the equipment if necessary.
FORT
A fairly large company, which includes more than one enterprise. "Sasta" - a plant that is part of this holding, carries out a full cycle of work on the production of metal-cutting machines: from design to assembly. The plant has each of 6 processing stages, the presence of which is necessary, according to the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation.
“Instrument Making Plant” is another member of this group, whose work has been focused on the production of machine tools for 7 years. At the plant, similar to the previous one, a full cycle of work is organized.
Equipment for working with metals from Warcom
The Italian company Warcom offers a wide selection of equipment for metal processing. Our product range includes press brakes, plasma and laser cutting machines, guillotines and other equipment used in the metalworking industry. You can choose budget models or machines for large enterprises with many functions. It is also possible to purchase used devices that have undergone pre-sale testing, guaranteeing their quality and performance.
STAN Group
The production association, which includes 7 factories, is the largest enterprise engaged in machine tool construction:
- "Machine Tool Building", an enterprise located in the city of Sterlitamak;
- "Stankotekh", an enterprise located in the city of Kolomna;
- "Ryazan Machine Tool Plant", an enterprise located in the city of Ryazan;
- "Grinding Machines", an enterprise located in Moscow;
- "Savelovsky Machine Tool Plant" - located in the city of Kimry;
- "Donpressmash", an enterprise located in Azov, Rostov region.
More than 50% of machine tool production is occupied by a group of these manufacturing enterprises. The range of products offered to consumers is quite wide: heavy machine tools are replaced by processing centers.
Classification of metal-cutting machines - all about equipment for metal processing
Metal-cutting machines produced by domestic manufacturers are divided into several categories, which are characterized by the corresponding classification. You can determine which category this or that equipment belongs to by its labeling, which says a lot to those who understand it. However, no matter what category the metal-cutting device belongs to, the essence of processing on it comes down to the fact that the cutting tool and the part perform form-building movements, and it is they that determine the configuration and dimensions of the finished product.
The most common types of metal-cutting machines: 1-6 - lathes, 7-10 - drilling, 11-14 - milling, 15-17 - planing, 18-19 - broaching, 20-24 - grinding.
Table of metal cutting machine shapes
| Name of machines | Group code | Type code | |||||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | ||
| Reserve | 0 | — | |||||||||
| Turning | 1 | Automatic and semi-automatic machines: | Turning-Turret | Drilling and cutting | Carousel | Lathe and face | Multi-cutters and copying machines | Specialized | Various lathes | ||
| specialized | single-spindle | multi-spindle | |||||||||
| Drilling and boring | 2 | — | Vertical drilling | Semi-automatic | Coordinate boring | Radial drilling | Horizontal boring | Diamond boring | Horizontal drilling | Various drilling | |
| single-spindle | multi-spindle | ||||||||||
| Grinding and finishing | 3 | Cylindrical grinders | Internal grinding | Roughing and grinding | Specialized grinding machines | — | Sharpening | Surface grinding | Lapping, polishing, honing, finishing | Various educational | |
| Electro-physical and electro-chemical | 4 | — | Light-beam | — | Electrochemical | Electro-spark | — | Electro-erosive, ultrasonic piercing | Anode-mechanical cutting | — | |
| Gear and thread processing | 5 | Threaded | Gear shaping machines for processing cylindrical wheels | Gear cutters for processing bevel wheels | Gear hobbing machines for machining cylindrical wheels and splined shafts | For cutting worm wheels | For machining the ends of wheel teeth | Thread milling | Gear finishing, testing and rolling | Gear and thread grinding machines | Various gear and thread machining |
| Milling | 6 | — | Vertical milling console | Continuous milling machines | Longitudinal single-post | Copying and engraving machines | Vertical, non-console | Longitudinal two-post | Console-milling operating rooms | Horizontal milling console | Various milling |
| Planing, slotting, broaching | 7 | Longitudinal | Cross-planing | Slotting | Long horizontal | Broaching vertical for broaching | — | Various planing | |||
| single-rack | two-post | internal | outdoor | ||||||||
| Split | 8 | Cutting, equipped | That's right - cutting | Saws | — | — | |||||
| turning tool | grinding wheel | smooth or grooved disc | tape | disk | Hacksaws | ||||||
| Different | 9 | Coupling and pipe processing | Saw-beetles | Correctly and centerless roughing | Balancing | For testing tools | Dividing machines | Balancing | — | — | |
Types of metal-cutting equipment
Depending on their purpose, metal-cutting machines are divided into nine main groups. These include the following devices:
- lathes - all types of lathe machines (in the marking they are indicated by the number “1”);
- drilling and boring - machines for performing drilling operations and boring (group “2”);
- grinding, polishing, finishing - metal-cutting machines for performing finishing, grinding, sharpening and polishing technological operations (group “3”);
- combined - metal-cutting devices for special purposes (group “4”);
- thread and gear processing - machines for processing elements of threaded and gear connections (group “5”);
- milling - machines for performing milling work (group “6”);
- slotting, planing and broaching - metal-cutting machines of various modifications, respectively, for planing, slotting and broaching (group “7”);
- cutting - equipment for performing cutting work, including saws (group “8”);
- different - examples of such metal-cutting units are centerless-grinding, saw-cutting and others (group “9”).
