Main components of a CNC machine
A CNC machine consists of the following key components:
- data input devices;
- BUS (machine control unit);
- actuator;
- drive systems;
- feedback systems;
- control panel.
The object processing program is loaded into the machine through the data input device.
Input devices are usually magnetic tape readers, punched tape readers, and computers operating via an RS-232-C port.
The BUS controls the unit, performing the following operations:
- reads and decrypts code instructions entered into it;
- Performs circular, linear and spiral interpolation to generate axis motion commands;
- transmits axis movement commands to the amplifier circuits to control the axis mechanisms;
- receives feedback regarding the positions and speeds of all drive axes;
- turns coolers or spindles on and off, changes tools, and performs other auxiliary functions.
CNC machines typically have movable tables and spindles that control speeds and positions. The actuators control the spindles in the Z-axis direction and the tables in the X- and Y-axis directions.
Drive systems include amplifier circuits, drive motors, and ball screw bearings (ball screws). The BUS sends signals about the speed and position of each axis to the amplifier circuits. These signals are then amplified to drive the drive motors. These motors rotate the ball screw to adjust the desired position of the work table.
The feedback system (also known as the measurement system) has built-in sensors, also known as transducers. They constantly monitor the speed and position of the cutting tools. Signals from the sensors are sent to the BUS, where the difference between the original signals and feedback signals is used to generate the next series of signals.
The operator can move the control panel to a convenient position. The display will show commands, programs and other necessary information.
Advantages
The main advantages of a machine controlled by a computer program are the accuracy and speed of woodworking, which make it possible to process both flat (2d) and three-dimensional (3d) parts, with elements of a wide variety of sizes and complexity. The process itself is fully automated, which completely eliminates the human factor from the milling process.
Also an undeniable advantage is visualization, which allows you to see the finished product on a computer monitor even before milling begins. Thanks to this, you can be completely confident that the final product will be exactly the product you saw on the screen.
What knowledge do you need to have to work with a CNC machine?
To successfully work on a CNC machine, you must be able to perform the following operations:
- create models of parts in graphic editors;
- install programs in the unit’s RAM;
- set optimal modes and control parameters for microstepping motors.
As work progresses, it will be necessary to visually monitor all technological operations through a panel that displays all current information in real time.
The most common software control systems today are Linux CNC, USB CNC, Mach3, OSAI, Fanuc, Rich Auto, OSP, Sinumerik, Heidenhain. All of them are more or less the same type, and only Heidenhain differs noticeably from the others in its management.
Basics of working on CNC machines (what skills you need to have)
The operator of a CNC machine requires less skill and experience than an operator of a similar traditional type device. Programmable equipment successfully copes with the following tasks:
- improves workflow productivity;
- guarantees the most accurate and high-quality processing;
- ensures the safety of human labor and solves numerous problems of production culture.
In fact, the operator must simply control the execution of those processes that were incorporated into the unit at the programming stage.
Scope of equipment
Milling machines of this type are capable of performing many tasks:
- end processing. Such a milling machine is capable of forming almost any grooves - through, windows, grooves and others;
- face milling. The unit is capable of processing large surfaces;
- shaped processing. The equipment is capable of making almost any recess of the desired shape and size;
- cutting operations. To perform this manipulation, special disk cutters are used.
CNC milling machine
How to learn to work on a CNC milling and lathe for wood and metal?
The use of CNC turning and milling machines is taught in colleges. They pay quite a lot of attention to both theory and practice. However, the internship completed before college may not meet the requirements that a particular employer will impose in the workplace. Therefore, many employers have vacancies with on-site training, where applicants are primarily required to have knowledge of theory.
The theory can be taken on the Internet. The minimum duration of the course via Skype is two weeks. In three days, contrary to advertising promises, you cannot learn anything.
Distance courses are good because students are given a lot of tasks to write control programs for machine tools and create vector images.
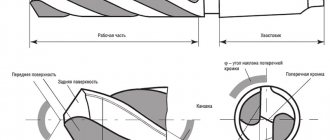
Types of cutters
CNC woodworking equipment is equipped with cutters, which act as the main working tool. They can have different shapes and sizes, which allows you to achieve certain qualities during wood processing.
Most units are equipped with single-thread cutters. They can process both different types of wood and soft metals. Such working tools are quite inexpensive, but you don’t need to expect high quality and accuracy from them. More effective cutters include the following varieties:
- two-way;
- shaped like a fish tail;
- spiral;
- cone-shaped and many others.
