Aluminum sheet is a rolled semi-finished product made from aluminum or alloys based on it. Thanks to the combination of high performance qualities and physical and chemical characteristics, this material finds the widest application in industry and various sectors of the national economy. You can buy aluminum sheets at a price of 220 rubles/kg from Sinara LLC.
- Aluminum sheet AMg6
- Aluminum sheet D16AM
- Aluminum sheet AMg2
- Aluminum sheet AMg3
- Aluminum sheet AMg5
- Aluminum sheet AMG2N2
- A5 aluminum sheet
- AMts Aluminum Sheet
- Aluminum sheet AD1
- Aluminum sheet D16AT
| Name | Alloy | Uncover | Price |
| Aluminum sheet 0.5 | 1105 Am, 1105 An2, AMG 2n2 | 1200×2000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 0.6 | 1105 Am | 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 0.7 | 1105 An2, A5 m, AMG 3n2, AMG 6BM, AMG 3m, AMG 2m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 6m, AMC n2 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 0.8 | 1105 Am, A5, AMG 2m, AMC m, AMC n2 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 1.0 | 1105 An2, A5 m, AMG 3n2, AMG 6BM, AMG 3m, AMG 2m, AMG 5m, AMC m | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 1.5 | 1105 An2, A5 m, AMG 3n2, AMG 6BM, AMG 3m, AMG 2m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 6m, AMC n2 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1700×3400,2000×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 1.8 | AMG 2n2, AMG 2n2 | 1200×2000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 2.0 | 1105 At, 1105 An, A5 m, A5 n, AMG 2m, AMG 3m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 2n2 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000, 1200×4000, 1500×3000, 1500×4000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum Sheet 3.0 | 1105 An, 1105 At, AMG 3m, AMG 2m, AMG 6m, AMC m | 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 4.0 | 1105 At, 1105 An, A5 m, A5 n, AMG 2m, AMG 3m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 2n2 | 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 5.0 | 1105 At, 1105 An, A5 m, A5 n, AMG 2m, AMG 3m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 2n2 | 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum Sheet 6.0 | 1105 At, 1105 An, A5 m, A5 n, AMG 2m, AMG 3m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 2n2 | 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1200×300 | Check the price |
| Aluminum Sheet 8.0 | 1105 At, 1105 An, A5 m, A5 n, AMG 2m, AMG 3m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 2n2 | 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 12.0 | 1105 At, 1105 An, A5 m, A5 n, AMG 2m, AMG 3m, AMG 5m, AMC m, AMC n2, AMG 2n2 | 1500×3000, 1500×4000, 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 14 | AMG2, AMG3, AMG5, AMG6, AMC, V95 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 16 | AMG2, AMG3, AMG5, AMG6, AMC, V95 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 18 | AMG2, AMG3, AMG5, AMG6, AMC, V95 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 20 | AMG2, AMG3, AMG5, AMG6, AMC, V95 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 25 | AMG2, AMG3, AMG5, AMG6, AMC, V95 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet 30 | AMG2, AMG3, AMG5, AMG6, AMC, V95 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
Aluminum sheet corrugated
| Name | Alloy | Uncover | Price |
| Aluminum sheet corrugated 1.5 Duet | AMG2N2 | 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet corrugated 1.5 Quintet | AMG2N2, AMG2nR | 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet corrugated 2.0 Quintet | AMG2n-2, AMG2nR, AMG 2NR | 1200×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet corrugated 2.0 Duet | AAMG2n2 | 1250×2500 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet corrugated 3.0 Quintet | AMG 2n2, AMG 3n2 | 1200×3000, 1500×3000 | Check the price |
| Aluminum sheet corrugated 4.0 Quintet | AMG 2nR | 1200×3000 | Check the price |
Design features and production of aluminum sheet
Aluminum sheet is manufactured according to GOST in accordance with regulatory requirements by hot or cold rolling. Cold rolling is used in the production of sheets up to 6 mm thick. For thicker products, the hot production method is used.
To give aluminum sheets additional strength and performance characteristics, they are subjected to post-processing - plating. This method involves applying a layer of aluminum, copper or steel to the surface. Depending on the purpose of the plating - anti-corrosion protection, improving technological characteristics during the rolling process, increasing the aesthetic properties of the product - the composition of the coating and its thickness may be different.