Classification
- Metalworking machines are classified according to various criteria, depending on the type of processing, the cutting tool used and the layout. All mass-produced machines are divided into nine groups, each group has nine types.
- Machines of the same type may differ in layout (for example, universal milling, horizontal, vertical), kinematics, i.e. a set of links transmitting motion, design, control system, dimensions, processing accuracy, etc.
✅ Group of lathes Consists of machines designed for processing rotating surfaces. The unifying feature of the machines of this group is the use of the rotational movement of the workpiece as a cutting movement.
✅ Group of drilling machines Also includes boring machines. The unifying feature of this group of machines is their purpose - processing round holes. The cutting movement is the rotational movement of the tool, which is usually also accompanied by a feed movement. In horizontal boring machines, feed can also be carried out by moving the table with the workpiece.
✅ Group of grinding machines Unites based on the use of abrasive grinding wheels as a cutting tool.
✅ Group of polishing and finishing machines Unites on the basis of the use of abrasive bars, abrasive belts, powders and pastes as cutting tools.
✅ Group of gear-processing machines Includes all machines that are used for processing wheel teeth, including grinding ones.
✅ Group of milling machines Consists of machines that use multi-edge tools - milling cutters - as cutting tools.
✅ Group of planing machines Consists of machines whose common feature is the use of a straight-line reciprocating movement of the cutter or workpiece as a cutting movement.
✅ Group of cutting machines Includes all types of machines designed for cutting and sawing rolled materials (rods, angles, channels, etc.).
✅ A group of broaching machines has one common feature: the use of special multi-bladed tools as a cutting tool - broaches.
✅ Group of thread-processing machines Includes all machines (except for turning machines) designed specifically for the production of threads.
✅ The group of miscellaneous and auxiliary machines unites all machines that do not belong to any of the groups listed above.
Machine markings
The classification of equipment intended for processing metal workpieces assumes that, having seen its markings, any specialist will immediately be able to tell which metal-cutting machine is in front of him. This marking contains alphabetic and numerical symbols that indicate individual characteristics of the device.
The first number is the group to which the metal-cutting machine belongs, the second is the type of device, its type, the third (and in some cases the fourth) is the main standard size of the unit.
Decoding the markings of metal-cutting machines
After the numbers listed in the model marking, there may be letters that determine whether the model of the metal-cutting machine has special characteristics. These characteristics of the device may include its level of accuracy or indication of modification. Often in the designation of a machine, the letter can be found after the first digit: this indicates that this is a modernized model, in the standard design of which some changes have been made.
As an example, you can decipher the markings of the 6M13P machine. The numbers in this designation indicate that we have a milling machine (“6”) of the first type (“1”), which belongs to the 3rd standard size (“3”) and allows processing with increased accuracy (letter “P” ). The letter “M” present in the marking of this device indicates that it has been modernized.
Design
Basically all devices consist of:
- strong frame;
- work area;
- clamps or other devices for holding the workpiece;
- engine and belts transmitting rotation;
- tool for cutting (grinding).
An interesting question is what paint coatings are applied to metalworking equipment. The peculiarity of paintwork is that it can withstand increased friction, as well as high temperatures.