How to work on a CNC machine?
Work on a CNC machine is carried out in the following sequence:
- The part processing program is entered into the control unit.
- The data is processed in the BUS. There, motion commands are prepared and sent to the drive system.
- The speed and movement of the unit blocks are controlled by the drive.
- Information about the speed of movement and the position of the axes is recorded by a feedback system that sends signals to the BUS.
- The BUS compares each incoming signal with the original one. If there are errors, they are corrected.
The operator controls the process all this time through a control panel with a display.
After pressing the power button, the unit will begin initialization. This term refers to the determination of the initial coordinates of the spindle position. All models of CNC machines have a constant zero point, the so-called machine zero. To perform initialization in manual mode, you need to press the “Home” button, but it is much more convenient to carry out this action in automatic mode. The working parts of the unit will alternately move along each axis until the limit switch, and movement will begin from the Z axis. As soon as the spindle reaches the extreme position along one of the axes, the limit switch will operate and the machine zero will be initialized. An unchangeable machine zero is needed so that the operator can set not one, but many zero points for processing the workpiece, and these points would be located in any desired location on the workbench.
For models with four or three axes, machine zeros are located in the corners of the tables. It is in relation to these points that all other basic positions of the device are adjusted.
For metal
All CNC machines for metal operate on a similar principle. Having dealt with one device, you can safely work with any new models. In addition to the instructions from the manufacturer, it makes sense to search the Internet for materials on working with g-codes and m-codes.
Part design
The design of the part is carried out in 2D or 3D format in a CAD program. In Russian, the abbreviation CAD stands for “computer-aided design system.”
CNC programming
A part created in a CAD program must be converted into g-code that the machine can understand. This happens in the CAM program. In Russian, the abbreviation CAM stands for “computer-aided production system.”
Machine setup
To set up the machine you need to do the following:
- Make sure that you have filled the coolant and oil to the maximum and in strict accordance with the instructions.
- Make sure that foreign objects do not enter the work area.
- Turn on the compressor and check that the pressure in it is exactly as indicated in the instructions.
- Connect the device to the power supply and start it up. Typically, the power button is located on the control panel in the upper left corner, and the main switch is located at the rear of the unit.
- Load tools into the carousel in the sequence specified in the CNC program list. If the unit has only one tool, the cutter must be installed in the spindle.
- Firmly secure the part on the table or in a vice.
- Set the correction indicator for the tool length. The tools must be moved to the top of the part in the sequence specified in the CNC program, and then the correction values must be set.
- Set the correction for the X and Y axes. After installing the vice or other parts, adjust the correction for the installation of the workpiece in order to find the starting points of X and Y.
After this, all that remains is to load the CNC program into the control system of the unit via a USB drive.
Part management and production
After setting up the machine, the production process is carried out in the following sequence:
- For a test run, the program is run in the air so that the tool operates at a height of approximately 5 cm from the object.
- The program runs when the tool makes contact with the workpiece, monitoring for error messages.
- Adjust the offsets and check the characteristics of the workpiece. Adjust tool length corrections to ensure that the workpiece meets the specified parameters.
Upon completion of the work, you need to remove the workpiece from the vice, remove the tools from the spindle, clean the work area and turn off the unit.
On wood
A CNC machine designed for working with metal can also handle wood successfully. But a unit that was initially oriented towards working with wood will not be able to cut metal efficiently - it will only perform shallow processing of the metal surface.
Part design
Designing a wooden workpiece in a CAD program is practically no different from preparing a model of a metal object. However, beginners are recommended to start with wood: mistakes are inevitable during the learning process, and wood is cheaper than metal, so spoiling the workpiece will not be so scary.
CNC programming
Metal working machines typically contain more electrical components than their wood working counterparts. For operators with little experience, it is more convenient to first learn woodworking programming.
Machine setup
The setup involves using one of three modes: manual control, manual data entry or automatic control. The key phase of setup is to correctly set the zero points in accordance with the machine instructions.
Part management and production
A woodworking machine is a little easier to operate than a metalworking machine. However, many beginners forget to wear safety glasses or assume they are not needed. This is a mistake: wood chips can cause just as serious eye injuries as metal particles, so it's important to follow safety precautions.