Chemical and electrical properties of D16AT (D16T)
The chemical composition of the alloy from which D16AT sheets are made is equivalent to D16T according to GOST 4784-97. D16 is a heat-strengthening alloy that can be refined before or after manufacturing the part. As for the mechanical properties of the material, after hardening and natural aging, the material increases its strength and hardness by more than two times, as can be seen from the table above. Thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity after hardening and aging drop by about 1.5 times.
Scope of application of aluminum sheet
Sheet aluminum is one of the most popular and widely used types of rolled metal. It is actively used in the following sectors of the national economy:
- construction;
- mechanical engineering;
- shipbuilding and aircraft construction;
- production of refrigeration units;
- food industry;
- medicine and pharmacology.
This type of aluminum rolled metal is used where it is necessary to ensure high strength using the most lightweight structures, as well as in enterprises and institutions where aesthetic and hygienic components are important.
Types of rolled products D16AT - material properties
Only three types of rolled metal are produced with the D16AT marking, not counting sheets after hardening and artificial aging (T1).
Under this brand are produced:
- Sheets D16AT according to GOST 21631 (after hardening and natural aging, or after aging and cold hardening);
- D16AT slabs after hardening and natural aging according to GOST 17232-99.
Considering the tendency of the material to corrosion, all sheets, without exception, are produced with normal AD1pl cladding.
Corrugated aluminum sheet
Corrugated aluminum sheet is very often used to create stair steps, floors and transitions between structures, overpasses in enterprises due to its anti-slip surface.
In addition, one should not discount the possibility of using this material for finishing premises: metal cladding of surfaces in production or warehouse premises allows for long-term operation of the building without the need for repairs even in the most unfavorable working conditions (high humidity, the presence of aggressive environments, possible mechanical damage and so on.).
Aluminum corrugated sheet is also distinguished by its low material weight and matte rough surface, which, thanks to its convex pattern, does not allow slipping. Patterns on the material are always located at a certain angle relative to each other. The technical characteristics of the material can be improved using anodizing or cladding technology (applying a foreign metal to the surface of aluminum to increase the corrosion resistance of the material).
Plating
Sheets D16AT are covered with a normal cladding of technical aluminum AD1, with a thickness of 2-4% of the thickness of the rolled product. Plating is applied to protect the material from corrosion, to which the alloy is prone under normal conditions, and at high temperatures it is also prone to the formation of intergranular corrosion. The advantage of using D16AT is that it no longer needs to be thermally treated, therefore the plating will not be damaged during processing, which reduces the cost of the final product, except in cases where more reliable protection against corrosion in the form of paint coating or anodizing may be needed.
Wholesale of aluminum sheets in Moscow
You can buy aluminum sheets of different sizes, shapes and grades from, which specializes in the production and sale of high-quality rolled metal.
Several reasons to buy sheet aluminum:
- low weight of aluminum sheet;
- high strength characteristics;
- plasticity and ease of processing;
- corrosion resistance and resistance to aggressive environments;
- high hygienic properties;
- affordable price for aluminum sheet.
To order and purchase aluminum sheets at retail or wholesale, contact our consultants at the numbers provided or leave a request on the website.
How D16AT sheets are used
D16AT sheets are used as a structural material and cladding in the aircraft industry. They have excellent structural strength, lightness, strength and high hardness. D16AT is the most common structural alloy, supplied in the form of rolled sheets.
D16AT or D16T slabs are also used in the aviation industry, along with the automotive industry and mechanical engineering.
D16AT has better structural strength than the more mechanically strong V95T alloy and is not prone to stress corrosion. It exhibits its properties perfectly at temperatures ranging from -230 to 120 ˚C.
Sintered aluminum alloys
A deformable heat-resistant alloy from sintered aluminum powder (SAP) is produced by pressing and sintering aluminum powder at 500-600°C
The resulting briquettes are used to make sheets, pipe rods, profiles and other semi-finished products. The density of SAP is 2.7 g/cm3. It welds well, is easy to cut and has high corrosion resistance
SAP is superior in heat resistance to aluminum alloys at 300-500° C and above. This is explained by the presence of aluminum oxide Al 2Oz . With an increase in aluminum oxide in various grades of SAP, the heat resistance increases, and the ductility decreases slightly
Parts made from SAP work for a long time up to 300–550° C and for a short time up to 700–1100° C. SAP is also recommended for use in parts operating in severe corrosive conditions
Sintered aluminum alloys (SAS) are produced by hot briquetting and subsequent pressing at 500°C of mixtures of aluminum powders with other elements.