In the article we talked about machines for metal processing, and to complete the topic, watch a video:
Automation levels
Types of lathes, as well as devices for any other purpose that are used in mass and large-scale production, are called aggregate. They received this name due to the fact that they are assembled from the same type of units (units): beds, working heads, tables, spindle units and other mechanisms. Completely different principles are used when creating machines that are necessary for small-scale and single-piece production. The design of such devices, which are highly versatile, can be completely unique.
CNC lathe
Classification of lathes (as well as equipment of any other categories) according to the level of automation implies their division into the following types:
- manual models, all operations on which are carried out manually;
- semi-automatic, in which part of the technological operations (installation of the workpiece, starting the device, removing the finished part) is performed manually (all other auxiliary operations are carried out in automatic mode);
- automatic, for which you only need to set processing parameters; they perform all other operations independently, in accordance with a given program;
- metal-cutting units with CNC (all processes on such machines are controlled by a special program that contains a coded system of numerical values);
- metal-cutting equipment belonging to the category of flexible automated modules.
The most prominent representatives of metal-cutting machines are CNC devices, the operation of which is controlled by a special computer program. Such a program, which is entered into the machine’s memory by its operator, determines almost all parameters of the unit’s operation: spindle speed, processing speed, etc.
Even the most compact desktop machines can be equipped with a CNC system
All types of metalworking machines equipped with a CNC system contain the following standard elements in their design.
- The operator's console (or console), through which a computer program that controls its operation is stored in the machine's memory. In addition, using such a remote control, you can manually control all parameters of the unit’s operation.
- The controller is an important element of the CNC system, with the help of which not only control commands are generated, transmitted to the working elements of the equipment, and the correctness of their execution is monitored, but also all the necessary calculations are made. Depending on the degree of complexity of the unit model, either a powerful compressor or a conventional microprocessor can be used as a controller to equip it.
- A screen or display that acts as a control and control panel for the operator. This element allows you to monitor the operation of a metal-cutting machine in real time, control the processing process, and, if necessary, quickly change parameters and settings.
The operating principle of metalworking machines equipped with a CNC system is simple. A program is first written that takes into account all the requirements for processing a specific workpiece, then the operator enters it into the machine controller using a special programmer. The commands embedded in such a program are sent to the working elements of the equipment, and after they are executed, the machine automatically turns off.
The use of metal-cutting machines equipped with numerical control allows processing with high accuracy and productivity, which is the reason for their active use to equip industrial enterprises that produce products in large series. Due to their high level of automation, such units are perfectly integrated into large automated lines.
What is a machine?
Let's start with the basics. Among other industrial units, the main difference between machines is the presence of a bed, on the upper surface of which, in fact, the main working “organ” is installed. The metalworking element can be a small abrasive wheel, a diamond bit, or even a drill - it all depends on what operation needs to be performed. Often, the general appearance of a metalworking machine is represented by a massive structure with an electric motor, a feed platform, various clamps, working equipment and other elements. It is worth noting that machines for home (household) and home workshops look much more modest than industrial units used in enterprises. And recently, machines have been produced not only stationary ones. Today you can find mobile desktop metal machines, as well as mini metal machines. Moreover, even the manufacturers themselves cannot always clearly define the line between a small-sized compact machine and a hand-held power tool.
One of the most prominent representatives of the category of mobile metalworking units is the desktop metal lathe. Of course, it is easier to buy desktop metal cutting machines, since their cost is an order of magnitude lower than their stationary counterparts, but at the same time, their compactness and the absence of certain processing and control elements do not make it possible to put them on a par with large-sized equipment.
Lathes
This is probably one of the most popular categories of metalworking machines. A metal lathe is capable of performing almost the entire range of operations associated with turning parts. On such a machine it is possible to adjust the shapes of metal workpieces that have their own bodies of rotation, as well as to carry out grooving, cutting and, in some cases, even drilling. To summarize, we can conclude that lathes are used for processing workpieces in the form of bodies of revolution. In this case, during the process of turning the workpiece, it acquires a cylindrical or conical shape. At the moment, there are various types of lathes used in various fields of industry. For example, in the woodworking industry, large-sized lathes are used to create round-shaped lumber, and for personal use, mini-metal lathes are used, which are compactly located in a private house or garage.