10 things that are useful for beginners in working with CNC
The following tips will be useful for beginners:
- Buy quality cutters from reliable manufacturers. Ideally, let it be a carbide. But if you have a limited budget, you can first make do with high-speed steel. For beginners, the optimal cutter sizes are: 4 mm, 6 mm, 13 mm. For steel, 4-flute cutters are suitable, for aluminum - 3- or 2-flute. Be sure to protect your eyes while working with glasses. While you gain experience, your cutters will often fail, but this is normal. Also purchase a set of twist drills.
- Buy a set of parallels, a set of clamps and a vice. The vice is designed to last for many years. If you buy a cheap Chinese vice to save money or do not secure the workpiece properly, all the work will go down the drain. The official name for "parallel" is parallel pads.
- Use fog or coolant. If coolant or a fog generator is not included in the machine design, purchase them separately. Most likely, you will first have to spend a lot of time setting up the coolant. But if you are too lazy to do this, overcutting the chips can lead to breakage of the cutter.
- Learn how to use a CNC controller. First you need to train on the X and Y axes, without affecting the Z. In this case, you cannot use G00, otherwise the unit will move at maximum speed and the limit of its capabilities. It is optimal to set G01 F20, while the indicator “20” will correspond to the value that you set yourself (for example, inches or centimeters).
- Make it a habit to use a cutter length measuring device. To base the spindle on the workpiece, use the edge finder. If the unit does not understand where the tip of the cutter is, there is a risk of equipment failure. As soon as the workpiece is installed in the vice and the cutter is in the spindle, you need to set the zeros.
- Adjust the machine and vice using the dial indicator. Check the position of the vice every time before starting work.
- If you are a beginner, don't try to work on stainless steel right away. Practice on mild steel, brass or aluminum first. If you start cutting difficult materials right away, the cutters will wear out and break too often.
- Get yourself several sets of aluminum step jaws. Use a saw to cut pieces of material so that their dimensions are slightly larger than the jaws of the vice. Then make passes with the end mill until you get a rectangular parallelepiped. Then adjust this figure to the dimensions you need, drill and countersink mounting holes in it.
- Master CAD and CAM programs in which you will write g-codes. Many programs have quite intelligible Russified manuals, as well as active communities of users on the Internet, always ready to help beginners.
- Learn in advance how to perform an emergency stop of the machine and restart it after an unplanned shutdown.
To see how prepared you are, try doing a Turner Cube (also known as a Meta Cube) on the machine. This figure consists of several nested cubes with holes, with all the inner cubes touching the outer one only with their vertices. Before equipping production with CNC machines, this is exactly the kind of figure that turners and milling operators were asked to perform during the hiring process in order to assess the level of their skill.
So now you have a basic understanding of how CNC machines function. On the Internet you can find many training videos devoted to different stages of setting up the unit and processing workpieces. If you have little experience yet, start with wood processing - it’s easier than creating metal products, and the material itself is cheaper.
- October 03, 2020
- 5868
General recommendations for cutting modes:
For soft wood (pine, larch, linden)
| Tool type | Working feed mm/min | Rotation speed (rpm) | Depth per pass |
| End 6mm | 2500-3500 | 20 000-24 000 | 7,5-8 |
| End 3mm | 1000-1500 | 20 000-24 000 | 4,5 |
| Engraver 30° * 0.2 | 800-600 | 20 000-24 000 | 3 |
For hard wood (beech, oak, plywood)
| End 6mm 3500 | 4500 | 20 000 — 24 000 | 34 |
| End face 3mm 2500 | 3000 | 20 000 — 24 000 | 2 |
| Engraver 30°x0.2 300 | 600 | 20 000 — 24 000 | 2 |
For two-layer plastic
| End 3 mm | 2000 | 12000 | 0.3 |
| Engraver 30°x0.2 | 2000 | 20000 | 0.3 |
For acrylic and polystyrene
| End 6 mm | 1000 — 1300 | 10 000 — 12 000 | 3 |
| End 3 mm | 800 — 1000 | 12 000 — 16 000 | 1,5 |
| Engraver 30°x0.2 | 300 — 500 | 18 000 — 20 000 | 0,30,6 |
For PVC
| End 6 mm | 1500 — 2000 | 12000 | 8-10 |
| End 3 mm | 1500 — 2000 | 12000-15000 | 4-6 |