In SAS 1 add 25-30% Si and 5-7% Ni and in SAS 4 10-15% Si and 17-25% SiC SAS alloys have a low linear expansion coefficient and are used for the manufacture of devices
Alloys SAS D16, SAS V96 have been developed in their properties similar to alloys D16 and V96 but without technological defects associated with casting (oxide and slag inclusions in segregation zones) and pressure treatment (anisotropy of properties)
Composition and properties of sintered alloys and powders SAS 1 contains 6-9% Al2O3 σв=280 N/mm2, δ=5%, σв = 40 N/mm2 at 500°С
SAP2 contains 9 -13% Al2O3 σв=320 N/mm2 δ=4% at 500°С σв = 100 N/mm2,
SAP3 contains 13 -18% Al2O3 σв = 400 N/mm2 δ=3%, at 500°С σв-= 130 N/mm2,
SAP4 contains 18-22% Al2O3> σв = 450 N/mm2, δ = 15% at 500°С σв = 130 N/mm2
Where is duralumin plate used and how does it differ from duralumin sheets
The difference is in the thickness of the rolled product. Sheets are supplied in thicknesses from 0.3 to 10.5 mm, plates - from 11 to 200 mm. The range and technical conditions of duralumin sheets are regulated by GOST 21631-76, plates - GOST 17232-99. What is the application. Plates are a semi-finished product for the production of a large range of products using stamping, pressing forging, etc. The slabs are supplied without heat treatment, but in terms of chemical composition and the presence of a cladding layer, they fully meet the requirements of the final product.
Alloys
For domestic aluminum alloys, alphanumeric and numeric designation systems are used. There is no system laid down in the alphanumeric marking (although these alloys were later assigned a digital marking, but it did not “take root”). The letters can symbolize aluminum and the main alloying component - AMts (Al-Mn), AMg1 (Al-Mg), the purpose of the alloy ( AK6, AK4-1 - forging aluminum), the name of the alloy ( AV - avial, D16 - duralumin), can be associated with the name of the institute that developed the alloy ( VAD1, VAD23 - VIAM - All-Russian Institute of Aviation Materials, wrought aluminum), etc. The numbers after the letters do not reflect the chemical composition.
At the end of the sixties, four-digit digital marking was introduced. The first number indicates the base of the aluminum alloy. Aluminum and alloys based on it are marked with the number “1”. The second digit indicates the main alloying component or main alloying components. The second number “0” denotes various grades of aluminum, sintered aluminum alloys (SAS), various grades of aluminum foam. The number “1” denotes alloys based on the Al-Cu-Mg system; number “2” - alloys based on the Al-Cu system; number “3” - alloys based on the Al-Mg-Si system; number “4” - alloys based on the Al-Li system, as well as alloys alloyed with poorly soluble components, for example, transition metals (manganese, chromium, zirconium); alloys marked with the number “5” are based on the Al-Mg system and are called magnalium; alloys based on the Al-Zn-Mg or Al-Zn-Mg-Cu systems are designated by the number “9”. Numbers 6, 7 and 8 are reserved.
In the Russian Federation, GOST 4784 “Aluminum and wrought aluminum alloys. Marks." provides marking of alloys in three ways: both in alphanumeric form and only in digital form, as well as taking into account the requirements of the international standard (international marking) ISO 209-1 (ISO 209-1 Wrought aluminum and aluminum alloys -Chemical composition and forms of products -Part 1: Chemical composition). At the same time, the digital marking according to GOST does not coincide with the international marking of aluminum alloys.
Digital marking of wrought aluminum alloys
| Brand | Group of alloys, main alloying system |
| 1000-1018 | Technical aluminum |
| 1019, 1029, etc. | Powder alloys |
| 1020-1025 | Foamed aluminum |
| 1100-1190 | Al-Cu-Mg, Al-Cu-Mg-Fe-Ni |
| 1200-1290 | Al-Cu-Mn, Al-Cu-Li-Mn-Cd |
| 1300-1390 | Al-Mg-Si, Al-Mg-Si-Cu |
| 1319, 1329, etc. | Al-Si, SAS powder alloys |
| 1400-1419 | Al-Mn, Al-Be-Mg |
| 1420-1490 | Al-Li |
| 1500-1590 | Al-Mg |
| 1900-1990 | Al-Zn-Mg, Al-Zn-Mg-Cu |
Show table
The last two digits in the digital designation of an aluminum alloy are its serial number. The last digit carries additional information: alloys ending in an odd number are wrought, alloys ending in an even number are casting, 7 is a wire alloy, 9 is a metal-ceramic alloy. If the alloy is experimental and is not used in mass production, then the number “0” (01570, 01970) is placed in front of the mark and the marking becomes five-digit.