Sawing machines
This category of machines includes units capable of sawing a workpiece into several parts. Such cutting units include a metal band saw, as well as a circular metal cutting machine. Circular devices only carry out cross-cutting of workpieces; this is usually done in flow mode. Such models of machines are actively used in households, since their operational capabilities are very popular. Band saws can perform longitudinal cuts of workpieces. For example, a single-saw band saw can cut a workpiece lengthwise into two equal parts, and a double-saw unit can “divide” the workpiece at two levels, thus cutting it into three parts.
Milling machines
Units of this type are focused on creating profiles of a certain type. Often, milling is used to process flat workpieces by removing edges to a specified height. Such machines are used for both wood processing and metal work. In wood production, full-fledged building materials are produced using one milling cutter - tenons, lining, skirting boards, etc.
Hole drilling machines
Special drilling machines are no less in demand in home workshops, as well as in production. With their help you can easily create a through or blind hole. These machines, unlike conventional electric drills, provide more accurate drilling. In addition, drilling machines are much more powerful, which allows them to make large-diameter holes. The most common are vertical drilling machines with an overhead spindle. Drilling and slotting machines should be placed in a separate category, which, in addition to drilling operations, can also perform some milling operations. But since this is still a drilling machine, milling on it is not entirely traditional, but somewhat narrowly focused.
Surface treatment machines
A fairly wide range of machine tools is presented in the segment of equipment for surface processing of workpieces and parts. In general, such operations are positioned as grinding, but it is worth noting that this is only part of the functions that such units can perform. The type of processing that any particular machine will perform depends only on its design.
Machine design
All machines belonging to the metalworking category have many common features in their design. In fact, the design and technical characteristics of such units must ensure the correct execution of two types of technological movements:
- the feed movement performed by the cutting fixture or the workpiece itself;
- the movement by which cutting is accomplished.
To perform these movements, as well as to ensure the stable functioning of all other elements of metalworking equipment, its design includes the following working parts:
- a control system responsible for starting and stopping the machine, monitoring all parameters of its operation;
- a unit with the help of which the movement from the electric motor is converted and transmitted to the actuator;
- directly the drive itself, which can be electrical, mechanical, pneumatic or hydraulic.
An important design element is also the units of metal-cutting equipment on which the cutting tool is installed and secured. It is with the help of such units that the main function of the device is realized - processing parts made of metal.
Marking of metal-cutting machines
The designation of each metal-cutting unit contains numbers and letters:
- the first digital code indicates the group to which the device belongs;
- the second characterizes the variety, type;
- the third (sometimes the fourth) indicates its main standard size;
- a letter (usually the letter “M”) located immediately after the first digit (if present) means that the standard design has been modernized;
- The numbers may be followed by letter designations characterizing the degree of accuracy provided by the device, as well as identifying the manufacturer.
Tables of groups and types of metal-cutting units
Classification of machines by type.
Machines of the same type may differ in layout (for example, universal milling, horizontal, vertical), kinematics, i.e. a set of links transmitting motion, design, control system, dimensions, processing accuracy, etc.
Standards establish the basic dimensions characterizing machines of each type. For lathes and cylindrical grinding machines, this is the largest diameter of the workpiece being processed; for milling machines, this is the length and width of the table on which the workpieces or fixtures are mounted; for cross-planing machines, this is the largest stroke of the slide with the cutter.
A group of machines of the same type, having a similar layout, kinematics and design, but different main dimensions, constitutes a size range. Thus, according to the standard, for general-purpose gear hobbing machines there are 12 standard sizes with a diameter of the installed product from 80 mm to 12.5 m.
The design of a machine of each standard size, designed for given processing conditions, is called a model. Each model is assigned its own code - a number consisting of several numbers and letters. The first digit indicates the machine group, the second its type, the third digit or the third and fourth digits reflect the main size of the machine. For example, model 16K20 means: a screw-cutting lathe with the largest diameter of the workpiece being processed is 400 mm. The letter between the second and third digits means a certain modernization of the main basic model of the machine.
Categories of metal cutting machines
Turning
In the marking they are indicated by the number 1 . This equipment is most often used for processing cylindrical, conical, shaped surfaces. It is divided according to the degree of accuracy that it can provide into: special (C), high (B), especially high (A), normal (N), increased (P). Machines of this group, as a rule, have the main components: a bed, an apron, a spindle head, a support, a gearbox, and electrical equipment. According to the range of operations performed, machines are distinguished:
- Revolving . They are used for the production of single workpieces placed on the machine on several surfaces at once. Setting up such installations is a complex undertaking. It is simplified by the presence of a turret head, on which there are several slots that serve to accommodate cutting elements.