To indicate the condition of deformed semi-finished products made from aluminum alloys, an alphanumeric designation system is used after the alloy grade. Without designation means without heat treatment.
P - semi-finished product (alloys for cold stamping from wire);
M - soft annealed;
N - hard-worked;
H3 - three-quarters hard-worked;
H2 - hard-worked to one half;
H1 - one-quarter hard-worked;
T - hardened and naturally aged;
T1 - hardened and artificially aged for maximum strength;
T2, T3 - artificial aging modes that ensure overaging of the material (softening artificial aging modes);
T5 - hardening of semi-finished products from the end temperature of hot pressure treatment and subsequent artificial aging to maximum strength;
T7 - hardening, enhanced tensile straightening (1.5-3%) and artificial aging for maximum strength;
A – normal cladding;
B - sheets without cladding or with technological cladding;
U - thickened cladding (8% per side);
B - increased quality of rolling out hardened and aged sheets;
O - increased quality of rolling out annealed sheets;
GK - hot-rolled sheets, slabs;
TPP - hardened and aged profiles of increased strength (for D16).
At the end of the brand there may be letters characterizing the features of this alloy:
“ch” – clean;
“pch” – increased purity;
“och” – special purity;
“l” – casting alloys;
“s” – selective.
Aluminum-based composite materials
Composite materials are complex materials that contain insoluble or poorly soluble components that differ greatly in properties. They have high strength, resistance to brittle fracture, heat resistance, elasticity and thermal stability properties. Fibrous and dispersion-strengthened fillers. Based on the shape of the filler, composite materials are divided into fibrous and dispersion-strengthened. The former are strengthened with fibers or thread-like crystals of refractory compounds and elements (Al2O3, SiC C, B, etc.), as well as thin micron tungsten or strong steel wire. The latter are strengthened with fillers made of finely dispersed refractory particles of oxides of carbides, borides, and nitrides
VKA-1 alloy is a composite material based on aluminum and its alloys. The elastic modulus, tensile strength and endurance up to temperatures of 500 C in composite materials are 2-3 times higher than in conventional aluminum alloys
Figure 2.4 shows the dependence of the elastic modulus and tensile strength on the test temperature of the VKA-1 composite material on an aluminum base, strengthened with high-modulus continuous boron fibers, in comparison with the high-strength alloy V95 and the heat-resistant aluminum alloy AK4 1. The VKA-1 alloy contains 50% boron fibers in diameter 100 microns with σв = 2500–3500 N/hm2 and E = 400 kN/mm2, which provides it with σв = 1000–1200 N/mm2 at 20°С, and at 400°С σв = 600 N/mm2 (like an alloy B95 at room temperature). The density of VKA 1 is 2.65 g/cm3, and the specific strength is σb/y = 41, i.e. higher than that of high-strength steels and titanium alloys.
Replacing the V95 alloy in the manufacture of an aircraft wing spar with a titanium alloy with reinforcing elements from the VKA 1 alloy increases its rigidity by 45% and saves weight by about 42%. In addition, dispersion-strengthened alloys do not have anisotropy of properties, like fibrous composite materials.
Source: Handbook of aviation materials and technologies for their use.
What is the difference between alloys D16, D16T and D16B in plate markings
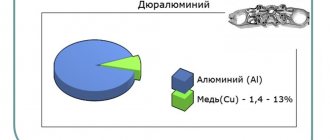
All of the listed grades are one alloy of duralumin D16, containing, according to GOST 4784-97, in addition to aluminum, 3.8-4.9% Cu; 1.2-1.8% Mg; 0.3-0.9% Mn. The difference is in the processing of the alloy. In particular, the marking “D16 plate” indicates only the composition of the alloy. D16T slab – incorrect marking, because index “T” corresponds to the heat-treated state (hardening + natural aging), and the slabs are supplied without heat treatment.
The indices “A” and “B” indicate the presence of cladding, normal and technological, respectively. Those. The marking “D16B plate” corresponds to duralumin with technological cladding.