- Carousel . They are in demand for working with workpieces of short length but significant diameter - flywheels, gears. Used for turning, boring, and end processing. They can be equipped with additional devices that significantly expand the functionality of the units.
- Screw-cutting . The most common group of machines. Models 16K20, 16K50, 16B16A are found in almost every machine-building enterprise. Such units perform almost a complete list of basic turning operations.
- Multi-spindle automatic lathes . Complex, multifunctional, high-performance equipment that provides high precision when working with semi-finished products from pipe, square, hexagonal cold-rolled steel. It is used for cutting and rolling threads, boring, roughing and shaped turning.
- Automatic lathes for longitudinal turning . They are in demand in large-scale production for working with rods of various cross sections.
Drilling and boring
In the marking they are indicated by the number 2 . This is a wide group, including equipment for the production of through and blind holes, their finishing (countersinking, reaming), and cutting internal threads. Drilling machines:
- Vertical drilling is the most common model. They are divided into tabletop and column-mounted.
- Radial drilling . Heavy engineering enterprises use units transported on rails along workpieces or installed directly on large-sized products or structures.
- Multi-spindle . They are a complex of several single-spindle machines located on one table and bed. Such equipment ensures high productivity of the process, which includes several operations repeated in a certain sequence. For example, drilling, countersinking, reaming.
Other types of drilling machines:
- Drilling and milling . They are in demand for inclined face and horizontal milling, grinding with drills, reamers, and taps.
- Boring - horizontal boring (the most common), jig boring, diamond boring.
- Special units for the production of large-scale and mass batches. They are based on universal drilling machines equipped with multi-spindle heads and automation equipment.
Grinding, polishing, finishing
In the marking they are indicated by the number 3 . These are units capable of performing highly specialized functions or a set of operations to obtain a given degree of cleanliness of cylindrical, conical, profile, flat surfaces, including internal (cylindrical and conical). Manufacturers offer both compact devices used in home or small repair shops, and for large enterprises in the mass production of parts, products, and structures. To prepare samples for metallographic studies, benchtop grinding and polishing systems are designed to produce a very high quality surface.
Combined (special purpose)
In the marking they are indicated by the number 4 . This group includes electroerosive, electrochemical, electrospark, electromechanical, ultrasonic and others machines.
For the production of threads and gear elements
In the marking they are indicated by the number 5 . There are many methods and types of equipment for cutting threads. This operation can be carried out on a screw-cutting lathe using a cutter, on a drilling unit using a tap, or on a milling machine. However, for high-performance processes, specialized devices are used that can be used to produce threads of all standards - metric and inch on pipes, cylindrical, conical, trapezoidal.
- Thread rolling . The design resembles vertical drilling units. Thread rolling (internal and external) is carried out on conical and cylindrical workpieces and pipes. When rolling, threads are obtained not by removing chips, but by plastic deformation. This technology is used in large-scale and mass production.
- Thread milling machines . These are the most highly productive machines. A disk cutter produces threads of considerable length and pitch, while a comb cutter produces short, small threads.
- Thread grinding machines . Single- or multi-thread wheels with abrasive are installed on them.
Machines for making gear profiles:
- Gear cutters - for cylindrical and bevel wheels.
- Gear hobbing horizontal, vertical and others - allow you to produce a gear involute profile. Complex surfaces are produced using rolling technology. CNC units provide high precision operations and productivity.
- Gear grinding . They are used to obtain precise geometric dimensions and high levels of surface cleanliness of gears, shafts, and racks. Depending on the task and model, the equipment is equipped with grinding wheels of various types: worm, profile, flat, conical, disc.
Milling
In the marking they are designated by the number 6 . Units of this type process workpieces mounted on a table. In this case, the cutting tool is characterized by rotational motion, and the workpiece is characterized by reciprocating motion. The group of cantilever milling machines includes models:
- Horizontal milling machines with a fixed table . These units were most popular in factories built and equipped during the Soviet Union. They have a simple design that allows you to mill one surface without changing the cutter or reinstalling the part.
- Horizontal milling machines with rotary table . This unit can process several surfaces at the same time.
- Vertical milling . Structurally similar to vertical drilling. Can be used for drilling, boring, countersinking.
- Widely versatile . They differ from vertical milling machines by an additional spindle head. Perform operations: milling, drilling, boring.
Main components and mechanisms of metal-cutting machines
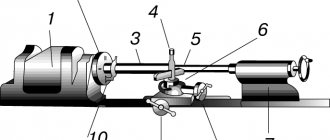
Let's look at the main components and mechanisms of metal-cutting machines using the example of a lathe. A general view of the lathe is shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7 – General view of the machine
The main components of the machine are shown in Figure 8.
Figure 8 – Main components of the machine
The machine bed is most often made of cast iron and is the basis for attachments, shown in Figure 9.
Figure 9 – Machine bed
The required relative position of machine components and the possibility of relative movement of the tool and workpiece are provided by guides (Figure 10).
Figure 10 – Adjusting elements with a longitudinal (a) and transverse (b) wedge, with a clamping (c) and overhead fitting (d) strip
According to their purpose and design, guides can be classified according to the following criteria:
- by type of movement: guides of the main movement (for example, a table-bed of a longitudinal planing machine); feed movement guides; directing rearrangements of mating and auxiliary parts and assemblies that are stationary during processing;
- along the trajectory of movement: guides of rectilinear and circular movement;
- in the direction of the node’s movement trajectory in space: horizontal, vertical and inclined;
- by geometric shape: prismatic, flat, cylindrical, conical (for circular motion only) and their combinations.
The most widespread in machine tools are sliding and rolling guides. Sliding guides (Figure 11) are usually made of gray cast iron. Cast iron is used in cases where the guides are made as one piece with the frame or moving unit.
Figure 11 – Basic cross-sectional shapes of sliding guides: a – flat; b – prismatic; c – dovetail-shaped; g – cylindrical
Based on the type of sliding friction, the following guides are distinguished:
- hydrostatic – guides of the main movement and feed; in these guides, the lubricating layer is created by supplying oil under high pressure into special pockets of the required size;
- with mixed lubrication - most feed movement guides;
- with boundary lubrication – feed guides operating at very low sliding speeds;
- with air lubrication - aerostatic.
Rolling guides are widely used in machine tools using balls and rollers as intermediate rolling bodies. The advantage of rolling guides is low friction, independent of the speed of movement. Rolling guides provide high accuracy of movements, uniformity of slow movements, they are more durable than sliding guides. Like sliding guides, rolling guides can be closed or open.
The headstock is most often called the spindle headstock (Figure 12), since its main unit is the spindle (Figure 13). The spindle holds chucks, various mandrels into which the workpieces are installed and secured. In addition, the gearbox, pulley and bearings are located here.
Figure 12 – Headstock
A spindle is the shaft of a metal-cutting machine that transmits rotation to the tool or workpiece fixed in it.
The structural shape of the spindle depends on the method of fastening the clamping fixture or tool on it, the fit of the drive elements and the types of supports used. Spindles are made hollow for the passage of the rod, as well as to reduce its weight.
Rolling and sliding bearings are used as supports for machine tool spindles. Since high precision is required from spindles, rolling bearings must be of high accuracy classes. The front support uses more precise bearings than the rear one. Spindles and bearings must be reliably protected from contamination and cutting out of lubricant; for this purpose, various seals are used.
Figure 13 – Spindle
The tailstock consists of a bottom plate and a quill holder. A tool or fixture can be installed in the tailstock (Figure 14). Most often, the tailstock is used when processing long parts, pressing the end of the part with a cone. The guides along which the tailstock moves must be clean and lubricated.
Figure 14 – Tailstock
A support is a machine unit in which a cutting tool is installed and which allows it to be moved in the longitudinal, transverse and oblique directions. The carriage provides longitudinal movement along the slide, the upper part of the support provides transverse movement. Tool holders are installed in the upper part of the caliper (Figure 15).
Figure 15 – Machine support
Apron. To ensure the longitudinal and transverse movement of the caliper, gears located in the apron have been developed (Figure 16). With the help of these gears, the rotational movement of the lead screw is converted into the translational movement of the caliper.
Figure 16 – Machine apron: 1 – manual feed flywheel, 2 – roller, 3 – button for turning on mechanical feed from the roller, 4 – gear, 5 – rack and pinion, 6 – gear, 7 – rack, 8 – gear wheel, 9 – worm, 10 – split nut, 11 – lead screw, 12 – handle for turning on the mechanical feed from the lead screw when cutting threads, 13 – handle for turning on the mechanical feed
All components and mechanisms of the equipment must be kept in good condition, that is, all rubbing parts must be clean and lubricated with appropriate lubricant. This is the task of the equipment operation service, but maintenance personnel must also monitor the condition of the equipment, for example, monitor the timely replacement of filters, cutting fluid, and even, depending on the operating hours, monitor the timely replacement of oil in the hydraulic system of the machine.
Types of CNC equipment
Equipment that operates after setting up numerical control is divided into separate groups according to various factors:
- Options for supplying work items.
- Arrangement of spindles.
- Movement of the portal along guides.
Based on the layout of the installations, they can be divided into several main groups:
- Lathes.
- Vertical units.
- Longitudinal structures.
- Milling machines.
- Cantilever structures.
- Widely versatile - multi-profile machines.
Separate groups include cutting models, which can be gas, arc, plasma, laser, waterjet.
During operation of the CNC machine, the mechanisms move automatically. Movements are read by sensors that can operate on two principles:
- Closed system. The working process is controlled by several sensors, the mechanisms move due to a special drive.
- Open-loop system. The equipment is equipped with stepper motors that precisely control the movements of key structural elements.
At a hardware store you can buy a desktop CNC milling machine or order large-sized equipment for the enterprise.
Main types of lathes
All existing turning equipment can be divided into several groups according to the types of processed materials and parts.
Turning and screw-cutting equipment
Screw-cutting lathes belong to the category of universal units that are widely used in the manufacture of parts in a single copy or as part of mass production. The main task of the equipment is cutting inch, metric, and modular threads. It is also used to perform other metalworking operations.
The basis of the design of a screw-cutting lathe is:
- spindle head with gearbox;
- a frame on which the main structural elements of the equipment are mounted;
- a support designed to fix the cutting tool;
- an apron used to convert the movement of a screw or roller into movement in a given direction of the support;
- tailstock, necessary for fixing the workpiece in the optimal position (in most cases it is equipped with additional tools).
Show prices for screw-cutting lathes
Turret lathes
The turret group equipment is used for processing parts made from calibrated rods. With their help, you can perform a long list of technological operations. They include shaped turning, boring, reaming, threading, countersinking, and drilling.
The tools are mounted on the machine using a special holder. Depending on the modification of the equipment, it can be driven or static (the first option has greater functionality).
Show prices for turret lathes
Lathe units
The machines are used when it is necessary to process frontal, conical, cylindrical surfaces. Many models do not have a tailstock. An important feature of models of this type is the ability to process heavy parts of short length (this is possible due to the fact that the spindle rotates in a horizontal plane and the presence of sufficient free space). At manufacturing enterprises, when heavy loads are expected to be placed on the lathe, carousel units are used as a replacement.
Vertical lathes
The equipment is used to work with large-sized workpieces. Among their key features, it is worth highlighting the ability to:
- using the machine to form grooves of any configuration;
- thread cutting;
- turning conical or cylindrical surfaces;
- performing end cutting, milling, and grinding operations.
If the machine is equipped with additional equipment, it can be used to grind shaped surfaces using a copier.
During operation of the equipment, the workpiece is fixed on a faceplate, the diameter of which directly determines the overall dimensions of the unit. According to this parameter, there are single-post (up to 2000 mm) or two-post models (more than 2000 mm).
Show prices for rotary lathes
Turning and milling machining centers
The center is a multifunctional device with electronic programmable equipment and complex kinematics.
Models with vertical or horizontal spindle rotation are available.
In the first case, it is possible to process workpieces with high weight and size parameters. Such machining centers are equipped with an external cooling system, due to which the productivity of the machine is significantly increased by increasing the speed of rotation of the parts.
Most models with vertical spindle rotation have an automatic cutting tool change function. When positioned horizontally, centers are often equipped with tilt-rotary or rotary tables. Belt-type mechanisms are used to change tools.
Such machining centers are distinguished by the presence of a vibration damping system, the ability to use up to 120 tools in operation, thanks to the tracked mounting system.
Show prices for turning and milling machining centers
Automatic longitudinal turning
For small-scale production of parts, automatic longitudinal turning machines are widely used (equipment productivity can be up to 40 finished parts per minute). In this case, a shaped profile, wire, calibrated or cold-drawn rod can be used as blanks. There are models with movable and fixed spindle head.
Show prices for automatic longitudinal turning machine
Multi-spindle lathes
The equipment is used for processing workpieces with complex geometries, which are made from pipes, cold-drawn rods of any cross-section, as part of mass production.
High performance is ensured by high drive power.
When developing models of multi-spindle lathes, the use of structures of increased rigidity is envisaged. The equipment is capable of performing several technological operations simultaneously.
Show prices for multi-spindle lathes
CNC machines
Numerical control allows for high precision machining of workpieces and increased productivity. Automation of all processes greatly facilitates the operation of equipment.
Work processes are managed in one of three ways:
- contour (the machine operates continuously in accordance with the parameters specified by the user);
- along a rectangular contour (relevant when it is necessary to process step-shaped parts; the transverse and longitudinal transmission in them is switched automatically);
- positionally (in this case it is envisaged that the mechanism will initially be located at a given starting point, only after which processing begins).
CNC machine tools use self-adjusting, closed-loop or open-loop systems. They differ from each other in the principle of receiving information, reading and measuring mechanism.
Show prices for CNC machines
Pipe cutting units
The machines are highly specialized equipment used only for cutting steel pipes. They are widely used in geological exploration, gas and oil production, and other industries.
The operation scheme of CNC units is as follows: first, the workpiece is fixed in the chuck, then a program is installed for automated elimination of defects.
If it is necessary to perform additional operations, the machine is equipped with the required type of cartridges, a turret, and a cutter.
Show prices for pipe cutting units
Equipment with continuously variable drive
A feature of machines of this type is the ability to continuously change the spindle speed. With its help, it is possible to process both the external and internal surfaces of the workpiece.
Machines with stepless drives allow you to select the optimal speed mode at each stage of part processing.
Equipment with a continuously variable drive is characterized by consistently high reliability, ease of control, and long service life. Due to the absence of a gearbox, the machines have a relatively long overhaul interval. It is possible to adjust the spindle speed using hydraulics, as well as mechanically or electrically.
Bench lathes
A special table is used to install the equipment. Mini-machines are characterized by relatively small overall dimensions and weight.
They are used to process workpieces made of wood, metal, and plastic. Their main functions are boring, drilling, milling.
In most cases, equipment of this type is used for small-scale production or in private workshops. The machines are in demand due to their low cost and low energy consumption.
Show prices for benchtop lathes
Design features
CNC metalworking devices consist of several key elements that are configured through a program and operate automatically. Main components of machines with automated control:
- Cast frame, which is the base that dampens vibrations that occur during the working process. The remaining parts are installed on it.
- Sliding guides designed to move the working part of the unit.
- CNC system, stepper motors, display, control panel.
- Electric motor with spindle as the main mechanism of the machine.
There are two types of spindles. The first option is an electric motor with a rotor. This is the main element of a desktop milling machine, lathes, and drilling machines. The second option is a mechanism connected to the drive using a belt drive, a clutch.
Requirements for control systems
The quality of metal processing on CNC machines depends on some nuances of the control system. In order for the working elements to move quickly, the design must be equipped with digital controllers. If the model has a PC remote control, it can be controlled remotely. Thanks to this, there is no need for operator intervention during the work process.
Program-controlled units run on the Windows NT operating system. It allows you to control the operation of equipment in real time via the Internet. Step microprocessors effectively control the instrumentation system. They transmit information about the state of equipment to the control computer and can automatically replace equipment.
About the difference between manually controlled devices and CNC devices
The strengths of CNC machines include:
- Minimizes operator effort. He does not have to manually set up workpieces, adjust dimensions, change equipment, or manage working parts. The operator needs to configure the program to perform a specific technological process and set the action algorithm.
- The accuracy of operations is higher than that of manual installations.
- High productivity, minimum defects with a correctly configured program.
- The feed speed of cutters, milling cutters, and drills is higher than that of manual models.
- Automation of the process of supplying blanks and changing consumables.
However, CNC models are much more expensive. To configure and control them, the operator must have practical experience working with programs. Errors that arise require the ability to correct them in order to restore the workflow.